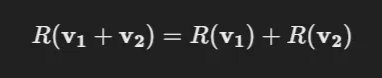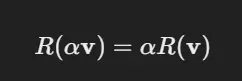선형대수
- MATLAB의 경우 행렬과 벡터를 다루는 데 강력한 기능을 제공한다.
- 때문에 선형 대수에서 행렬연산, 벡터연산, 고유값/eigenvalue 계산, 선형 변환 등 다양한 수학적 작업을 수행하는데 중요한 역할을 할 수 있다.
회전변환
- 회전 변환은 벡터 공간에서 벡터를 회전시키는 작업으로, 주로 행렬 곱셈을 통해 표현된다.
- 회전 변환 행렬 (rotation matrix)
- 2D 공간에서 점 θ만큼 회전시키는 회전 행렬
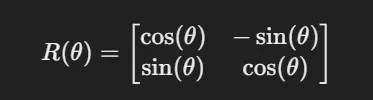
- 이를 이용하여 회전 2D 회전 변환을 표현할 수 있다.
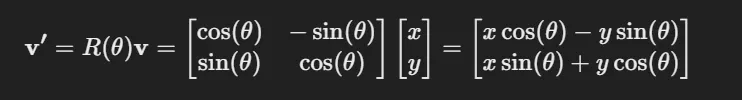
- 2D 공간에서 점 θ만큼 회전시키는 회전 행렬
💡 회전변환이 선형변환인 이유
회전 변환은 벡터 공간에서 벡터의 방향을 변경하는 변환으로 회전 행렬을 사용하여 수행된다.
이때, 이 행렬은 벡터에 곱하여 해당 벡터를 회전시키며, 선형 변환의 두가지 핵심 성질을 만족한다.
선형 변환의 핵심 성질
덧셈에 대해 닫힘 : 두 벡터 v1와 v2의 합을 먼저 회전한 결과와, 각 벡터를 회전한 후 그 합을 구하는 것이 동일
스칼라 곱에 대해 닫힘 : 벡터 v와 스칼라 α에 대해 스칼라 배수를 곱한 후 회전한 결과는, 벡터를 회전시킨 후 스칼라 배수를 곱한 것과 동일
닫힘: 특정연산을 적용한 후 결과가 원래 벡터 공간에 여전히 속한다.
- 따라서, 회전변환의 경우 선형 변환으로 볼 수 있다.
예시
p = [1 0; 2 0; 2 1; 1 1; 1 0];
plot(p(:,1), p(:,2), '.-', 'markersize', 20, 'linewidth', 2)
axis([-4 4 -4 4]); hold on
thetas = [30 70 180 225 270];
for i = 1:length(thetas)
theta = thetas(i);
ang = [cosd(theta) -sind(theta); sind(theta) cosd(theta)];
trans = ang*p';
trans = trans';
plot(trans(:,1), trans(:,2), '.-', 'markersize', 20, 'linewidth', 2)
end
hold off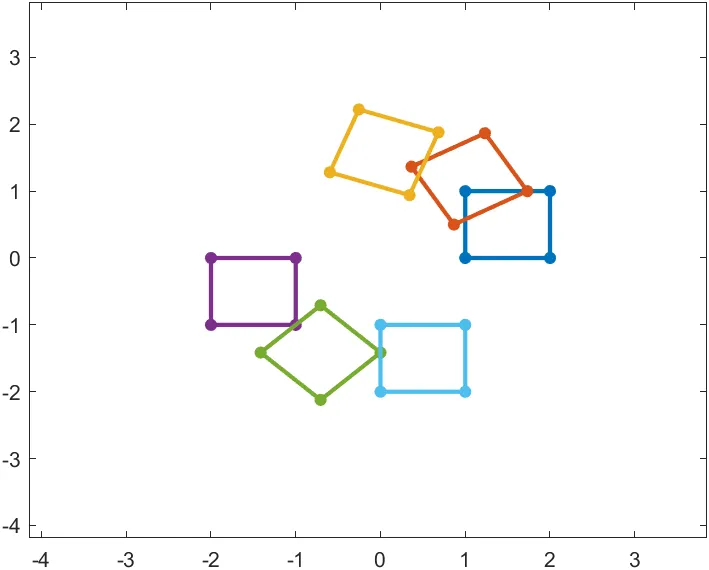
- 파란색 사각형이 회전 변환에 의해 30, 70, 180, 225, 270도로 회전했을 때의 위치를 시각화한 그림이다.
- 이때 라디안 값이 아닌 도 단위로 값을 받기 위해
cosd(),sind()를 사용하였다.
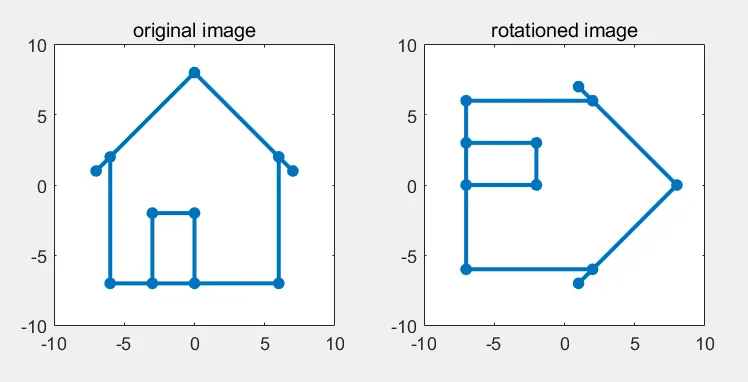
응용 (집 그림 회전)
- 좌표로 만들어준 집 그림에 대해 회전 변환을 적용하여 90도로 눕히기
X = [-6 -6 -7 0 7 6 6 -3 -3 0 0;
-7 2 1 8 1 2 -7 -7 -2 -2 -7]
subplot(1, 2, 1)
trans(X, 0) % 회전 변환을 하지 않은 이미지
title('original image')
subplot(1, 2, 2)
trans(X, 270) % 270도 회전 변환을 적용한 이미지
title('rotationed image')
function trans(X, theta)
X(:, end+1) = X(:, 1);
ang = [cosd(theta) -sind(theta); sind(theta) cosd(theta)];
trans = ang * X;
plot(trans(1, :), trans(2, :), '.-', 'markersize', 20, 'lineWidth', 2)
axis(10 * [-1 1 -1 1])
axis square
end
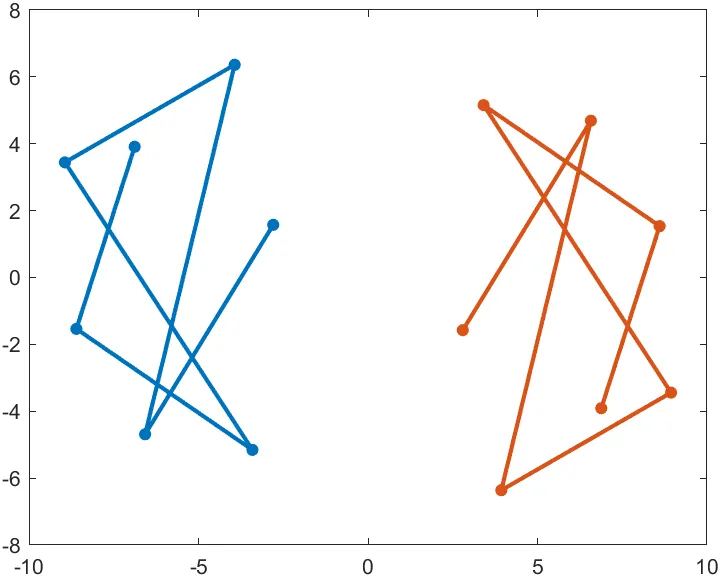
ginput을 이용한 회전변환 구현
clear all;figure;axis(10*[-1 1 -1 1])
[x,y] = ginput; p = [x y]';
plot(p(1,:),p(2,:),'.-','markersize',20,'linewidth',2)
hold on
theta=180;
ang=[cosd(theta) -sind(theta);sind(theta) cosd(theta)];
trans=ang*p;
plot(trans(1,:),trans(2,:),'.-','markersize',20,'linewidth',2)
hold offginput함수는 그래픽 창에서 마우스를 클릭하여 입력을 받는다.- 매개변수 없이 호출된 경우에는 사용자가 enter를 입력할때까지 마우스 입력을 받는다.
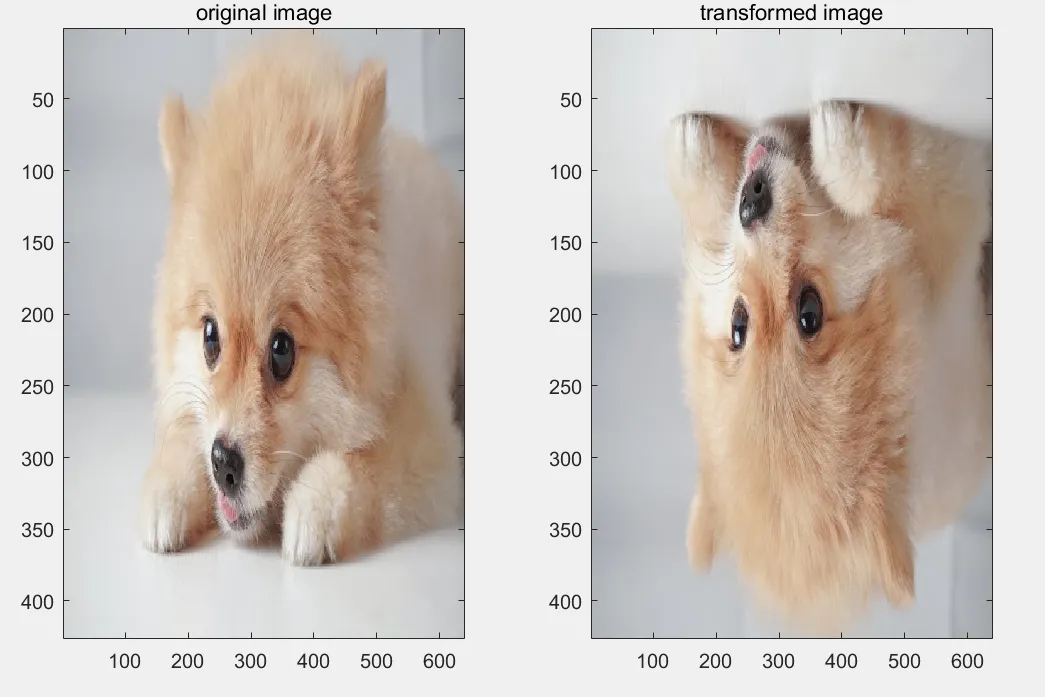
이미지 좌우/상하 반전
- 회전 변환 행렬 말고도 회전, 반전, 확대/축소, 이동(평행 이동) 등 다양한 기하학적 변환을 수행할 수 있다.
- 좌우/상하 반전의 경우에는 회전 변환처럼 행렬의 곱 연산을 통해 구현이 가능하다.
% 이미지 로드 및 크기 확인
A = imread('image.jpg');
% 창 위치 및 크기 조정
figure('Position', [200, 200, 800, 500]);
% original image 출력
subplot(1, 2, 1);
image(A)
title('original image')
% 상하/좌우 변환 입력
answer = input("Enter lrflip or tbflip : ", "s");
[rows, cols, ch] = size(A);
% 변환 행렬 설정
if strcmp(answer, 'tbflip')
ang = [1 0
0 -1];
elseif strcmp(answer, 'lrflip')
ang = [-1 0
0 1];
else
error('Wrong input. Please enter a valid option.');
end
transformed_A = zeros(rows, cols, ch, 'uint8');
% 중심 좌표
h = (1 + cols) / 2;
k = (1 + rows) / 2;
for x = 1:cols
for y = 1:rows
coord = [x - h; y - k];
trans = ang * coord;
trans = trans';
new_x = trans(1) + h; % 변환된 x 좌표
new_y = trans(2) + k; % 변환된 y 좌표
transformed_A(new_y, new_x, :) = A(y, x, :); % y축 -> rows, x축 -> cols
end
end
subplot(1, 2, 2);
image(transformed_A)
title('transformed image')- lrflip 입력시, 이미지 좌우 반전
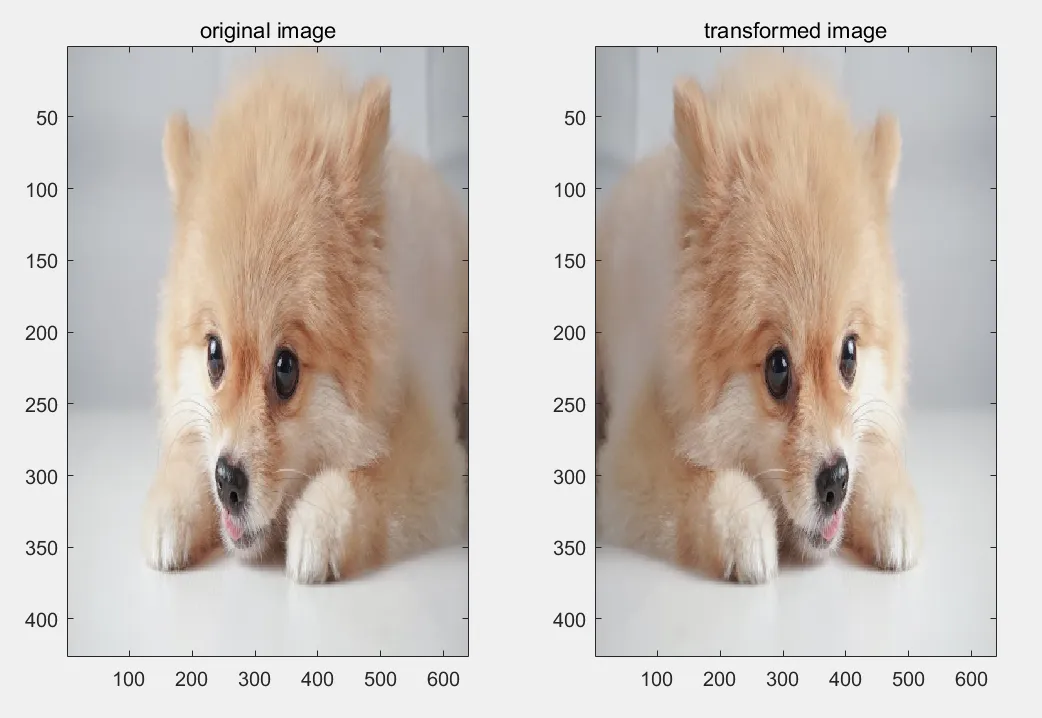
- tbflip 입력시, 이미지 상하 반전