🏫 Java Collections
🏫 Java Collections
💡
Collection (no interface)represents a group ofobjects,elements, ordata.
💡
Java Collections Frameworkis aunified architecturethat provides optimaldata structuresand essentialalgorithmsfor efficientdata storageandmanipulation.
Java Collections Framework enables developers to concentrate on managing and processing data without having to implement the underlying logic themselves, by offering standardised and optimal data structures and related algorithms as the framework simplifies tasks like searching, sorting, and organising data.
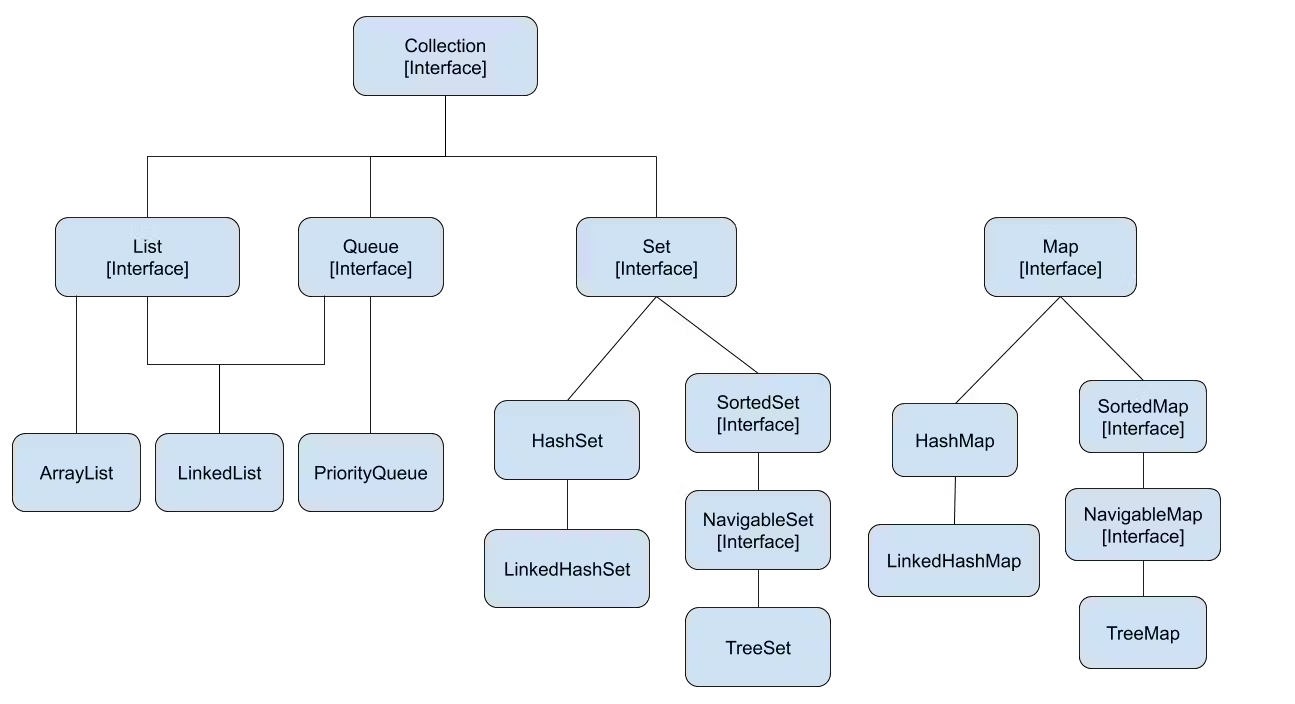
Collection Framework, specifically, implements the Collection interface in the java.util package where the interface is further implemented to other critical interfaces including:
- 🎴
Set - 〰️
List - 🖨️
Queue
List is further extended to a Stack, and the Map interface is a component of a Java Collections Framework that does not implement the Collection interface, however, implements the Map interface.
Overall, this can be graphically represented as below:
👴 Iterable
💡
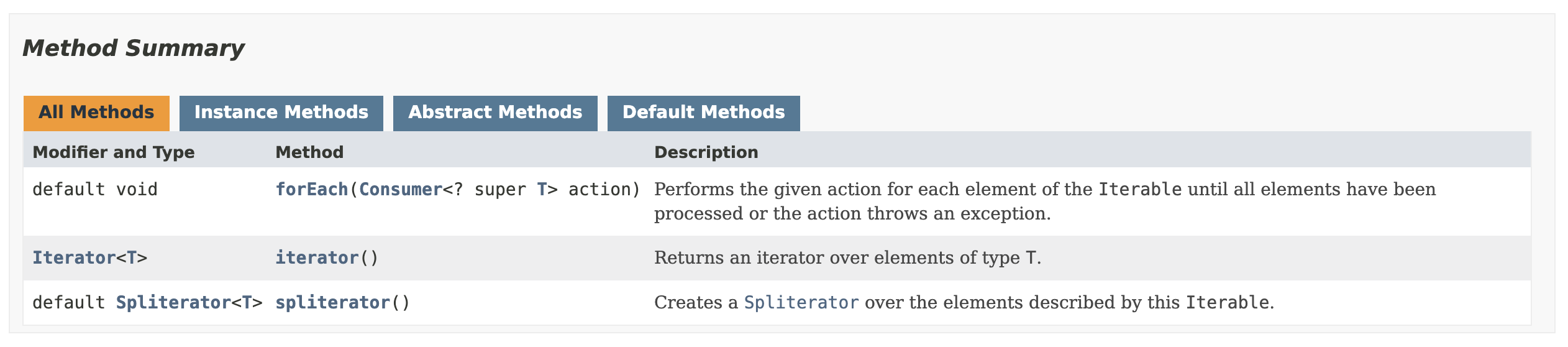
Interable Interfaceis implemented to theCollection Interface.
Implementing the iterable interface implies that the data will be sequentially managed followed by iterator() and other iterating methods.
👨 Collection
💡
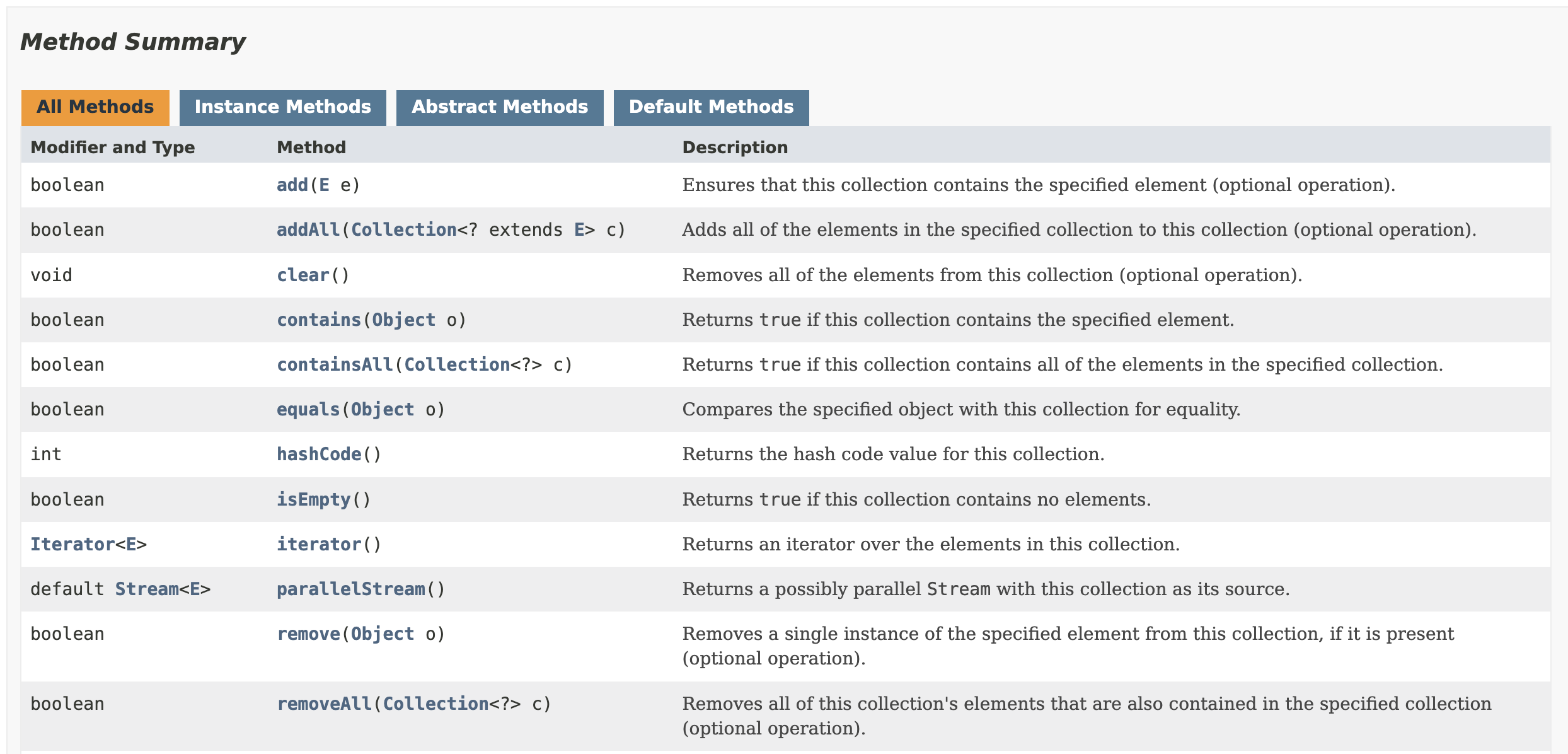
Collection Interfaceis virtually a rootinterfacein theCollectionhierarchy in theCollection Framework.
Many methods strictly related to data management are defined where these methods can be implemented individually in the collection classes.

🎴 Set
💡
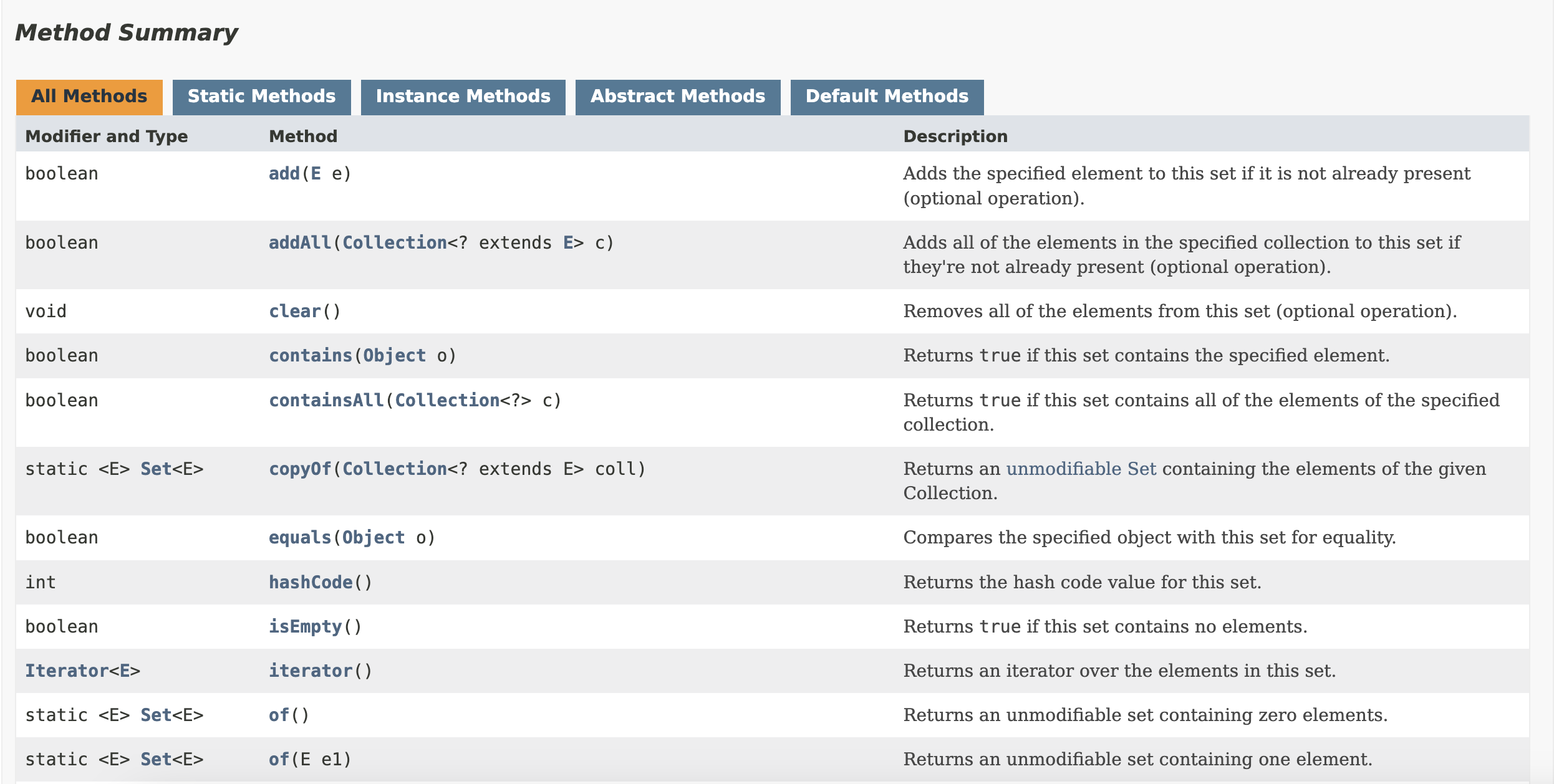
Setis acollectionthat containsno duplicateandnon-sequentialelementsordata.
Set places stronger emphasis on some methods from the Collection interface including add, equals, and hashcode methods. The beyond is the list of methods that has to be implemented in the Set classes.
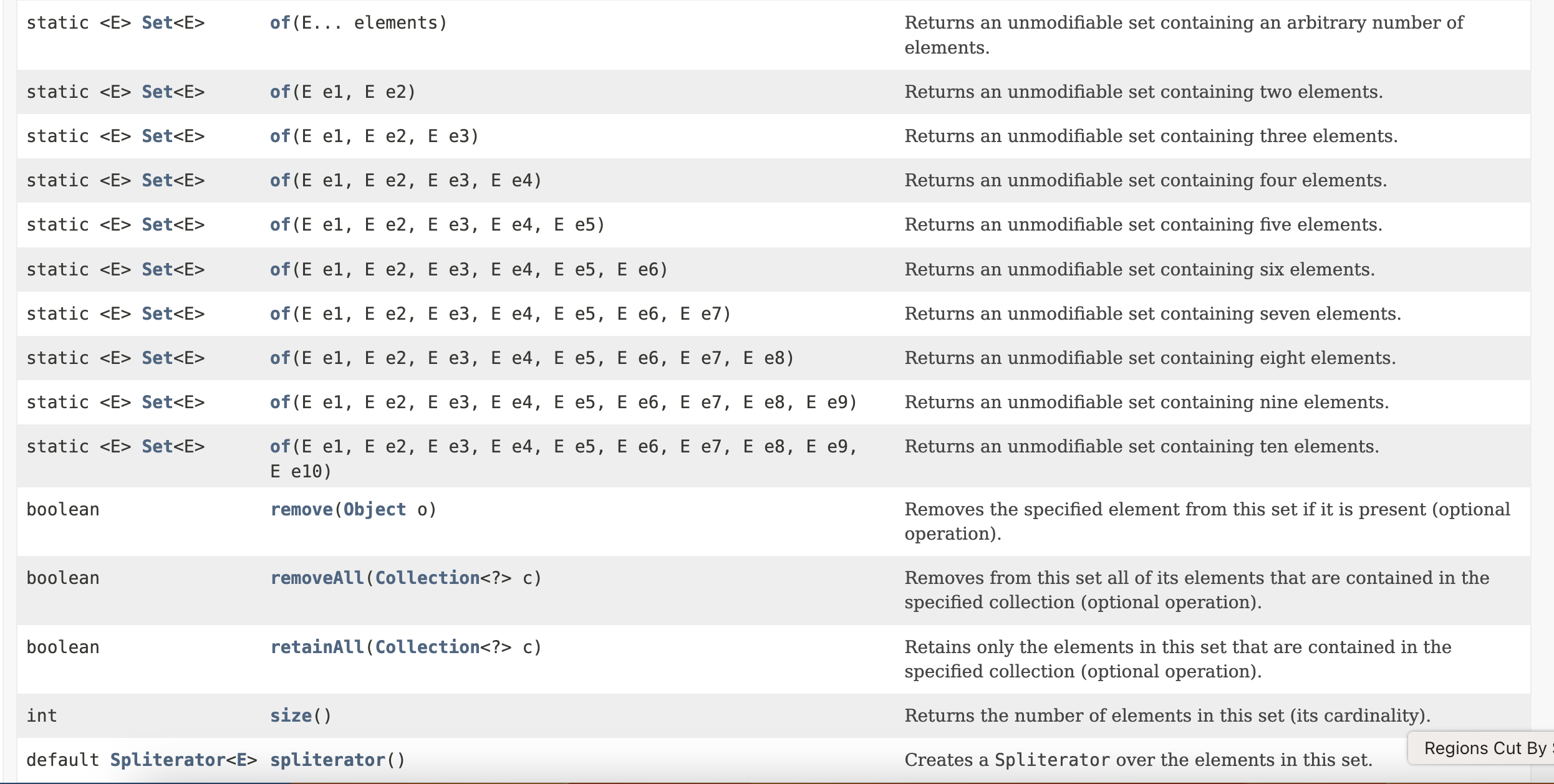

The most popular classes implementing the set interface are:
-
HashSet- offers the constant time operation
O(1). non-sequential iterationorder.- is backed by the
HashMap class.
- offers the constant time operation
-
LinkedHashSet- offers the constant time operation
O(1)(except for iteration). sequential iterationorder.- is backed by
HashSetand, ultimately theLinked HashMap class.
- offers the constant time operation
-
TreeSetlog(n)time operation- orders data by the user set
Comparatoror by default by theNATURAL_ORDERING. - is backed by a
TreeMap Classand hence theRed-Black Tree structure.
LinkedHashSet specifically uses a constructor only designed for the LinkedHashSet class in the HashSet class where a constructor initialises the map to an instance of the LinkedHashMap class.
HashSet & LinkedHashSet
public class HashSet<E>
extends AbstractSet<E>
implements Set<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean dummy) {
map = new LinkedHashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
}
}
public class LinkedHashSet<E>
extends HashSet<E>
implements Set<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {
...
public LinkedHashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor, true);
}
}〰️ List
💡
Listis adata structureappropriate for theordered collectionwhere a developer has full control of insertion and thedatacan be accessed via index.
List allows duplicate data as a part of a collection and the operation cost varies from O(1) to O(n) depending on the operations.
List Interface includes the following methods that are left for individual implementation from implementing classes:
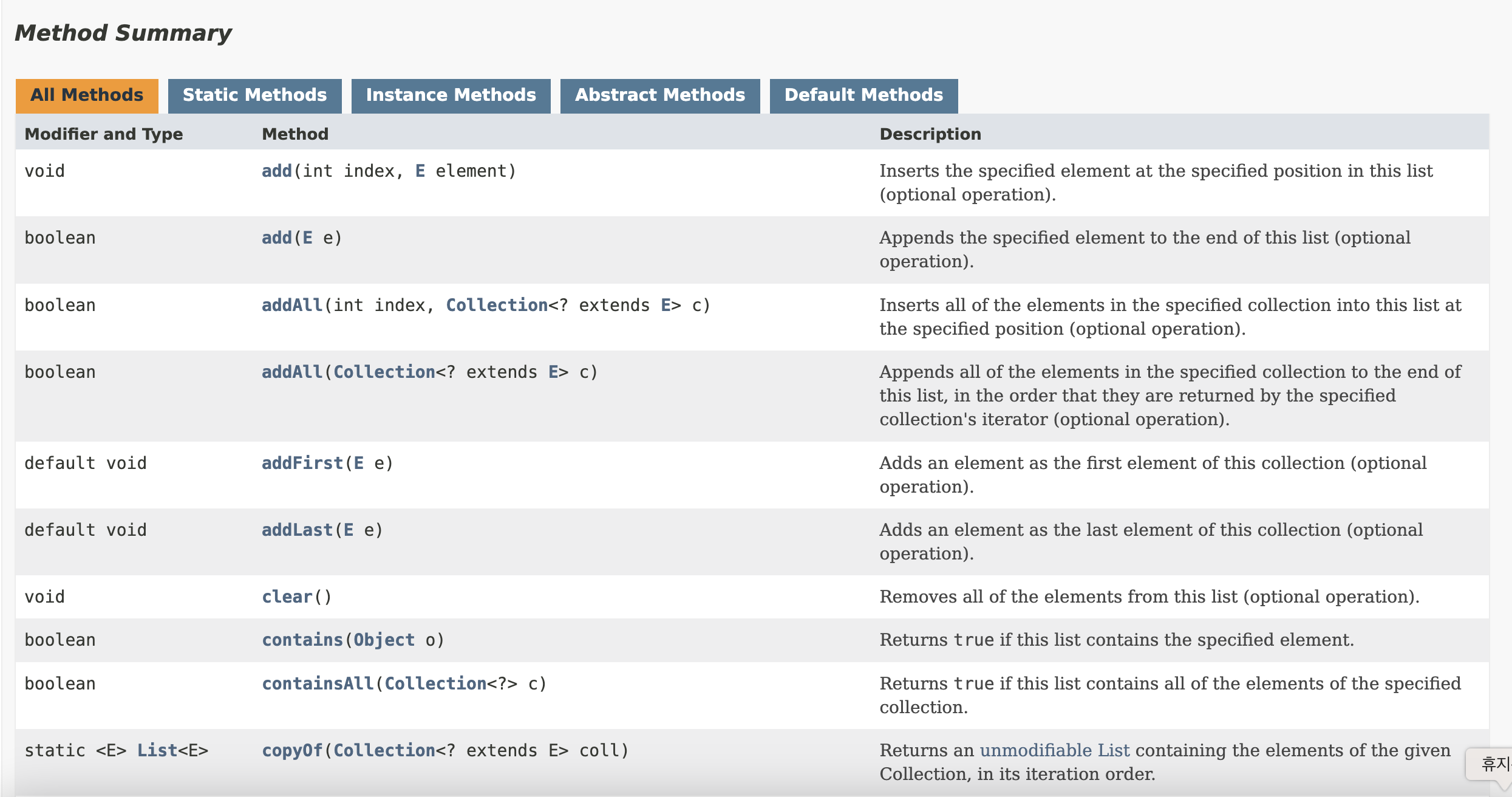
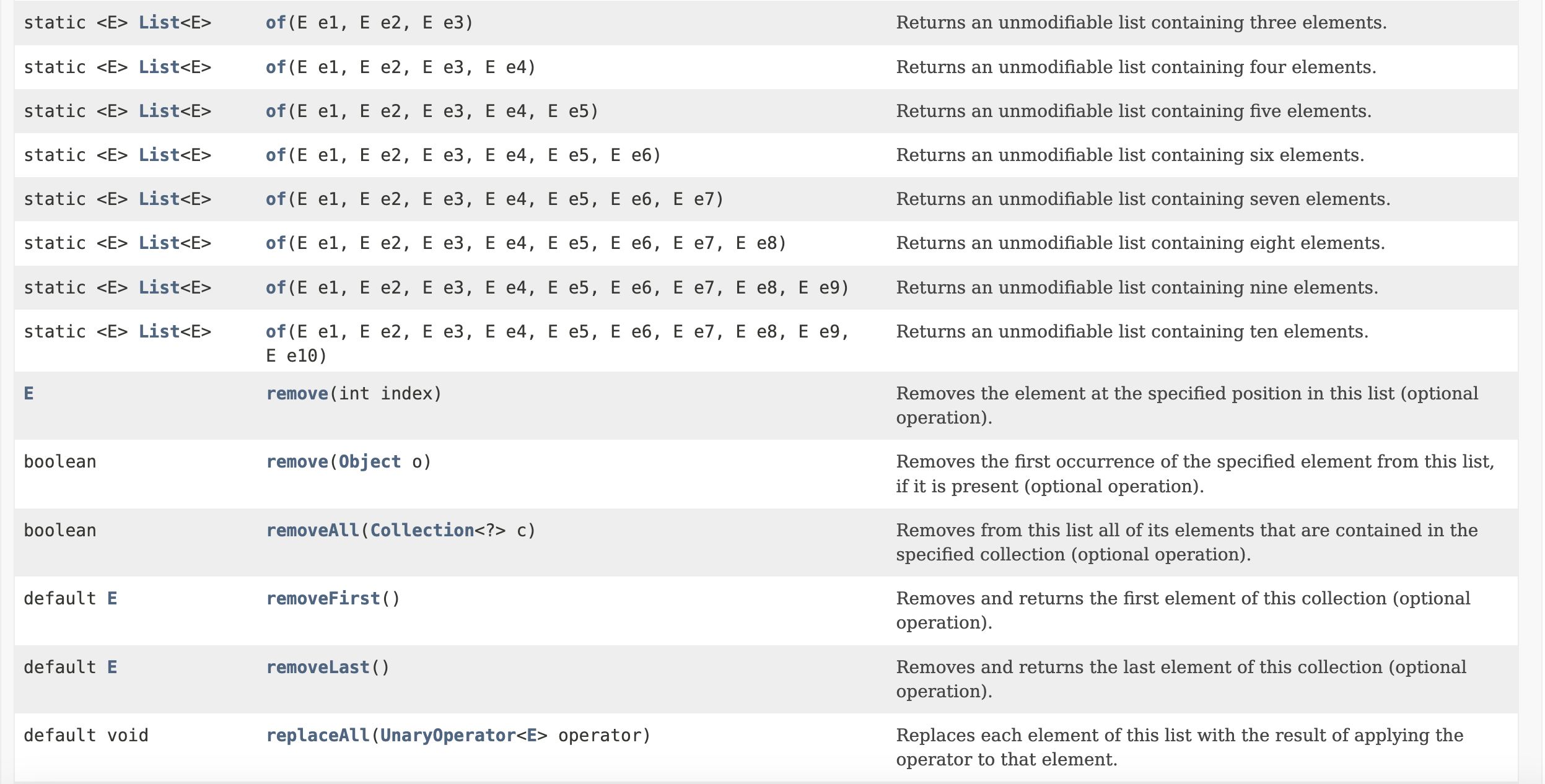

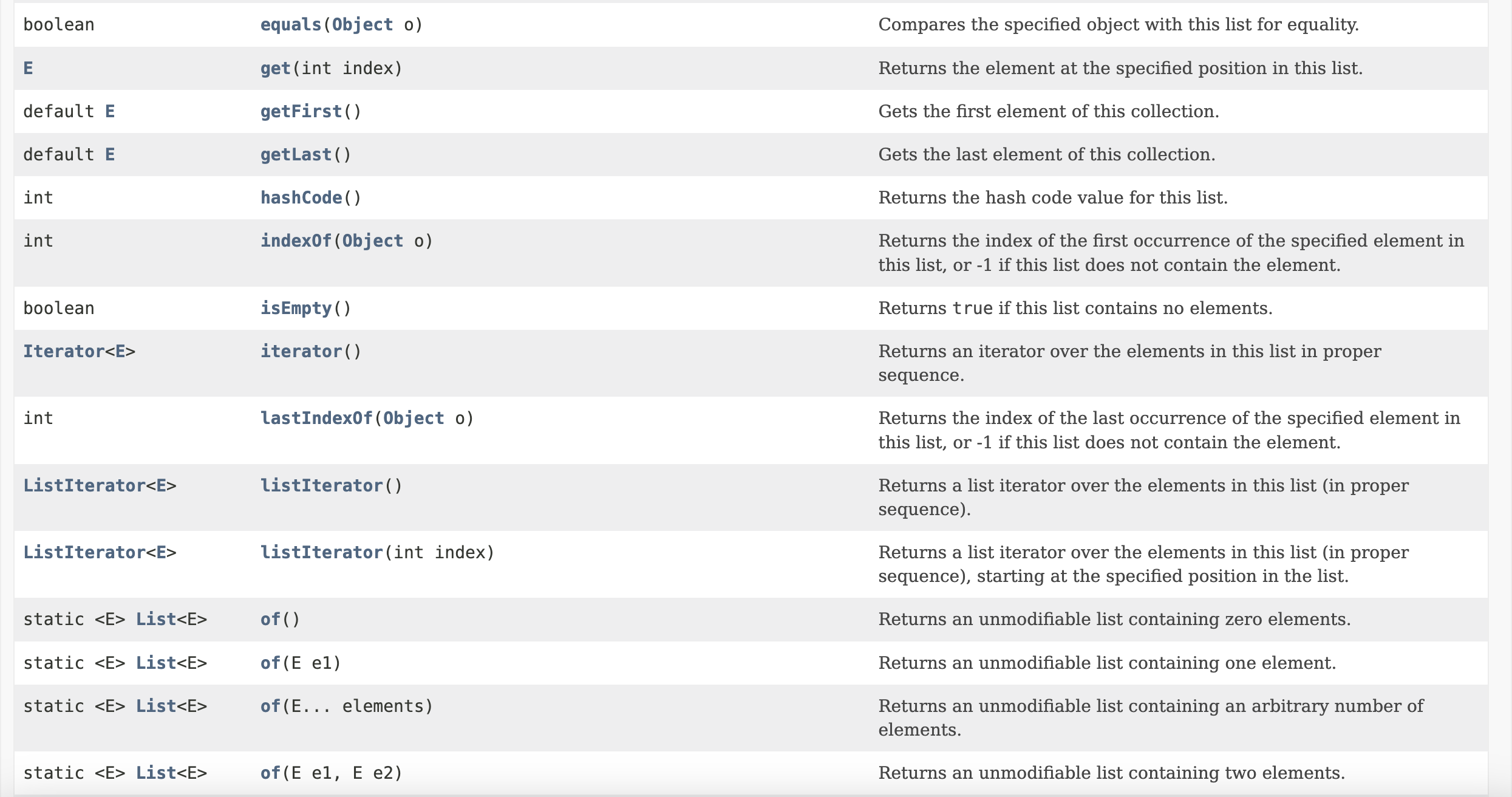
Popular classes implementing the List interface are namely:
- ✅
ArrayList - 🖨️
Queue - 🦩
Vector - 🧱
Stack
✅ ArrayList
💡
ArrayListis an implementation of theList interface, which dynamically resizes itself when thedataexceeds its capacity.
-
ArrayListmaintains the order ofdata storageand allows duplicate values. -
ArrayListoffers strengths in fastretrieval(O(1)for accessing elements by index), but operations likeinsertionanddeletioncan be slower (O(n)), especially when modifying elements in the middle of the list. -
In-depth, it is backed by an
Object array,Object[], in which if the size of thedata,n, reaches a cetain threashold resizes followed by itsresizing methodcombined withArrays.copyOf().
🖨️ Queue
💡
Queueis aFIFO(First In, First Out)data structure, commonly used to handle tasks insequential order.
-
Queueensures that the first element added is the first one to be removed. -
Common operations include
offer(adding an element) andpoll(removing an element), typically having a time complexity ofO(1)for both. -
In
Java,queueis often implemented viaLinkedList Classwhere it implementsListandQueueinterfaces together. -
LinkedList Classinternally contains theNode Classwhere theNode objectcontains adataand previous and nextNode information, implying it is aDoubly-LinkedList.
🦩 Vector
💡
Vectoris a legacyCollection Classwhere it is essentially similar to theArrayList Class, however, isthread-safe.
-
Vectoris implemented via resisableObject array,Object[]like theArrayList Class. -
Vectoristhread-safeand it is followed by alldata operational methodsbeingsynchronized methods.
🧱 Stack
💡
Stackis aLIFO(Last In, First Out)data structure, where the most recently added element is the first one to be removed.
-
Stackis widely used in tasks like function call management, expression evaluation, and undo features. -
Common operations include
push(adding an element) andpop(removing the top element). -
Extends the
Vector Class, where it implies that theStackisthred-safe.
🗺️ Map
💡
Mapis akey-valuedata structurewhere there are no duplicatekeys.
Map almost always ensures a constant time for basic operations (O(1)), including search, add, remove, and etc, and hence if often used by the developers for performance's sake.
Some methods that are left for individual implementation from the Map classes are:
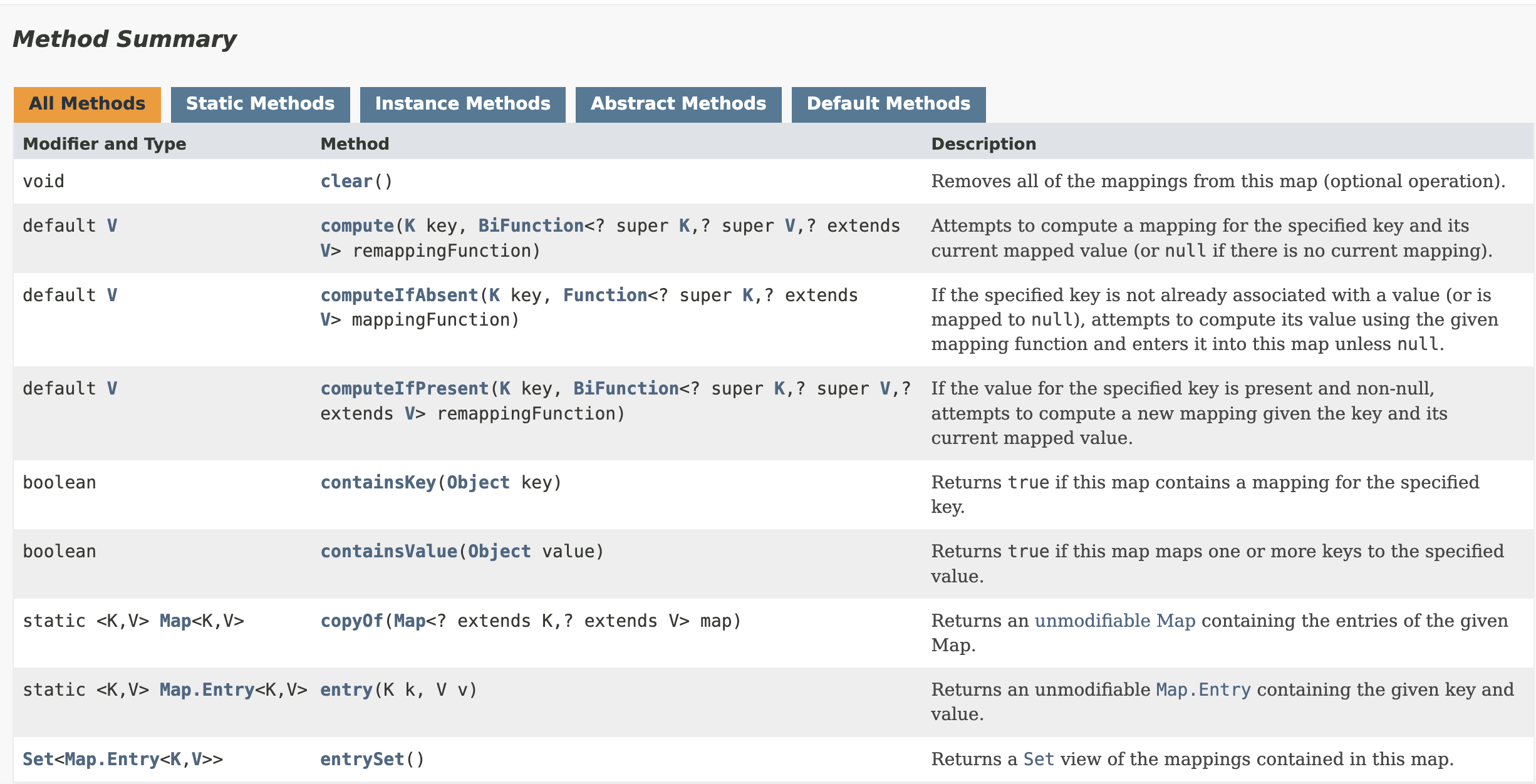
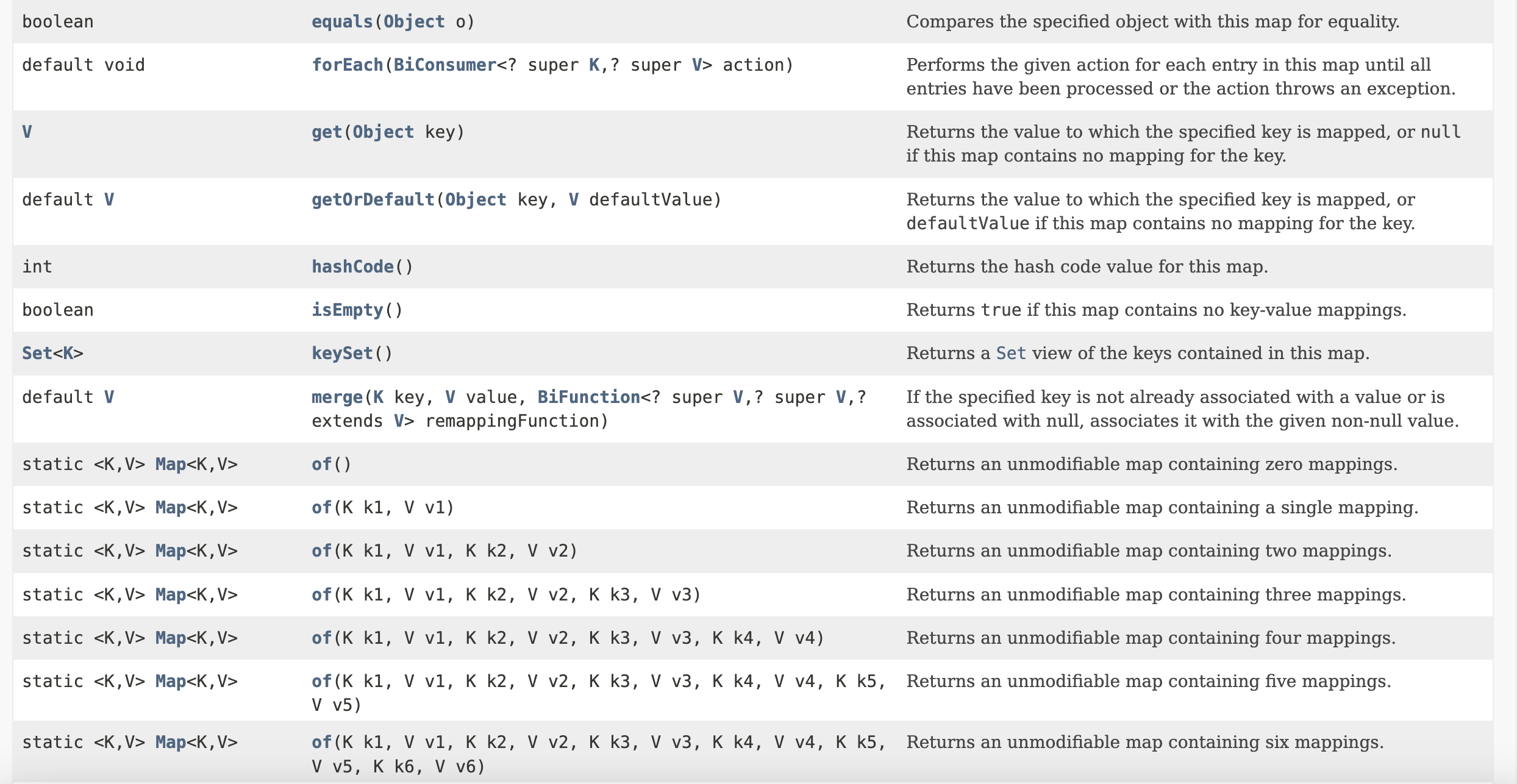

Most popular classes that implements the map interface are:
-
HashMap- constant-time performance (
O(1)). - roughly equivalent to
HashTable. - permits
nullkey.
- constant-time performance (
-
LinkedHashMap- constant-time performance (
O(1)). - implements the
HashMap& adoubly-linked list. - maintains a
doubly-linked listrunning through all of itsentries(preserves key insertion order).
- constant-time performance (
-
TreeMap- constant-time performance (
O(log n)). - orders value by the user set
Comparatoror by default by theNATURAL_ORDERING. - A
Red-Black treebasedNavigableMapimplementation.
- constant-time performance (
-
Hashtable- constant-time performance (
O(1)). Java’s legacy classes for storingkey-valuepairs.synchronised(thread safety) where specifically alldata operational methodsaresynchronized methods.
- constant-time performance (
📚 References
자바의 신
TechBum
Oracle (1)
Oracle (2)
Oracle (3)
Oracle (4)
Oracle (5)
