1. Market Power
- So far, we have assumed that no market participant has the ability to
influence the marke tpricethrough its individual actions - A market where all participants act as
price takersis said to haveperfect competition- Achieving or approximating
perfect competitionis a verydesirable goalfrom a global perspective because it ensures that themarginal costof production isequalto themarginal valueof the goods to the consumers - In
perfectly competitive market, themarket priceis a parameter over which firms have no control - Each firm should
increase its productionup to the point where itsmarginal costis equal to themarket price
- Achieving or approximating
- When competition is
not perfect, each firm must consider how thequantityit produces might affect themarket price
2. Monopoly
-
The
minimum efficient size(MES) of a firm in a particular industry provides a rough indication of the number of competitors that one is likly to find in the market for the product of this industry -
The shape of this curve is determined by the
technology used to producethe goods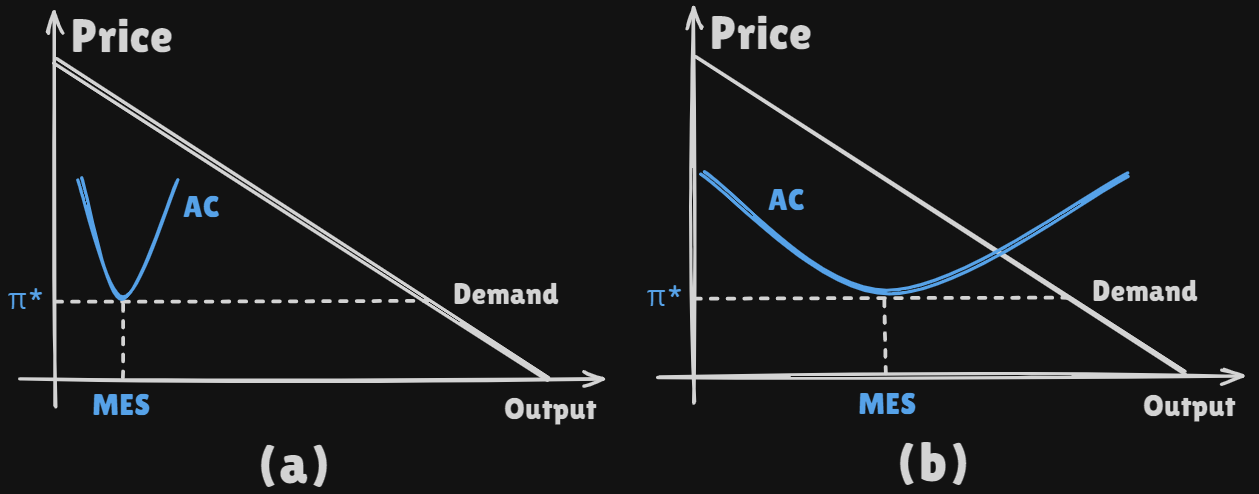
- On (a), the
MESis muchsmallerthan thedemandfor the goods at thisminimum average cost, the market should be able to support alasrge number of competitors - On (b), the
MESis comparable to thedemand, the market cannot support two profitable firms andmonopoly situationis likely to develop
- On (a), the
-
A
monopolistwill reduce itsoutputand raise itspriceabove itsmarginal costof productions to maximize its profit -
From a
global perspective, this isnot satisfactorybecause consumers purchase less of the goods than if they were sold on acompetitive basis
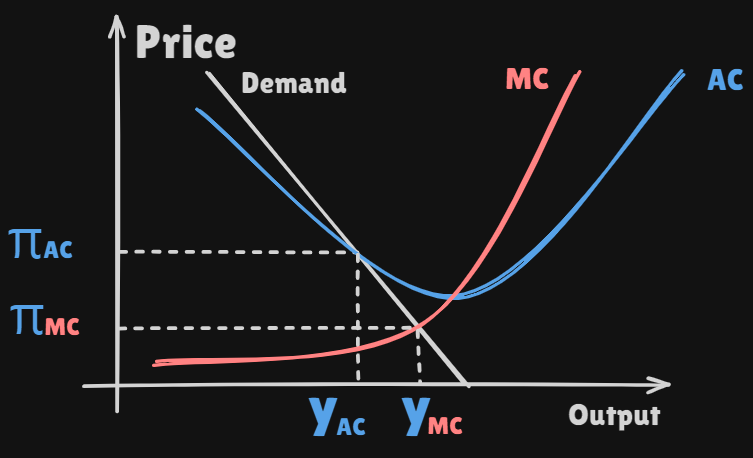
- The
intersectionof thedemandandmarginal cost curvegives a price that islowerthan theaverage costof production- To avoid driving the monopolist out of busincess, the
regulatormust set thepriceat leat at the value given by theintersectionof thedemand curveand theaverage cost curve - Such a situation is called a
natural monopoly
- To avoid driving the monopolist out of busincess, the
