ORACLE - DAY 49
clustering factor
- 특정 컬럼을 기준(인덱스가 걸려있는)으로 서로 다른 행들의 데이터가 같은 블록에 모여 있는 정도
- clustering factor가 좋은 컬럼에 인덱스를 range scan으로 이용할때 I/O를 줄일 수 있다. buffer pinning 수행되기 때문에 latch를 획득할 필요가 없다.
clustering factor 계산
- count 변수를 선언
- leaf 블록을 처음부터 끝까지 스캔하면서 rowid로 부터 block번호를 찾는다.
- 찾은 블록 주소(DBA)가 바로 직전의 블록 주소(DBA)와 다를때마다 count 변수를 1씩 증가시킨다.
- 이 작업을 끝까지 수행하면 count 변수에 있는 값을 clustering_factor 인덱스 통계 정보에 저장한다.
- ctas로 테이블을 만들 경우 nologging 모드로 만드는게 좋다
- 불필요한 redo entry를 줄이기 위해
create table hr.c_table
nologging
as
select * from all_objects order by object_id;- 테이블 생성할때만 nologging 모드로 하고 만든 이후에 발생되는 transaction에 대해서는 백업 차원에서 redo entry가 필요하기 때문에 logging 모드로 변경해야 한다.
select num_rows, blocks, avg_row_len, logging
from dba_tables
where owner = 'HR'
and table_name = 'C_TABLE';
alter table hr.c_table logging;
select num_rows, blocks, avg_row_len, logging
from dba_tables
where owner = 'HR'
and table_name = 'C_TABLE';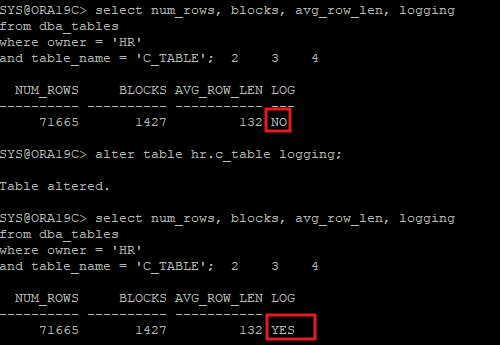
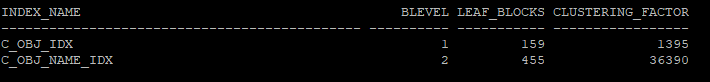
- clustering factor를 확인하기 위해 index를 생성
desc hr.c_table
create index hr.c_obj_idx on hr.c_table(object_id);
create index hr.c_obj_name_idx on hr.c_table(object_name);- 생성한 인덱스 정보 확인
blevel: leaf block까지의 깊이 (예 2라고 하면 root, brach가 2개의 block으로 나뉘어져 있다)leaf_blocks: 인덱스의 리프 블록(leaf blocks) 수clustering_factor: 테이블이 사용하고 있는 block의 수하고 비슷하면 좋고, 테이블의 row수하고 비슷하면 나쁜 상태이다.
select index_name, blevel, leaf_blocks, clustering_factor
from dba_indexes
where owner='HR'
and table_name='C_TABLE';
- clustering factor가 좋은 인덱스를 이용했을때 실행계획을 확인해보면 buffer pinning 때문에 i/o 수가 많이 줄어있다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics index(c c_obj_idx) */ count(*)
from hr.c_table c
where object_id >= 0
and object_name >= ' ';
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));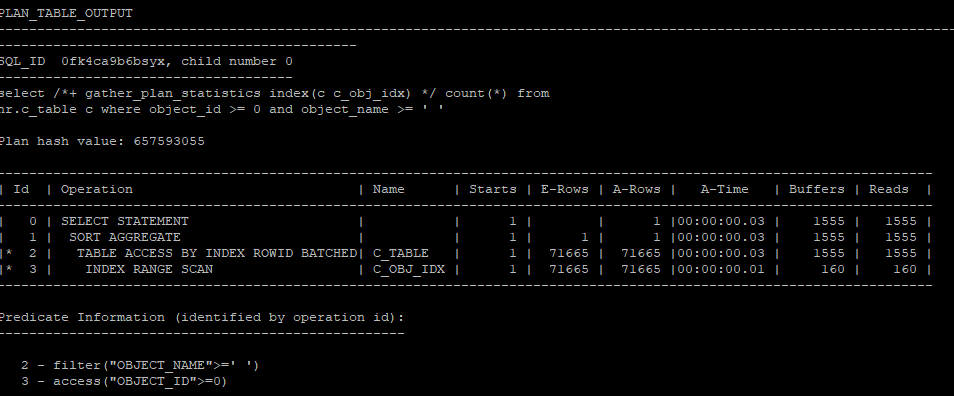
- 1555-160 = 1395 = c_obj_idx의 clustering_factor의 수
- clustering factor가 좋지 않은 인덱스를 이용해서 실행계획을 보았을때는 i/o수가 나빠져있다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics index(c c_obj_name_idx) */ count(*)
from hr.c_table c
where object_id >= 0
and object_name >= ' ';
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));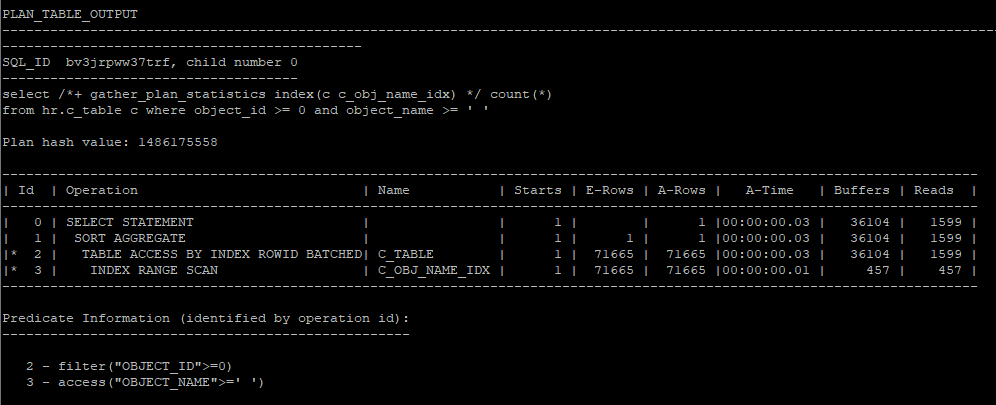
- 36104 - 457 = 35647 = c_obj_name_idx의 clustering factor의 수
row chaining
- insert시에 한 블록 안에 한행의 값이 다 저장되지 못하고 여러 블록으로 조각이 되어서 저장되는 현상
row migration
- update시에 증가하려고 하는데 프리공간이 없어서 다른 블록으로 이전되는 현상
row chaining & migration 시나리오
1. 테이블 생성 및 데이터 삽입
먼저, MIG_TABLE 테이블을 생성합니다. 여기서 PCTFREE를 0으로 설정하여, 블록 내에 여유 공간을 남기지 않도록 합니다. 이 설정은 나중에 Row Migration과 Row Chaining을 유발하는 조건을 만듭니다.
create table hr.mig_table(id number, l_name varchar2(2000), f_name varchar2(2000)) pctfree 0;다음으로, 데이터를 삽입합니다. level을 사용하여 1000개의 행을 삽입하며, 행의 크기를 2000 바이트로 맞춥니다. 일부는 NULL로 설정되며, rpad('x', 2000, 'x')을 사용해 각 행의 길이를 2000자로 고정합니다.
insert into hr.mig_table(id, l_name, f_name)
select level,
decode(mod(level,3),1,null, rpad('x',2000,'x')),
decode(mod(level,3),1,null, rpad('x',2000,'x'))
from dual
connect by level <= 1000;
commit;
2. 초기 통계 확인 및 통계 수집
다음으로, 테이블의 초기 통계를 확인합니다. 이 단계에서는 통계가 자동으로 수집되지 않았기 때문에, 데이터를 삽입한 후 수동으로 통계 정보를 수집해야 합니다.
select num_rows, blocks, chain_cnt from dba_tables where owner='HR' and table_name = 'MIG_TABLE';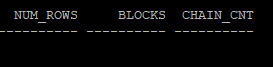
통계가 수집되지 않았으므로 다음 명령어를 실행하여 통계를 수집합니다.
execute dbms_stats.gather_table_stats('hr','mig_table');이후 다시 통계 정보를 조회하여 CHAIN_CNT(Row Chaining 또는 Row Migration이 발생한 행의 수)를 확인합니다.
select num_rows, blocks, chain_cnt from dba_tables where owner='HR' and table_name = 'MIG_TABLE';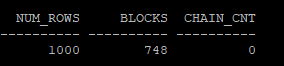
3. 인덱스 생성 및 Row Migration 유도
테이블에 인덱스를 생성합니다. ID 컬럼에 인덱스를 생성하여, 이후 쿼리에서 인덱스 스캔을 강제할 수 있습니다.
create index hr.mig_table_idx on hr.mig_table(id);이후, 업데이트 작업을 통해 Row Migration을 유도합니다. mod(id, 3) = 1인 행의 크기를 2000바이트로 업데이트하여 기존 블록에 더 이상 맞지 않도록 하고, Row Migration이 발생하게 합니다.
update hr.mig_table
set l_name = rpad('x',2000,'x'), f_name = rpad('x',1000,'x')
where mod(id,3)=1;
commit;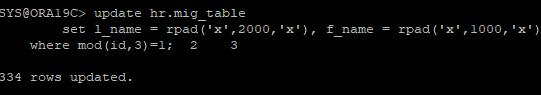
4. 통계 수집 후 결과 확인
업데이트 이후에도 통계가 자동으로 수집되지 않기 때문에 다시 통계를 수집합니다.
execute dbms_stats.gather_table_stats('hr','mig_table');다시 통계 정보를 조회하지만, CHAIN_CNT 값은 DBMS_STATS를 사용한 통계 수집만으로는 변하지 않습니다. 이는 Row Migration이 발생하더라도 CHAIN_CNT 값이 반영되지 않는다는 것을 의미합니다.
select num_rows, blocks, chain_cnt,avg_row_len,pct_free from dba_tables where owner='HR' and table_name = 'MIG_TABLE';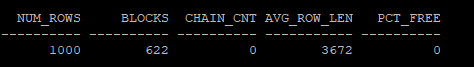
이 단계에서 Row Migration이 발생했는지 확인하려면, table fetch continued row 통계값을 확인해야 합니다. v$sysstat 뷰를 통해 이를 조회할 수 있습니다.
- table fetch continued row는 하나의 행을 가져오기 위해 두 개 이상의 블록을 읽을 때 발생하는 추가적인 블록 조회를 나타내는 통계입니다.
- 이 값은 Row Migration 또는 Row Chaining과 관련이 있으며, 블록 간의 이동이나 블록 분할로 인해 여러 블록에 걸쳐 저장된 행을 읽을 때 증가합니다.
select * from v$sysstat where name='table fetch continued row';
<<sys session>>
select to_char(sysdate,'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss') day, a.sid, vss.username, a.name, a.value
from (
select vst.sid, vst.value, vsn.name, vsn.statistic#
from v$statname vsn, v$sesstat vst
where vsn.statistic# = vst.statistic#
order by vst.value desc) a, v$session vss
where a.sid = vss.sid
and vss.username = 'HR'
and a.name = 'table fetch continued row';
5. HR 세션에서 쿼리 실행 및 Row Migration 확인
다음으로, 인덱스를 강제 사용하여 데이터를 조회하는 쿼리를 실행합니다. 이 쿼리를 통해 Row Migration이 발생한 행을 읽는 작업을 유도할 수 있습니다.
select /*+ index(t mig_table_idx) */ count(l_name)
from hr.mig_table t
where id > 0;이후 SYS 세션에서 v$sysstat을 다시 조회하여, table fetch continued row 통계값의 변화량을 확인합니다. 여기서 변화한 값만큼 Row Migration이 발생한 행의 수를 알 수 있습니다.
- 1404 - 1070 = 334 만큼 row의 migration 진행
select to_char(sysdate,'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss') day, a.sid, vss.username, a.name, a.value
from (
select vst.sid, vst.value, vsn.name, vsn.statistic#
from v$statname vsn, v$sesstat vst
where vsn.statistic# = vst.statistic#
order by vst.value desc) a, v$session vss
where a.sid = vss.sid
and vss.username = 'HR'
and a.name = 'table fetch continued row';
select * from v$sysstat where name='table fetch continued row';
row migration 통계수집은 못한다.
execute dbms_stats.gather_table_stats('hr','mig_table');row migration 통계 수집
analyze table hr.mig_table compute statistics;
- row의 migration이 수집된걸 확인 할 수 있다.
- chain_cnt값이 증가되었다.
select num_rows, blocks, chain_cnt,avg_row_len,pct_free from dba_tables where owner='HR' and table_name = 'MIG_TABLE';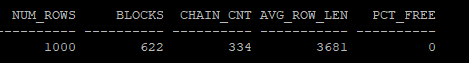
- object_id 와 data_object_id는 원래는 똑같다
select object_id, data_object_id from dba_objects where owner='HR' and object_name = 'MIG_TABLE';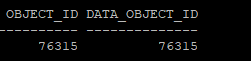
6. Row Migration 문제 해결: 테이블 재구성
Row Migration 문제를 해결하기 위해, 테이블을 재구성(MOVE)합니다. 이 과정에서 PCTFREE 값을 10으로 설정하여, 향후 업데이트 시 충분한 공간을 남겨 Row Migration을 방지할 수 있습니다.
alter table hr.mig_table pctfree 10;
alter table hr.mig_table move;- data_object_id가 변경되어 rowid도 변경되고, index도 unusable 상태가 된다.
select object_id, data_object_id from dba_objects where owner='HR' and object_name = 'MIG_TABLE';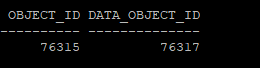
- 인덱스 상태를 확인해보면 unusable상태가 되었다
select index_name, status from dba_indexes where owner='HR' and table_name='MIG_TABLE';
- 인덱스를 사용해서 실행하려고 하면 오류가 발생한다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics index(t mig_table_idx) */ count(l_name)
from hr.mig_table t
where id > 0;
테이블을 재구성한 후, 인덱스가 UNUSABLE 상태가 되므로 이를 재구성해야 합니다.
alter index hr.mig_table_idx rebuild online;- 다시 인덱스를 사용해서 조회해보면 정상 조회가 된다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics index(t mig_table_idx) */ count(l_name)
from hr.mig_table t
where id > 0;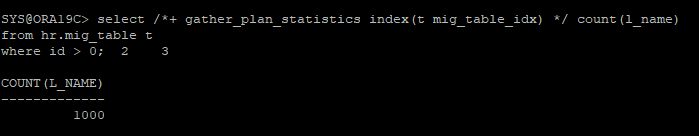
- 아직 row migration에 대한 통계수집 하기 전이여서 이전 값이 그대로 보인다
select num_rows, blocks, chain_cnt,avg_row_len,pct_free from dba_tables where owner='HR' and table_name = 'MIG_TABLE';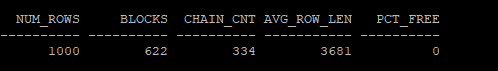
7. 최종 통계 수집 및 결과 확인
마지막으로, ANALYZE TABLE 명령어를 사용하여 정확한 통계 정보를 수집합니다. 이 명령어는 DBMS_STATS와 달리 Row Migration 통계를 정확히 반영합니다.
analyze table hr.mig_table compute statistics;이후 통계 정보를 다시 조회하여, CHAIN_CNT 값이 0으로 줄어든 것을 확인합니다. 이는 Row Migration 문제가 해결되었음을 의미합니다.
select num_rows, blocks, chain_cnt,avg_row_len,pct_free from dba_tables where owner='HR' and table_name = 'MIG_TABLE';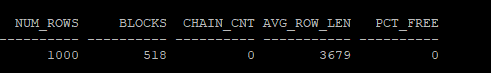
B * Tree
- Balanced Tree
- Binary Tree
- Balanced Binary Search Tree
B * Tree 구조의 인덱스 생성 기준
- where 조건절 자주 사용되는 컬럼중에 유일키값으로 구성되어 있는 컬럼
- 컬럼 null값은 제외하고 인덱스 생성, null에 대해서는 인덱스 스캔하지 않습니다.
- 테이블이 크고 대부분의 쿼리가 테이블에서 2 ~ 4% 미만의 행을 검색할때 유용하다.
- DML 비용이 저렴하다 (row level lock)
- 그중에서도 update는 비용이 크다.(인덱스에서 값을 삭제하고 생성해야 하기 때문이다)
- OLTP(Online Transaction Processing) 환경
- and 연산자 사용시 효율적이다.
데이터 블록의 PCTFREE는 주로 업데이트 시 변경된 데이터를 저장할 여유 공간을 확보하는 데 목적이 있습니다. 하지만 인덱스의 PCTFREE는 다른 목적을 가집니다.
인덱스는 데이터의 순서를 유지해야 하므로, 중간에 값이 삽입될 때 기존 리프 블록에 공간이 부족하면 블록 분할(Split)이 발생합니다. 이때 뒤에 있는 인덱스 값을 새로운 리프 블록으로 이동시켜야 합니다. 이러한 블록 분할을 줄이고 삽입 작업을 원활하게 처리하기 위해, 인덱스의 PCTFREE는 삽입 작업을 위한 공간을 미리 확보하는 데 사용됩니다.
즉, 인덱스의 PCTFREE는 삽입 시 발생할 수 있는 블록 분할을 최소화하기 위한 목적으로 존재합니다.
Bitmap index
- where 조건절 자주 사용되는 컬럼중에 데이터의 값이 중복성많은 컬럼에 유용하다.
- 컬럼에 null값을 포함해서 인덱스를 생성하기 때문에 null 체크시에 인덱스 스캔이 수행된다.
- bitmap index는 수정할때 segment 레벨에서 lock이 걸리기 때문에 다른 transaction이 다 막혀버려서 oltp환경에서는 맞지 않다.
- 그러나 각 컬럼에 다른 index가 걸려있을때 각각의 rowid를 찾아 merge 하는거 보다 bitmap으로 수행하는게 성능이 좋을 수 있다.
- DML 비용이 크다(테이블 데이터에 대해서 row level lock, bitmap index는 segment level lock 발생)
- and,or 연산자 사용시 효율적이다
- DW(Data Warehouse), DSS(Decision Support System,의사결정시스템) 업무에 적합

index_combine
- B*Tree index를 bitmap index로 변환해서 수행하는 hint
select ix.index_name, ix.uniqueness, ic.column_name
from dba_indexes ix, dba_ind_columns ic
where ix.index_name = ic.index_name
and ix.table_name = 'EMP'
and ix.owner='HR';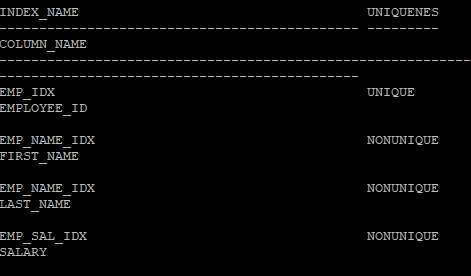
create index hr.emp_sal_idx on hr.emp(salary);
select ix.index_name, ix.uniqueness, ic.column_name
from dba_indexes ix, dba_ind_columns ic
where ix.index_name = ic.index_name
and ix.table_name = 'EMP'
and ix.owner='HR';
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics index_combine(e emp_idx emp_sal_idx) */ employee_id, salary
from hr.emp e
where employee_id = 100
and salary = 10000;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));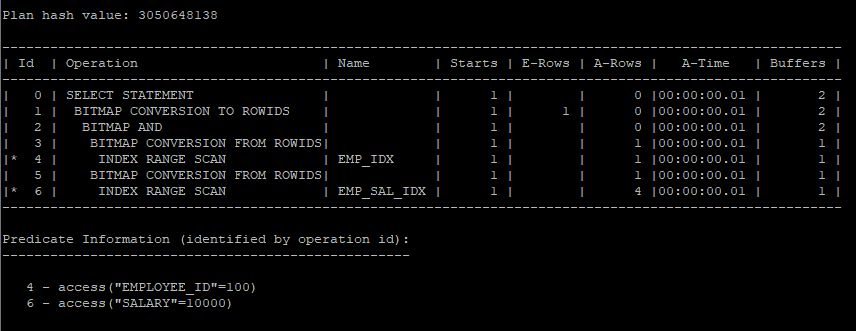
조인 방법
1. nested loop join
- 조인의 건수가 작을때 유리하다.
- 인덱스를 통해서 데이터를 액세스하는 조인
use_nlhint 사용- outer를 1쪽 집합으로, inner를 m쪽 집합으로 설정하는게 i/o 수를 줄인다.
2. sort merge join
- 조인의 건수가 많을때 유리하다.
- sort에 대한 성능의 문제가 발생할 수 있다.
use_mergehint 사용
3. hash join
- 조인의 건수가 많을때 유리하다.
- hash 알고리즘으로 수행한다.(CPU좋으면 괜찮다)
use_hashhint 사용
조인 순서에 관련된 hint
1. ordered
- from절에서 나열된 테이블 순서대로 조인의 순서가 결정된다.
2. leading
- leading 힌트안에 나열된 테이블 순서대로 조인의 순서가 결정된다.
- join 후 실행계획 확인
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ e.employee_id, e.salary, d.department_name
from hr.employees e, hr.departments d
where e.department_id = d.department_id
and e.employee_id = 100;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));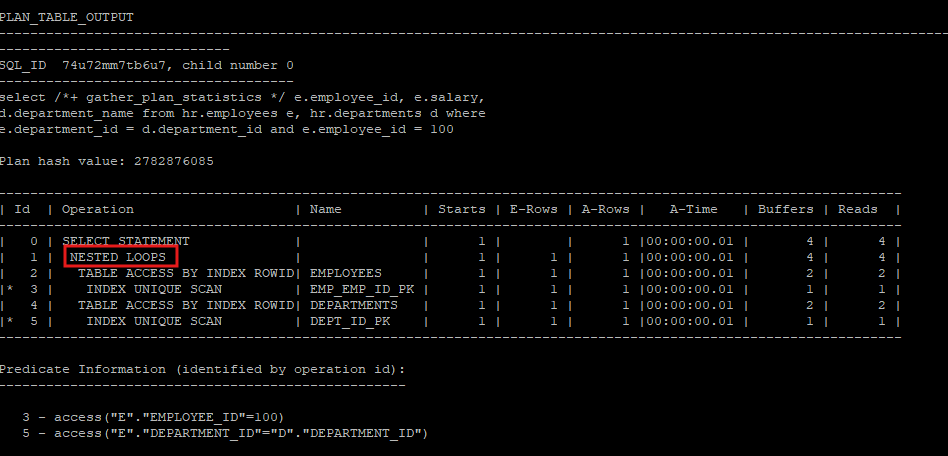
의도적으로 e.department_id를 비조인술어로 조인 쿼리를 작성하였지만 옵티마이저는 departments를 driving으로 선택하여 실행계획을 만들었다.
-
Driving (OUTER): NESTED LOOP에서 먼저 처리되는 테이블로, 이 테이블의 각 행이 조인 과정에서 다른 테이블에 전달됩니다.
-
Driven (INNER): Driving 테이블의 행에 맞춰 조회되는 테이블로, 드라이빙 테이블의 각 행에 대해 매번 검색이 이루어집니다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ e.employee_id, e.salary, d.department_name
from hr.employees e, hr.departments d
where e.department_id = d.department_id
and e.department_id = 20;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));NESTED LOOP
OUTER / DRIVING = DEPARTMENTS
INNER / DRIVEN = EMPLOYEES
Plan hash value: 1475904561
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Starts | E-Rows | A-Rows | A-Time | Buffers |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | | 2 |00:00:00.01 | 6 |
| 1 | NESTED LOOPS | | 1 | 2 | 2 |00:00:00.01 | 6 |
| 2 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID | DEPARTMENTS | 1 | 1 | 1 |00:00:00.01 | 2 |
|* 3 | INDEX UNIQUE SCAN | DEPT_ID_PK | 1 | 1 | 1 |00:00:00.01 | 1 |
| 4 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID BATCHED| EMPLOYEES | 1 | 2 | 2 |00:00:00.01 | 4 |
|* 5 | INDEX RANGE SCAN | EMP_DEPARTMENT_IX | 1 | 2 | 2 |00:00:00.01 | 2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
3 - access("D"."DEPARTMENT_ID"=20)
5 - access("E"."DEPARTMENT_ID"=20)중복 nested loop
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ e.employee_id, e.salary, d.department_name, l.city
from hr.employees e, hr.departments d, hr.locations l
where e.department_id = d.department_id
and d.location_id = l.location_id
and e.department_id = 20;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));NESTED LOOP
OUTER / DRIVING = 2번 , 3번
INNER / DRIVEN = 7번, 5번
Plan hash value: 2907726130
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Starts | E-Rows | A-Rows | A-Time | Buffers | Reads |
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | | 2 |00:00:00.01 | 8 | 2 |
| 1 | NESTED LOOPS | | 1 | 2 | 2 |00:00:00.01 | 8 | 2 |
| 2 | NESTED LOOPS | | 1 | 1 | 1 |00:00:00.01 | 4 | 2 |
| 3 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID | DEPARTMENTS | 1 | 1 | 1 |00:00:00.01 | 2 | 0 |
|* 4 | INDEX UNIQUE SCAN | DEPT_ID_PK | 1 | 1 | 1 |00:00:00.01 | 1 | 0 |
| 5 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID | LOCATIONS | 1 | 1 | 1 |00:00:00.01 | 2 | 2 |
|* 6 | INDEX UNIQUE SCAN | LOC_ID_PK | 1 | 1 | 1 |00:00:00.01 | 1 | 1 |
| 7 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID BATCHED| EMPLOYEES | 1 | 2 | 2 |00:00:00.01 | 4 | 0 |
|* 8 | INDEX RANGE SCAN | EMP_DEPARTMENT_IX | 1 | 2 | 2 |00:00:00.01 | 2 | 0 |
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
4 - access("D"."DEPARTMENT_ID"=20)
6 - access("D"."LOCATION_ID"="L"."LOCATION_ID")
8 - access("E"."DEPARTMENT_ID"=20)실행 계획 설명
1. Id 4 | INDEX UNIQUE SCAN | DEPT_ID_PK
설명: 첫 번째로 DEPT_ID_PK 인덱스를 사용하여 DEPARTMENT_ID = 20인 행을 DEPARTMENTS 테이블에서 찾습니다.
2. Id 3 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID | DEPARTMENTS
설명: DEPT_ID_PK 인덱스를 통해 찾아낸 ROWID를 사용하여 DEPARTMENTS 테이블에서 해당 행을 조회합니다.
3. Id 6 | INDEX UNIQUE SCAN | LOC_ID_PK
설명: DEPARTMENTS 테이블에서 조회한 LOCATION_ID를 사용하여, LOCATIONS 테이블에서 LOC_ID_PK 인덱스를 사용하여 해당 LOCATION_ID를 조회합니다.
4. Id 5 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID | LOCATIONS
설명: LOC_ID_PK 인덱스를 통해 찾아낸 ROWID를 사용해 LOCATIONS 테이블에서 관련 데이터를 조회합니다.
5. Id 2 | NESTED LOOPS
설명: 위에서 조회된 DEPARTMENTS와 LOCATIONS 테이블의 결과를 NESTED LOOPS 방식으로 결합하여 조인합니다.
6. Id 8 | INDEX RANGE SCAN | EMP_DEPARTMENT_IX
설명: EMPLOYEES 테이블에서 EMP_DEPARTMENT_IX 인덱스를 사용하여 DEPARTMENT_ID = 20인 모든 행을 범위 스캔합니다.
7. Id 7 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID BATCHED | EMPLOYEES
설명: EMP_DEPARTMENT_IX 인덱스를 통해 찾아낸 ROWID를 사용하여 EMPLOYEES 테이블의 행을 배치 방식(BATCHED)으로 읽어옵니다.
8. Id 1 | NESTED LOOPS
설명: 조인된 DEPARTMENTS와 LOCATIONS 테이블의 결과와 EMPLOYEES 테이블의 결과를 NESTED LOOPS 방식으로 최종 결합합니다.
9. Id 0 | SELECT STATEMENT
설명: 최종적으로 SELECT 구문이 완료되고, 2개의 행이 반환됩니다.
조인의 순서를 ordered로 설정해서 driving과 driven을 설정
- use_n(inner을 사용)
- 원래 nested loops의 수는 테이블의수 - 1개여야 한다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics ordered use_nl(d) */ e.employee_id, e.salary, d.department_name
from hr.employees e, hr.departments d
where e.department_id = d.department_id
and e.department_id = 20;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));Plan hash value: 2639287409
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Starts | E-Rows | A-Rows | A-Time | Buffers |
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | | 2 |00:00:00.01 | 8 |
| 1 | NESTED LOOPS | | 1 | 2 | 2 |00:00:00.01 | 8 |
| 2 | NESTED LOOPS | | 1 | 2 | 2 |00:00:00.01 | 6 |
| 3 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID BATCHED| EMPLOYEES | 1 | 2 | 2 |00:00:00.01 | 4 |
|* 4 | INDEX RANGE SCAN | EMP_DEPARTMENT_IX | 1 | 2 | 2 |00:00:00.01 | 2 |
|* 5 | INDEX UNIQUE SCAN | DEPT_ID_PK | 2 | 1 | 2 |00:00:00.01 | 2 |
| 6 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID | DEPARTMENTS | 2 | 1 | 2 |00:00:00.01 | 2 |
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
4 - access("E"."DEPARTMENT_ID"=20)
5 - access("D"."DEPARTMENT_ID"=20)조인의 순서를 leading로 설정해서 outer와 inner을 설정
- leading(순서 설정)
- use_n(inner을 사용)
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics leading(d,e) use_nl(e) */ e.employee_id, e.salary, d.department_name
from hr.employees e, hr.departments d
where e.department_id = d.department_id
and e.department_id = 20;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));Plan hash value: 1475904561
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Starts | E-Rows | A-Rows | A-Time | Buffers |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | | 2 |00:00:00.01 | 6 |
| 1 | NESTED LOOPS | | 1 | 2 | 2 |00:00:00.01 | 6 |
| 2 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID | DEPARTMENTS | 1 | 1 | 1 |00:00:00.01 | 2 |
|* 3 | INDEX UNIQUE SCAN | DEPT_ID_PK | 1 | 1 | 1 |00:00:00.01 | 1 |
| 4 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID BATCHED| EMPLOYEES | 1 | 2 | 2 |00:00:00.01 | 4 |
|* 5 | INDEX RANGE SCAN | EMP_DEPARTMENT_IX | 1 | 2 | 2 |00:00:00.01 | 2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
3 - access("D"."DEPARTMENT_ID"=20)
5 - access("E"."DEPARTMENT_ID"=20)카테시안 곱으로 쿼리를 수행해도 nested loop로 수행한다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ e.employee_id, e.salary, d.department_name
from hr.employees e, hr.departments d
where d.department_id = 20
and e.department_id = 20;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));Plan hash value: 1475904561
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Starts | E-Rows | A-Rows | A-Time | Buffers |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | | 2 |00:00:00.01 | 6 |
| 1 | NESTED LOOPS | | 1 | 2 | 2 |00:00:00.01 | 6 |
| 2 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID | DEPARTMENTS | 1 | 1 | 1 |00:00:00.01 | 2 |
|* 3 | INDEX UNIQUE SCAN | DEPT_ID_PK | 1 | 1 | 1 |00:00:00.01 | 1 |
| 4 | TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID BATCHED| EMPLOYEES | 1 | 2 | 2 |00:00:00.01 | 4 |
|* 5 | INDEX RANGE SCAN | EMP_DEPARTMENT_IX | 1 | 2 | 2 |00:00:00.01 | 2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
3 - access("D"."DEPARTMENT_ID"=20)
5 - access("E"."DEPARTMENT_ID"=20)

