outer join
- Outer Join의 드라이빙 테이블: 오라클에서는 외부 조인(Outer Join)을 수행할 때 (+)가 없는 테이블이 항상 드라이빙 테이블(outer, first, build)로 선택됩니다. 즉, leading 힌트를 사용하더라도 (+)가 없는 테이블이 실행 계획에서 드라이빙 테이블로 선택됩니다.
1. Nested Loop Join 및 Hash Join 동작
- 실행 계획에서는 leading 힌트와 use_nlj 힌트를 사용했음에도 불구하고, Hash Join으로 변환되어 실행되며, employees 테이블이 드라이빙 테이블로 사용됩니다. 이처럼 외부 조인의 경우, Oracle은 강제로 (+)가 없는 테이블을 기준으로 최적화를 진행합니다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics
leading(d,e)
use_nlj(e)
*/
e.*, d.*
from hr.departments d, hr.employees e
where e.department_id = d.department_id(+);
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));Plan hash value: 2296652067
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Starts | E-Rows | A-Rows | A-Time | Buffers | OMem | 1Mem | Used-Mem |
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | | 107 |00:00:00.01 | 11 | | | |
|* 1 | HASH JOIN OUTER | | 1 | 107 | 107 |00:00:00.01 | 11 | 908K| 908K| 1226K (0)|
| 2 | TABLE ACCESS FULL| EMPLOYEES | 1 | 107 | 107 |00:00:00.01 | 4 | | | |
| 3 | TABLE ACCESS FULL| DEPARTMENTS | 1 | 27 | 27 |00:00:00.01 | 7 | | | |
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
1 - access("E"."DEPARTMENT_ID"="D"."DEPARTMENT_ID")
Note
-----
- dynamic statistics used: dynamic sampling (level=2)
- this is an adaptive plan
2. sort merge 조인으로 풀 경우에도 (+) 반대 테이블을 드라이빙 테이블로 설정해서 실행계획을 수행한다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics
use_merge(d)*/
e.*, d.*
from hr.departments d, hr.employees e
where e.department_id = d.department_id(+);
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));Plan hash value: 2462675903
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Starts | E-Rows | A-Rows | A-Time | Buffers | OMem | 1Mem | Used-Mem |
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | | 107 |00:00:00.01 | 6 | | | |
| 1 | MERGE JOIN OUTER | | 1 | 107 | 107 |00:00:00.01 | 6 | | | |
| 2 | SORT JOIN | | 1 | 107 | 107 |00:00:00.01 | 4 | 15360 | 15360 |14336 (0)|
| 3 | TABLE ACCESS FULL| EMPLOYEES | 1 | 107 | 107 |00:00:00.01 | 4 | | | |
|* 4 | SORT JOIN | | 107 | 27 | 106 |00:00:00.01 | 2 | 2048 | 2048 | 2048 (0)|
| 5 | TABLE ACCESS FULL| DEPARTMENTS | 1 | 27 | 27 |00:00:00.01 | 2 | | | |
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
4 - access("E"."DEPARTMENT_ID"="D"."DEPARTMENT_ID")
filter("E"."DEPARTMENT_ID"="D"."DEPARTMENT_ID")3. hint를 사용하지 않고 기본적으로 수행할 경우 옵티마이저는 내부적으로 swap_join_inputs을 사용하여 드라이빙 테이블을 작은 테이블로 변경한다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics
*/
e.*, d.*
from hr.departments d, hr.employees e
where e.department_id = d.department_id(+);
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));Plan hash value: 4017029581
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Starts | E-Rows | A-Rows | A-Time | Buffers | OMem | 1Mem | Used-Mem |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | | 107 |00:00:00.01 | 14 | | | |
|* 1 | HASH JOIN RIGHT OUTER| | 1 | 107 | 107 |00:00:00.01 | 14 | 1376K| 1376K| 1511K (0)|
| 2 | TABLE ACCESS FULL | DEPARTMENTS | 1 | 27 | 27 |00:00:00.01 | 2 | | | |
| 3 | TABLE ACCESS FULL | EMPLOYEES | 1 | 107 | 107 |00:00:00.01 | 12 | | | |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
1 - access("E"."DEPARTMENT_ID"="D"."DEPARTMENT_ID")4. 기본 hash join으로 풀었을때는 (+)이 붙지 않은 반대 테이블을 드라이빙 테이블로 실행계획을 생성한다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics
leading(d,e)
use_hash(e)
*/
e.*, d.*
from hr.departments d, hr.employees e
where e.department_id = d.department_id(+);
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));Plan hash value: 2296652067
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Starts | E-Rows | A-Rows | A-Time | Buffers | OMem | 1Mem | Used-Mem |
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | | 107 |00:00:00.01 | 11 | | | |
|* 1 | HASH JOIN OUTER | | 1 | 107 | 107 |00:00:00.01 | 11 | 908K| 908K| 1222K (0)|
| 2 | TABLE ACCESS FULL| EMPLOYEES | 1 | 107 | 107 |00:00:00.01 | 4 | | | |
| 3 | TABLE ACCESS FULL| DEPARTMENTS | 1 | 27 | 27 |00:00:00.01 | 7 | | | |
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
1 - access("E"."DEPARTMENT_ID"="D"."DEPARTMENT_ID")
Note
-----
- dynamic statistics used: dynamic sampling (level=2)
- this is an adaptive plan5. 하지만 swap_join_inputs을 사용하여 outer join의 드라이빙 테이블을 변경할 수있는건 hash join 만 가능하다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics
leading(d,e)
use_hash(e)
swap_join_inputs(d)*/
e.*, d.*
from hr.departments d, hr.employees e
where e.department_id = d.department_id(+);
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));Plan hash value: 4017029581
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Id | Operation | Name | Starts | E-Rows | A-Rows | A-Time | Buffers | OMem | 1Mem | Used-Mem |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 1 | | 107 |00:00:00.01 | 14 | | | |
|* 1 | HASH JOIN RIGHT OUTER| | 1 | 107 | 107 |00:00:00.01 | 14 | 1376K| 1376K| 1569K (0)|
| 2 | TABLE ACCESS FULL | DEPARTMENTS | 1 | 27 | 27 |00:00:00.01 | 2 | | | |
| 3 | TABLE ACCESS FULL | EMPLOYEES | 1 | 107 | 107 |00:00:00.01 | 12 | | | |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Predicate Information (identified by operation id):
---------------------------------------------------
1 - access("E"."DEPARTMENT_ID"="D"."DEPARTMENT_ID")Query Transformation
- SQL문을 분석해 의미적으로 동일하면서 더 나은 성능이 기대되는 형태로 재작성하는 것을 의미한다.
- OPTIMIZER가 실행계획을 생성하기 전에 사용자가 작성한 SQL문 결과는 똑같은데 비용(COST)이 더 적게 발생할것 같으면 쿼리를 변경한다.
서브쿼리 처리 방식
- 서브쿼리(subquery)는 하나의 SQL문장 내에서 괄호로 묶인 별도의 쿼리 블록(Query Block)을 말한다. (SELECT)
inline view: from 절 괄호안에 select문nested subquerycorrelated subquery(상호관련, 상관관계있는) : 메인쿼리에 있는 컬럼이 서브쿼리에 있는 형태scalar subquery(스칼라 서브쿼리) : select절의 컬럼 위치에 select 문
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics
leading(e,d)
use_nl(d)
*/
e.employee_id, e.department_id, d.department_name
from hr.departments d join hr.employees e
on e.department_id = d.department_id;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));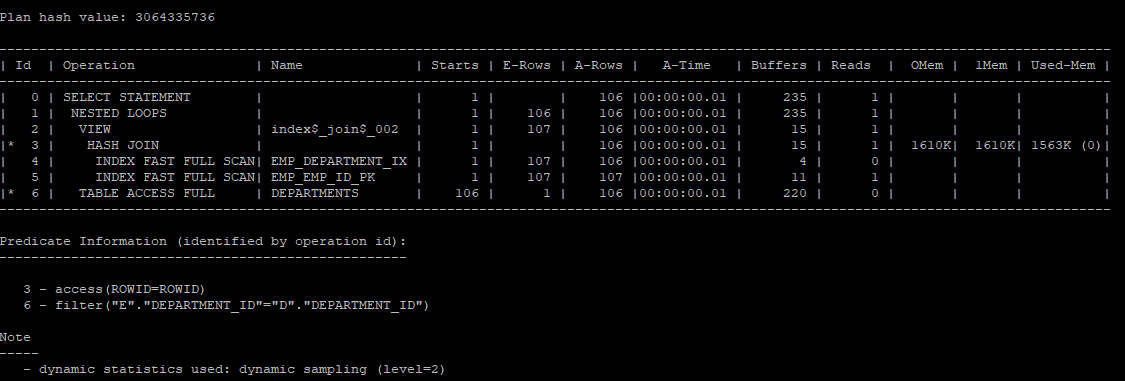
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics
leading(e,d)
use_nl(d)
*/
e.employee_id,e.salary, e.department_id, d.department_name
from hr.departments d join hr.employees e
on e.department_id = d.department_id;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));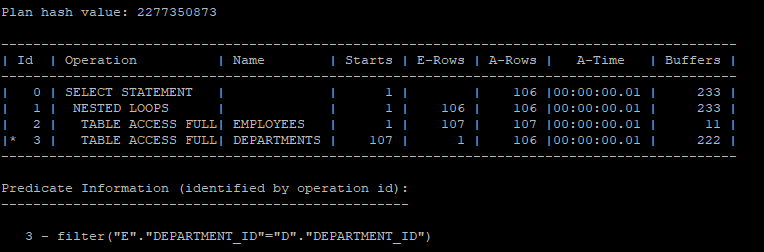
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics
leading(e,d)
use_nl(d)
*/
e.employee_id,e.salary, e.department_id, d.department_name
from hr.departments d join hr.employees e
on e.department_id = d.department_id
order by 3;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));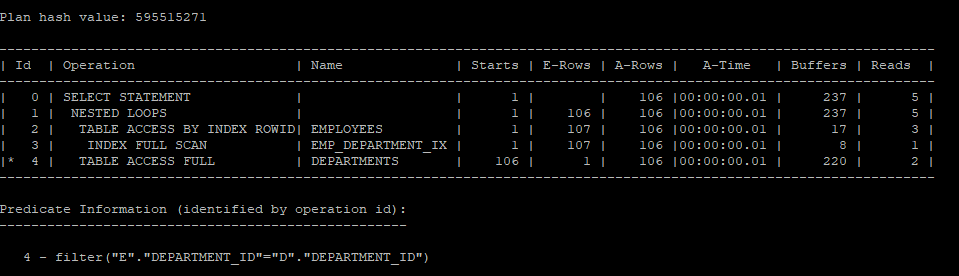
이 쿼리는 스칼라 서브쿼리(Scalar Subquery)를 사용하여 department_id에 맞는 department_name을 조회합니다. 스칼라 서브쿼리는 동일한 department_id 값이 반복해서 들어올 때 Query Execution Cache에 저장된 값을 반환하므로, I/O 작업이 줄어듭니다. 이는 성능 최적화를 가능하게 하여 중복 조회를 방지합니다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics*/
e.employee_id,e.salary, e.department_id,
(select department_name
from hr.departments
where department_id = e.department_id) dept_name
from hr.employees e;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));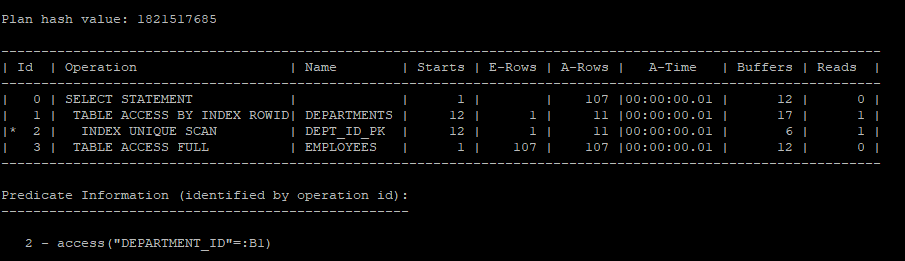
이 쿼리는 department_id에 대해 Primary Key와 Foreign Key 제약 조건이 적용되어 있기 때문에, 실제로는 departments 테이블을 조회하지 않고도 실행계획이 생성됩니다. 실행 계획에서는 employees 테이블만을 기반으로 쿼리가 처리되며, 이러한 제약 조건 덕분에 성능이 최적화되고 불필요한 테이블 스캔을 방지할 수 있습니다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ *
from hr.employees
where department_id in (select department_id from hr.departments);
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));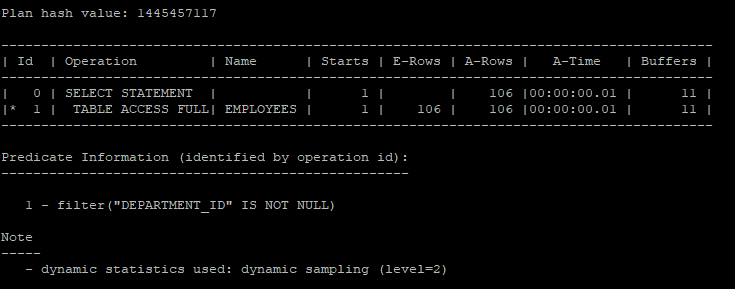
이 쿼리는 IN 연산자와 no_unnest 힌트를 사용해 filter 방식으로 처리됩니다. 메인 쿼리에서 각 행마다 서브쿼리를 반복 실행하여 department_id를 조건으로 데이터를 찾습니다. 내부적으로 상관 서브쿼리(correlated subquery)가 작동하며, 캐시 기능을 활용해 I/O를 줄이고 메인 테이블의 모든 데이터를 조회하지 않도록 최적화합니다.
- filter 방식 : 메인쿼리에서 읽히는 행마다 서브쿼리를 반복수행하면서 조건에 맞는 데이터를 찾는 방식(nested loop join 같은 작동방식)
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ *
from hr.employees
where department_id in (select /*+ no_unnest */ department_id from hr.departments);
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));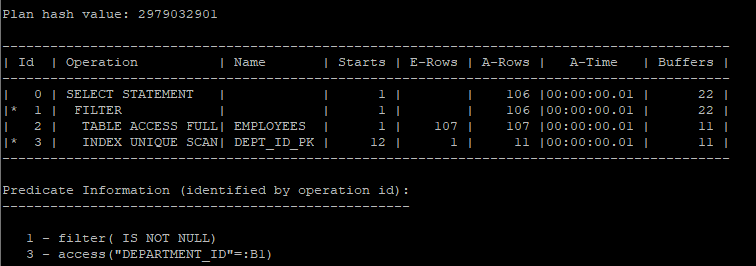
이 쿼리는 IN 연산자 대신 EXISTS를 사용해 상관 서브쿼리(correlated subquery) 방식으로 변환한 예시입니다. department_id가 hr.departments 테이블에 있는지를 확인하며, 내부적으로 캐시 기능을 활용해 전체 107개의 데이터를 모두 조회하지 않고 최적화된 방식으로 I/O를 줄입니다.
- 이는 unique scan이기 때문에 buffer pinning(random scan에서만 작동된다) 방식이 아닌 cache 기능이 돌아간걸 알 수 있다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ *
from hr.employees e
where exists (select /*+ no_unnest */ 'x' from hr.departments where department_id = e.department_id);
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));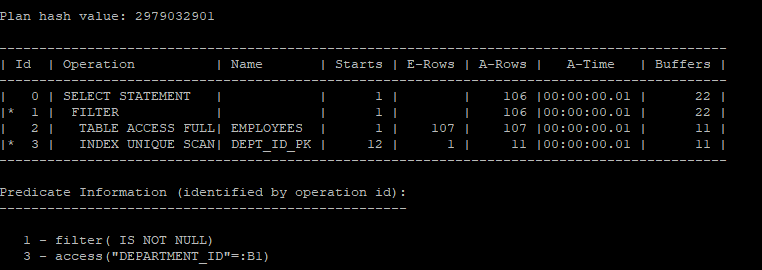
unnest 방식
- 동일한 결과를 보장한다면 서브쿼리를 조인문으로 변환한다.
- 조인으로 변환하면 다양한 액세스 경로, 조인 방법, 조인 순서를 결정할 수 있다.
- hint
unnest: filter 방식 보다는 조인 방식으로 실행계획을 만든다.no_unnest: filter 방식으로 실행계획을 만든다.
- exists : 후보행값이 조인으로 성공하면 결과 집합에 담고 다음 행을 수행한다.
- not exists : 후보행값이 조인으로 성공하면 그 행을 버리고 다음 행을 수행한다. 즉 후보행값이 조인으로 성공하지 않으면 결과 집합에 담는다.
unnest 방식이면서 조인제거가 되어있는 실행계획
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ *
from hr.employees e
where exists (select 'x' from hr.departments where department_id = e.department_id);
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'))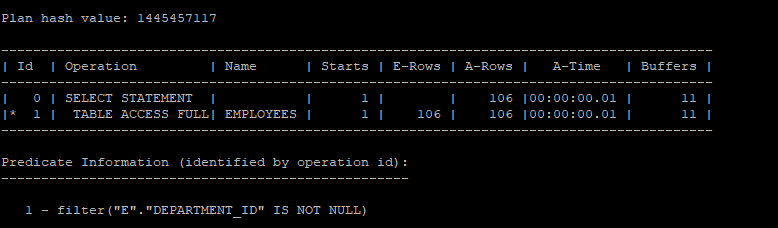
조인제거
- 1:M 관계인 두 테이블을 조인하는 쿼리문에서 1쪽 테이블을 참조하지 않는다면 1쪽 테이블을 읽지 않아도 된다.
- 즉, 조인제거 기능이 작동되려면 primary key, foreign key 설정되어 있어야만 조인제거(join elmination) 기능이 수행된다.
- hint
eliminate_joinno_eliminate_join
- 제약조건이 걸려있는걸 확인할 수 있다.
select c.column_name ,u.constraint_name, u.constraint_type, u.search_condition,u.r_constraint_name, u.index_name
from dba_constraints u, dba_cons_columns c
where u.constraint_name = c.constraint_name
and u.table_name in ('EMPLOYEES','DEPARTMENTS')
and u.owner = 'HR'
order by 1;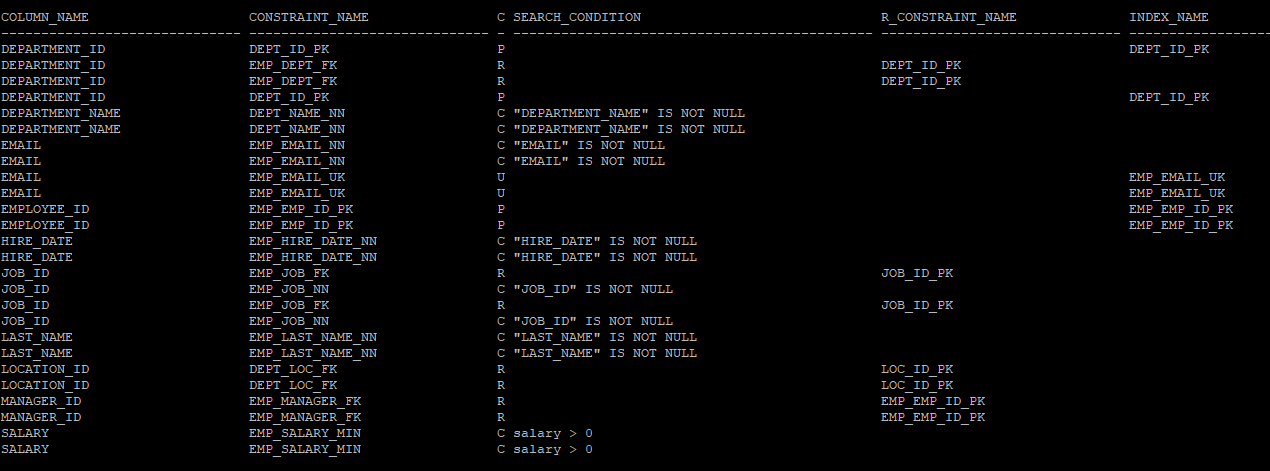
의도적으로 no_eliminate_join을 이용해 조인제거를 해보았더니 i/o가 더 좋지 않아졌다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ *
from hr.employees e
where exists (select /*+ no_eliminate_join(d) */ 'x' from hr.departments d where department_id = e.department_id);
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));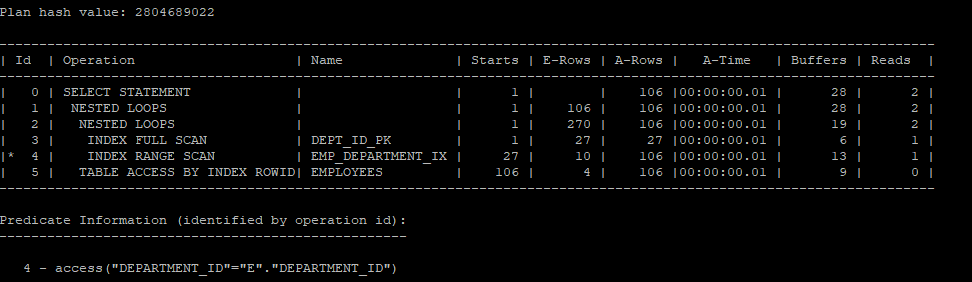
히든파라미터로 기본적으로 조인제거가 활성화 되어있는걸 알 수 있다.
select a.ksppinm as parameter,b.ksppstvl as session_value, c.ksppstvl as instance_value
from x$ksppi a, x$ksppcv b, x$ksppsv c
where a.indx = b.indx
and a.indx = c.indx
and a.ksppinm = '_optimizer_join_elimination_enabled';
primary key, foreign key 제약조건이 걸려 있기 때문에 employees 테이블만 조회하는 경우에도 조인제거 기능이 수행되는걸 볼 수 있다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ e.*
from hr.departments d join hr.employees e
on e.department_id = d.department_id;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));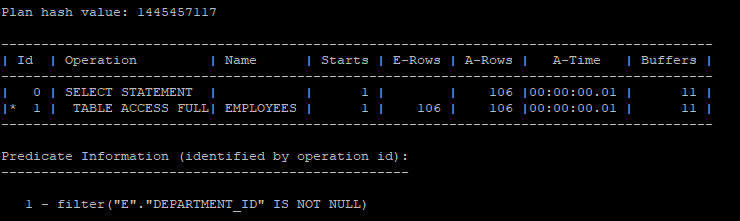
조인제거 비활성화
alter session set "_optimizer_join_elimination_enabled" = false;
조인제거가 비활성화 되어 nested loops join으로 수행한다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ e.*
from hr.departments d join hr.employees e
on e.department_id = d.department_id;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));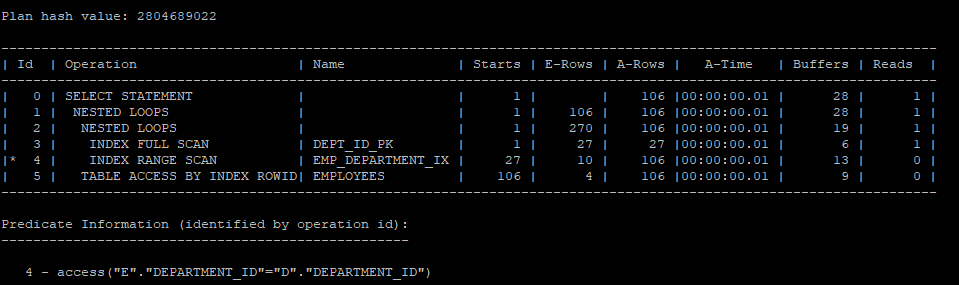
department_id는 foreign key 제약조건이 걸려있기 때문에 굳이 exists로 쿼리를 작성하지 않아도 된다. exists로 작성하여도 옵티마이저는 내부적으로 해당 쿼리문으로 변경하여 실행계획을 생성한다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ *
from hr.employees
where department_id is not null;filter 방식과 unnest의 차이
1. 첫 번째 쿼리 (no_unnest 힌트 사용):
- 이 쿼리는 no_unnest 힌트를 사용하여 서브쿼리를 필터 방식으로 처리합니다. 서브쿼리가 메인 쿼리의 각 행마다 반복적으로 실행되어 결과를 반환하는 방식입니다.
- 실행 계획에서 서브쿼리가 분리되어 있고, 필터링에 많은 리소스가 사용될 수 있습니다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ *
from hr.employees
where department_id in (select /*+ no_unnest */ department_id
from hr.departments
where location_id = 1500);
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));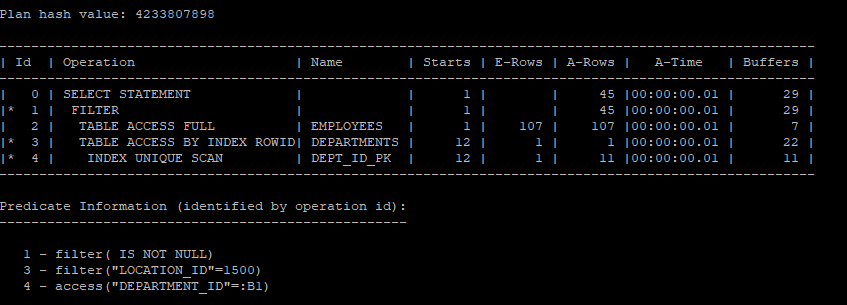
2. 두 번째 쿼리 (unnest 힌트 사용):
- 이 쿼리는 unnest 힌트를 사용해 서브쿼리를 조인 방식으로 변환합니다. 이 방식은 서브쿼리를 메인 쿼리와 병합하여 동시에 처리하게 됩니다.
- 실행 계획에서 서브쿼리가 메인 쿼리와 조인되어 빠르게 처리되며, 더 효율적인 방식으로 리소스 소비를 줄입니다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ *
from hr.employees
where department_id in (select /*+ unnest */ department_id
from hr.departments
where location_id = 1500);
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));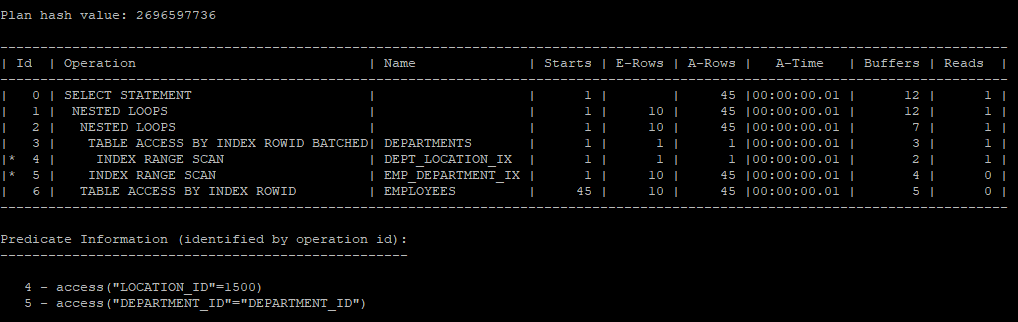
3. 서브쿼리를 조인으로 변환
- 메인쿼리의 employees 테이블과 서브쿼리의 departments 테이블과의 관계는 m:1 이기때문에 조인문으로 바꾸더라도 쿼리 결과가 보장된다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ e.*
from hr.employees e, hr.departments d
where e.department_id = d.department_id
and d.location_id = 1500;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));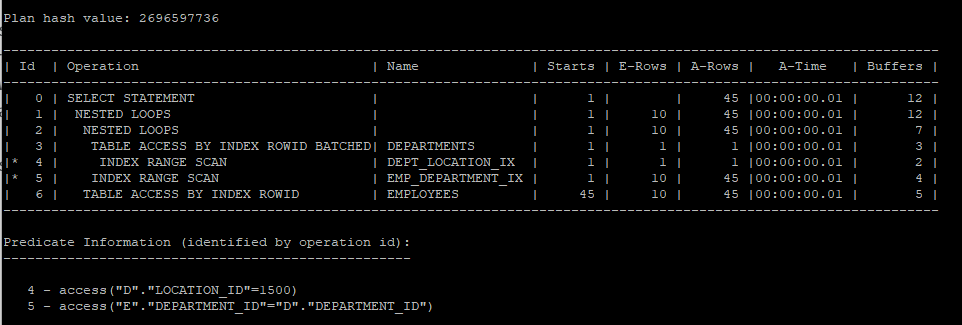
4. 메인쿼리를 1쪽 집합으로 하고 서브쿼리를 m쪽 집합으로 하게 되면 nested loops semi 조인을 하게 된다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ *
from hr.departments d
where exists (select 'x'
from hr.employees
where department_id = d.department_id);
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));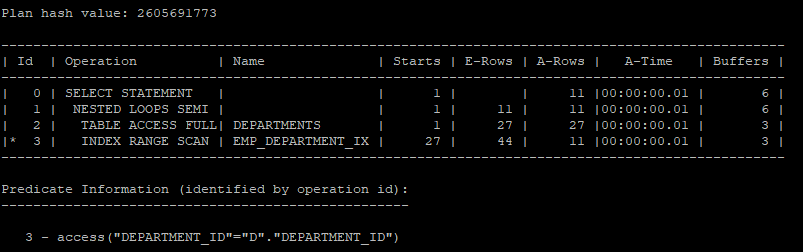
서브쿼리를 조인으로 변환의 문제점
- 메인쿼리 테이블이 1쪽 집합인 경우 조인 결과 집합이 1쪽 집합의 총 건수를 넘지 않아야 한다.
만약에 조인문장으로 변환한다면 1:m 관계일 경우 m쪽 집합처럼 건수가 나오기 때문에 잘못된 결과가 발생한다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ d.*
from hr.employees e, hr.departments d
where e.department_id = d.department_id;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));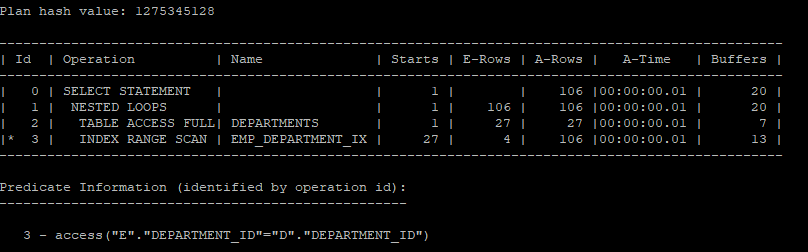
M쪽 집합을 1쪽 집합처럼 변환 시 문제점
- 의도적으로 M:1 관계를 만들기 위해 employees 테이블에서 distinct를 사용해 department_id를 중복 제거하고 조인하면, 불필요한 해시 함수가 발생해 성능이 저하될 수 있습니다.
- 이렇게 하면 해시 함수가 실행되면서 불필요한 리소스 소모가 발생하여 성능이 저하되고 악성 쿼리가 될 수 있습니다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ d.*
from (select distinct department_id from hr.employees) e, hr.departments d
where e.department_id = d.department_id;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));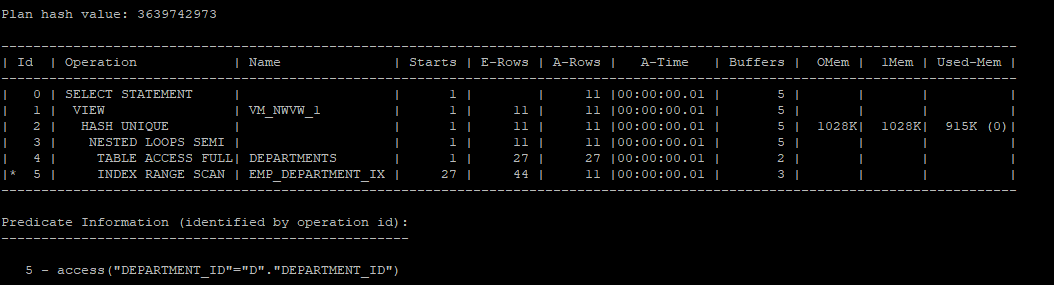
semi join
- 서브쿼리를 조인으로 바꾼다.
- 조인으로 바뀐 서브쿼리를 항상 후행(inner)처리가 된다.
- 메인쿼리의 행이 서브쿼리의 행과 조인조건이 만족하면 더이상 조인검색하지 않고(break) 조인결과 집합으로 만들고 다음 행을 수행한다.
- hint
nl_sjmerge_sjhash_sj
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ *
from hr.departments d -- departments는 1쪽 집합이다
where exists (select 'x'
from hr.employees -- m쪽 집합
where department_id = d.department_id);
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));
nested semi join 실습
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ *
from hr.departments d
where exists (select /*+ unnest nl_sj */'x'
from hr.employees
where department_id = d.department_id);
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));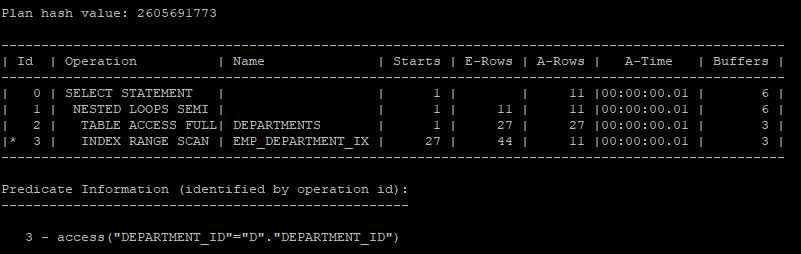
sort merge semi join 실습
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ *
from hr.departments d
where exists (select /*+ unnest merge_sj */'x'
from hr.employees
where department_id = d.department_id);
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));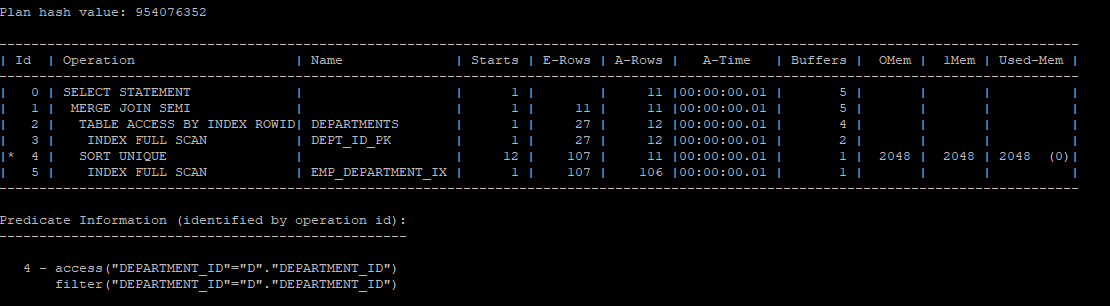
hash semi join 실습
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ *
from hr.departments d
where exists (select /*+ unnest hash_sj */'x'
from hr.employees
where department_id = d.department_id);
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));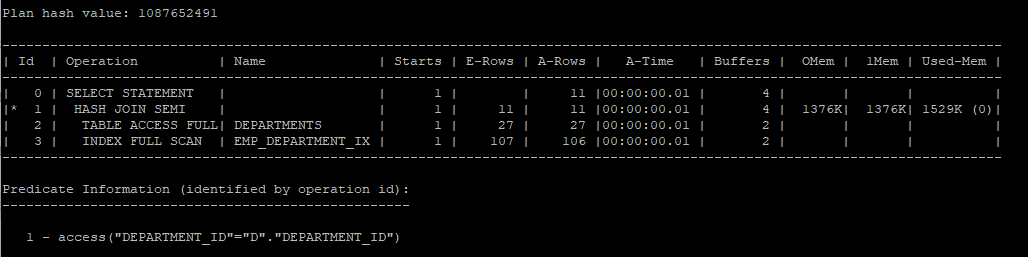
anti join
- 조인의 값이 존재하지 않은 행을 찾는다.
- 서브쿼리를 조인으로 바꾼다.
- 조인으로 바뀐 서브쿼리는 항상 후행(inner)처리가 된다.
- 메인쿼리의 행이 서브쿼리의 행과 조인으로 성립되면 버리고, 다음 행을 수행하면서 조인으로 성립되지 않으면(break) 결과집합으로 생성한다.
- hint
nl_ajmerge_ajhash_aj
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ *
from hr.departments d
where not exists (select 'x'
from hr.employees
where department_id = d.department_id);
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));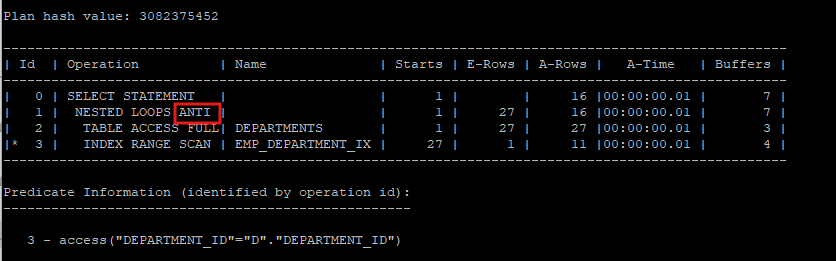
nested anti join 실습
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ *
from hr.departments d
where not exists (select /*+ unnest nl_aj */'x'
from hr.employees
where department_id = d.department_id);
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));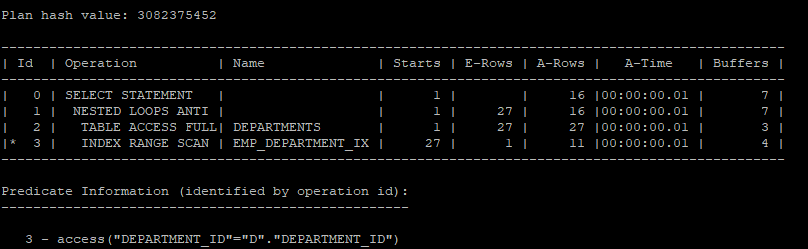
sort merge anti join 실습
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ *
from hr.departments d
where not exists (select /*+ unnest merge_aj */'x'
from hr.employees
where department_id = d.department_id);
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));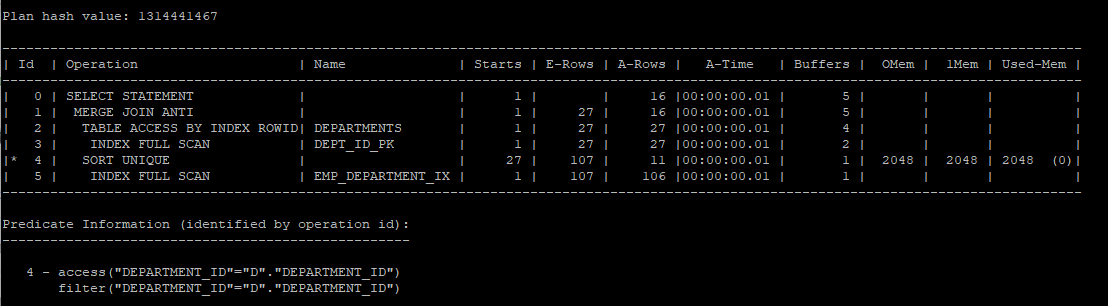
hash anti join 실습
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ *
from hr.departments d
where not exists (select /*+ unnest hash_aj */'x'
from hr.employees
where department_id = d.department_id);
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));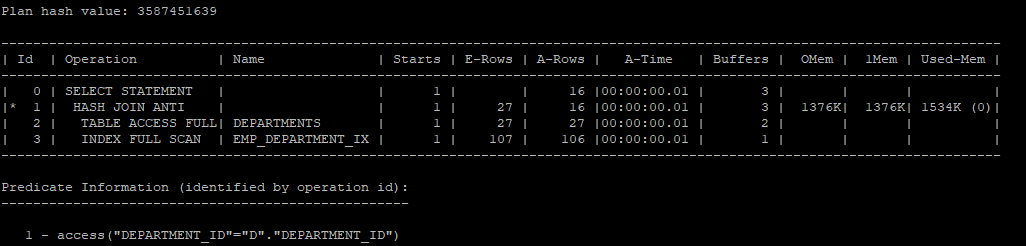
3개의 테이블을 join으로 실행계획 생성
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ e.*,d.*
from hr.employees e, hr.departments d, hr.locations l
where e.department_id = d.department_id
and d.location_id = l.location_id
and l.city = 'London';
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));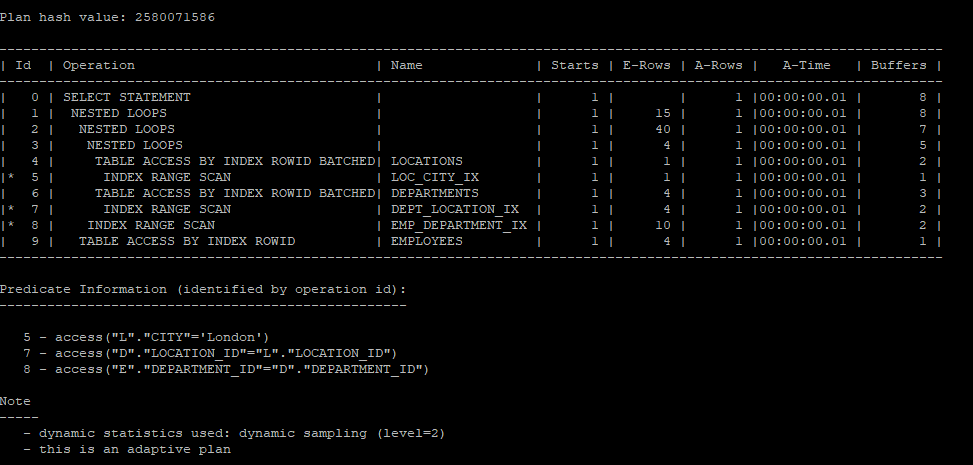
subquery절을 사용하였지만 unnest기능이 수행되었기 때문에 join처럼 수행된다.
- employees 테이블과 departments 테이블의 조인값이 m쪽 집합, locations 테이블은 1쪽 집합이기 때문에 semi 조인하지 않고 일반적인 join을 수행한다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ e.*,d.*
from hr.employees e, hr.departments d
where e.department_id = d.department_id
and exists (select *
from hr.locations
where location_id = d.location_id
and city = 'London');
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));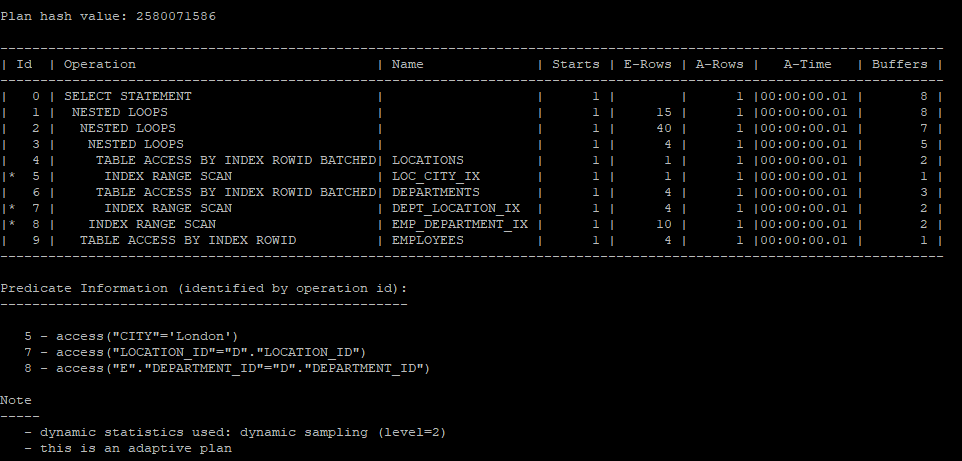
의도적으로 filter 방식을 사용하기 위해 no_unnest 사용
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ e.*,d.*
from hr.employees e, hr.departments d
where e.department_id = d.department_id
and exists (select /*+ no_unnest */ *
from hr.locations
where location_id = d.location_id
and city = 'London');
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));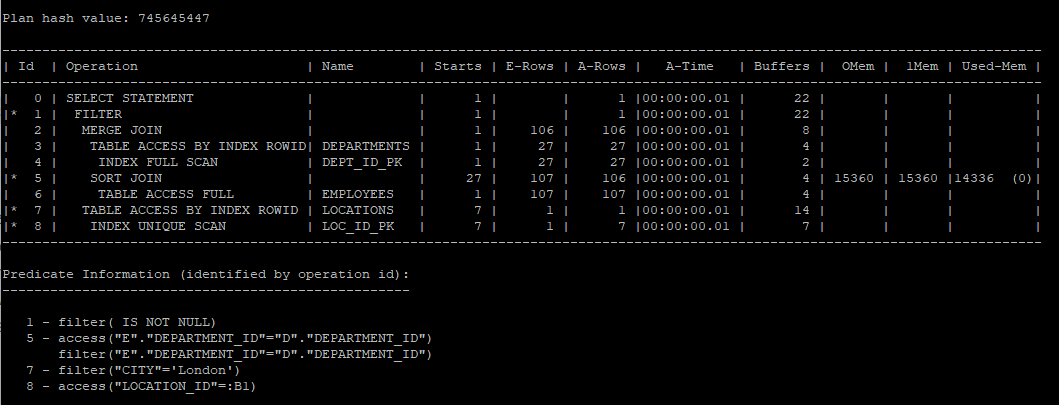
pushing subqeury
- 실행계획상 가능한 앞 단계에서 서브쿼리 필터링을 먼저 처리함으로써 다음 수행단계로 넘어가는 행수를 줄일수 있는 기능
- unnesting 되지 않은 서브쿼리 처리 순서를 제어하는 기능
- hint
push_subq
push_subq 힌트를 사용해서 locations 테이블을
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ e.*,d.*
from hr.employees e, hr.departments d
where e.department_id = d.department_id
and exists (select /*+ no_unnest push_subq */ *
from hr.locations
where location_id = d.location_id
and city = 'London');
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));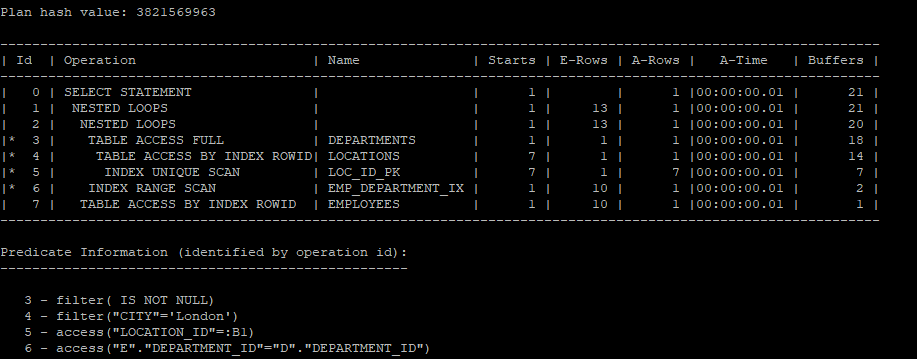
- 위의 3,4,5 부분을 쿼리로 풀어서 작성
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ *
from hr.departments d
where exists (select 'x'
from hr.locations
where location_id = d.location_id
and city = 'London')
and location_id is not null;view merging
- view를 해체하여 메인쿼리와 통합한다.
- hint
merge: view를 해체no_merge: view를 해체하지 않는다.
inline view를 사용하였지만 merge 되어 view를 해체하였다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ *
from (select * from hr.employees where manager_id = 145) e,
(select * from hr.departments where location_id = 2500) d
where e.department_id = d.department_id;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));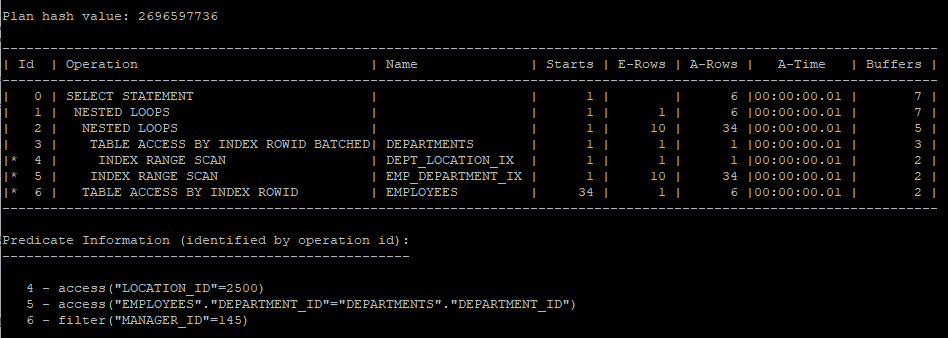
inline view로 작성한 쿼리문은 내부적으로는 아래 조인처럼 풀린다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ *
from hr.employees e, hr.departments d
where e.department_id = d.department_id
and e.manager_id = 145
and d.location_id = 2500;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));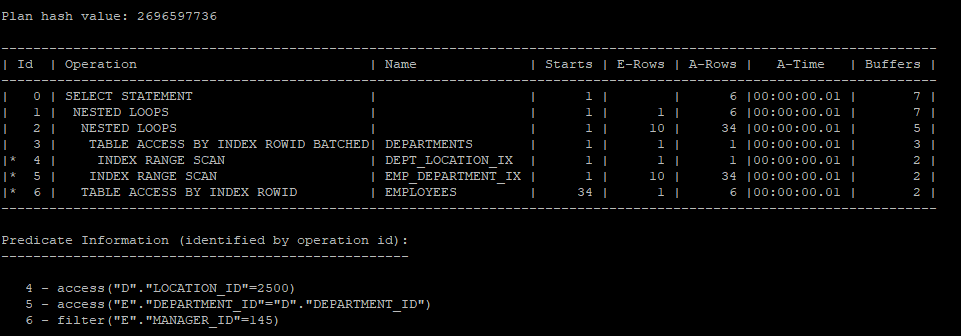
no_merge 힌트를 사용하여 view를 해체하지 않는 실행계획 생성
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ *
from (select /*+ no_merge */ * from hr.employees where manager_id = 145) e,
(select /*+ no_merge */ * from hr.departments where location_id = 2500) d
where e.department_id = d.department_id;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));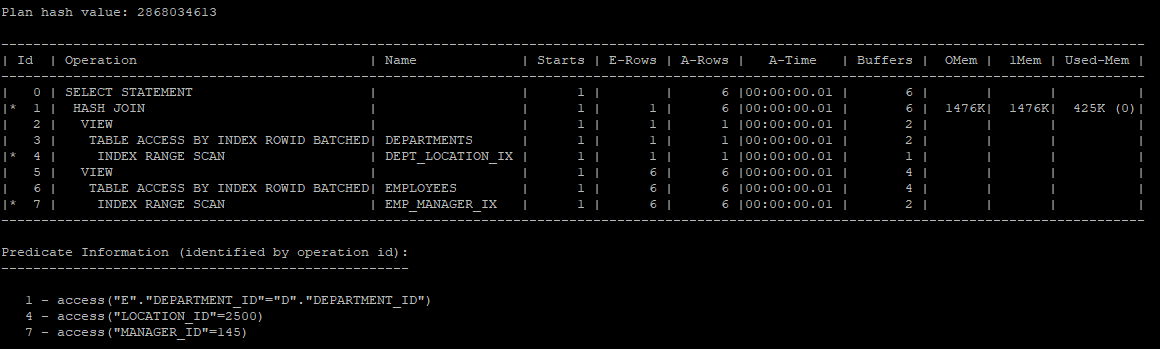
inline view가 사용되었지만 merge 되어 view가 해체되었고, 실행계획을 보게되면 departments의 department_id는 primary key로 1건만 있을걸 알기 때문에 카네시안 곱으로 실행계획을 풀어버린다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ *
from hr.employees e, (select * from hr.departments where department_id = 20) d
where e.department_id = d.department_id ;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));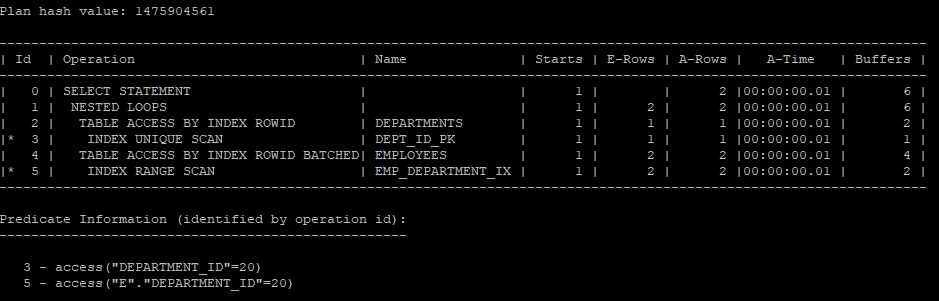
optimizer 내부적으로는 아래 쿼리문으로 변환되어서 실행계획을 만든거다.(카테시안곱)
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ *
from hr.employees e, hr.departments d
where e.department_id = 20
d.department_id = 20;view 해체하였을때 실행계획
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ d.department_id,
d.department_name, e.avg_sal
from hr.departments d,
(select department_id, avg(salary) avg_sal
from hr.employees
group by department_id) e
where e.department_id = d.department_id
and d.location_id = 1800;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));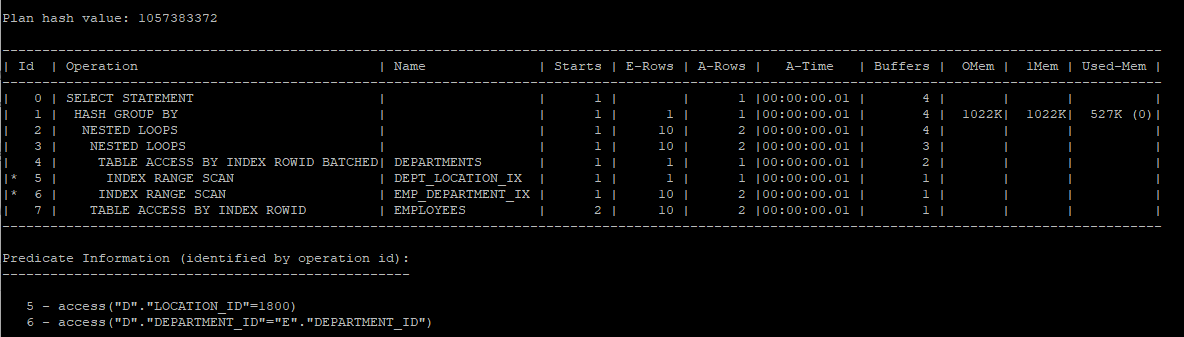
조인조건 pushdown
- 조인 조건절을 뷰 쿼리 블록안으로 넣어서 조인수행시 드라이빙 테이블에서 읽은 조인 컬럼값을 inner쪽 뷰 쿼리 블록 내에서 참조할 수 있도록 하는 기능
- 단 뷰 merge가 안되는 경우 발생
view 해체작업이 안되었을 경우 실행계획
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ d.department_id, d.department_name, e.avg_sal
from hr.departments d, (select /*+ no_merge */ department_id, avg(salary) avg_sal
from hr.employees
group by department_id) e
where e.department_id = d.department_id
and d.location_id = 1800;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));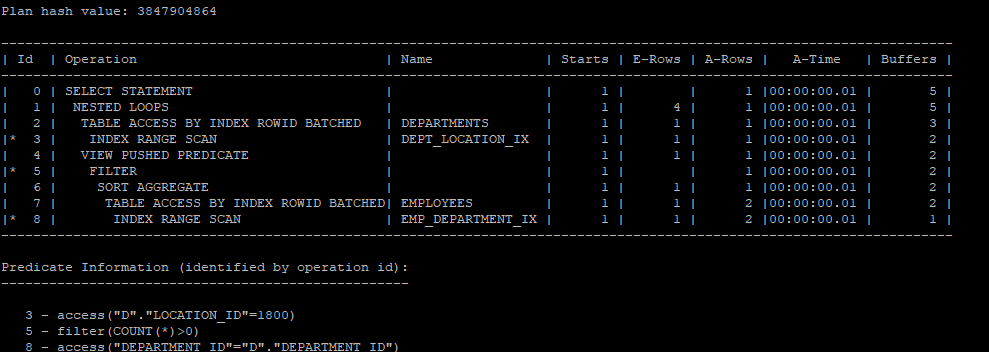
2,3 번 수행구문
select *
from hr.departments
where location_id = 1800;4번 : view 안의 조건부 술어에 department_id 값을 넣는다.
6,7,8번 수행구문, group 함수를 사용하면 sort aggregate operation이 발생(sort가 발생하는것이 아니라 그냥 이름일 뿐이다)
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ avg(salary) avg_sal
from hr.employees
where department_id = 20;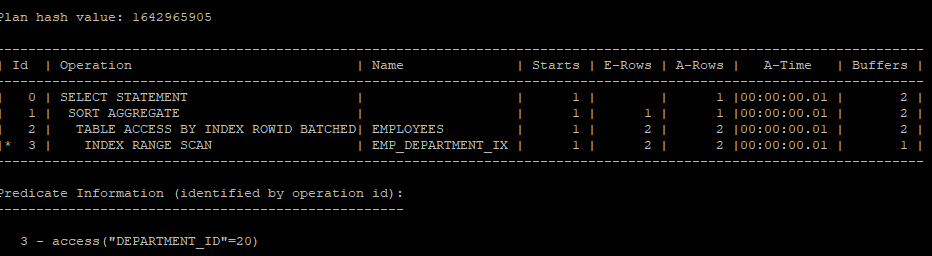
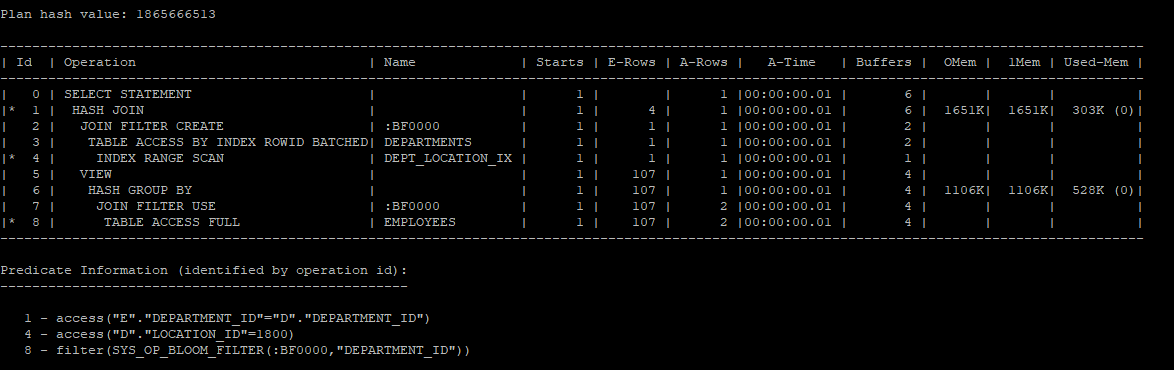
bloom filter
- hash join시 probe 테이블에서 조인에 참여하는 건수를 줄임으로써 조인 시간을 단축시키는 알고리즘
push_predicate를 적용하지 않겠다.
- 해시테이블에서 join filter를 create 하고 probe쪽에서 join filter use를 사용해서 걸러서 해시테이블로 올린다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ d.department_id, d.department_name, e.avg_sal
from hr.departments d, (select /*+ no_merge no_push_pred */ department_id, avg(salary) avg_sal
from hr.employees
group by department_id) e
where e.department_id = d.department_id
and d.location_id = 1800;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));