조건절 pushdown
- group by 절에 포함된 복합 뷰는 merging에 실패했을 경우(group by가 사용된 뷰는 veiw merging(해체) 처리를 할 수 없다) 쿼리 블록 밖에 있는 조건절을 쿼리 블록 안쪽으로 입력함으로써 group by 해야할 데이터 양을 줄일 수 있다.
원래는 where절의 조건 컬럼은 인라인뷰 안의 컬럼이기 때문에 index scan을 할 수 없다. 하지만 내부적으로 pushdown이 돌아가기 때문에 조건절이 인라인뷰 안으로 들어가서 수행된다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ *
from (select department_id, sum(salary) sum_sal from hr.employees group by department_id)
where department_id = 20;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));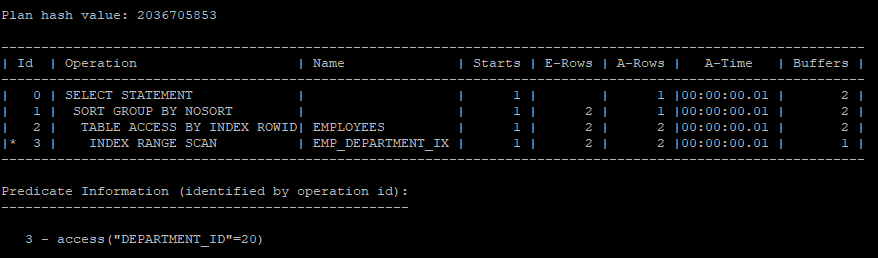
- 내부적으로는 아래 쿼리가 돌아간거다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ *
from (select department_id, sum(salary) sum_sal
from hr.employees
where department_id = 20
group by department_id);
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));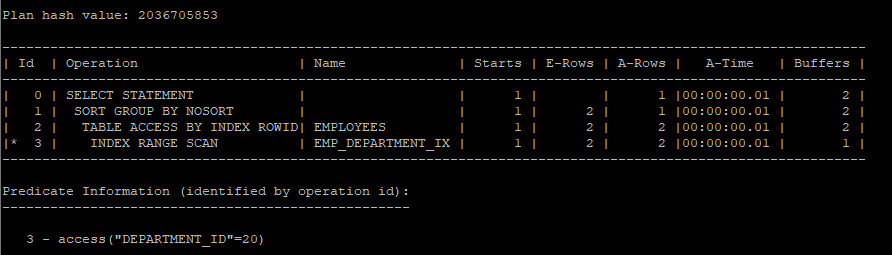
- 20번 부서만 한정해서 salary의 합을 구하는 거기 때문에 아래 쿼리로 간단하게 작성할 수 있다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ 20 as department_id, sum(salary) as sum_sal
from hr.employees
where department_id = 20;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));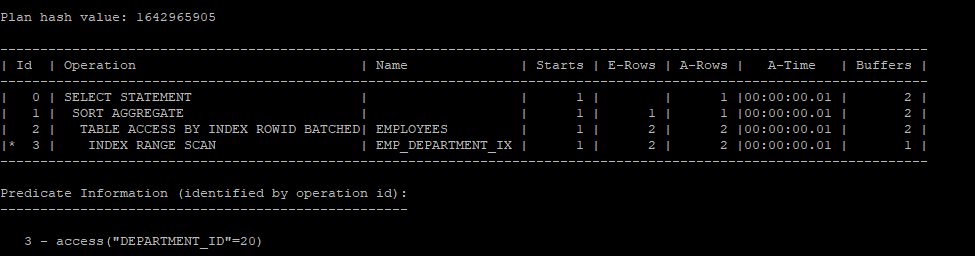
조건절 pullup
- 조건절을 쿼리 블록 안으로 밀어 넣을 뿐만 아니라 안쪽에 있는 조건들을 바깥쪽으로 끄집어 내기도 하는데 이를 조건절 pullup 이라고 한다.
개발자 입장에서 잘못 작성한 코드
- 내부적으로 department_id = 20의 조건절을 바깥으로 내보낸뒤(조건절 pullup) 다시 안으로 push down 시키는 방식으로 옵티마이저는 처리한다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ a.department_id, a.sum_sal, b.max_sal, b.min_sal
from (select department_id, sum(salary) sum_sal
from hr.employees
where department_id = 20
group by department_id) a,
(select department_id, max(salary) max_sal, min(salary) min_sal
from hr.employees
group by department_id) b
where a.department_id = b.department_id;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));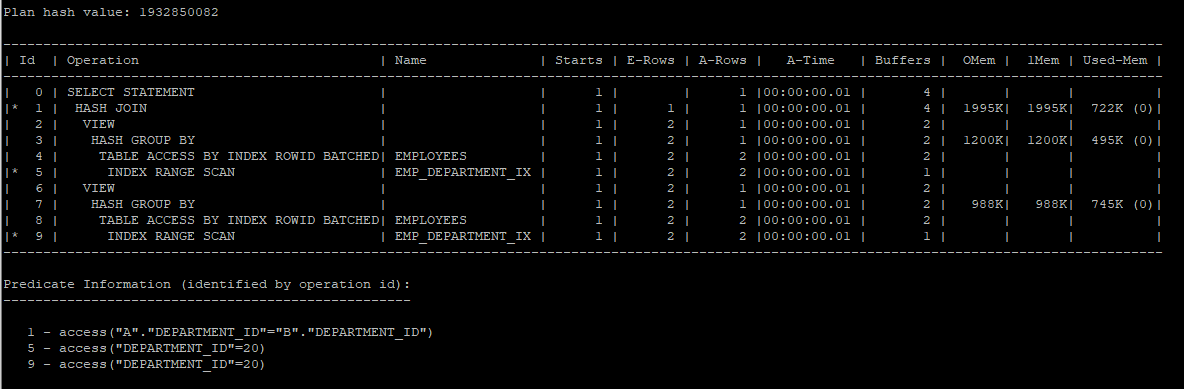
- 옵티마이저는 아래 쿼리문으로 수행하고 있다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ a.department_id, a.sum_sal, b.max_sal, b.min_sal
from (select department_id, sum(salary) sum_sal
from hr.employees
where department_id = 20
group by department_id) a,
(select department_id, max(salary) max_sal, min(salary) min_sal
from hr.employees
where department_id = 20
group by department_id) b
where a.department_id = b.department_id;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));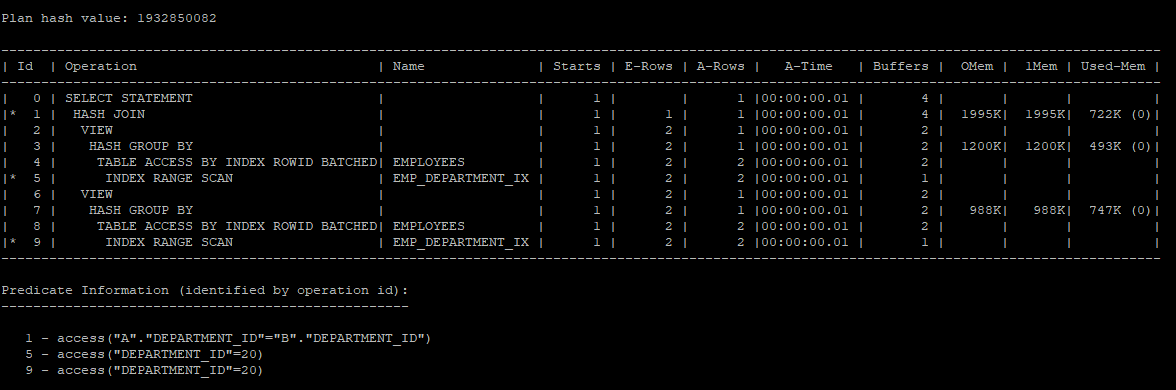
- 아래 쿼리문으로 간단하게 변경할 수 있다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ 20 as department_id, sum(salary) as sum_sal, max(salary) max_sal, min(salary) min_sal
from hr.employees
where department_id = 20;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));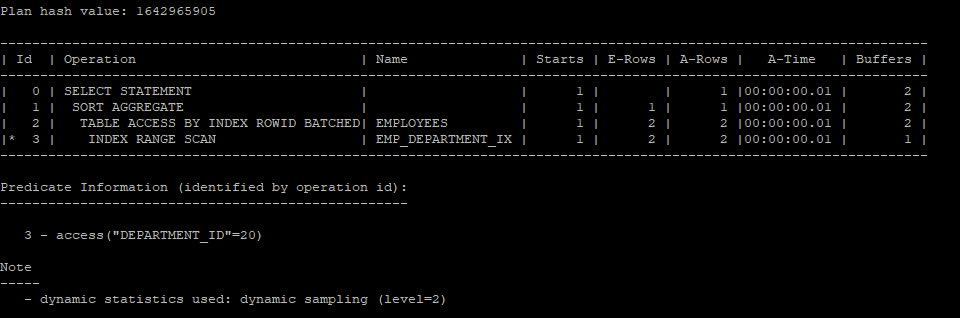
- 조건절의 이동을 막는 hint를 사용하였기 때문에 두번째 인라인뷰는 full table scan을 하게 된다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics no_push_pred(b)
opt_param('_pred_move_around','false') */ a.department_id, a.sum_sal, b.max_sal, b.min_sal
from (select department_id, sum(salary) sum_sal
from hr.employees
where department_id = 20
group by department_id) a,
(select department_id, max(salary) max_sal, min(salary) min_sal
from hr.employees
group by department_id) b
where a.department_id = b.department_id;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));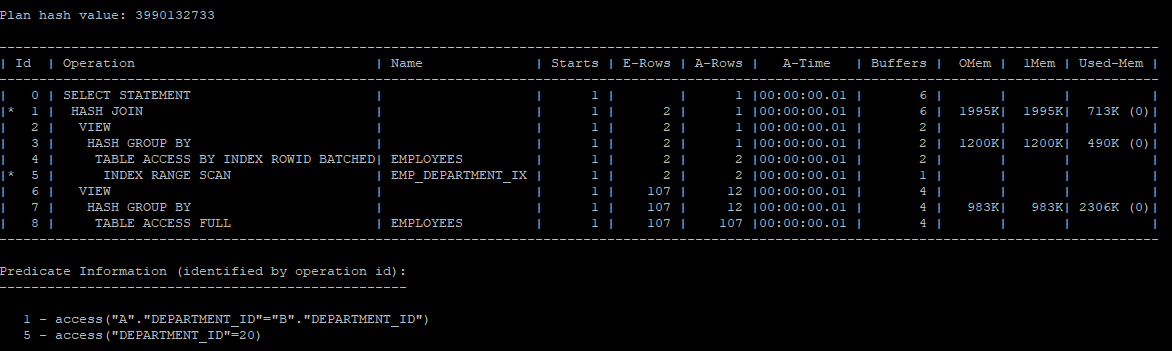
or - expansion
- 사용자의 쿼리를 직접 바꾸지 않아도 optimizer가 or 조건을 full table scan 처리가 아닌 index range scan을 수행하면서 union all 형태로 변경처리하는 기능
- hint
use_concat: or - expansion 유도no_expand: or - expansion 유도 방지
or 조건으로 실행계획을 생성했을때는 full table scan을 한다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ *
from hr.employees
where job_id = 'IT_PROG' or department_id = 20;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));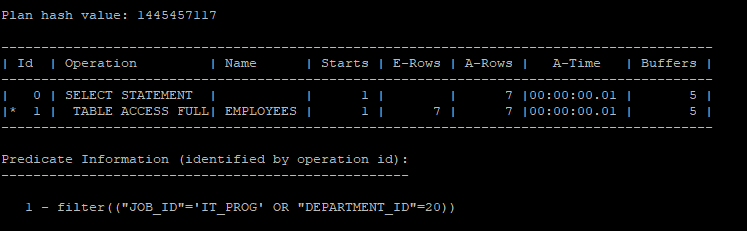
- 조건들을 따로따로 실행하게 되면 index range scan을 하게 된다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ *
from hr.employees
where job_id = 'IT_PROG';
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));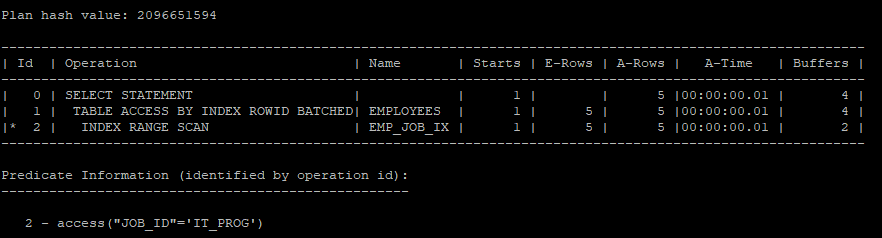
- 조건들을 따로따로 실행하게 되면 index range scan을 하게 된다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ *
from hr.employees
where department_id = 20;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));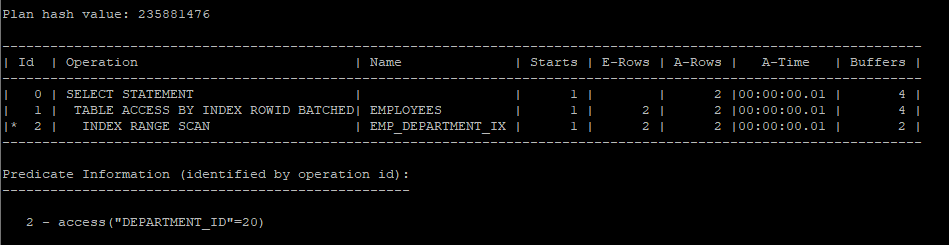
- 실행계획을 따로따로 수행 한뒤 합쳐주는걸 확인 할 수 있다.
- 하지만 union으로 중복을 제거하기 위해 sort를 유발한다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ *
from hr.employees
where job_id = 'IT_PROG'
union
select *
from hr.employees
where department_id = 20;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));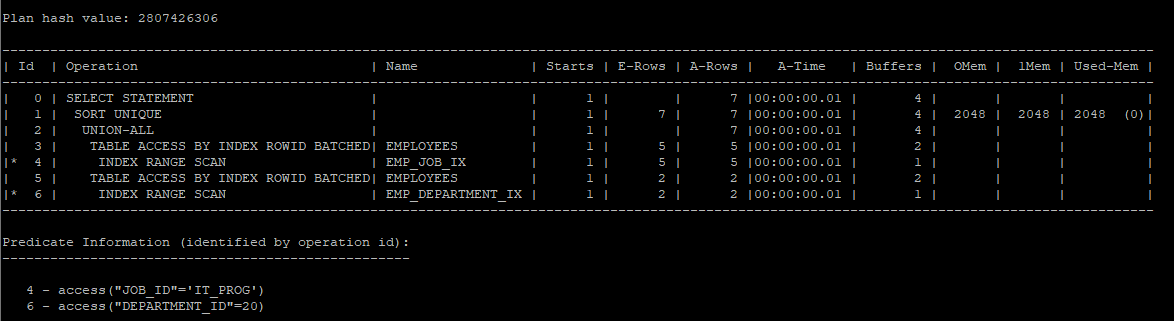
- 중복된게 없다고 가정하고 union all을 하게 되면 sort operation는 나타나지 않는다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ *
from hr.employees
where job_id = 'IT_PROG'
union all
select *
from hr.employees
where department_id = 20;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));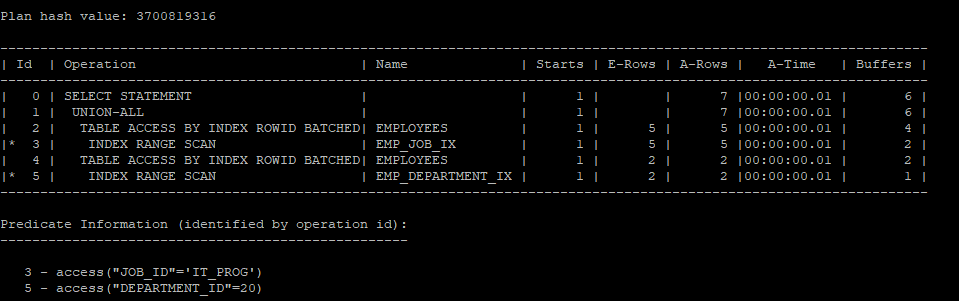
- lnnvl 함수를 이용해서 조건주기
- LNNVL 함수는 NULL 값이 포함된 논리적 조건식에서 NULL을 TRUE로 처리해 부정 논리를 명확하게 평가하는 Oracle 함수입니다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ *
from hr.employees
where job_id = 'IT_PROG'
and lnnvl(department_id = 20); # (department_id <> 20 or department_id is null);
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));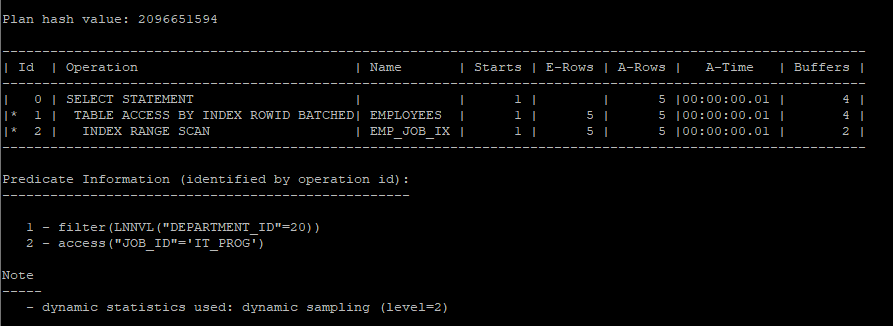
- lnnvl 함수를 이용해서 union을 사용하지 않고 union all로 쿼리를 작성할 수있다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ *
from hr.employees
where job_id = 'IT_PROG'
and lnnvl(department_id = 20)
union all
select *
from hr.employees
where department_id = 20;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));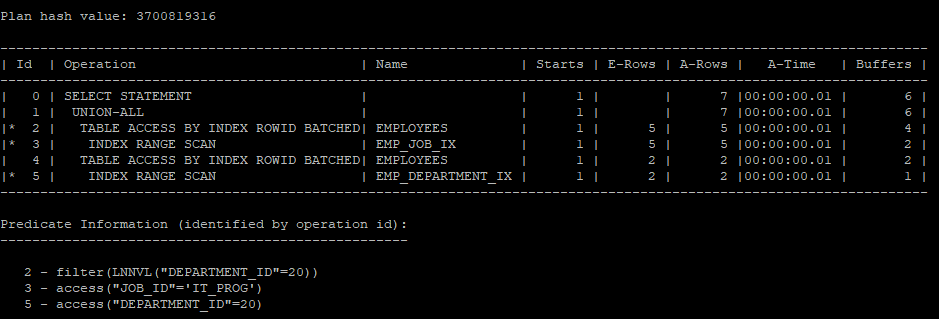
- 하지만 함수를 사용하지 않아도 hint를 사용하면 lnnvl 함수를 사용한 거처럼 실행계획을 생성한다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics use_concat */ *
from hr.employees
where job_id = 'IT_PROG' or department_id = 20;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));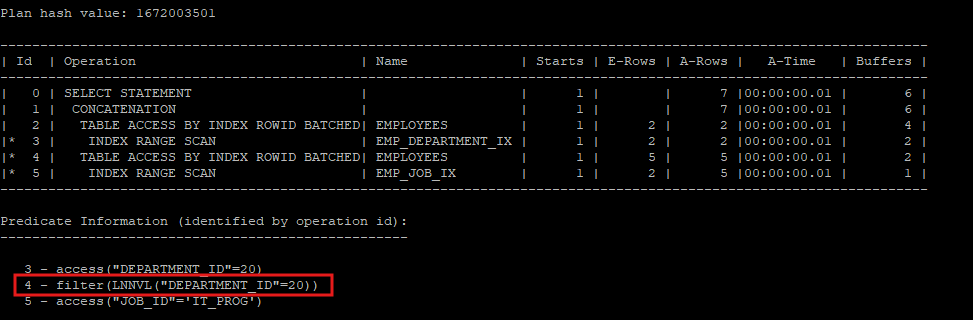
- 50번 부서의 사원은 대부분 이기 때문에 실행계획을 분리할 경우 오히려 i/o가 좋지 않다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics use_concat */ *
from hr.employees
where job_id = 'IT_PROG' or department_id = 50;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));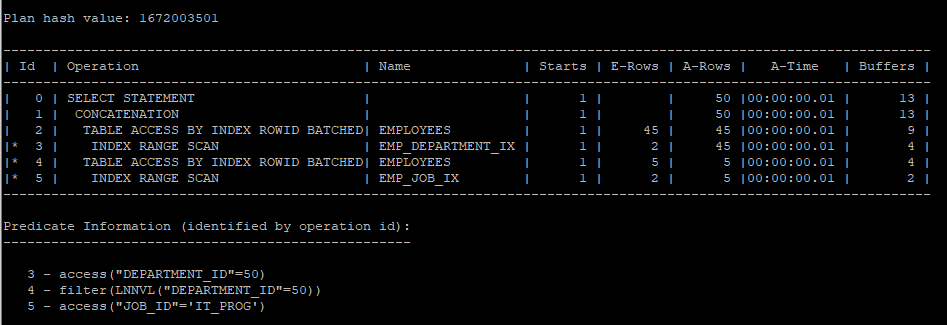
- 이럴 경우에는 실행계획을 분리하지 않고 full table scan을 하는게 i/o측면에서 유리하다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics no_expand */ *
from hr.employees
where job_id = 'IT_PROG' or department_id = 50;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));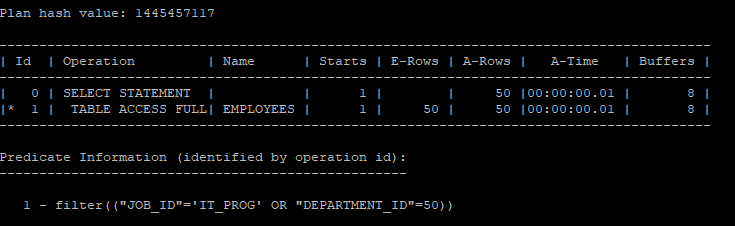
- index scan을 유도했지만 full table scan보다 i/o가 증가하였기때문에 꼭 index scan이 좋은 것만은 아니다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ *
from hr.employees
where job_id = 'IT_PROG'
and lnnvl(department_id = 50)
union all
select /*+ index(e emp_department_ix) */ *
from hr.employees e
where department_id = 50;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));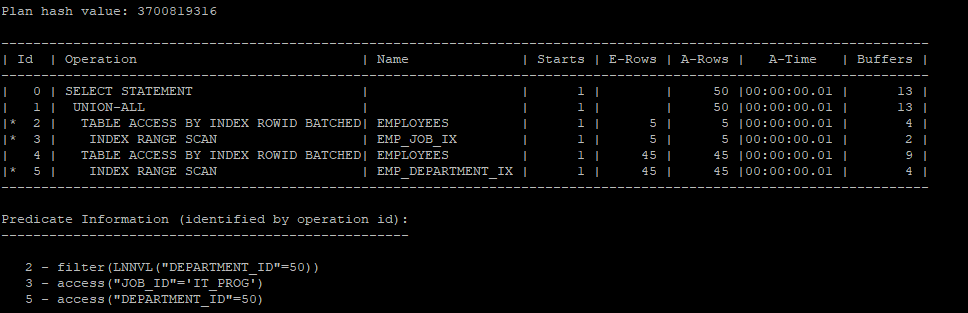
- 꼭 실행계획을 분리해서 생성하고 싶다면 크기가 큰 테이블은 full table scan을 유도해서 union all 해주는게 i/o 가 좋다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ *
from hr.employees
where job_id = 'IT_PROG'
and lnnvl(department_id = 50)
union all
select /*+ full(e) */ *
from hr.employees e
where department_id = 50;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));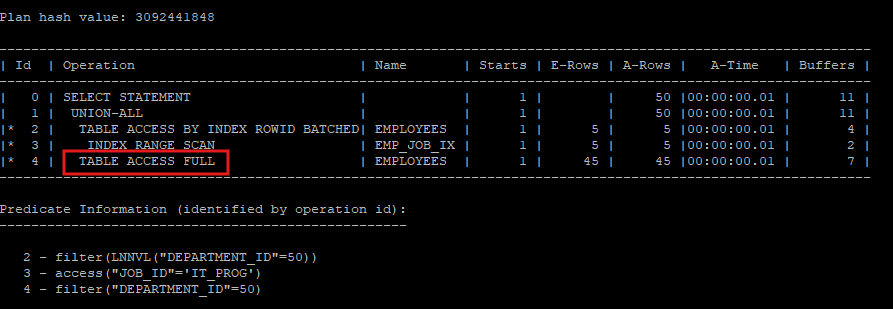
문제
자신의 부서 평균 급여보다 더 많이 받는 사원들의 employee_id, salary, department_name 조회
- 처음에는 correlated subquery로 작성하였다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ e.employee_id, e.salary, d.department_name
from hr.employees e, hr.departments d
where e.department_id = d.department_id
and e.salary > (select avg(salary)
from hr.employees
where department_id = e.department_id);
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));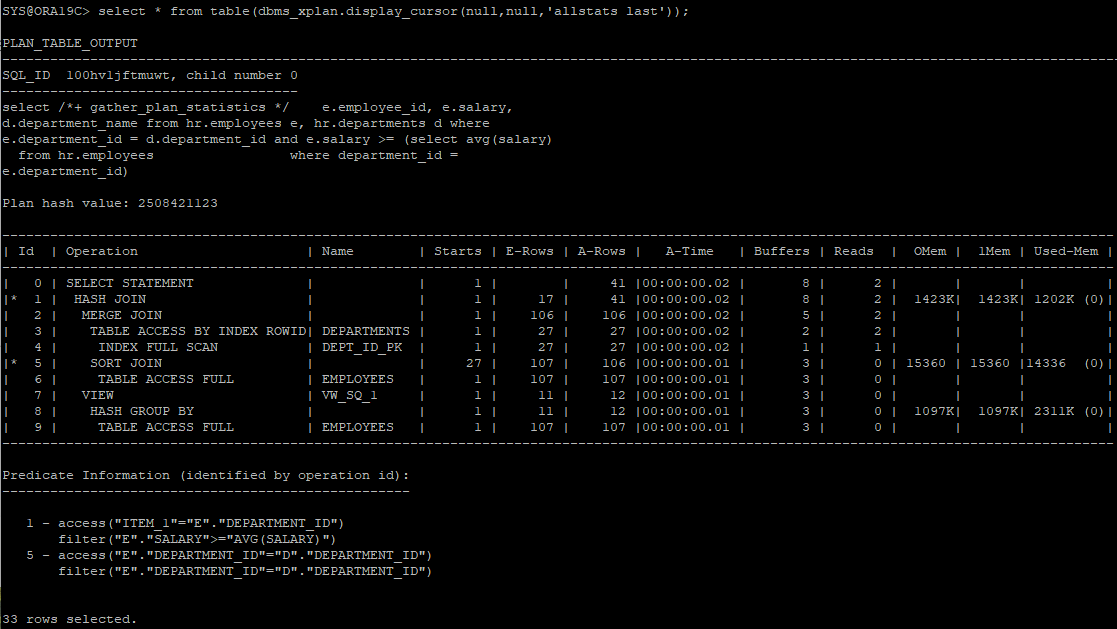
- correlated subquery를 사용하면 메인쿼리의 값의 수 만큼 서브쿼리를 반복 수행해야 하기 때문에 따로 테이블을 그룹화해서 조인하는게 좋다
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ e.employee_id, e.salary, d.department_name
from hr.employees e, hr.departments d,
(select department_id, avg(salary) avg_sal
from hr.employees
group by department_id) dept_avg
where e.department_id = d.department_id
and e.department_id = dept_avg.department_id
and e.salary > dept_avg.avg_sal;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));
- 대용량 테이블은 employees의 중복을 없애기 위해서 분석함수를 사용했다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ *
from(
select
e.employee_id,
e.salary,
d.department_name,
avg(salary) over (partition by e.department_id) dept_avg_sal,
case when e.salary >avg(salary) over (partition by e.department_id)
then 'o' end avg_sal
from hr.employees e, hr.departments d
where e.department_id = d.department_id
)
where avg_sal is not null;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));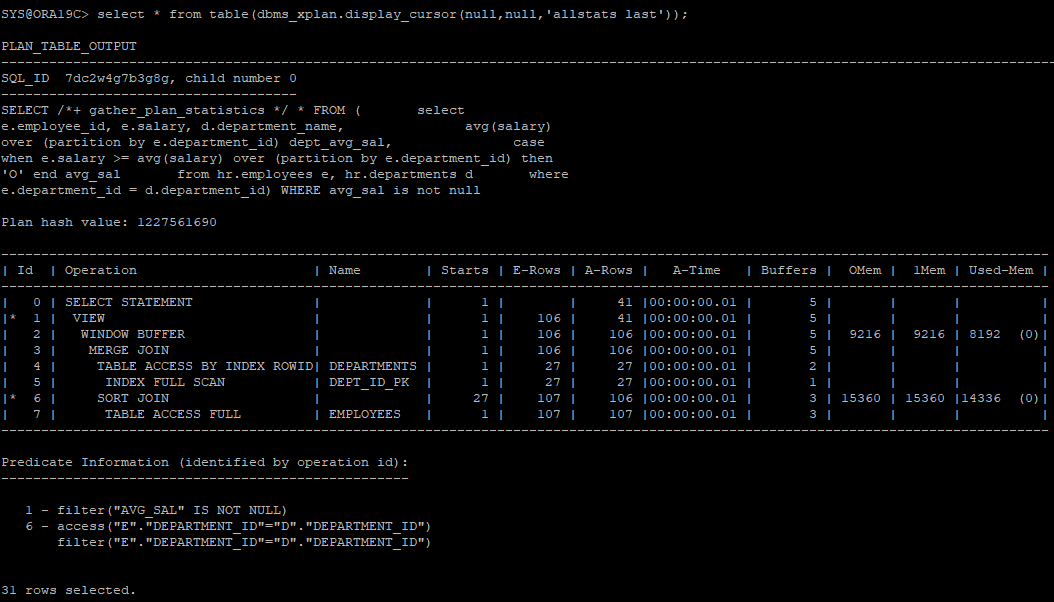
_remove_aggr_subquery: correlate subqeury를 사용할때 분석함수를 사용하여 서브쿼리를 제거한다(10g)
alter session set "_remove_aggr_subquery"=true;
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ e.employee_id, e.salary, d.department_name
from hr.employees e, hr.departments d
where e.department_id = d.department_id
and e.salary > (select avg(salary)
from hr.employees
where department_id = e.department_id);
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));optimizer
- 사용자가 요청한 SQL문을 가장 효율적으로 빠르게 수행할 수 있는 최저 비용의 처리 경로를 선택하는 엔진
1. Rule Based Optimization(RBO)
- 미리 정해진 규칙에 의한 순위에 따라 실행계획을 결정(순위 결정 방식)
- 데이터에 대한 통계 내지는 실제 SQL문을 수행할 경우에 소요될 비용에 대한 고려를 하지 않음
예) 인덱스가 있다면 무조건 사용(테이블 크기, 인덱스의 효율등 무시)
- 10g 부터는 RBO 지원 중단
- 조건절 컬럼에 인덱스가 있으면 무조건 인덱스 사용
- order by 절에 사용된 컬럼에 인덱스가 있으면 무조건 인덱스 사용
- 부등호 조건의 인덱스 보다 between and 조건의 인덱스가 우선RBO에서는 salary에 인덱스가 걸려있다는 가정하에 index rando scan을 하게 되면 너무 많은 i/o가 발생되었다. 그렇기 때문에 당시에는 hint를 사용해서 인덱스 사용을 조절하였다. select * from hr.emp where dept_id >= 100 and salary between 100 and 100000;
2. Cost Based Optimization(CBO)
- oracle 7부터 지원
- cost를 기반으로 SQL 최적화 수행
- 실제 SQL문을 수행할때 소요될 비용을 예측하고 그 값을 기준으로 실행계획을 설정
- OBJECT 통계
- 테이블 통계 (dba_tables, tab$)
- 컬럼 통계 (dba_tab_columns, col$)
- 인덱스 통계 (dba_indexes, ind$)
- SYSTEM 통계
- CPU 속도
- 디스크 I/O
SYSTEM 통계
- 9i 부터 하드웨어 및 애플리케이션 특성에 맞는 시스템 통계를 수집하고 활용
- I/O, CPU 성능 같은 하드웨어 특성
- cpu 속도
- 평균적인 single block I/O 속도
- 평균적인 multi block I/O 속도, 개수
- I/O 서브시스템의 최대 처리량(throughput)
- 병렬 slave 평균적 처리량(throughput)
- 확인하는 뷰
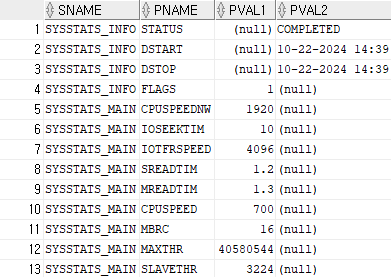
select * from sys.aux_stats$;
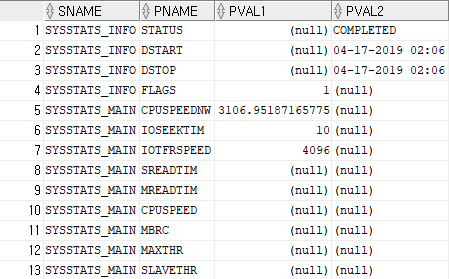
noworkload 시스템 통계(10g)
- 명시적으로 시스템 통계를 수집을 하지 않더라도 CPU 비용 모델을 사용할 수 있도록 하기 위해서 오라클이 내부적으로 시스템 통계 설정
CPUSPEEDNW: CPU 속도(백만/초)
IOSEEKTIM: 데이터를 읽으려고 디스크 헤드를 옮기는데 걸리는 시간, 보편적(5 ~ 15ms)
IOTFRSPEED: OS 프로세스 I/O 서브 시스템으로 부터 데이터를 읽는 속도(byte/ms)
# ms(millisecond) : 1/1000
- noworkload 시스템 통계 수집
execute dbms_stats.gather_system_stats(gathering_mode => 'noworkload');
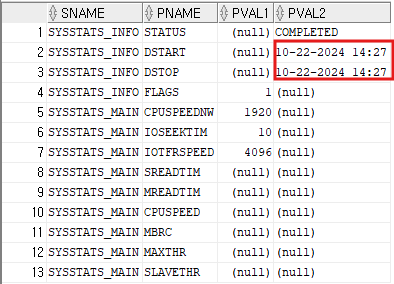
workload 시스템 통계
-
실제 애플리케이션에서 발생하는 부하를 측정한 값
SREADTIM: 평균적인 single block I/O 속도(ms(1/1000초))
MREADTIM: 평균적인 multi block I/O 속도(ms(1/1000초))
CPUSPEED: 단일 CPU가 초당 수행할 수 있는 오퍼레이션 수(백만/초)
MBRC: multi block I/O 발생시 평균적으로 읽는 블록수
MAXTHR: I/O 서브시스템의 초당 최대 처리량(byte/초)
SLAVETHR: 병렬 slave의 평균적인 초당 처리량 -
workload 시스템 통계 수집
- interval은 분단위로 설정
execute dbms_stats.gather_system_stats(gathering_mode => 'interval',interval => 1)
- interval은 분단위로 설정
전체 시스템 통계 수집
-
통계 수집 시작
execute dbms_stats.gather_system_stats(gathering_mode => 'start') -
통계 수집 종료
execute dbms_stats.gather_system_stats(gathering_mode => 'stop') -
확인
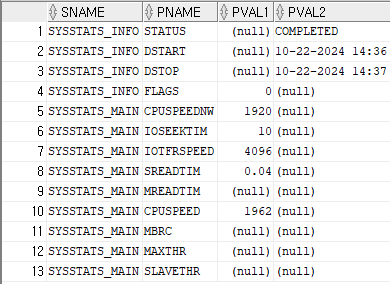
개발 데이터베이스 시스템 통계 정보를 운영 시스템 통계 정보로 반영
- 개발 db의 설정값을 보고 운영 db에 그대로 설정
begin
dbms_stats.set_system_stats('SREADTIM',1.2);
dbms_stats.set_system_stats('MREADTIM',1.3);
dbms_stats.set_system_stats('MBRC',16);
dbms_stats.set_system_stats('CPUSPEED',700);
dbms_stats.set_system_stats('MAXTHR',40580544);
dbms_stats.set_system_stats('SLAVETHR',3224);
end;
/- 설정값 확인
select * from sys.aux_stats$;
optimizer_mode
show parameter optimizer_mode: 옵티마이저 모드 확인
시스템 레벨에서는 변경하면 기존 실행계획이 전부 틀어질 수 있음.

choose : 통계 정보가 있으면 all_rows, 통계정보가 없으면 rule (9i 기본값)
rule : 통계 정보와 상관없이 RBO 사용
all_rows : 전체 처리율의 최적화(10g 기본값), DSS(의사결정시스템),BATCH 성 업무가 있는 환경
first_rows : 최소 응답속도 최적화, OLTP 환경
first_rows_n(n=1,10,100,1000) : 처음 결과가 나올때까지의 시간을 줄이기 위해 최적화, OLTP 환경
- 변경 예)
alter session set optimizer_mode = first_rows_1;- 시스템 레벨에서는 하지 않는다.
alter system set optimizer_mode = first_rows;
- 시스템 레벨에서는 하지 않는다.
- 기본적으로 조회하면 full table scan을 한다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics */ *
from hr.employees
where department_id = 50;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));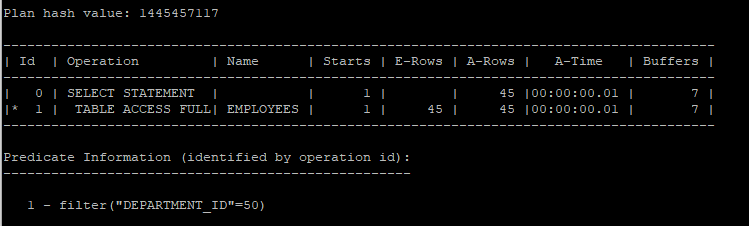
- first_row 옵티마이저 모드 변경하면 index range scan을 한다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics first_rows */ *
from hr.employees
where department_id = 50;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));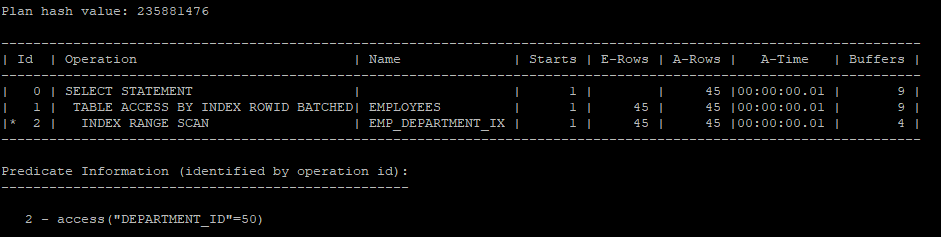
- all_rows 모드에서는 full table scan을 한다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics all_rows */ *
from hr.employees
where department_id = 50;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));
- first_rows_n 을 1로 설정하면 인덱스 스캔을 한다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics fisrt_rows(1) */ *
from hr.employees
where department_id = 50;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));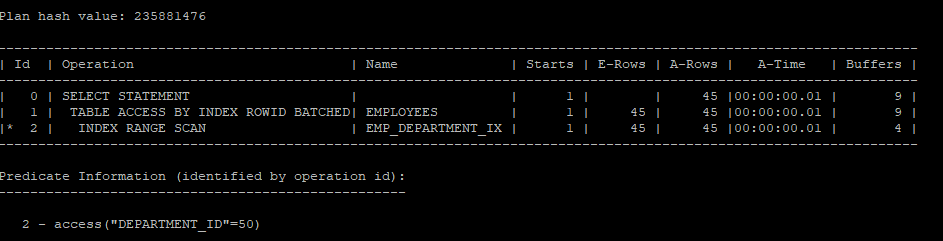
- first_rows_n 을 10으로 설정해도 인덱스 스캔을 한다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics fisrt_rows(10) */ *
from hr.employees
where department_id = 50;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));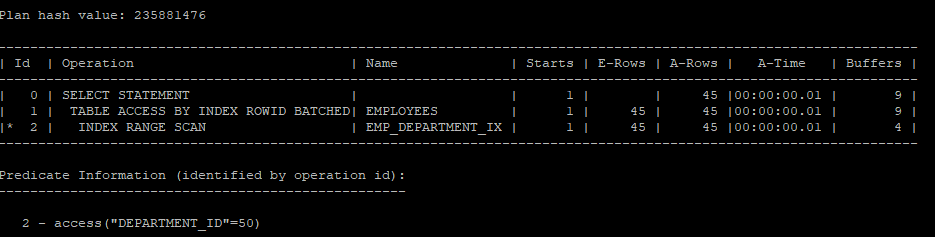
- first_rows_n을 100으로 설정해야 table full scan을 하게 된다.
select /*+ gather_plan_statistics fisrt_rows(100) */ *
from hr.employees
where department_id = 50;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));
optimizer에게 영향을 주는 요소
- 오라클 버전
- 옵티마이저 관련 파라미터
- 통계 정보
- 옵티마이저 힌트
- SQL문의 연산자
- 인덱스 설계
- 제약조건
SQL문 PARSER
Query Transformer -> Estimator -> Plan Generator
1. Query Transformer
- SQL문을 최적화 하기 쉬운 형태로 변환
2. Estimator
selectivity(선택도)
- 선택도는 1 / NUM_DISTINCT로 계산되며, 전체 행 중에서 고유한 값 하나가 선택될 확률을 나타냅니다.
- 예를 들어, EMPLOYEE_ID의 선택도는 0.009345794(약 0.9%)로, 이는 고유한 EMPLOYEE_ID 하나가 선택될 확률이 약 0.9%임을 의미합니다. 선택도가 낮을수록 더 많은 데이터가 반환됩니다.
cardinality
- 특정 액세스 단계를 거치고 나서 출력될 것으로 예상되는 결과 건수 (총행의 수 * selectivity(선택도) = num_rows/num_distict)
- 예를 들어, DEPARTMENT_ID의 카디널리티는 9.72727273로, 평균적으로 각 부서 ID가 약 9.7회 나타남을 의미합니다.
cost
- 특정 명령문을 실행하는데 필요한 표준화된 I/O에 대한 옵티마이저의 최적 예측 비용
_optimizer_cost_model= {io | cpu | choose}- i/o 비용(8i)
- cpu 비용(10g)
- choose : 시스템 통계가 있으면 cpu 비용, 없으면 i/o비용(9i)
cpu비용으로 하는게 좋기 때문에 workload가 없는걸 방지하기 위해 오라클이 기본적으로 no workload를 제공한다.
3. Plan Generator : 후보군이 될만한 실행계획들을 생성
추가설명
1. 카디널리티(Cardinality)와 실행 계획의 관계:
카디널리티는 쿼리의 특정 조건을 적용한 후 남는 행의 수를 추정하는 데 중요한 역할을 합니다. 카디널리티를 바탕으로 Oracle 옵티마이저는 어떤 접근 방법(Access Path)을 사용할지 결정합니다.
예시:
-
카디널리티가 낮은 경우: 예를 들어, EMPLOYEE_ID처럼 고유 값이 많고 카디널리티가 낮은 경우, 옵티마이저는 해당 컬럼에 인덱스 스캔(Index Scan)을 사용할 가능성이 큽니다. 왜냐하면 고유한 값을 빠르게 찾을 수 있기 때문입니다. 즉, 적은 수의 행을 읽으면 되므로 효율적입니다.
-
카디널리티가 높은 경우: 반면, DEPARTMENT_ID처럼 고유 값이 적고(카디널리티가 높은 경우), 하나의 부서에 많은 직원이 있을 수 있습니다. 이 경우 옵티마이저는 풀 테이블 스캔(Full Table Scan)이나 해시 조인(Hash Join)과 같은 방법을 고려할 수 있습니다. 이는 특정 값이 여러 번 반복되어 있기 때문에 인덱스보다 테이블 전체를 읽는 것이 더 빠를 수 있기 때문입니다.
카디널리티를 통해 옵티마이저는 어느 정도의 데이터를 처리할지를 예측하며, 이에 따라 실행 계획에서 사용할 접근 방식을 결정하게 됩니다.
2. 선택도(Selectivity)와 실행 계획의 관계:
선택도는 특정 조건이 주어졌을 때 얼마나 많은 행이 선택될지에 대한 확률을 의미합니다. 선택도는 1/NUM_DISTINCT으로 계산되며, 특정 컬럼의 고유 값이 많을수록 선택도는 낮아집니다. 이 값은 옵티마이저가 필터링 작업에서 얼마나 많은 데이터를 걸러낼지를 예측하는 데 사용됩니다.
예시:
-
선택도가 낮은 경우: EMPLOYEE_ID처럼 선택도가 낮은 경우, 즉 조건에 따라 소수의 행만 선택될 확률이 높은 경우, 옵티마이저는 인덱스 스캔을 선호할 수 있습니다. 이는 인덱스를 통해 적은 수의 행을 빠르게 찾아낼 수 있기 때문입니다.
-
선택도가 높은 경우: JOB_ID처럼 선택도가 높은 경우, 즉 조건을 만족하는 행이 많을 때는 옵티마이저가 테이블 스캔 또는 대량 데이터 처리 방식을 더 선호할 수 있습니다. 왜냐하면, 조건을 만족하는 행이 많다면 인덱스를 사용하는 것이 비효율적일 수 있기 때문입니다.
3. 비용(Cost)과 통계의 관계:
Oracle 옵티마이저는 쿼리의 실행 비용을 추정하기 위해 카디널리티와 선택도를 모두 사용합니다. 비용은 주로 CPU 사용량, 디스크 I/O 등을 고려한 예측 값입니다. 일반적으로 낮은 비용을 가진 실행 계획이 선택됩니다.
- 카디널리티가 낮고 선택도가 낮을 때: 옵티마이저는 인덱스를 사용하는 것이 더 비용이 낮을 것으로 예측합니다.
- 카디널리티가 높고 선택도가 높을 때: 테이블 스캔이나 대량 데이터 처리 방법이 비용이 적다고 판단할 수 있습니다.
실행 계획에서의 접근 방법 결정:
- 인덱스 스캔 (Index Scan):
- 카디널리티가 낮고, 선택도가 낮은 경우: EMPLOYEE_ID는 모든 행이 고유하므로 인덱스 스캔을 사용하기 적합합니다. 옵티마이저는 이를 보고 인덱스를 사용해 특정 EMPLOYEE_ID를 빠르게 찾는 것이 더 효율적이라고 판단할 것입니다.
- 풀 테이블 스캔 (Full Table Scan):
- 카디널리티가 높은 경우: 예를 들어, DEPARTMENT_ID는 하나의 값이 여러 번 반복됩니다. 이 경우 옵티마이저는 인덱스 스캔 대신 풀 테이블 스캔을 사용하는 것이 더 적합하다고 판단할 수 있습니다. 많은 행을 한 번에 읽어야 하는 경우, 전체 테이블을 스캔하는 것이 더 효율적일 수 있기 때문입니다.
- 조인 방식:
- 카디널리티와 선택도를 기반으로 조인 방식을 선택: 두 테이블을 조인할 때, 옵티마이저는 어떤 조인 방식(예: Nested Loop Join, Hash Join 등)을 사용할지를 결정합니다. 예를 들어, 조인 대상 테이블의 행 수가 적으면 Nested Loop Join이 효율적일 수 있지만, 많은 데이터를 조인해야 한다면 Hash Join이나 Sort Merge Join이 더 적합할 수 있습니다.
drop table hr.emp purge;
create table hr.emp as select * from hr.employees;- 컬럼별 통계정보 확인
select t.num_rows, c.column_name, c.num_nulls, c.num_distinct, 1/c.num_distinct
selectivity, t.num_rows/c.num_distinct cardinality
from dba_tables t, dba_tab_columns c
where t.owner = 'HR'
and t.table_name ='EMP'
and t.table_name = c.table_name;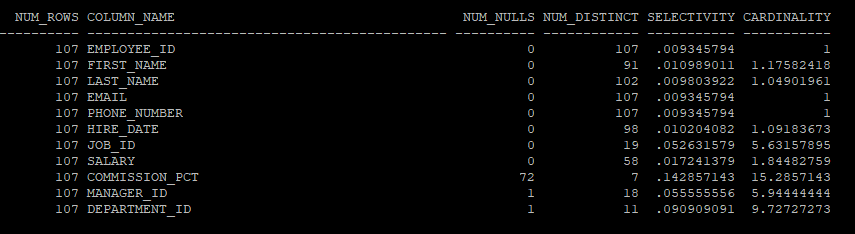
- job_id 컬럼의 값 분포도 조회
select job_id, count(*) from hr.emp group by job_id;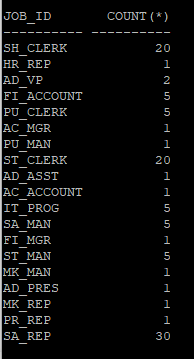
- 실행계획에서 나타난 job_id 컬럼의 평균 카디널리티는 6이다.
- rows 값이 카디널리티 값이다.
explain plan for select * from hr.emp where job_id = 'IT_PROG';
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display);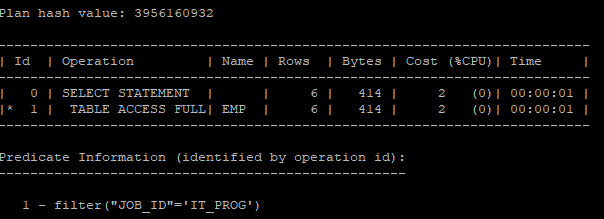
HISTOGRAM
- 조건절에 자주 사용되는 컬럼들 중에 값의 분포도가 균일하지 않은 컬럼에 히스토그램을 생성한다.
- 버킷개수의 수는 최대 254개만 허용한다.
- 히스토그램 유형
- 도수분포 히스토그램(Frequency)는
값의수 = 버킷갯수일때 사용됨 - 높이균형 히스토그램(Height-Balanced)는
값의수 > 버킷 개수일때 사용됨
- 도수분포 히스토그램(Frequency)는
- 테이블의 버킷 수 , 히스토그램 조회
select column_name, num_distinct, num_buckets, histogram
from dba_tab_col_statistics
where owner='HR'
and table_name='EMP';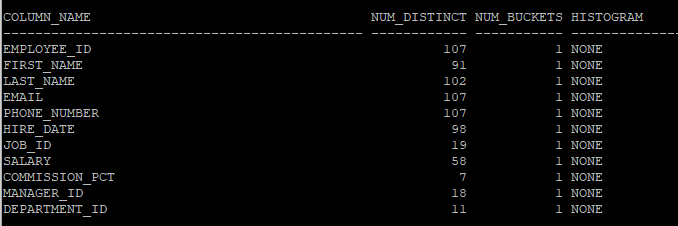
- 버킷의 갯수를 20개를 요청해도 job_id의 고유값은 19개 이기 때문에 버킷은 19개만 만들어진다.
execute dbms_stats.gather_table_stats('hr','emp',method_opt=>'for columns size 20 job_id') - 19개의 버킷과 도수분표 히스토그램이 만들어 졌다.
select column_name, num_distinct, num_buckets, histogram
from dba_tab_col_statistics
where owner='HR'
and table_name='EMP';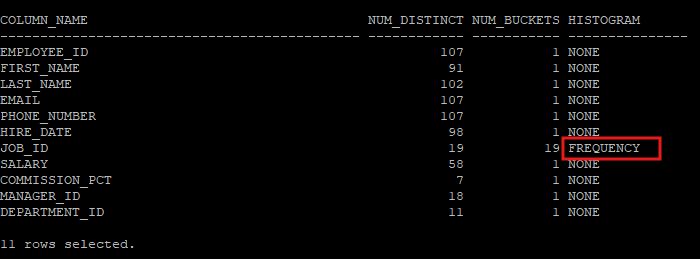
- 히스토그램을 생성 후 실행계획을 보면 정확하게 rows수를 예측한다.
explain plan for select * from hr.emp where job_id = 'IT_PROG';
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display);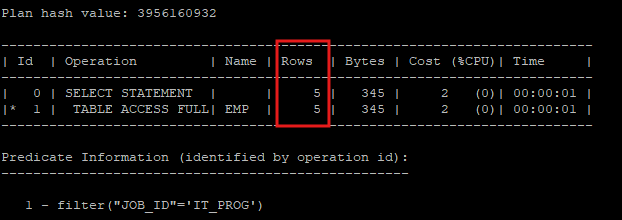
- 바인드 변수를 이용해 실행계획을 공유하게 되면 rows를 평균값으로 처리하기 때문에 값이 고르지 않은 컬럼에 히스토그램을 생성하였다면 바인드 변수처리는 하지 않는다.
explain plan for select * from hr.emp where job_id = :B1;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display);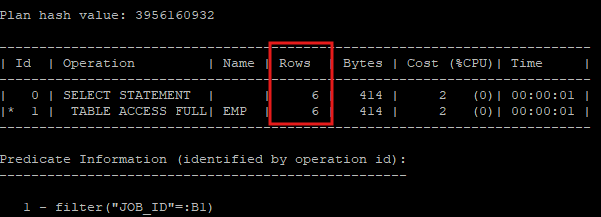
- 여러컬럼에 대해 히스토 그램을 만들 경우 처음 컬럼 앞에만 버킷의 수를 먼저 제안하고 그 뒤 컬럼 부터는 컬럼 뒤에 제안한다.
execute dbms_stats.gather_table_stats('hr','emp',method_opt=>'for columns size 20 job_id, department_id size 12') - 모든 컬럼에 대한 히스토그램 생성
execute dbms_stats.gather_table_stats('hr','emp',method_opt => 'for all columns size 254') - 다른 옵션들
method_opt => 'for all columns size repeat' : 히스토그램이 기존에 생성되어 있는 컬럼에만 히스토그램 생성
method_opt => 'for all columns size auto' : 컬럼이 조건절에 사용되는 비중이 높은 컬럼(col_usage$)을 찾아 히스토그램 생성, 데이터 분포를 기준으로 자동 결정
method_opt => 'for all columns size skewonly' : 데이터 분포를 분석해 균일하지 않은 컬럼에 대해서 히스토그램 생성
- 마지막으로 통계수집 한 날짜시간 확인
select num_rows, blocks, avg_row_len, to_char(last_analyzed,'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss')
from dba_tables
where owner='HR'
and table_name='EMP';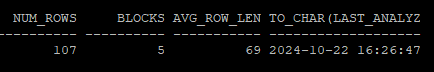
통계정보의 복구 실습
- 신규 테이블 생성 후 데이터 입력
create table hr.tab(col1 number, col2 number);
insert into hr.tab(col1, col2)
select mod(level, 100),level
from dual
connect by level <= 100;
commit;- 통계정보를 확인해보면 통계수집을 하지 않아 조회되지 않는다.
select num_rows, blocks, avg_row_len, to_char(last_analyzed,'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss')
from dba_tables
where owner='HR'
and table_name='TAB';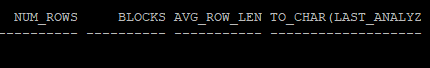
- 컬럼값 확인
select column_name, num_distinct, num_buckets, histogram
from dba_tab_columns
where owner='HR'
and table_name='TAB';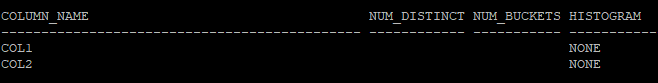
- 테이블, 컬럼 통계수집
execute dbms_stats.gather_table_stats('hr','tab',method_opt => 'for all columns size auto')- 테이블, 컬럼에 대한 통계정보 확인
- 컬럼을 한번도 사용하지 않아 히스토그램은 생성되지 않았다.
select num_rows, blocks, avg_row_len, to_char(last_analyzed,'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss')
from dba_tables
where owner='HR'
and table_name='TAB';
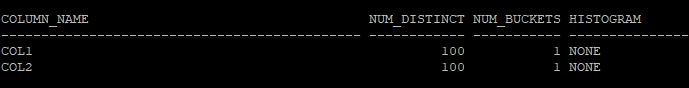
select column_name, num_distinct, num_buckets, histogram
from dba_tab_columns
where owner='HR'
and table_name='TAB';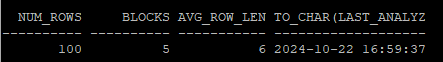
- 이전 통계정보 확인(기본 한달정도 기록 후 과거 순으로 삭제)
select * from dba_tab_stats_history where table_name='TAB' and owner='HR';
- 통계정보를 저장할 테이블 생성
execute dbms_stats.create_stat_table('hr','tab_stat')- 저장할 테이블 조회
- 통계정보를 아직 넣지 않아 조회되지 않는다.
select * from hr.tab_stat;
desc hr.tab_stat- 현재 tab 테이블 통계정보를 tab_stat 테이블로 export
execute dbms_stats.export_table_Stats(ownname=>'hr', tabname=>'tab', stattab=>'tab_stat');- 대량읠 데이터를 입력하여 기존의 통계정보로는 정확한 실행계획을 만들 수 없다.
insert into hr.tab(col1, col2)
select mod(level, 2),level
from dual
connect by level <= 1000;- 데이터 수 확인
select count(*) from hr.tab;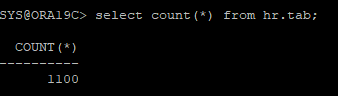
- 현재 통계정보 확인
select num_rows, blocks, avg_row_len, to_char(last_analyzed,'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss')
from dba_tables
where owner='HR'
and table_name='TAB';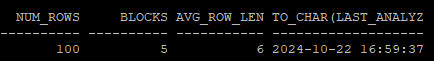
- co1 컬럼의 분포도를 보면 고르지 않다.
select col1, count(*) from hr.tab group by col1;- 정확한 실행계획을 만들기 위해 다시 통계수집 및 col1 컬럼에 대한 히스토그램 생성
execute dbms_stats.gather_table_stats('hr','tab',method_opt => 'for columns size 254 col1 ')- 테이블에 대한 통계정보 확인
select num_rows, blocks, avg_row_len, to_char(last_analyzed,'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss')
from dba_tables
where owner='HR'
and table_name='TAB';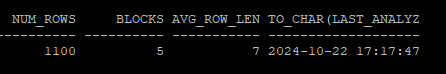
- 컬럼에 대한 통계정보 확인
select column_name, num_distinct, num_buckets, histogram
from dba_tab_columns
where owner='HR'
and table_name='TAB';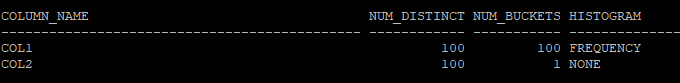
- 통계수집 history 확인
select * from dba_tab_stats_history where table_name='TAB' and owner='HR';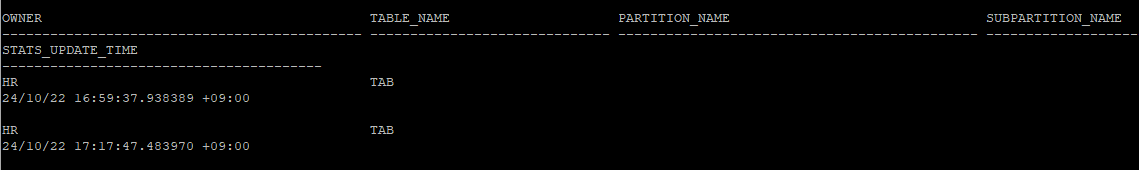
- 현재의 통계정보와 저장해놓은 과거 통계정보를 비교
set long 1000
select * from table(dbms_stats.diff_table_stats_in_stattab('hr','tab','tab_stat'));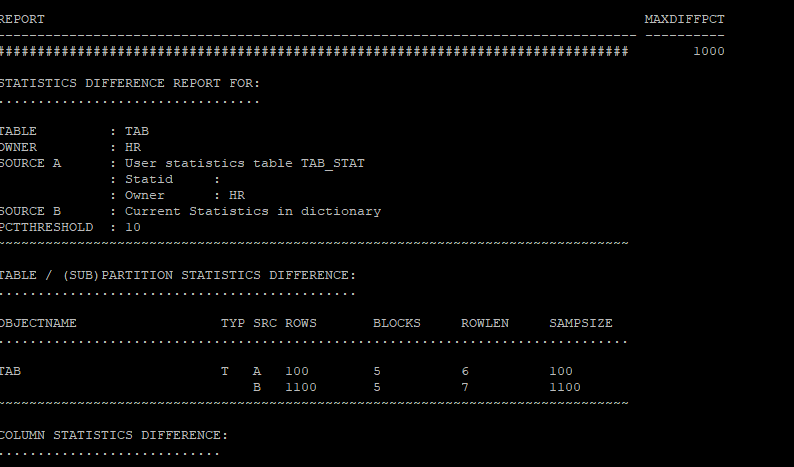
- 통계 정보 삭제
execute dbms_stats.delete_table_stats('hr','tab');- 통계 정보를 삭제 후 통계를 확인해 보면 전부 null 값으로 되어있다.
select num_rows, blocks, avg_row_len, to_char(last_analyzed,'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss')
from dba_tables
where owner='HR'
and table_name='TAB';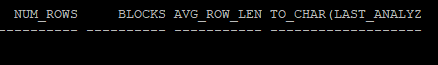
select column_name, num_distinct, num_buckets, histogram
from dba_tab_columns
where owner='HR'
and table_name='TAB';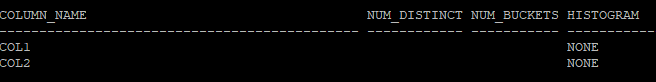
- export 받아놓은 과거 통계정보를 이용해서 복원
execute dbms_stats.import_table_stats(ownname=>'hr', tabname=>'tab',stattab=>'tab_stat')- 다시 통계정보를 확인해보면 과거 통계정보로 복원되었다.
select num_rows, blocks, avg_row_len, to_char(last_analyzed,'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss')
from dba_tables
where owner='HR'
and table_name='TAB';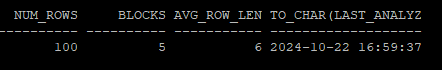
select column_name, num_distinct, num_buckets, histogram
from dba_tab_columns
where owner='HR'
and table_name='TAB';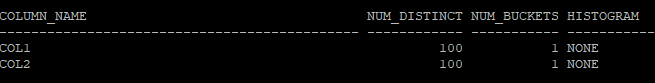
- 통계정보 history 확인해보기
- 삭제 정보도 history로 남는다.
select * from dba_tab_stats_history where table_name='TAB' and owner='HR';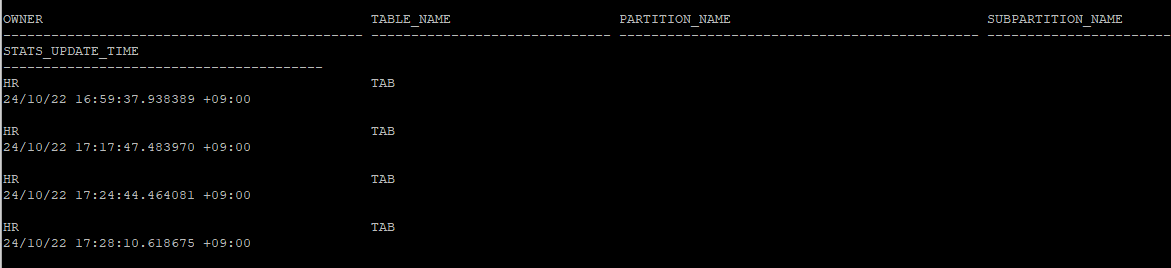
- 과거 통계정보를 이용해서 restore
- export 받아놓은 통계정보가 없는 상황에서는 통계정보 history 테이블에서 시간대를 보고 복원 작업도 가능하다.
execute dbms_stats.restore_table_stats('hr','tab','24/10/22 17:17:47.483970 +09:00');
- 복원된 통계정보를 확인
- 시간대 복구를 하면 테이블에 대한 통계정보는 복원이 되지만 컬럼에 대한 통계정보는 복원되지가 않는다.
select num_rows, blocks, avg_row_len, to_char(last_analyzed,'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss')
from dba_tables
where owner='HR'
and table_name='TAB';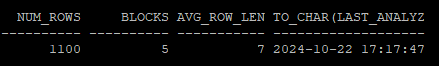
- 복원되지 않은 컬럼의 통계정보
select column_name, num_distinct, num_buckets, histogram
from dba_tab_columns
where owner='HR'
and table_name='TAB';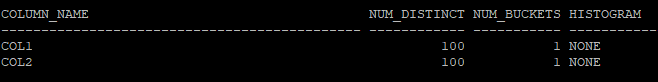
- 통계정보 history의 보관기간
- 기본적으로 31일로 설정되어 있다.
select dbms_stats.get_stats_history_retention from dual;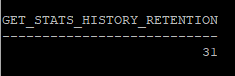
- restore이 가능한 가장 오래된 날짜 확인
select dbms_stats.get_stats_history_availability from dual;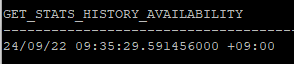
- 통계정보 보관 날짜 변경(일수)
execute dbms_stats.alter_stats_history_retention(7)
select dbms_stats.get_stats_history_retention from dual;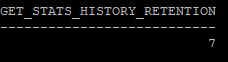
- 너무 많은 history도 용량낭비이기 때문에 과거 통계정보 삭제
-- 하루전 통계정보만 남기고 나머지 삭제
execute dbms_stats.purge_stats(systimestamp - 1)
select * from dba_tab_stats_history where owner='HR';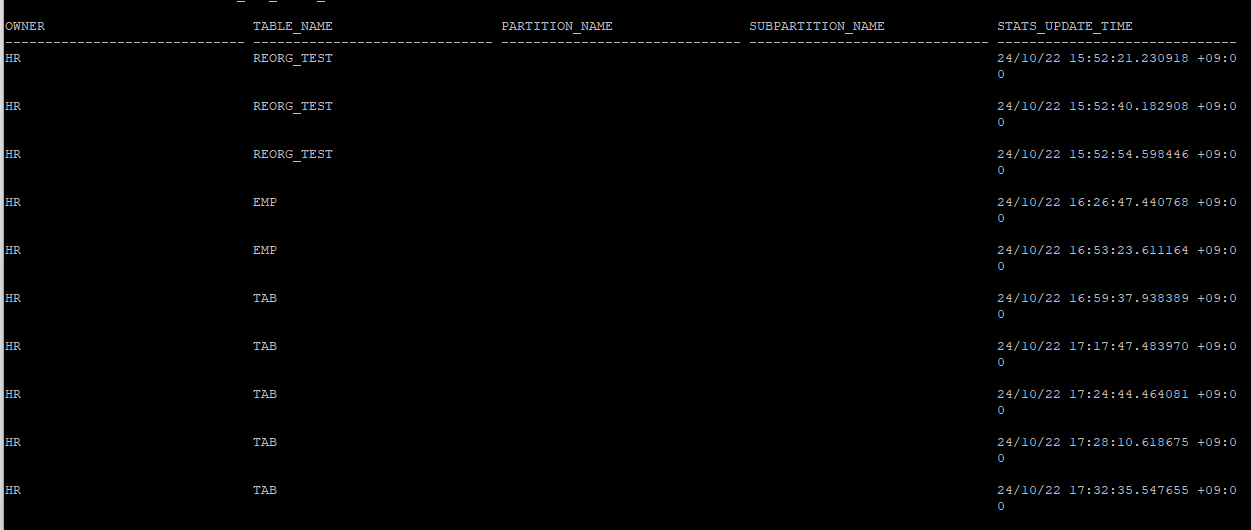
- 특정 시간대 이전 history 통계정보 삭제
execute dbms_stats.purge_stats(to_timestamp_tz('2024-10-22 15:52:54 +09:00','yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss tzh:tzm'))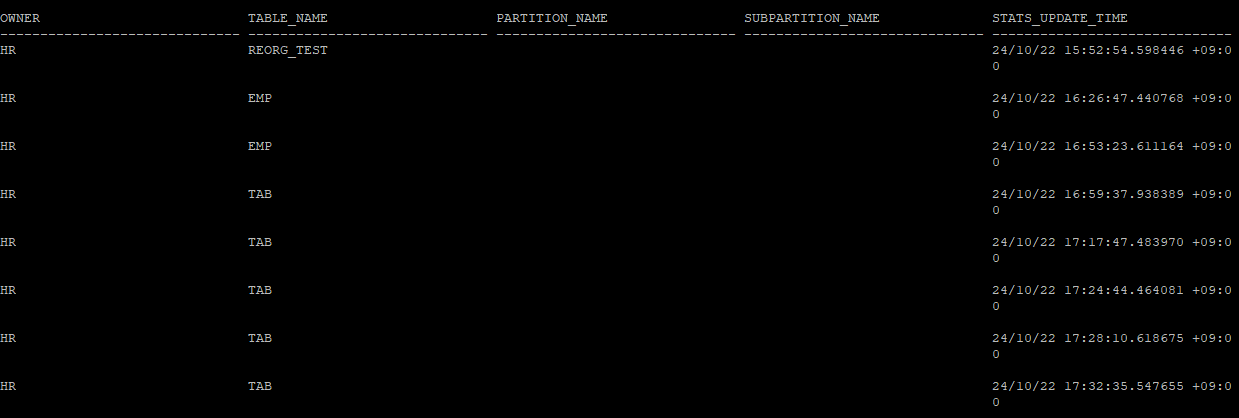
- 통계정보를 수동으로 설정
- 다른 DB의 통계정보를 가지고 수동으로 설정하려면 다른DB의 옵티마이저랑 설정이 똑같이 되어있어야 똑같은 실행계획을 생성할 수 있다.
execute dbms_stats.set_table_stats(ownname=>'hr', tabname=>'tab',numrows=>1100,numblks=>5, avgrlen=>7);
select num_rows, blocks, avg_row_len, to_char(last_analyzed,'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss')
from dba_tables
where owner='HR'
and table_name='TAB';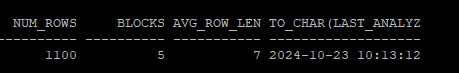
- 수동으로 설정한 통계정보도 history에 남는다.
select * from dba_tab_stats_history where owner='HR';
- 통계 lock을 설정
- 현재 해당 테이블의 lock은 설정되어 있지 않은 상태이다
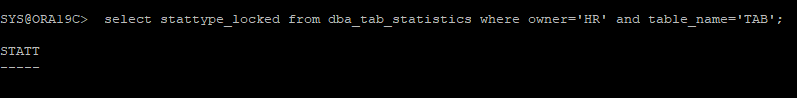
select stattype_locked from dba_tab_statistics where owner='HR' and table_name='TAB';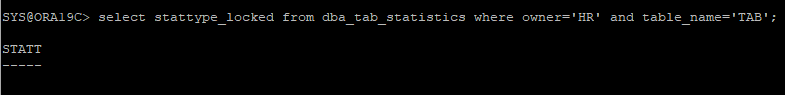
- lock을 설정 후 다시 조회
execute dbms_stats.lock_table_stats('hr','tab')
select stattype_locked from dba_tab_statistics where owner='HR' and table_name='TAB';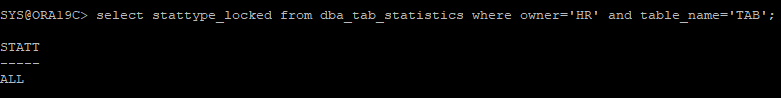
- 통계정보에 lock이 설정되어있기 때문에 삭제하려고 하면 오류가 발생한다.
execute dbms_stats.delete_table_stats('hr','tab')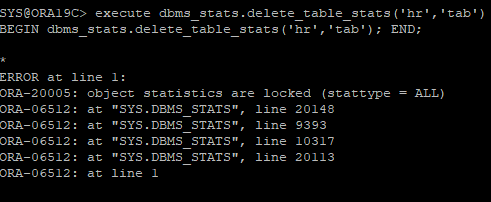
- 다시 lock 해제는 unlock 하면 된다.
execute dbms_stats.unlock_table_stats('hr','tab')
select stattype_locked from dba_tab_statistics where owner='HR' and table_name='TAB';