maxvalue partition 추가
- 바깥쪽이 아닌 안쪽으로 파티션을 추가할경우는 무조건 split으로 해야한다.
- 현재 파티션 정보 확인
select partition_name, subpartition_count,high_value, tablespace_name, num_rows,blocks,avg_row_len
from dba_tab_partitions
where table_owner='HR'
and table_name='SAL_EMP';
- 데이터를 입력하려고 했지만 파티션 키 컬럼의 값이 어느 파티션에도 부합하지 않아 오류가 발생한다.
insert into hr.sal_emp(employee_id, last_name, salary, department_id)
values(300,'oracle',30000,20);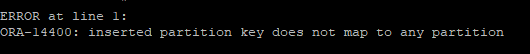
- maxvalue 파티션 추가
alter table hr.sal_emp add partition pmax values less than(maxvalue);- 추가된 파티션 정보 확인
select partition_name, subpartition_count,high_value, tablespace_name, num_rows,blocks,avg_row_len
from dba_tab_partitions
where table_owner='HR'
and table_name='SAL_EMP';
- 다시 데이터를 입력해보면 정상적으로 입력이 된다.
insert into hr.sal_emp(employee_id, last_name, salary, department_id)
values(300,'oracle',30000,20);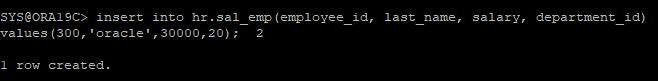
- 입력값 확인
select * from hr.sal_emp partition(pmax);
- 새로운값 입력, 입력된 값은 pmax 파티션으로 입력된다.
insert into hr.sal_emp(employee_id, last_name, salary, department_id)
values(400,'itwill',50000,10);
select * from hr.sal_emp partition(pmax);
- 40000을 기준으로 split 하기
alter table hr.sal_emp split partition pmax at(40000) into(partition p5, partition pmax);- split된 파티션 정보 확인
select partition_name, subpartition_count,high_value, tablespace_name, num_rows,blocks,avg_row_len
from dba_tab_partitions
where table_owner='HR'
and table_name='SAL_EMP';
partition merge
- 병합하기전 파티션 값들 확인
select * from hr.sal_emp partition(p4);
select * from hr.sal_emp partition(p5);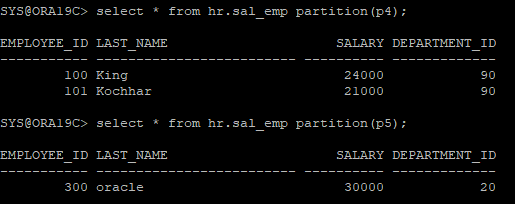
- p4,p5를 병합하는데 병합 파티션은 p5로 한다.(병합시 partitions로 복수형임을 주의하자)
alter table hr.sal_emp merge partitions p4,p5 into partition p5;- 파티션 정보를 확인해보면 기존 p4는 없어지고 병합된 파티션은 통계정보가 수집되어있다.
select partition_name, subpartition_count,high_value, tablespace_name, num_rows,blocks,avg_row_len
from dba_tab_partitions
where table_owner='HR'
and table_name='SAL_EMP';
- 병합된 데이터 확인
select * from hr.sal_emp partition(p5);
partition exchange
EXCHANGE PARTITION명령어는 데이터를 물리적으로 이동하지 않고, 메타데이터만 교환합니다. 즉, 파티션 p5의 데이터는 물리적으로 그대로 남아있고, 논리적으로만 hr.exchange_emp 테이블의 데이터로 간주됩니다. 데이터의 물리적 저장 위치는 변경되지 않으며, 그래서 ROWID도 변하지 않습니다.
- exchange할 비어있는 테이블 생성
create table hr.exchange_emp
as
select employee_id, last_name, salary, department_id
from hr.employees
where 1=2;- p5 파티션 데이터값 확인
select * from hr.sal_emp partition(p5);
- p5테이블과 exchange_emp 테이블을 exchange(내부적으로는 rename작동이라고 한다)
alter table hr.sal_emp exchange partition p5 with table hr.exchange_emp;
- exchange 되었기 때문에 p5 파티션는 비어있다.
select * from hr.sal_emp partition(p5);
- p5에 있던 값이 조회된다
select * from hr.exchange_emp;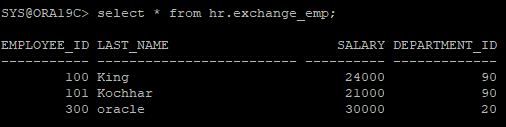
- 다시 exchange_emp에서 p5로 exchange
alter table hr.sal_emp exchange partition p5 with table hr.exchange_emp;- exchange된 값 확인
select * from hr.sal_emp partition(p5);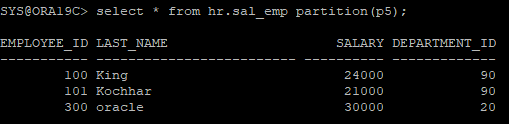
- exchange된 값 확인
select * from hr.exchange_emp;
- 파티션 정보 확인
select partition_name, subpartition_count,high_value, tablespace_name, num_rows,blocks,avg_row_len
from dba_tab_partitions
where table_owner='HR'
and table_name='SAL_EMP';
- partition 이름 변경
alter table hr.sal_emp rename partition p5 to p4;- 이름 변경 확인
select partition_name, subpartition_count,high_value, tablespace_name, num_rows,blocks,avg_row_len
from dba_tab_partitions
where table_owner='HR'
and table_name='SAL_EMP';
partition export import
- dump file을 export 받기위한 논리적인 direcotry 확인
select * from dba_directories where directory_name='DATA_PUMP_DIR';
- 물리적으로 export 받기
! expdp system/oracle directory=data_pump_dir tables=hr.sal_emp dumpfile=hr_sal_emp.pump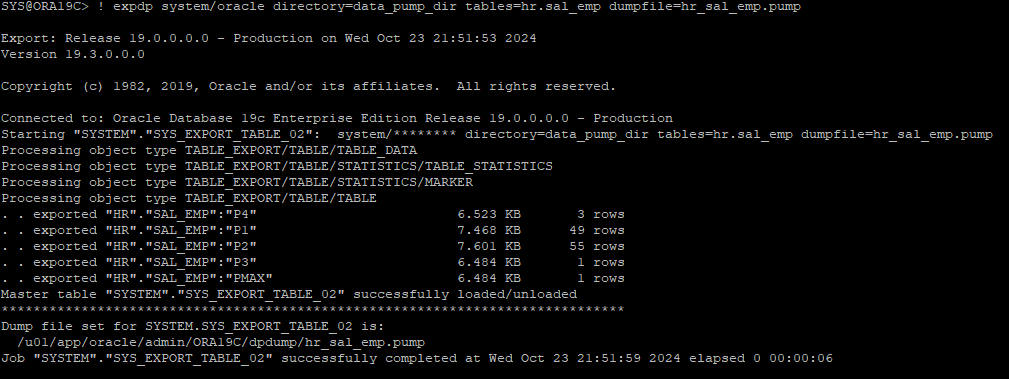
- 테이블 삭제
drop table hr.sal_emp purge;- 딕셔너리 정보 확인
select partition_name, subpartition_count,high_value, tablespace_name, num_rows,blocks,avg_row_len
from dba_tab_partitions
where table_owner='HR'
and table_name='SAL_EMP';
- dumpfile import 받기
! impdp system/oracle directory=data_pump_dir tables=hr.sal_emp dumpfile=hr_sal_emp.pump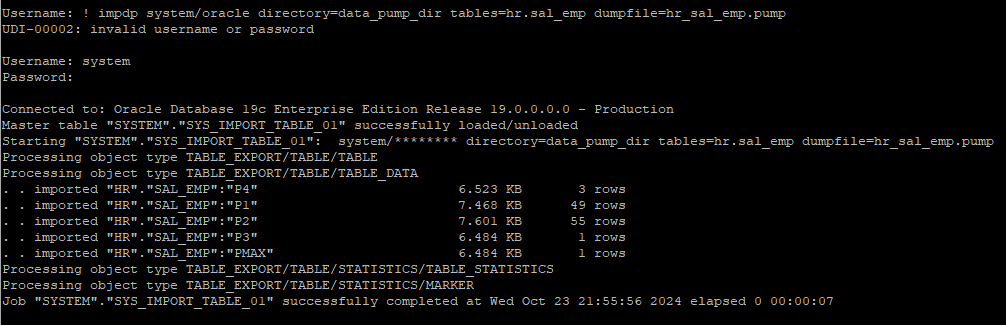
- 다시 딕셔너리 정보를 조회해보면 복구된걸 확인 할 수 있다.
select partition_name, subpartition_count,high_value, tablespace_name, num_rows,blocks,avg_row_len
from dba_tab_partitions
where table_owner='HR'
and table_name='SAL_EMP';
- 특정 파티션 삭제 후 확인
alter table hr.sal_emp drop partition p4;
select partition_name, subpartition_count,high_value, tablespace_name, num_rows,blocks,avg_row_len
from dba_tab_partitions
where table_owner='HR'
and table_name='SAL_EMP';
- 파티션이 삭제된 상태에서는 dump file에서 해당 파티션의 데이터만 import할 수 있지만, 새로 파티션을 생성한 후에만 가능합니다. 삭제된 파티션의 기준을 모르기 때문에 스크립트를 생성 후 파티션 기준 값 확인
! impdp system/oracle directory=data_pump_dir dumpfile=hr_sal_emp.pump sqlfile=sql_emp.sql content=metadata_only
vi sql_emp.sql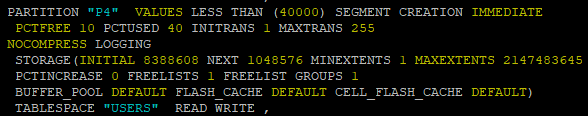
- 기준값을 확인후 파티션 split으로 파티션들 사이에 새로운 파티션 생성
alter table hr.sal_emp split partition pmax at(40000) into(partition p4, partition pmax);- p4 파티션에 대해서만 import 하기
! impdp system/oracle directory=data_pump_dir dumpfile=hr_sal_emp.pump tables=hr.sal_emp:p4 content=data_only- 파티션 정보 조회
select partition_name, subpartition_count,high_value, tablespace_name, num_rows,blocks,avg_row_len
from dba_tab_partitions
where table_owner='HR'
and table_name='SAL_EMP';
- p3 파티션 데이터 조회
select * from hr.sal_emp partition(p3)
- p3파티션의 껍질은 남겨놓은채 안의 데이터만 삭제
alter table hr.sal_emp truncate partition p3;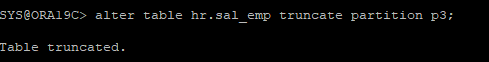
- 내부의 데이터가 없는걸 알 수 있다.
select * from hr.sal_emp partition(p3);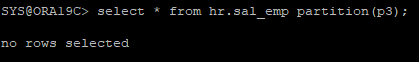
- p3 파티션 껍데기는 존재하기 때문에 바로 p3 data만 import 가능하다.
! impdp system/oracle directory=data_pump_dir dumpfile=hr_sal_emp.pump tables=hr.sal_emp:p3 content=data_only
- import 된 데이터 확인
select * from hr.sal_emp partition(p3);
특정 partition export
- sal_emp 테이블의 p4 파티션만 export 받기
! expdp system/oracle directory=data_pump_dir tables=hr.sal_emp:p4 dumpfile=hr_sal_emp_p4.pump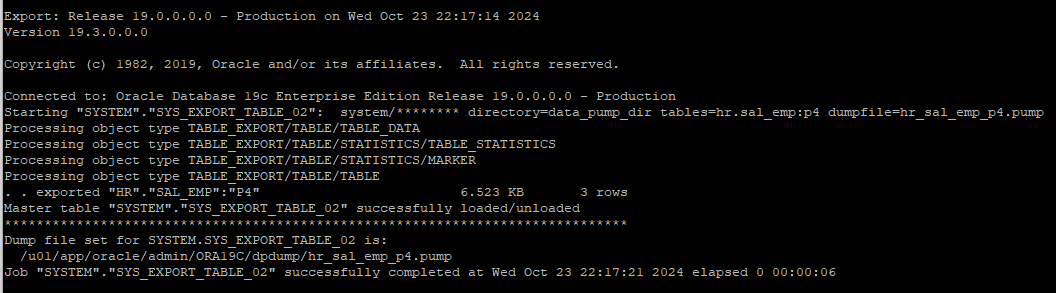
- 생성된 dump file 확인
ls /u01/app/oracle/admin/ORA19C/dpdump/
- p4 파티션 데이터 확인
select * from hr.sal_emp partition(p4);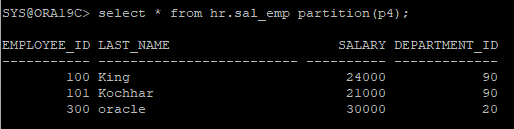
- p4 파티션 데이터 truncate
alter table hr.sal_emp truncate partition p4;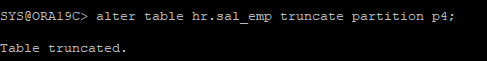
- 비어있는 데이터 확인
select * from hr.sal_emp partition(p4);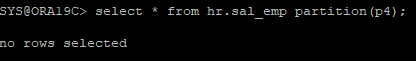
- p4 파티션의 데이터만 import 받기
! impdp system/oracle directory=data_pump_dir dumpfile=hr_sal_emp_p4.pump tables=hr.sal_emp:p4 content=data_only;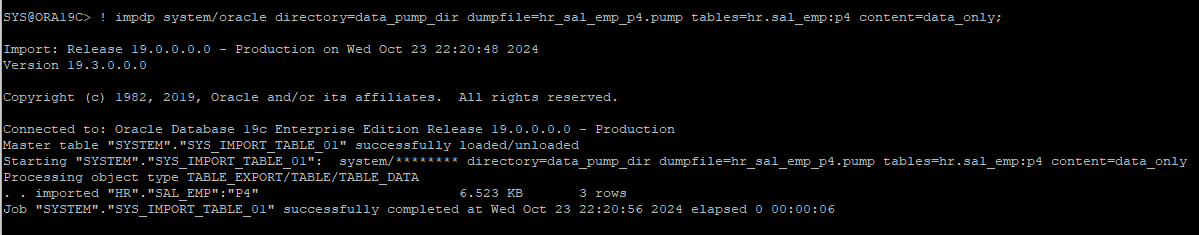
- p4 파티션 데이터가 복구되었다.
select * from hr.sal_emp partition(p4);
특정 partition의 통계수집
- 통계정보 확인
select partition_name,high_value, tablespace_name, num_rows,blocks,avg_row_len, to_char(last_analyzed,'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss')
from dba_tab_partitions
where table_owner='HR'
and table_name='SAL_EMP';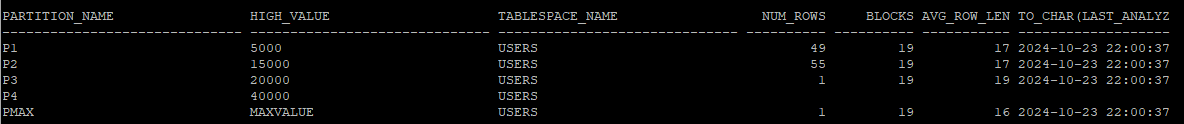
- 파티션까지도 통계수집이 된다.
execute dbms_stats.gather_table_stats('hr','sal_emp');
select partition_name,high_value, tablespace_name, num_rows,blocks,avg_row_len, to_char(last_analyzed,'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss')
from dba_tab_partitions
where table_owner='HR'
and table_name='SAL_EMP';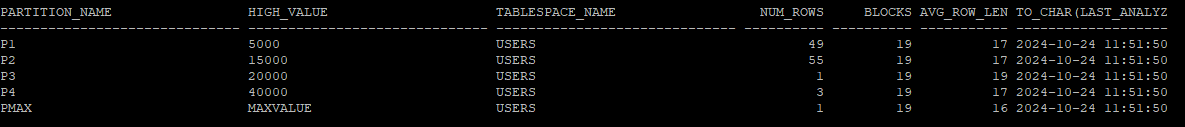
- 실제 사용하고 있는 block은 파티션당 19개인데 할당되어있는 block은 1024개로 되어있다.(버그성 의심)
select partition_name, tablespace_name, blocks, bytes from dba_segments where segment_name= 'SAL_EMP';
- 특정 파티션의 통계정보만 삭제
execute dbms_stats.delete_table_stats('hr','sal_emp',partname=>'p4')
select partition_name,high_value, tablespace_name, num_rows,blocks,avg_row_len, to_char(last_analyzed,'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss')
from dba_tab_partitions
where table_owner='HR'
and table_name='SAL_EMP';
- 특정 파티션의 통계정보만 수집
execute dbms_stats.gather_table_stats('hr','sal_emp',partname=>'p4')
select partition_name,high_value, tablespace_name, num_rows,blocks,avg_row_len, to_char(last_analyzed,'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss')
from dba_tab_partitions
where table_owner='HR'
and table_name='SAL_EMP';
부분범위 처리(arraysize)
ARRAYSIZE는 Oracle SQL*Plus에서 한 번에 가져오는 행(row)의 개수를 설정하는 옵션입니다. 값을 크게 하면 한 번에 더 많은 데이터를 가져와 네트워크 왕복 횟수를 줄여 성능을 향상시킬 수 있지만, 클라이언트 메모리 사용이 증가할 수 있습니다.- SQL에서 주어진 조건을 만족하는 데이터를 한 번에 전체 범위로 처리하지 않고, 운반 단위(ARRAYSIZE)까지만 처리한 후, 그 결과를 사용자 프로세스에 전달하고, 사용자의 추가 요청이 있을 때까지 작업을 일시 중단하는 처리 방식.
예) 10000건의 데이터를 스캔해야 할때 1000건만 읽어서 운반단위를 채울 수 있다면 10000건을 한꺼번에 다 읽지 않고 1000개씩 10번으로 나누어서 처리할 수 있다.
부분범위 처리를 할 수 없는 경우
- 그룹함수를 사용하는 경우
- order by 절을 사용하는 경우
- union, minus, intersect를 사용하는 경우(중복체크)
부분범위를 처리를 할 수 없는 경우 대체할 수 있는 방안은?
- order by 절에 사용된 컬럼에 index를 이용하면 부분범위 처리할 수 있다.
- union -> union all + not exist
- minus -> not exist
- intersect -> exists
test
- 대용량 테이블 생성
drop table hr.sal_emp purge;
create table hr.sal_emp
nologging
as
select rownum as employee_id, last_name, first_name, hire_date, job_id, salary, manager_id, department_id
from hr.employees e, (select level as id from dual connect by level <= 5000);- 통계정보 확인
select num_rows, blocks, avg_row_len, to_char(last_analyzed,'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss')
from dba_tables
where owner='HR'
and table_name='SAL_EMP';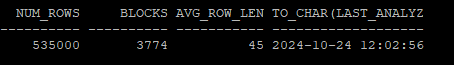
- 쿼리문을 fetch는 하되 출력결과는 보여주지 않고 통계정보만 확인
set autotrace trace stat
select * from hr.sal_emp;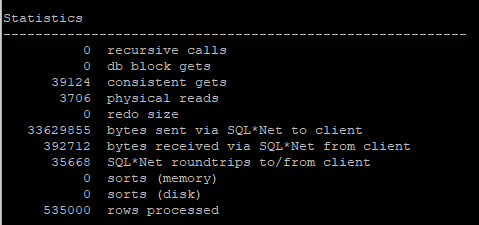
Statistics
----------------------------------------------------------
0 recursive calls
0 db block gets
39124 consistent gets : 읽은 블록의 수
3706 physical reads
0 redo size
33629855 bytes sent via SQL*Net to client
392712 bytes received via SQL*Net from client
35668 SQL*Net roundtrips to/from client : fetch count 수
0 sorts (memory)
0 sorts (disk)
535000 rows processed : 읽은 행의 수535000(row) / 35668(fetch count) = 15(한번에 fetch 할수있는 row 수)
테이블이 사용하고 있는 block의 수는 3774개 인데 실제 읽은 block의 수가 39124개로 더 많은 이유는 서버프로세스가 유저 프로세스에게 데이터를 보낼때 15개의 row 밖에 못보내기 때문에 그만큼 같은 block을 중복 i/o 해야 하는 경우가 많아져 consistent gets의 수가 늘어났다.
show arraysize : 서버프로세스가 유저프로세스에게 전달할수 있는 row의 수
- arraysize를 조절 후 쿼리문을 수행하면 consistent gets block i/o가 확실히 줄어들었다.
set arraysize 100
set autotrace trace stat
select * from hr.sal_emp;Statistics
----------------------------------------------------------
0 recursive calls
0 db block gets
9022 consistent gets
3706 physical reads
0 redo size
27748357 bytes sent via SQL*Net to client
59225 bytes received via SQL*Net from client
5351 SQL*Net roundtrips to/from client
0 sorts (memory)
0 sorts (disk)
535000 rows processed535000(rows)/5351(fetch count) = 100
- arraysize를 2000으로 설정하면 어느정도 크기 이상부터는 i/o수가 크게 줄어들지는 않는다.
set arraysize 2000
set autotrace trace stat
select * from hr.sal_emp;Statistics
----------------------------------------------------------
0 recursive calls
0 db block gets
3975 consistent gets
3706 physical reads
0 redo size
26762449 bytes sent via SQL*Net to client
3323 bytes received via SQL*Net from client
269 SQL*Net roundtrips to/from client
0 sorts (memory)
0 sorts (disk)
535000 rows processed535000(rows)/269(fetch count) = 2000
alter session set statistics_level = all;
select * from hr.sal_emp where salary between 5000 and 8000;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));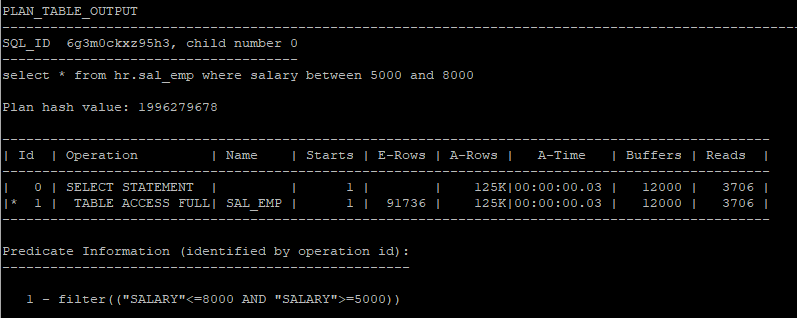
show parameter db_file_multiblock_read_count
- ARRAYSIZE와 I/O 수는 밀접한 상관관계를 가집니다. ARRAYSIZE를 크게 설정하면 한 번의 데이터베이스 접근(I/O)으로 더 많은 데이터를 가져오기 때문에 I/O 횟수가 줄어듭니다. 반대로 작게 설정하면 데이터를 여러 번 나누어 가져오기 때문에 I/O 횟수가 증가하게 됩니다.
- 이전 12000 i/o에서 3829 i/o로 줄어들었다.
set arraysize 1000
select * from hr.sal_emp where salary between 5000 and 8000;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));
- arraysize가 일정크기 이상부터는 i/o가 크게 감소되지 않는다.
set arraysize 5000
select * from hr.sal_emp where salary between 5000 and 8000;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));
- 대용량 데이터를 인덱스 스캔을 하게되면 full table scan보다 많은 i/o를 유발한다.
create index hr.sal_emp_idx on hr.sal_emp(salary);
set arraysize 1000
select /*+ index(s sal_emp_idx) */ * from hr.sal_emp s where salary between 5000 and 8000;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));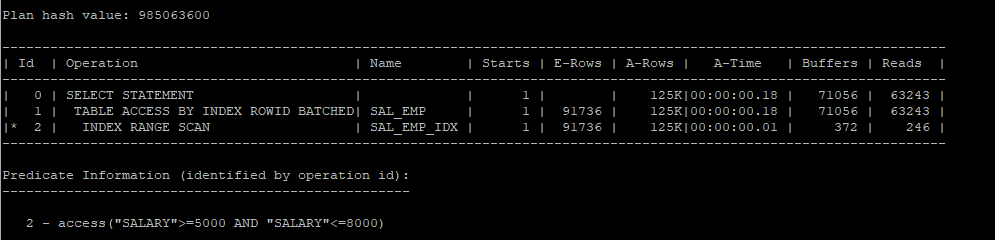
- 기존 생성되어있는 테이블에 파티션 설정
alter table hr.sal_emp
modify
partition by range(salary)
(partition p1 values less than(5000),
partition p2 values less than(10000),
partition p3 values less than(30000),
partition pmax values less than(maxvalue));- 통계수집
execute dbms_stats.gather_table_stats('hr','sal_emp');- 파티션 통계정보 확인
select partition_name,high_value, tablespace_name, num_rows,blocks,avg_row_len, to_char(last_analyzed,'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss')
from dba_tab_partitions
where table_owner='HR'
and table_name='SAL_EMP';
- partition pruning 기능이 작동되어 full table scan을 하더라도 특정 파티션만 scan 하기 때문에 i/o가 현저히 줄었다.
set arraysize 1000
select * from hr.sal_emp s where salary between 5000 and 8000;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last'));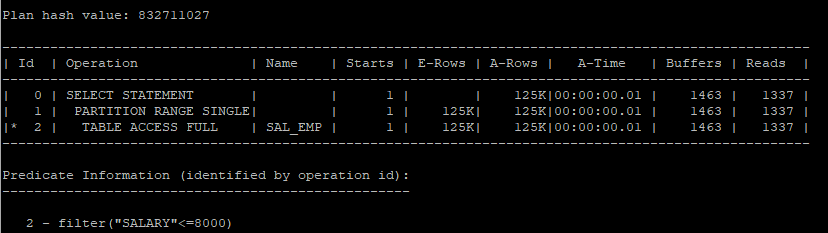
- allstats last partition : 파티션 정보까지 같이 실행계획에 나타냄
- 파티션 테이블 스캔 정보
- Pstart : 시작 파티션 번호
- Pstop : 종료 파티션 번호
select * from hr.sal_emp s where salary between 5000 and 8000;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last partition'));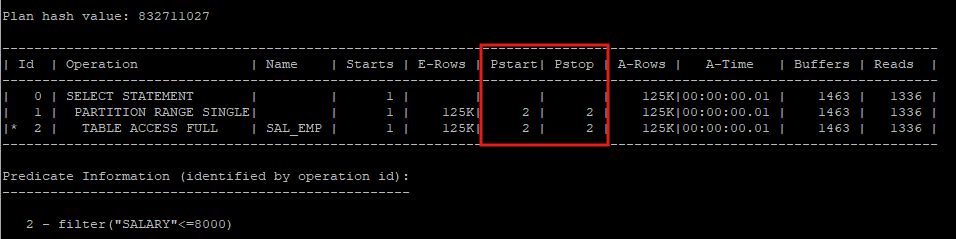
- salary의 범위를 5000~11000까지 하게 되면 2개의 파티션을 읽게 된다.
select * from hr.sal_emp s where salary between 5000 and 11000;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last partition'));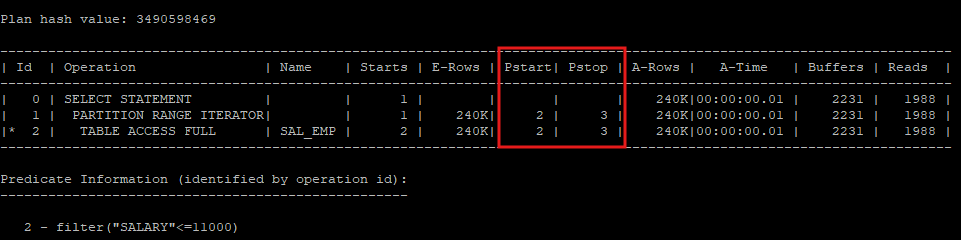
partition pruning
- SQL 조건절을 분석하여 읽지 않아도 되는 파티션 세그먼트를 액세스 대상에서 제외시키는 기능
정적(static) partition pruning
- 파티션 키 컬럼을 상수 조건으로 조회
예)select * from hr.sal_emp s where salary between 5000 and 11000; - 액세스할 파티션을 쿼리 최적화 시점에 결정(실행계획을 생성할때)
동적(dynamic) partition pruning
- 파티션 키 컬럼을 바인드 변수로 조회
- 액세스할 파티션을 쿼리 최적화 시점에 결정할 수 없다.(실행시점에 결정된다)
- 바인드 변수로 조회한다고 해서 i/o 성능이 떨어지지는 않는다.
- pstart, pstop이 KEY로 되어있으면 변수 처리 되어있는것이다.
variable b_start number
variable b_stop number
execute :b_start := 5000
execute :b_stop := 8000
select * from hr.sal_emp s where salary between :b_start and :b_stop;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last partition'));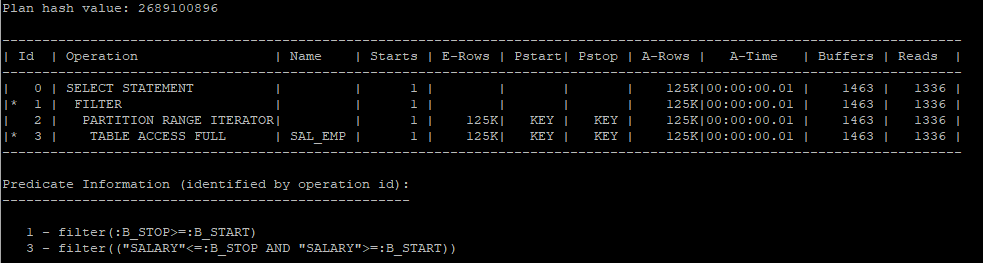
로컬(local) 파티션 인덱스
- 파티션 테이블의 각 파티션과 파티션 인덱스의 각 파티션이 1 대 1로 맵핑이 되는 인덱스
- 테이블 파티션의 갯수와 인덱스 파티션의 개수가 일치하며 파티션 테이블의 파티션 키와 인덱스 파티션의 인덱스 키가 일치한다.
- 유지 관리 작업은 오라클이 자동으로 관리한다.
- 다른 파티션에 영향을 주지 않는다.
prefixed: 파티션 인덱스를 생성할때 파티션 키 컬럼을 인덱스 키 컬럼 왼쪽 선두에 두는것을 의미noprefixed: 파티션 인덱스를 생성할때 파티션 키 컬럼을 인덱스 키 컬럼 왼쪽 선두에 두지 않는 것을 의미
- 테이블 생성
create table hr.emp_local
partition by range(employee_id)
(partition p1 values less than(20000),
partition p2 values less than(40000),
partition p3 values less than(80000),
partition p4 values less than(100000),
partition p5 values less than(120000),
partition pmax values less than(maxvalue))
as
select rownum as employee_id, last_name, first_name, hire_date, job_id, salary, manager_id, department_id
from hr.employees e, (select level as id from dual connect by level <= 1000);- 통계수집
execute dbms_stats.gather_table_stats('hr','emp_local');- 파티션 통계정보 확인
select partition_position,partition_name,high_value, tablespace_name, num_rows,blocks,avg_row_len, to_char(last_analyzed,'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss')
from dba_tab_partitions
where table_owner='HR'
and table_name='EMP_LOCAL';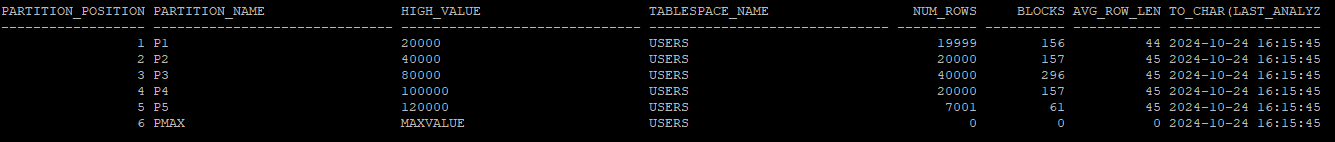
- 1번 파티션을 사용해서 조회한다.
select * from hr.emp_local where employee_id = 1000;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last partition'));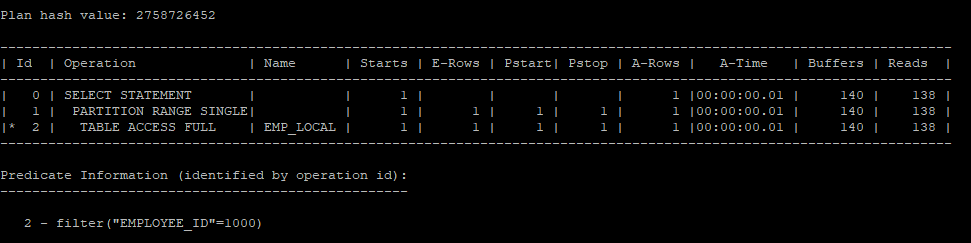
- 범위가 넒어 여러개의 파티션을 읽어야 하기 때문에 iterator으로 실행되었다.
select count(*) from hr.emp_local where employee_id between 1000 and 25000;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last partition'));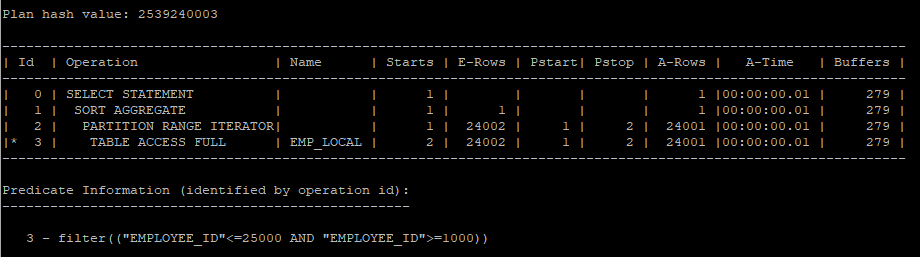
- local 인덱스 생성
create unique index hr.emp_local_idx on hr.emp_local(employee_id) local;- 생성 인덱스 정보 확인
- local 인덱스로 생성하였기 때문에 파티션과 1 대 1 매칭으로 6개가 생성되었다.
select i.index_name, i.uniqueness, p.locality, p.alignment, i.partitioned, p.partition_count
from dba_indexes i, dba_part_indexes p
where i.table_name = 'EMP_LOCAL'
and i.owner = 'HR'
and p.table_name = i.table_name
and p.index_name = i.index_name;
- index unique scan을 통해 i/o가 획기적으로 줄었다.
select * from hr.emp_local where employee_id = 1000;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last partition'));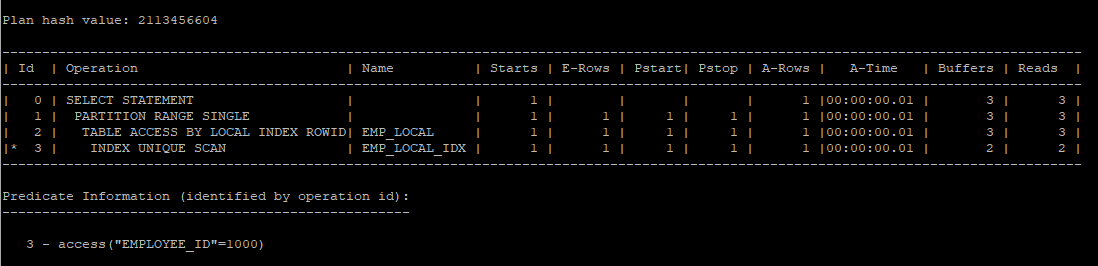
- 기존 full table scan 보다 index range scan이 i/o가 훨씬 줄었다.
select /*+ index(e emp_local_idx) */ count(*) from hr.emp_local e where employee_id between 1000 and 25000;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last partition'));
- 인덱스의 파티션 설정 확인
select index_name, partition_name
from dba_ind_partitions
where index_name = 'EMP_LOCAL_IDX';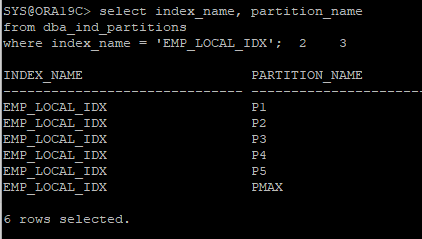
글로벌(GLOBAL) 파티션 인덱스
- 파티션 테이블의 파티션 개수와 인덱스 파티션의 파티션 개수가 일치하지 않는다.
- 파티션 테이블의 파티션 키와 인덱스 파티션 키가 일치 하지 않는다.
- 유지 관리는 DBA가 직접해야 한다.
- 테이블 생성
create table hr.emp_global
partition by range(employee_id)
(partition p1 values less than(20000),
partition p2 values less than(40000),
partition p3 values less than(80000),
partition p4 values less than(100000),
partition p5 values less than(120000),
partition pmax values less than(maxvalue))
as
select rownum as employee_id, last_name, first_name, hire_date, job_id, salary, manager_id, department_id
from hr.employees e, (select level as id from dual connect by level <= 1000);- 통계수집
execute dbms_stats.gather_table_stats('hr','emp_global');- 파티션 통계정보 확인
select partition_position,partition_name,high_value, tablespace_name, num_rows,blocks,avg_row_len, to_char(last_analyzed,'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss')
from dba_tab_partitions
where table_owner='HR'
and table_name='EMP_GLOBAL';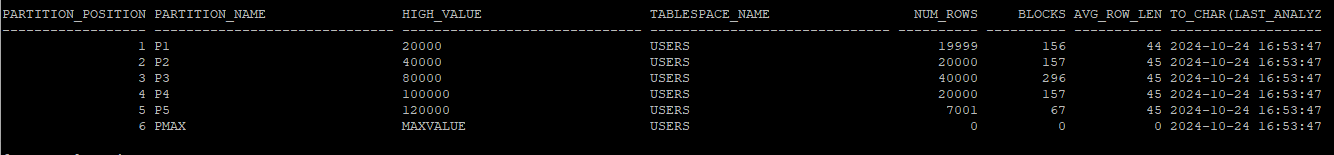
- global 인덱스 생성
- 테이블 파티션 키 컬럼과 인덱스 파티션 키 컬럼이 상이하다.
create index hr.emp_global_idx on hr.emp_global(hire_date) global
partition by range(hire_date)
(partition p2004 values less than(to_date('2005-01-01','yyyy-mm-dd')),
partition p2005 values less than(to_date('2006-01-01','yyyy-mm-dd')),
partition p2006 values less than(to_date('2007-01-01','yyyy-mm-dd')),
partition pmax values less than(maxvalue));- 인덱스의 파티션 설정 확인
select index_name, partition_name,high_value,blevel, leaf_blocks, num_rows,clustering_factor, to_char(last_analyzed,'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss'),pct_free
from dba_ind_partitions
where index_name = 'EMP_GLOBAL_IDX';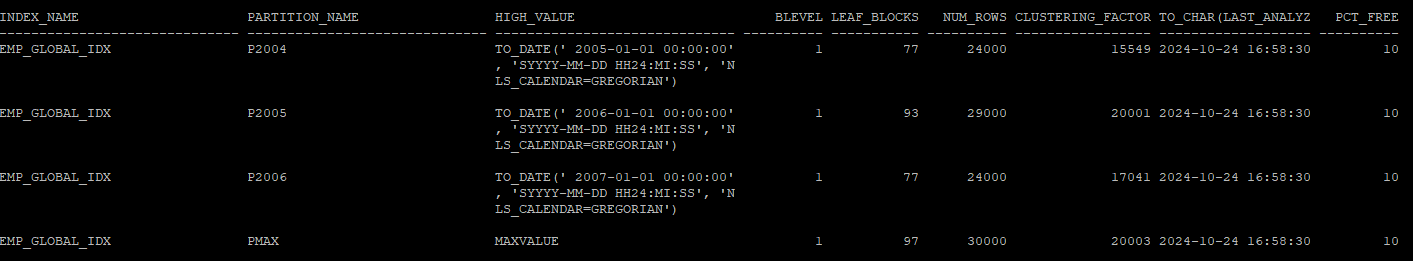
- 테이블 파티션은 6개 이지만 인덱스 파티션은 4개이다.
select i.index_name, i.uniqueness, p.locality, p.alignment, i.partitioned, p.partition_count
from dba_indexes i, dba_part_indexes p
where i.table_name = 'EMP_GLOBAL'
and i.owner = 'HR'
and p.table_name = i.table_name
and p.index_name = i.index_name;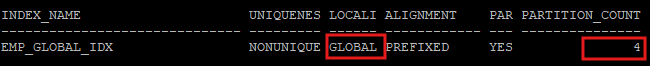
- employee_id 에는 인덱스가 설정되어 있지 않아 full table scan을 실행하였다.
select * from hr.emp_global where employee_id = 100;
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last partition'));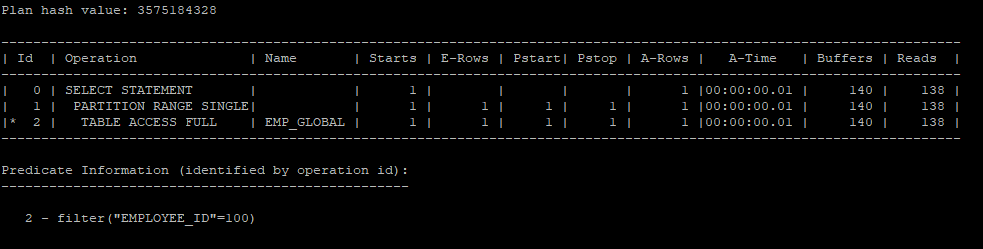
- 조건을 인덱스가 설정된 hire_date 컬럼을 이용하여 index scan을 유도하였다.
- 하지만 인덱스의 파티션 키 컬럼과 테이블 파티션의 키 컬럼이 달라 많은 i/o를 유발한다.
select /*+ index(e emp_global_idx) */ * from hr.emp_global e where hire_date >= to_date('2001-01-01','yyyy-mm-dd') and hire_date < to_date('2002-01-01','yyyy-mm-dd');
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last partition'));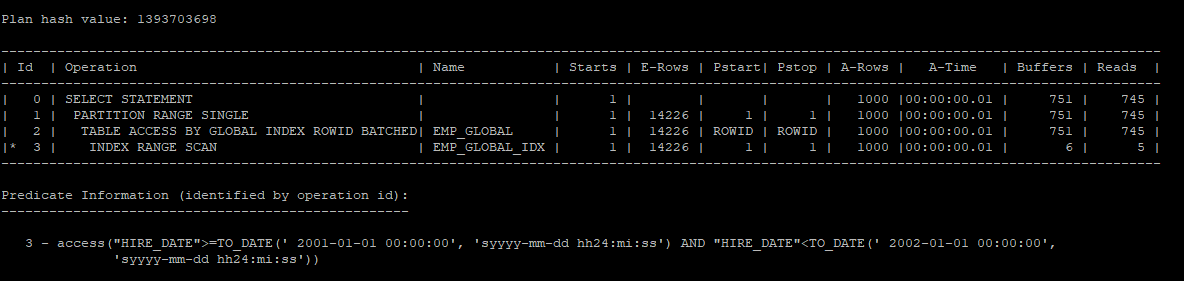
- 건수를 조회할 때, INDEX FAST FULL SCAN은 전체 인덱스 블록을 멀티 블록 I/O 방식으로 읽고, 그 중에서 조건에 맞는 데이터를 찾아 처리합니다.
select count(*) from hr.emp_global e where hire_date >= to_date('2001-01-01','yyyy-mm-dd') and hire_date < to_date('2002-01-01','yyyy-mm-dd');
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last partition'));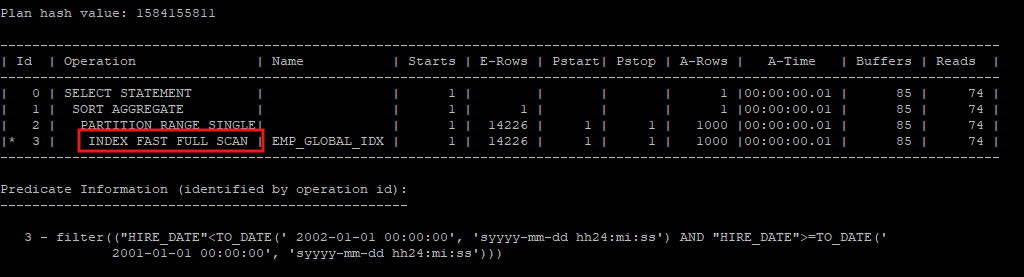
- 조건절의 컬럼이 파티션된 인덱스를 사용하면, INDEX RANGE SCAN이 건수를 셀 때 더 나은 I/O 성능을 제공할 수 있어, INDEX FAST FULL SCAN이 항상 좋은 선택은 아니다.
select /*+ index_rs(e emp_global_idx) */ count(*) from hr.emp_global e where hire_date >= to_date('2001-01-01','yyyy-mm-dd') and hire_date < to_date('2002-01-01','yyyy-mm-dd');
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor(null,null,'allstats last partition'));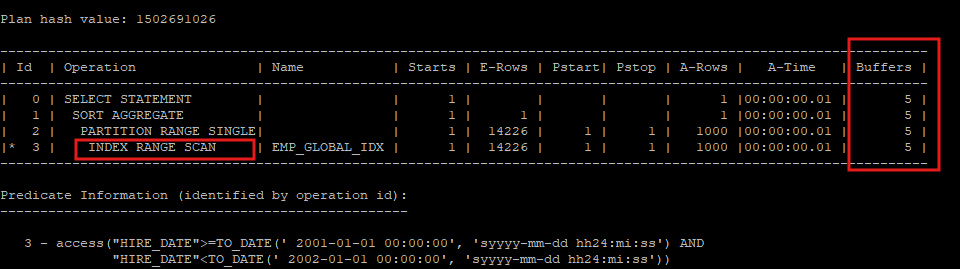
테이블 파티션 삭제시 글로벌 인덱스 영향
- local 인덱스 같은 경우 오라클이 자동으로 관리하기 때문에 같이 삭제된다.
- 테이블의 파티션 정보 확인
select partition_position,partition_name,high_value, tablespace_name, num_rows,blocks,avg_row_len, to_char(last_analyzed,'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss')
from dba_tab_partitions
where table_owner='HR'
and table_name='EMP_GLOBAL';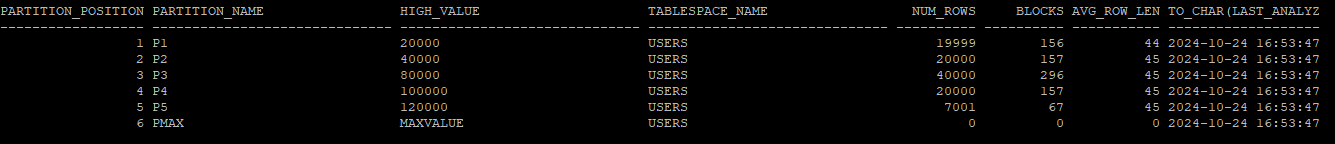
- 인덱스의 파티션 정보 확인
select index_name, partition_name,high_value,blevel, leaf_blocks, num_rows,clustering_factor, to_char(last_analyzed,'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss'),pct_free,status
from dba_ind_partitions
where index_name = 'EMP_GLOBAL_IDX';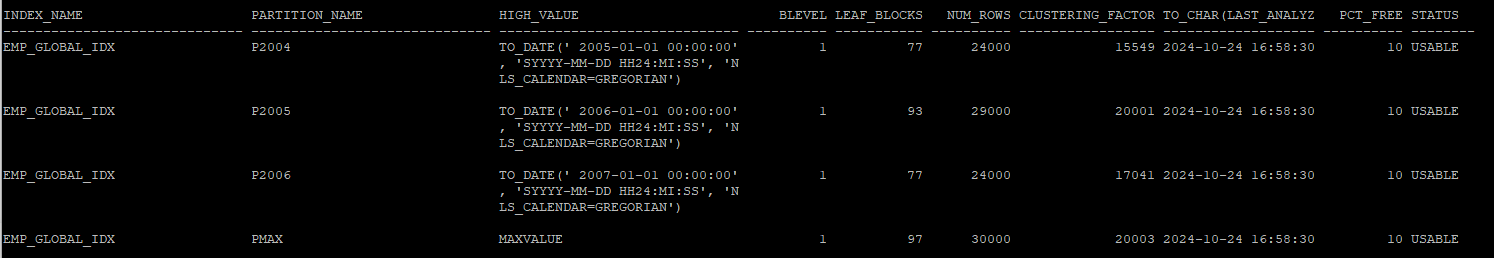
- 테이블 파티션을 삭제하면 해당 데이터과 연결되어있던 global index들은 unusable 상태로 변경된다.
alter table hr.emp_global drop partition p4;
select index_name, partition_name,high_value,blevel, leaf_blocks, num_rows,clustering_factor, to_char(last_analyzed,'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss'),pct_free,status
from dba_ind_partitions
where index_name = 'EMP_GLOBAL_IDX';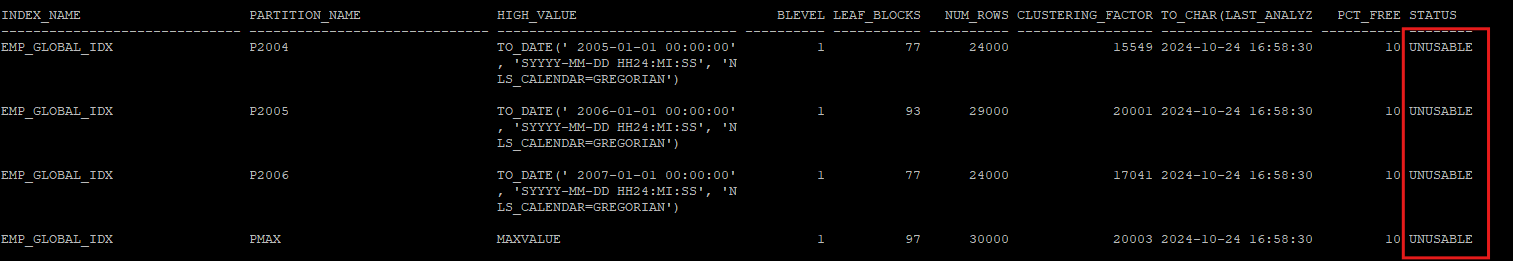
- 인덱스가 unusable 상태이면 인데스를 이용한 scan이 불가능하기 때문에 오류가 발생한다.
select /*+ index_rs(e emp_global_idx) */ count(*) from hr.emp_global e where hire_date >= to_date('2001-01-01','yyyy-mm-dd') and hire_date < to_date('2002-01-01','yyyy-mm-dd');
- unusable 상태가 된 인덱스는 다시 rebuild 해줘야 한다.
- 하지만 한번에 전체 rebuild는 안되기 때문에 개별적으로 해야한다.
alter index hr.emp_global_idx rebuild partition p2004;
alter index hr.emp_global_idx rebuild partition p2005;
alter index hr.emp_global_idx rebuild partition p2006;
alter index hr.emp_global_idx rebuild partition pmax;- 다시 인덱스 파티션 정보를 조회해보면 usable로 변경되었다.
select index_name, partition_name,high_value,blevel, leaf_blocks, num_rows,clustering_factor, to_char(last_analyzed,'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss'),pct_free,status
from dba_ind_partitions
where index_name = 'EMP_GLOBAL_IDX';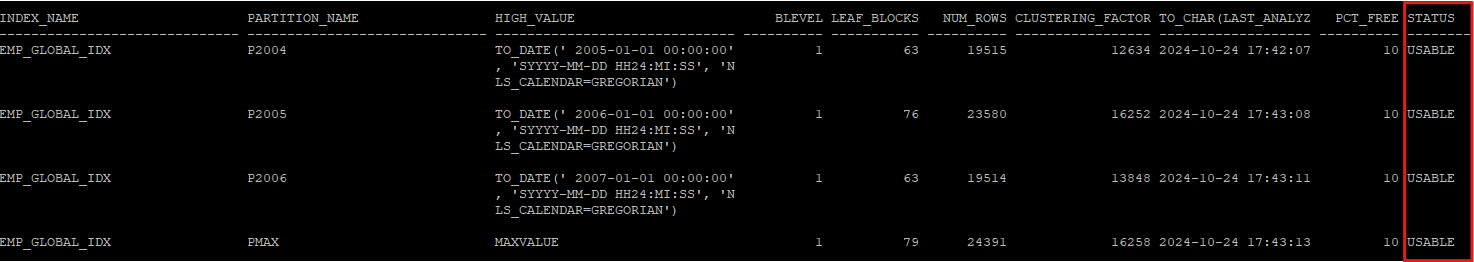
global partition 분할(split)
- global 인덱스에 대해 split 하게 되어도 상태에는 아무런 문제가 되지 않는다.
alter index hr.emp_global_idx split partition pmax at(to_date('2008-01-01','yyyy-mm-dd')) into (partition p2007, partition pmax);
select index_name, partition_name,high_value,blevel, leaf_blocks, num_rows,clustering_factor, to_char(last_analyzed,'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss'),pct_free,status
from dba_ind_partitions
where index_name = 'EMP_GLOBAL_IDX';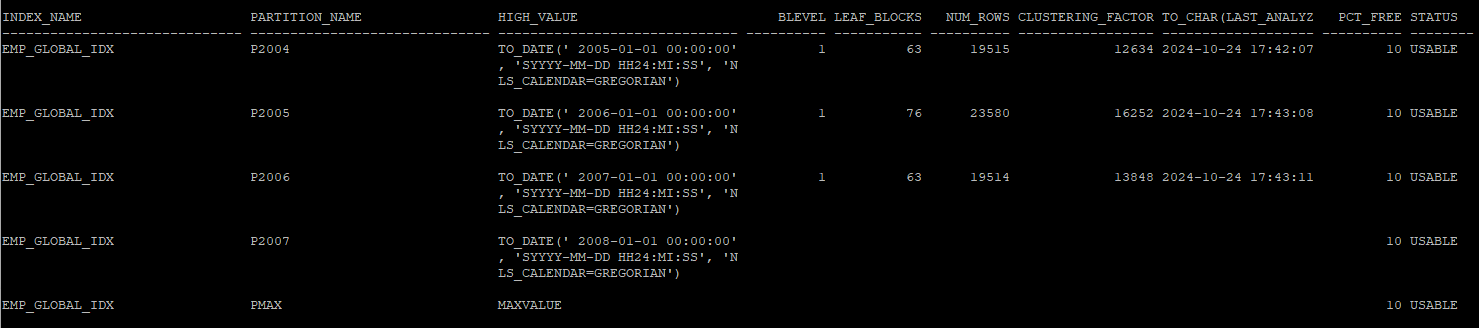
- 기존 p2007 인덱스가 바라보던 데이터들은 pmax 인덱스로 넘어가기 때문에 unusable 상태로 변경되었다.
alter index hr.emp_global_idx drop partition p2007;
select index_name, partition_name,high_value,blevel, leaf_blocks, num_rows,clustering_factor, to_char(last_analyzed,'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss'),pct_free,status
from dba_ind_partitions
where index_name = 'EMP_GLOBAL_IDX';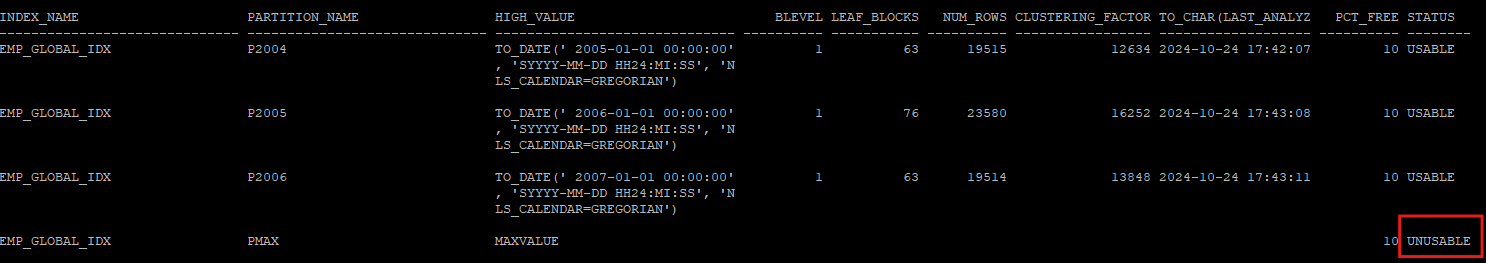
alter index hr.emp_global_idx rebuild partition pmax;