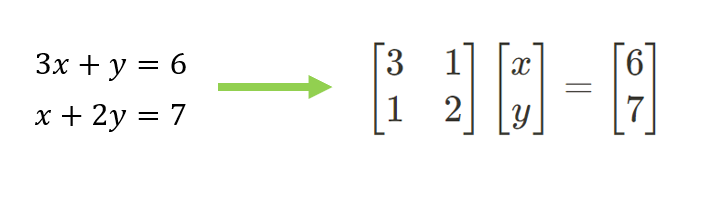이번 포스팅에서는 행렬을 주제로 다뤄보겠습니다.
위키백과에 따르면 수학에서의 행렬은 다항식을 직사각형의 모양으로 배열한 것입니다. x, y의 변수를 가진 다항식에 대해 살펴보겠습니다.
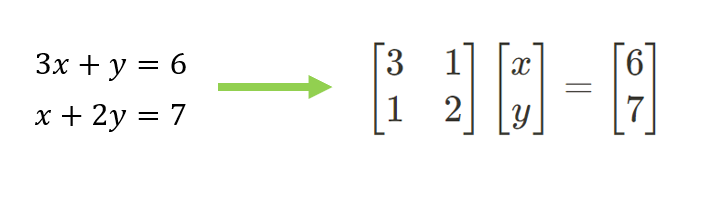
위 다항식의 값을 행렬의 연산을 이용해 해결하면 다음과 같습니다.
sol>
[3112][xy]=[67]⇒⇒⇒[6122][xy]=[127][5102][xy]=[57]x=1 & y=3
행렬은 이처럼 다항식을 표현하고 해를 구하는 목적 그리고 수들을 표현하기 위한 목적으로 사용되고 있습니다. 이 행렬에 대해 정의부터 차근차근 알아보겠습니다.
Def> matrix

위키백과의 정의는 위와 같습니다. 즉, 사각형에 숫자들을 담고 있는데 그 숫자(= aij)들이 순서가 있는 숫자들의 배열(Array)이라 할 수 있을 것 같습니다. i가 행(row)을 의미하고 j는 열(column)을 의미합니다.
그리고 aij가 실수 영역인지 복소수 영역인지에 따라 실수 행렬, 복소수 행렬이라 합니다. 이번 포스팅에서는 실수 행렬(real matrix)만 다루겠습니다.
Notation
행렬은 기본적으로 "[]" 혹은 "()"를 통해 묶어서 표현합니다. 다음은 m×n 행렬의 표현방법입니다.
A=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎡a11a21a31⋮am1a12a22a32⋮am2a13a23a33⋮am3⋯⋯⋯⋱⋯a1na2na3n⋮amn⎦⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎤=⎝⎜⎜⎜⎜⎜⎜⎛a11a21a31⋮am1a12a22a32⋮am2a13a23a33⋮am3⋯⋯⋯⋱⋯a1na2na3n⋮amn⎠⎟⎟⎟⎟⎟⎟⎞
행렬의 기본연산에 들어가기 앞서 Numpy 모듈을 소개하려 합니다. Numpy는 Python언어의 matrix연산을 수행할 수 있는 모듈이고 이번 포스팅에서도 사용하려 합니다.
기본 연산
행렬의 연산인 +(Addition), ⋅(Scalar multiplication), −(Subtraction), T(Transposition)에 대해 알아보겠습니다.
Addition
For m×n matrix A and B,
A+B=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎡a11+b11a21+b21a31+b31⋮am1+bm1a12+b12a22+b22a32+b32⋮am2+bm2a13+b13a23+b23a33+b33⋮am3+bm3⋯⋯⋯⋱⋯a1n+b1na2n+b2na3n+b3n⋮amn+bmn⎦⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎤
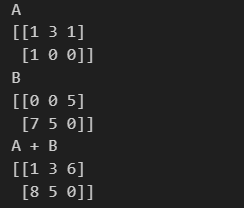
example : 2×3 matrix A and B
A=[113010],B=[070550]
sol>
A+B=[1+01+73+00+51+50+0]=[183560]
python code
import numpy as np
A = np.array([[1,3,1],
[1,0,0]])
B = np.array([[0,0,5],
[7,5,0]])
print(f"A\n{A}")
print(f"B\n{B}")
print(f"A + B \n{A + B}")
result
Scalar multiplication
For c∈R and n×m matrix A,
c⋅A=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎡c⋅a11c⋅a21c⋅a31⋮c⋅am1c⋅a12c⋅a22c⋅a32⋮c⋅am2c⋅a13c⋅a23c⋅a33⋮c⋅am3⋯⋯⋯⋱⋯c⋅a1nc⋅a2nc⋅a3n⋮c⋅amn⎦⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎤
example : 2×3 matrix A and c∈R
c=2andA=[148−2−35]
sol>
c⋅A=[2⋅12⋅42⋅82⋅(−2)2⋅(−3)2⋅5]=[2816−4−610]
python code
import numpy as np
A = np.array([[1,8,-3],
[4,-2,5]])
c = 2
print(f"A\n{A}")
print(f"c = {c}")
print(f"cA \n{c * A}")
result

Subtraction
For m×n matrix A and B,
A−B=A+(−1)⋅B
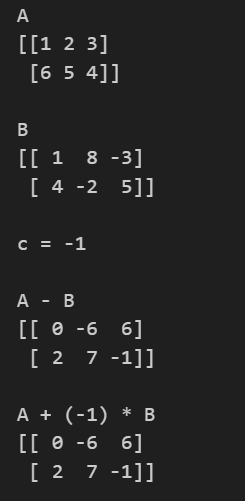
example : 2×3 matrix A and B
A=[162534],B=[148−2−35]
sol>
A−B====A+(−1)⋅B[162534]+(−1)⋅[148−2−35][162534]+[−1−4−823−5][02−676−1]
python code
import numpy as np
A = np.array([[1,2,3],
[6,5,4]])
B = np.array([[1,8,-3],
[4,-2,5]])
c = -1
print(f"A\n{A}\n")
print(f"B\n{B}\n")
print(f"c = {c}\n")
print(f"A - B\n{A - B}\n")
print(f"A + (-1) * B \n{A + (-1) * B}\n")
result
Transposition
For m×n matrix A,
AT=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎡a11a12a13⋮a1na21a22a23⋮a2na31a32a33⋮a3n⋯⋯⋯⋱⋯am1am2am3⋮amn⎦⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎤:n×m matrix
example : 2×3 matrix A
A=[162534]⇒AT=⎣⎢⎡123654⎦⎥⎤
python code
import numpy as np
A = np.array([[1,2,3],
[6,5,4]])
print(f"A\n{A}\n")
print(f"A^T \n {A.T}\n")
print(f"A^T \n {A.transpose()}")
result
이렇게 기본 연산 과정에 대해 다뤄 보았습니다. 포스팅이 길어지는 만큼 행렬 곱셈, 선형 변환, 행렬의 노름, 행렬의 종류, 행렬식에 대해서는 다음 포스팅에 작성하겠습니다.
읽어주셔서 감사합니다. 오탈자 혹은 잘못된 내용이 있을 경우에 댓글 주시면 감사하겠습니다.
Reference