앞선 과정에서는 단일 변수의 계산그래프를 표현한 것. 이를 행렬로 확장해서 계산그래프를 그릴 수 있다.
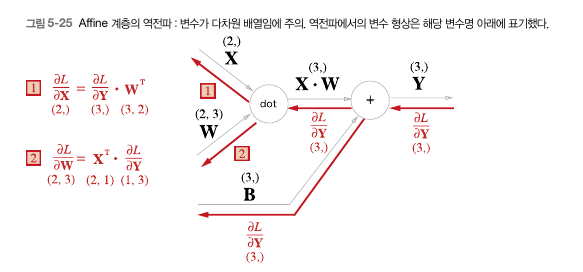
신경망에서 학습은 위의 WX+B와 활성화함수의 반복을 통한 순전파와, 역전파로인한 매개변수 갱신으로 이루어진다. 이때 WX+B의 계산이 이루어지는 계층을 AFFINE 계층이라고 할 때 AFFINE 계층 클래스를 다음과 같이 구현 시킬 수 있다.
- 계층으로 표현한 신경망
class Affine:
def __init__(self,W,b):
self.W = W
self.b = b
self.x = None
self.dW = None
self.db = None
def forward(self,x):
self.x = x
out = np.dot(x,self.W)+self.b
return out
def backward(self,dout):
dx = np.dot(dout,self.W.T)
self.dW = np.dot(self.x.T,dout)
self.db = np.sum(dout,axis= 0)- Affine class 구현
# coding: utf-8
import numpy as np
def identity_function(x):
return x
def step_function(x):
return np.array(x > 0, dtype=np.int)
def sigmoid(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def sigmoid_grad(x):
return (1.0 - sigmoid(x)) * sigmoid(x)
def relu(x):
return np.maximum(0, x)
def relu_grad(x):
grad = np.zeros(x)
grad[x>=0] = 1
return grad
def softmax(x):
if x.ndim == 2:
x = x.T
x = x - np.max(x, axis=0)
y = np.exp(x) / np.sum(np.exp(x), axis=0)
return y.T
x = x - np.max(x) # 오버플로 대책
return np.exp(x) / np.sum(np.exp(x))
def mean_squared_error(y, t):
return 0.5 * np.sum((y-t)**2)
def cross_entropy_error(y, t):
if y.ndim == 1:
t = t.reshape(1, t.size)
y = y.reshape(1, y.size)
# 훈련 데이터가 원-핫 벡터라면 정답 레이블의 인덱스로 반환
if t.size == y.size:
t = t.argmax(axis=1)
batch_size = y.shape[0]
return -np.sum(np.log(y[np.arange(batch_size), t] + 1e-7)) / batch_size
def softmax_loss(X, t):
y = softmax(X)
return cross_entropy_error(y, t)- functions.py (모든 활성화 함수, 손실함수를 정리해놓은 파일)
import numpy as np
from functions import *
from util import im2col, col2im
class Relu:
def __init__(self):
self.mask = None
def forward(self, x):
self.mask = (x <= 0)
out = x.copy()
out[self.mask] = 0
return out
def backward(self, dout):
dout[self.mask] = 0
dx = dout
return dx
class Sigmoid:
def __init__(self):
self.out = None
def forward(self, x):
out = sigmoid(x)
self.out = out
return out
def backward(self, dout):
dx = dout * (1.0 - self.out) * self.out
return dx
class Affine:
def __init__(self, W, b):
self.W = W
self.b = b
self.x = None
self.original_x_shape = None
# 가중치와 편향 매개변수의 미분
self.dW = None
self.db = None
def forward(self, x):
# 텐서 대응
self.original_x_shape = x.shape
x = x.reshape(x.shape[0], -1)
self.x = x
out = np.dot(self.x, self.W) + self.b
return out
def backward(self, dout):
dx = np.dot(dout, self.W.T)
self.dW = np.dot(self.x.T, dout)
self.db = np.sum(dout, axis=0)
dx = dx.reshape(*self.original_x_shape) # 입력 데이터 모양 변경(텐서 대응)
return dx
class SoftmaxWithLoss:
def __init__(self):
self.loss = None # 손실함수
self.y = None # softmax의 출력
self.t = None # 정답 레이블(원-핫 인코딩 형태)
def forward(self, x, t):
self.t = t
self.y = softmax(x)
self.loss = cross_entropy_error(self.y, self.t)
return self.loss
def backward(self, dout=1):
batch_size = self.t.shape[0]
if self.t.size == self.y.size: # 정답 레이블이 원-핫 인코딩 형태일 때
dx = (self.y - self.t) / batch_size
else:
dx = self.y.copy()
dx[np.arange(batch_size), self.t] -= 1
dx = dx / batch_size
return dx- layers.py 모든 계층 class를 정리해놓은 파일
import numpy as np
from layers import *
from collections import OrderedDict
class TwoLayerNet:
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, output_size, weight_init_std = 0.01):
# 가중치 초기화
self.params = {}
self.params['W1'] = weight_init_std * np.random.randn(input_size, hidden_size)
self.params['b1'] = np.zeros(hidden_size)
self.params['W2'] = weight_init_std * np.random.randn(hidden_size, output_size)
self.params['b2'] = np.zeros(output_size)
# 계층 생성
self.layers = OrderedDict()
self.layers['Affine1'] = Affine(self.params['W1'], self.params['b1'])
self.layers['Relu1'] = Relu()
self.layers['Affine2'] = Affine(self.params['W2'], self.params['b2'])
self.lastLayer = SoftmaxWithLoss()
def predict(self, x):
for layer in self.layers.values():
x = layer.forward(x)
return x
# x : 입력 데이터, t : 정답 레이블
def loss(self, x, t):
y = self.predict(x)
return self.lastLayer.forward(y, t)
def accuracy(self, x, t):
y = self.predict(x)
y = np.argmax(y, axis=1)
if t.ndim != 1 : t = np.argmax(t, axis=1)
accuracy = np.sum(y == t) / float(x.shape[0])
return accuracy
# x : 입력 데이터, t : 정답 레이블
def gradient(self, x, t):
# forward
self.loss(x, t)
# backward
dout = 1
dout = self.lastLayer.backward(dout)
layers = list(self.layers.values())
layers.reverse()
for layer in layers:
dout = layer.backward(dout)
# 결과 저장
grads = {}
grads['W1'], grads['b1'] = self.layers['Affine1'].dW, self.layers['Affine1'].db
grads['W2'], grads['b2'] = self.layers['Affine2'].dW, self.layers['Affine2'].db
return grads
- Network.py (2층 신경망 class)
import numpy as np
import Network as nt
from mnist import load_mnist
(x_train,t_train) , (x_test,t_test) = load_mnist(normalize=True,one_hot_label=True)
train_loss_list = []
iters_num = 10000
train_size = x_train.shape[0]
batch_size = 100
learning_rate = 0.1
train_loss_list = []
train_acc_list = []
test_acc_list = []
iter_per_epoch = max(train_size/batch_size,1)
net = nt.TwoLayerNet(784,50,10)
for i in range(iters_num):
print(i)
batch_mask = np.random.choice(train_size,batch_size)
x_batch = x_train[batch_mask]
t_batch = t_train[batch_mask]
grad = net.gradient(x_batch,t_batch)
for key in ('W1','b1','W2','b2'):
net.params[key] -= learning_rate*grad[key]
loss = net.loss(x_batch,t_batch)
train_loss_list.append(loss)
print(train_loss_list)- mnist data set 불러와 학습시켜보기 마지막에 손실함수 값 list를 출력시키면, 값이 점점 줄어드는것을 확인할 수 있다.
