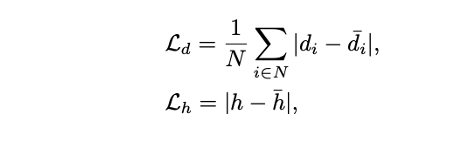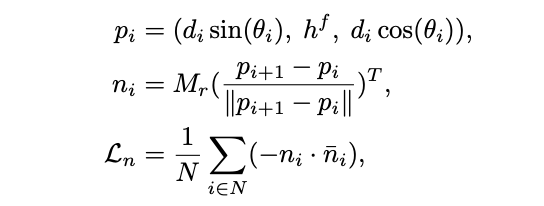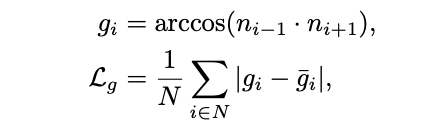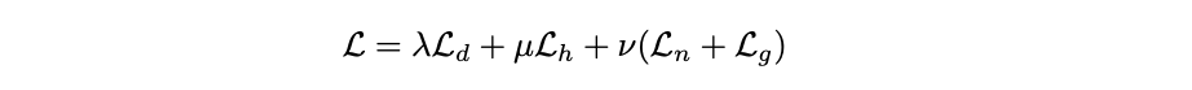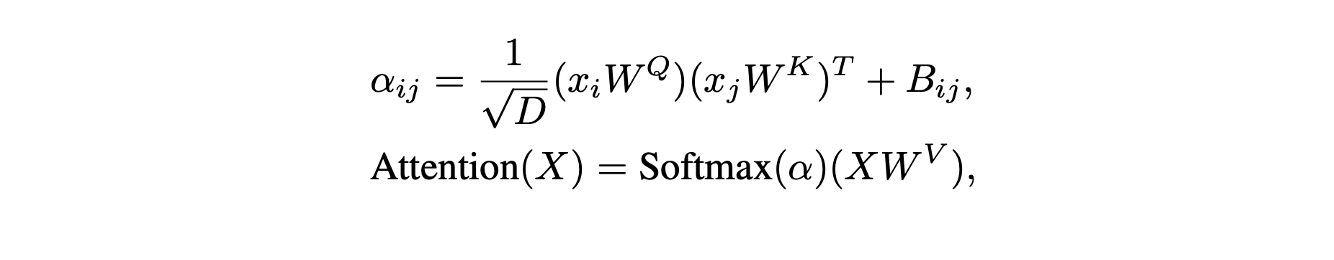[논문 리뷰] LGT-Net: Indoor Panoramic Room Layout Estimation with Geometry-Aware
Transformer Network
Approach
Panoramic Room Layout Representation
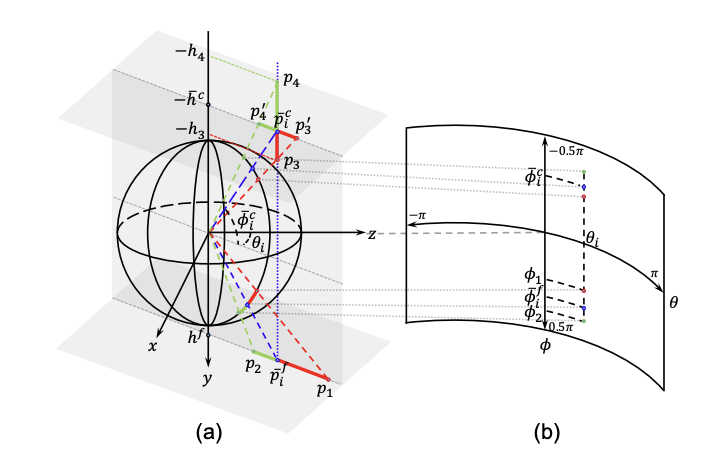
- 본 논문에서는 room layout을 floor boundary와 room heigth로 표현한다.
- 동일한 경도 간격으로 N개(논문에서는 256)의 point를 샘플링한 후 horizon-depth로 변환한다.
- HorizonNet에서는 floor/ceiling의 위도를 예측하고 error를 계산하지만 위도 상 error가 동일하지만 horizon-depth error는 다른 경우가 있다.
(e.g. ∣ϕ1−ϕˉif∣=∣ϕ1−ϕˉif∣,∣D(p1)−D(pˉif)∣>∣D(p2)−D(pˉif)∣
- 또한, height는 수직 방향의 영향을 크게 받기 때문에 동일한 horizon-depth error를 가지더라도 room height error는 다른 경우가 있다.
(e.g. ∣D(p3′)−D(pˉic)∣=∣D(p4′)−D(pˉic)∣,∣h3−hˉc∣<∣h4−hˉc∣
- 따라서, horizon-depth와 room height의 error를 계산하는 omnidirectional-geometry aware loss function을 사용한다.
Loss function
Horizon-Depth and Room Height
- Horizon-detph와 room height에 대해 L1 loss를 적용한다.
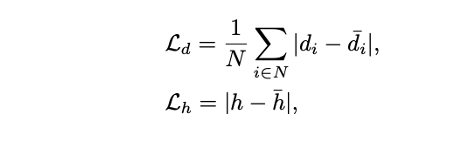
Normals
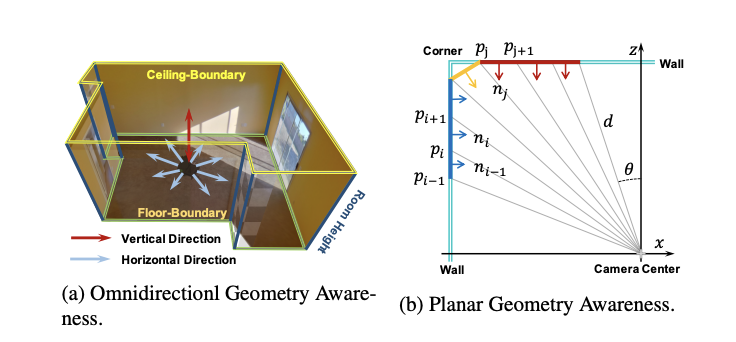
- 각 벽들이 plane임에도 불구하고 위치에 따라 horizon-depth는 다를 수 있지만 normal vector는 동일하다.
- 따라서, horizon-depth di를 3D point pi로 변환한 뒤 normal vector를 구해 ground truth와의 -cosine similarity를 loss로 정의한다.
- Mr은 2π의 rotation matrix, nˉi은 normal vector의 ground truth이다.
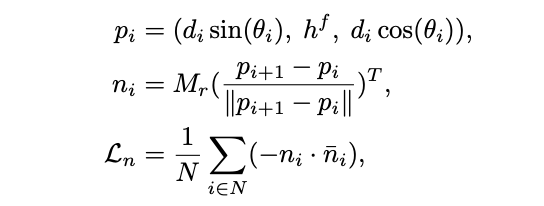
Gradient of normals
- Corner에서의 normal은 변하기 때문에 gradient를 활용해 supervise 한다.
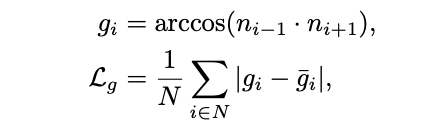
Total loss
- Horizon-depth와 room height에 대한 loss는 omnidirectional-geometry awareness를 normal을 활용한 loss는 planar-geometry awareness를 향상시킨다고 볼 수 있다.
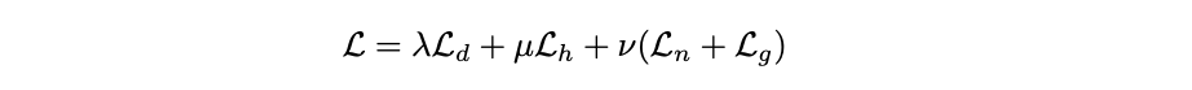
Network
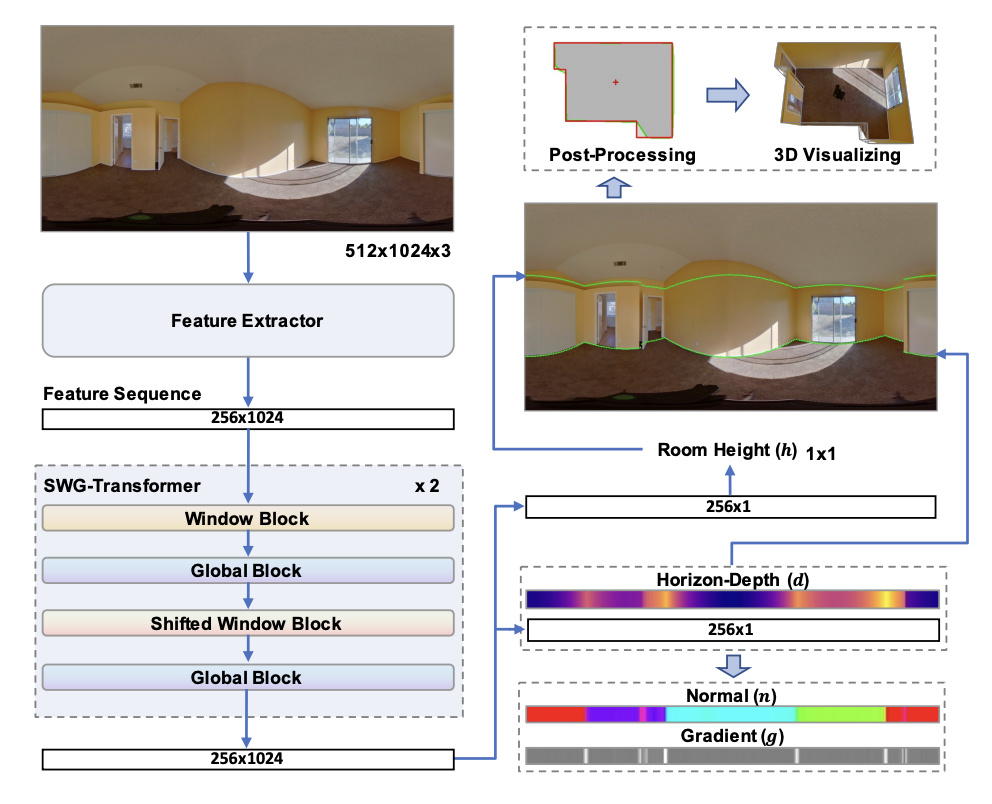
- 512 X 1024 X 3을 input으로 받아 ResNet-50으로부터 서로 다른 scale의 4개의 2D feature map을 뽑는다.
- Height를 압축하고 각 feature map에서 width N개를 샘플링하여 RN×4D의 1D feature sequences를 만든다.
- 4개를 연결하여 RN×D의 feature sequence를 output으로 낸다. D는 1024.
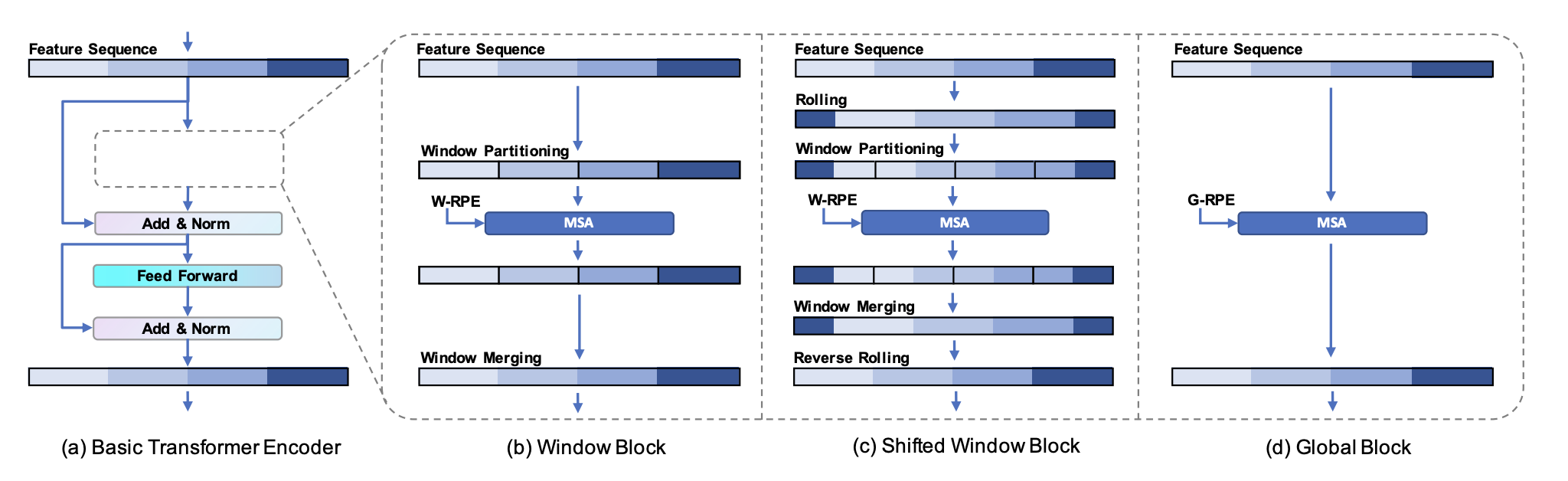
- SWG-Transformer는 Window Block, Global Block, Shifted Window Block, Global Block으로 구성되며 2번의 loop를 돌아 총 8개의 block을 통과한다.
- Window Block은 local geometry relations를 학습하는 역할로 MSA(Multi head Self-Attention) 이전에 NwN(16) window feature sequences RNw×D를 구성한 후 MSA 이후 다시 merge 한다. (Nw=16)
- Shifted Window Block은 인접한 window들을 연결하여 정보들이 상호작용할 수 있도록 만든다. Window partition 전에 feature sequence를 roll하며 원위치시키기 위해 merge 이후 reverse roll을 해준다.
- Global Window Block은 global geometry relations를 학습하는 역할로 original Transformer의 방식을 따른다.
Position Embedding
- Pure attention module이 토큰들의 위치를 구분하는데 적합하지 않기 때문에 relative position embedding을 활용한다.
- MSA의 input sequence를 X={xi}i=1M, M은 sequence length, xi∈RD라 할 때 bias matrix B∈RM×M가 기존 Transformer의 Scaled Query-Key product에 추가된다.
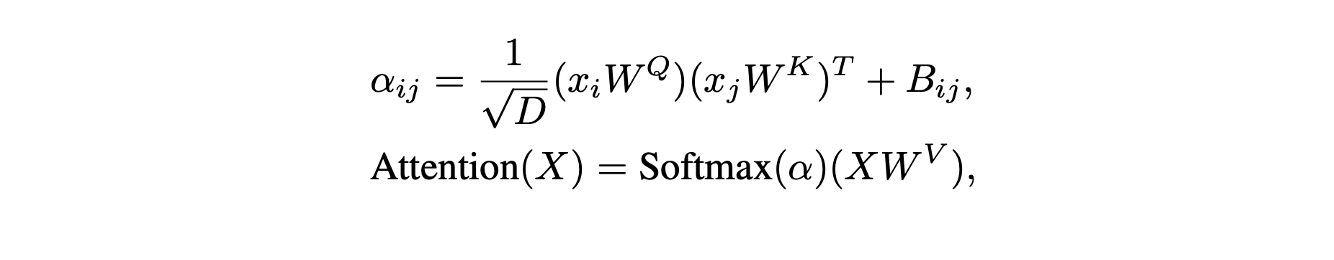
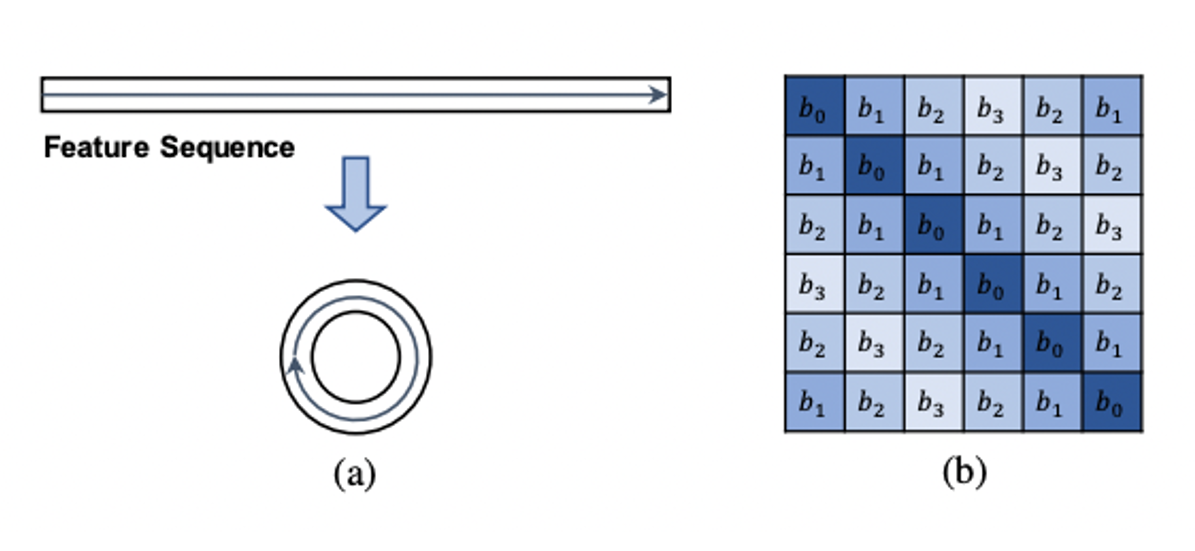
- (Shifted) Window Block에서는 M=Nw(16)이며 learnable scalar table을 {bk}k=−Nw+1Nw=−1로 정의하고 Bij는 bj−i에 해당한다. 이 과정을 W−RPE로 정의한다.
- Global Block에서는 M=N(256)이며 feature sequence가 순환하는 구조를 가지기 때문에 bj−1와 bj−N−i가 동일하다. 따라서, ∣j−i∣≤2N일 때는 Bij=b∣j−i∣이고 그렇지 않으면 Bij=bN−∣j−i∣인 symmetric scalar table {bk}k=0n을 만든다. 이 과정을 G−RPE로 정의한다.
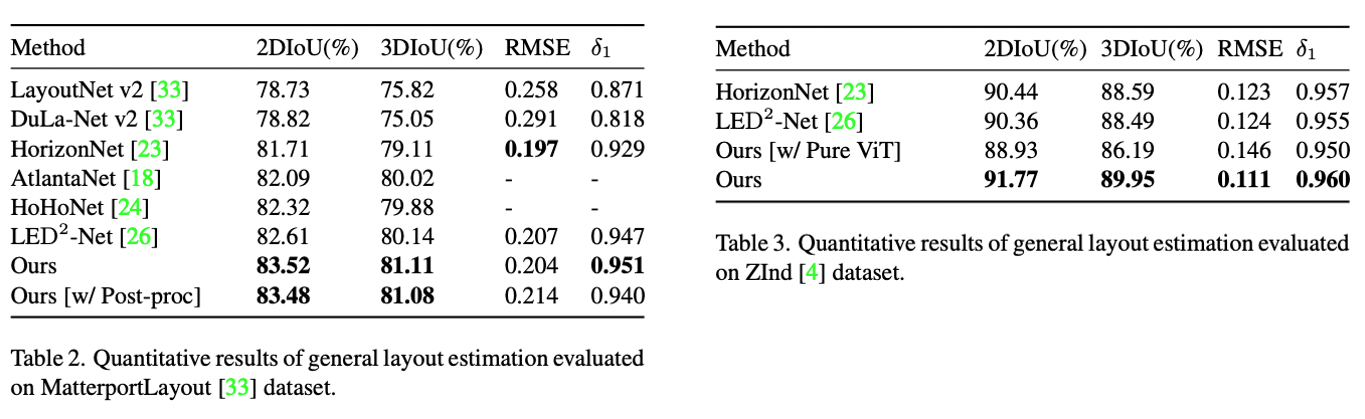
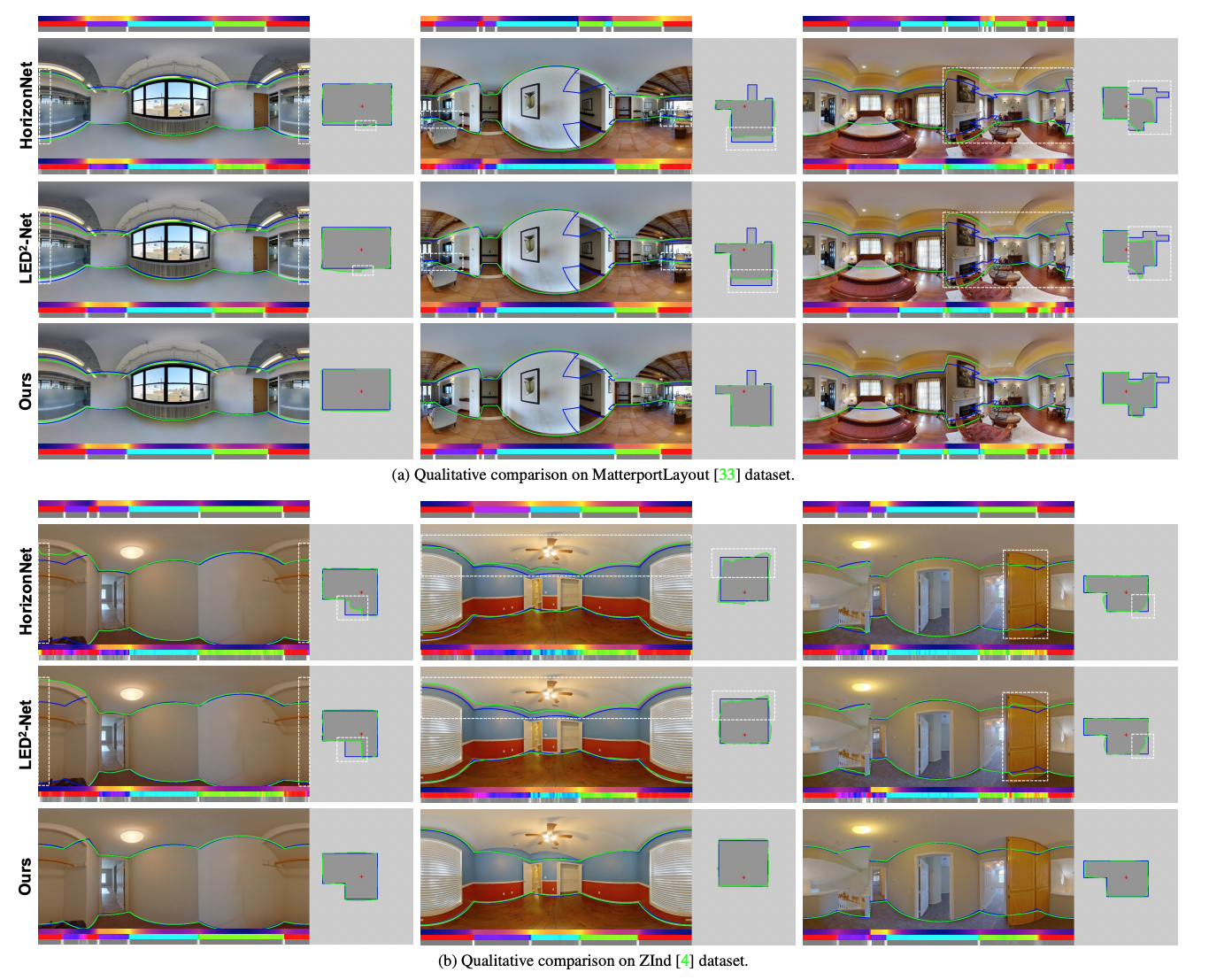
Experiments
Reference