네이버 환율 및 환율 관련 기사 크롤링하기
- 사용 언어: Python
- 사용 라이브러리: BeautifulSoup, Pandas, Requests
상수 설정
# Constants Start
# 뉴스 기사 카테고리 환율,유가,금시세,금리,원자재
CATEGORIES = ("exchange", "oil", "gold", "interest", "material")
# 네이버 금융, 환율전체, 특정국가 환율, 금융 관련 뉴스 페이지 URL
BASE_URL = "https://finance.naver.com"
EX_URL = "/marketindex/exchangeList.nhn"
FX_URL = "/marketindex/exchangeDailyQuote.nhn?marketindexCd="
NEWS_URL = "/marketindex/news/newsList.nhn?category=%s&date=%s"
# 과거의 뉴스가 언제부터 있는가. 이미 고정되어 있기 때문에 상수 저장함.
NEWS_LIMIT = {
CATEGORIES[0]: date(2009, 1, 19),
CATEGORIES[1]: date(2009, 2, 27),
CATEGORIES[2]: date(2009, 5, 20),
CATEGORIES[3]: date(2009, 2, 11),
CATEGORIES[4]: date(2009, 11, 29),
}
# Constants End전역변수 설정
# Global Variable Start
today = date.today() # 프로그램 실행일
this_year = today.year # 프로그램을 실행하는 당일의 연도
# 프로그램 실행 당일과, 각 카테고리의 뉴스가 존재하는 첫 날의 날짜 차이를 일수로 계산한다.
news_date_gap = {
CATEGORIES[0]: (today - NEWS_LIMIT[CATEGORIES[0]]).days,
CATEGORIES[1]: (today - NEWS_LIMIT[CATEGORIES[1]]).days,
CATEGORIES[2]: (today - NEWS_LIMIT[CATEGORIES[2]]).days,
CATEGORIES[3]: (today - NEWS_LIMIT[CATEGORIES[3]]).days,
CATEGORIES[4]: (today - NEWS_LIMIT[CATEGORIES[4]]).days,
}
# Global Variable End환율정보 취득
get_exchange 함수 정의
def get_exchange():
"""환율 정보를 가져온다."""
# Requests를 사용하여 환율 정보 페이지의 Response를 받아온다.
resp = requests.get(BASE_URL + EX_URL)
# BeautifulSoup를 사용하여 Response의 소스 정보를 html로 파싱하여 soup 변수에 저장한다.
soup = BeautifulSoup(resp.text, "html.parser")
# soup에서 class td인 td를 모두 가져온다.
td = soup.find_all("td", class_="tit")
# 각 td에 a태그가 있으므로 a태그를 국가 리스트를 생성하여 집어넣는다.
country_list = [c.find("a") for c in td]
del td # td는 필요 없으므로 삭제(메모리 공간을 최대한 절약하기 위해 더 이상 사용되지 않는 obj를 삭제한다.이미지 1. td의 모습
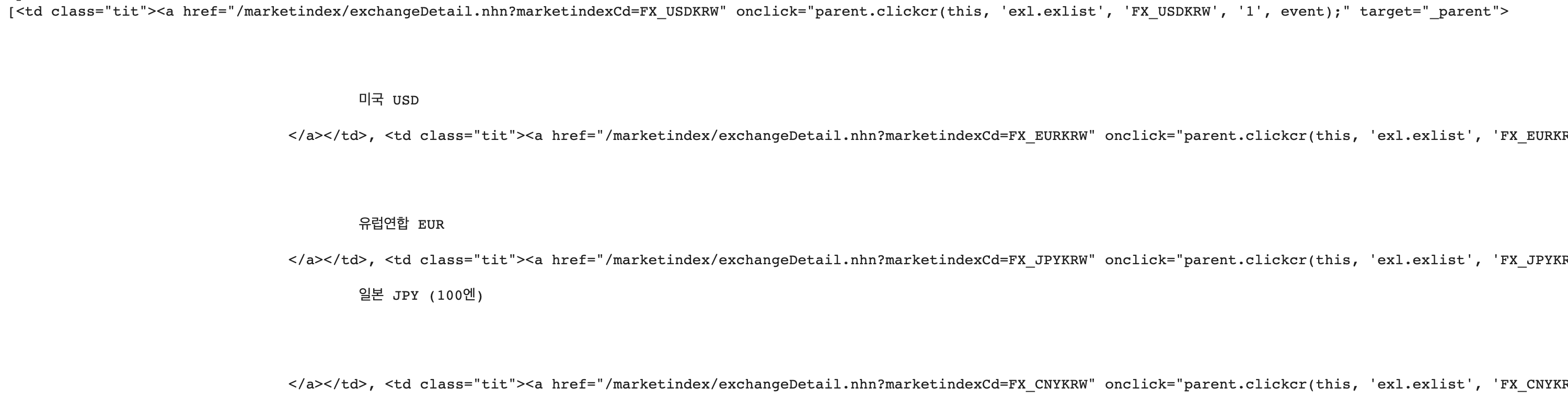
이미지 2. td의 각 요소에서 a태그만 가져온 모습
국가명과 환율 코드가 앞뒤로 상당히 많은 공백을 함께하므로 strip 해주어야 한다.

국가명과 환율코드를 strip하여 리스트에 담는다.
# 전세계 당일환율을 가져오는 옵션을 주기 위해 country_dict를 초기화하고 전세계 옵션을 0번으로 준비한다.
country_dict = {0: ("전세계", EX_URL)}
# country_dict의 Key를 1부터 시작해야 하기 때문에 i을 1로 초기화해서 준비한다.
i = 1
# country_list에서 국가명과 url을 tuple 형식으로 country_dict에 넣는다.
for country in country_list:
country_dict[i] = (country.get_text().strip(), country["href"].split("=")[-1])
i += 1
country_length = len(country_dict) # 환율 개수country_dict는 아래와 같은 모습으로 가공되었다.
{
0: ('전세계', '/marketindex/exchangeList.nhn'),
1: ('미국 USD', 'FX_USDKRW'),
2: ('유럽연합 EUR', 'FX_EURKRW'),
...
42: ('러시아 RUB', 'FX_RUBKRW'),
43: ('헝가리 HUF', 'FX_HUFKRW'),
44: ('폴란드 PLN', 'FX_PLNKRW')
} # 조회할 국가를 입력받는다.
print("환율을 조회하고 싶은 국가 번호를 입력해 주세요.")
[print(f"{key}: {country_dict[key][0]}") for key in country_dict.keys()]이미지3.환율 리스트를 제시하여 앞의 코드를 입력하게 한다.
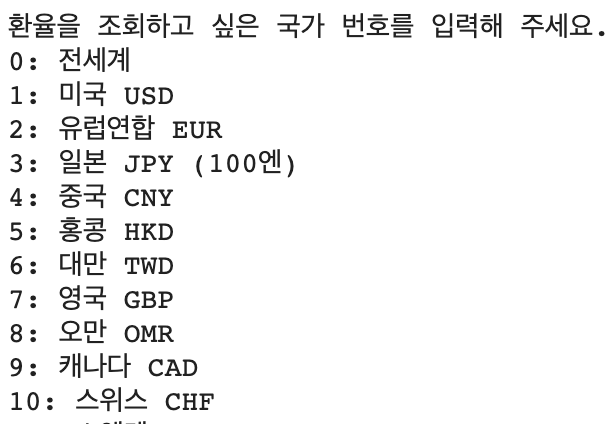
number = 0
# 국가 수 + 1(전세계) - 1의 수 중에서 하나를 입력받을 때까지 계속 입력 받는다.
while True:
try:
number = int(input())
if number >= country_length or number < 0:
print("허용되지 않는 번호를 입력하셨습니다.")
else:
break
except ValueError:
print("숫자가 아닌 문자를 입력할 수 없습니다.")
if number == 0: # 세계환율 선택시
tr = soup.select("tr")
inter_df = pd.concat(
[
pd.DataFrame(
[
[
tr[row].select("a")[0].get_text().strip(),
tr[row].select("td")[1].get_text(),
tr[row].select("td")[2].get_text(),
tr[row].select("td")[3].get_text(),
tr[row].select("td")[4].get_text(),
tr[row].select("td")[5].get_text(),
tr[row].select("td")[6].get_text(),
]
],
columns=[
"통화명",
"매매기준율",
"현찰_살 때",
"현찰_팔 때",
"송금_보낼 때",
"송금_받을 때",
"미화환산율",
],
index=[row - 2],
)
for row in range(2, len(tr))
]
)
inter_df.reset_index(inplace=True)
inter_df.drop('index', axis=1, inplace=True)
inter_df.to_json('world_fx.json')
print("world_fx.json 파일을 저장하였습니다.")
del inter_df
print("끝")
else:
print(f"{country_dict[number][0]}을/를 선택하셨습니다.")
page = 1
fx_df = pd.DataFrame()
while True:
fx_resp = requests.get(
BASE_URL + FX_URL + country_dict[number][1] + "&page=%d" % (page)
)
fx_soup = BeautifulSoup(fx_resp.text, "html.parser")
fx_tr = fx_soup.find_all("tr")
if len(fx_tr) < 3: # 헤더만 있다는 뜻이므로 멈춤.
break
fx_df = pd.concat(
[
fx_df,
pd.concat(
[
pd.DataFrame(
[
[
fx_tr[row].select("td")[0].get_text().strip(), # 날짜
fx_tr[row].select("td")[1].get_text(), # 매매기준율
"""
전일대비의 경우 up/down이 존재하는데,
원 소스에서 up 또는 down 클래스로 나뉘어져 있으므로
클래스에 따라 기호를 부가한다.
"""
fx_tr[row].select("td")[2].get_text()
if fx_tr[row]["class"][0] == "up"
else (
"-" + fx_tr[row].select("td")[2].get_text()
), # 전일대비
fx_tr[row].select("td")[3].get_text(), # 현찰 살 때
fx_tr[row].select("td")[4].get_text(), # 현찰 팔 때
fx_tr[row].select("td")[5].get_text(), # 송금 보낼 때
fx_tr[row].select("td")[6].get_text(), # 송금 받을 때
fx_tr[row]
.select("td")[8]
.get_text()
.strip(), # 외화수표 팔 때
]
],
columns=[
"날짜",
"매매기준율",
"전일대비",
"현찰_살 때",
"현찰_팔 때",
"송금_보낼 때",
"송금_받을 때",
"외화수표 팔 때",
],
index=[row - 2],
)
for row in range(2, len(fx_tr))
]
),
]
)
page += 1
first_date = f"{fx_df.iloc[-1, 0]}".split()[0] # 환율이 존재하는 첫 날
recent_date = f"{fx_df.iloc[0, 0]}".split()[0] # 환율이 존재하는 가장 최근 날
fx_df.reset_index(inplace=True)
print(f"{country_dict[number][0]}의 {first_date}부터 {recent_date}까지의 환율정보를 취득하였습니다.")
fx_df.to_json(f"{country_dict[number][1]}.json")
print(f"{country_dict[number][1]}.json 파일을 저장하였습니다.")
del fx_df
print("끝")
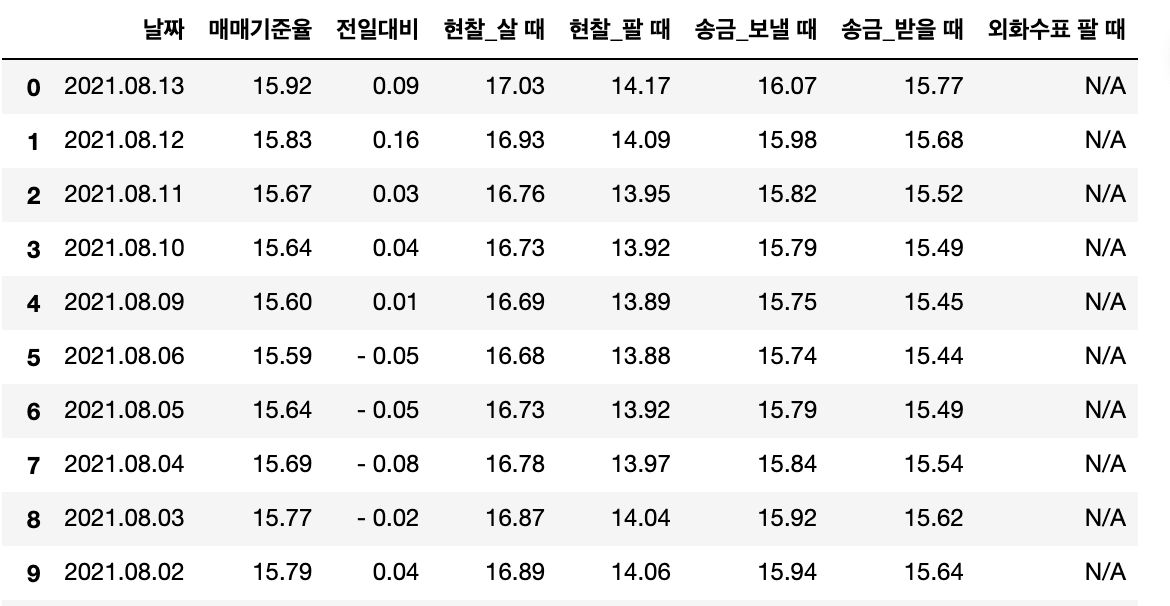
42 러시아를 선택해 보았다.
이 글을 쓰고 있는 날은 토요일이라, 전날인 금요일(2021.8.21)까지의 환율까지 가져오게 되었다.
가져온 환율은 json 파일로 저장하였다.
이미지4.크롤링한 러시아 환율을 json 저장한 뒤에 다시 불러와본 테이블
이미지5.실제 네이버 환율 페이지에 있는 러시아 환율
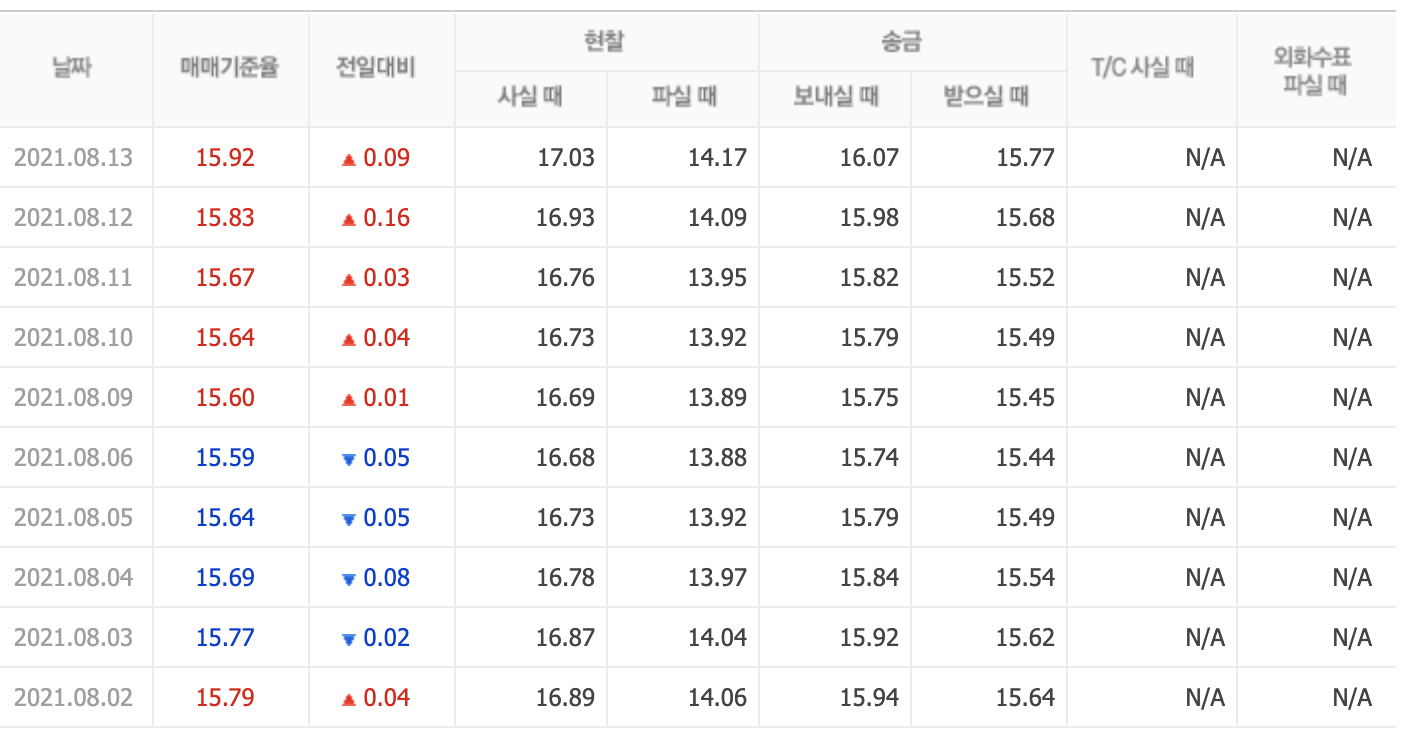
(T/C 사실 때는 항상 N/A만 나와서 크롤링에서 제외하였다.)
내용을 보면 수치가 전부 정확하게 일치한다.
세계환율 선택시에는 출력 내용이 살짝 다르다.
이미지6.세계 환율 선택시 파이썬 출력 내용

world_fx.json 파일로 저장하게 하였다.
이미지7.세계 환율 json 파일 출력내용
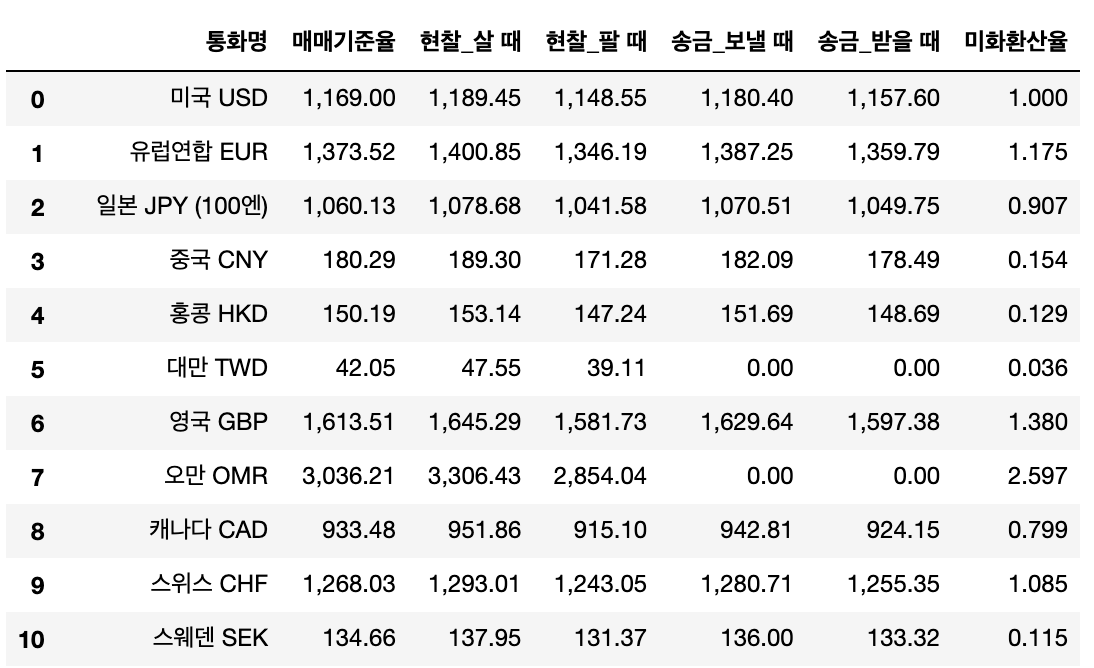
이미지8.세계 환율 네이버 환율 페이지 출력 내용
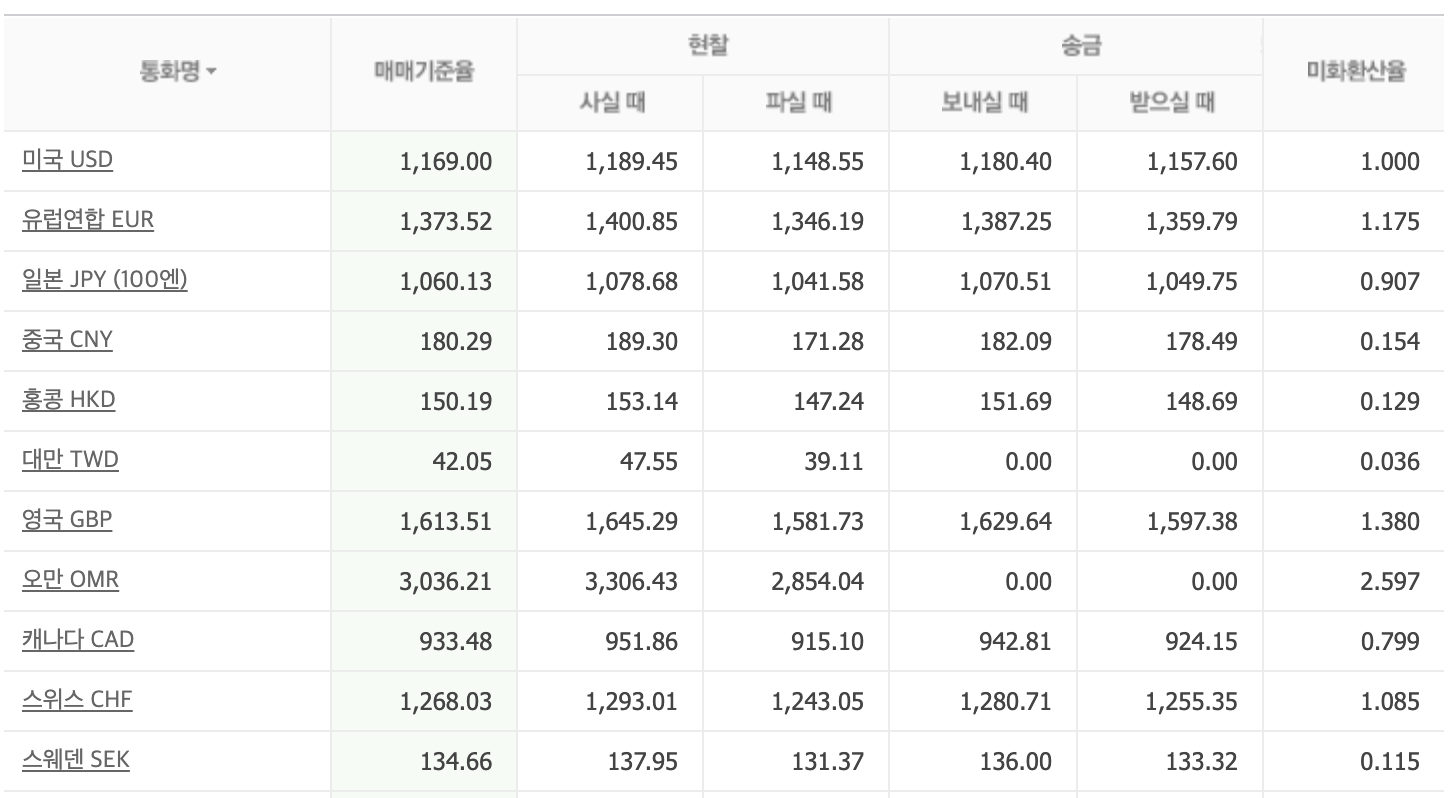
역시 수치가 동일하다.
(이하, 소스 이어붙인 전문)
def get_exchange():
"""
"""
# HTTP Response
resp = requests.get(BASE_URL + EX_URL)
soup = BeautifulSoup(resp.text, "html.parser")
# class td인 td를 모두 가져온다.
td = soup.find_all("td", class_="tit")
# 각 td에 a태그가 있으므로 a태그를 국가 리스트를 생성하여 집어넣는다.
country_list = [c.find("a") for c in td]
del td # td는 필요 없으므로 삭제(메모리 공간을 최대한 절약하기 위해 더 이상 사용되지 않는 obj를 삭제한다.
# 전세계 당일환율을 가져오는 옵션을 주기 위해 country_dict를 초기화하고 전세계 옵션을 0번으로 준비한다.
country_dict = {0: ("전세계", EX_URL)}
i = 1
for country in country_list:
country_dict[i] = (country.get_text().strip(), country["href"].split("=")[-1])
i += 1
country_length = len(country_dict) # 환율 개수
# 조회할 국가를 입력받는다.
print("환율을 조회하고 싶은 국가 번호를 입력해 주세요.")
[print(f"{key}: {country_dict[key][0]}") for key in country_dict.keys()]
number = 0
# 국가 수 + 1(전세계) - 1의 수 중에서 하나를 입력받을 때까지 계속 입력 받는다.
while True:
try:
number = int(input())
if number >= country_length or number < 0:
print("허용되지 않는 번호를 입력하셨습니다.")
else:
break
except ValueError:
print("숫자가 아닌 문자를 입력할 수 없습니다.")
if number == 0: # 세계환율 선택시
tr = soup.select("tr")
inter_df = pd.concat(
[
pd.DataFrame(
[
[
tr[row].select("a")[0].get_text().strip(),
tr[row].select("td")[1].get_text(),
tr[row].select("td")[2].get_text(),
tr[row].select("td")[3].get_text(),
tr[row].select("td")[4].get_text(),
tr[row].select("td")[5].get_text(),
tr[row].select("td")[6].get_text(),
]
],
columns=[
"통화명",
"매매기준율",
"현찰_살 때",
"현찰_팔 때",
"송금_보낼 때",
"송금_받을 때",
"미화환산율",
],
index=[row - 2],
)
for row in range(2, len(tr))
]
)
inter_df.reset_index(inplace=True)
inter_df.drop('index', axis=1, inplace=True)
inter_df.to_json('world_fx.json')
print("world_fx.json 파일을 저장하였습니다.")
del inter_df
print("끝")
else:
print(f"{country_dict[number][0]}을/를 선택하셨습니다.")
page = 1
fx_df = pd.DataFrame()
while True:
fx_resp = requests.get(
BASE_URL + FX_URL + country_dict[number][1] + "&page=%d" % (page)
)
fx_soup = BeautifulSoup(fx_resp.text, "html.parser")
fx_tr = fx_soup.find_all("tr")
if len(fx_tr) < 3: # 헤더만 있다는 뜻이므로 멈춤.
break
fx_df = pd.concat(
[
fx_df,
pd.concat(
[
pd.DataFrame(
[
[
fx_tr[row].select("td")[0].get_text().strip(), # 날짜
fx_tr[row].select("td")[1].get_text(), # 매매기준율
fx_tr[row].select("td")[2].get_text() if fx_tr[row]["class"][0] == "up" else ("-" + fx_tr[row].select("td")[2].get_text()), # 전일대비
fx_tr[row].select("td")[3].get_text(), # 현찰 살 때
fx_tr[row].select("td")[4].get_text(), # 현찰 팔 때
fx_tr[row].select("td")[5].get_text(), # 송금 보낼 때
fx_tr[row].select("td")[6].get_text(), # 송금 받을 때
fx_tr[row]
.select("td")[8]
.get_text()
.strip(), # 외화수표 팔 때
]
],
columns=[
"날짜",
"매매기준율",
"전일대비",
"현찰_살 때",
"현찰_팔 때",
"송금_보낼 때",
"송금_받을 때",
"외화수표 팔 때",
],
index=[row - 2],
)
for row in range(2, len(fx_tr))
]
),
]
)
page += 1
first_date = f"{fx_df.iloc[-1, 0]}".split()[0] # 환율이 존재하는 첫 날
recent_date = f"{fx_df.iloc[0, 0]}".split()[0] # 환율이 존재하는 가장 최근 날
fx_df.reset_index(inplace=True)
fx_df.drop('index', axis=1, inplace=True)
print(f"{country_dict[number][0]}의 {first_date}부터 {recent_date}까지의 환율정보를 취득하였습니다.")
fx_df.to_json(f"{country_dict[number][1]}.json")
print(f"{country_dict[number][1]}.json 파일을 저장하였습니다.")
del fx_df
print("끝")
이 글은 이만 마치며, 다음은 크롤링(2)환율관련 뉴스기사 가져오기를 써보도록 하겠다.
