그래프
- node와 edge로 구성된 집합
- node : 데이터를 표현하는 단위
- edge : 노드를 연결
- 그래프는 여러 알고리즘에 많이 사용되는 자료구조
- 유니온 파인드, 위상 정렬, 다익스트라, 최소 신장 트리 등등에 사용
그래프를 표현하는 3가지 방법
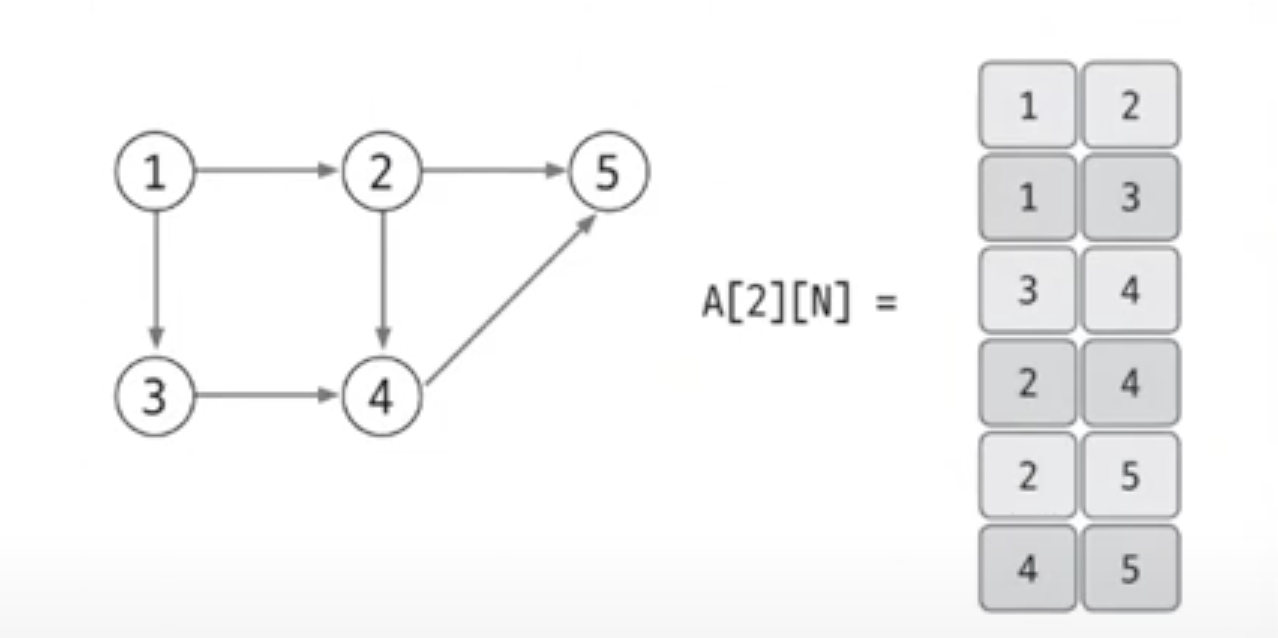
엣지 리스트
- 엣지를 중심으로 표현
- 출발 노드, 도착 노드, 가중치를 저장
- 가중치가 없는 그래프
- 가중치가 없는 그래프는 출발 노드와 도착 노드만 표현하으로 배열의 열은 2개면 충분
-
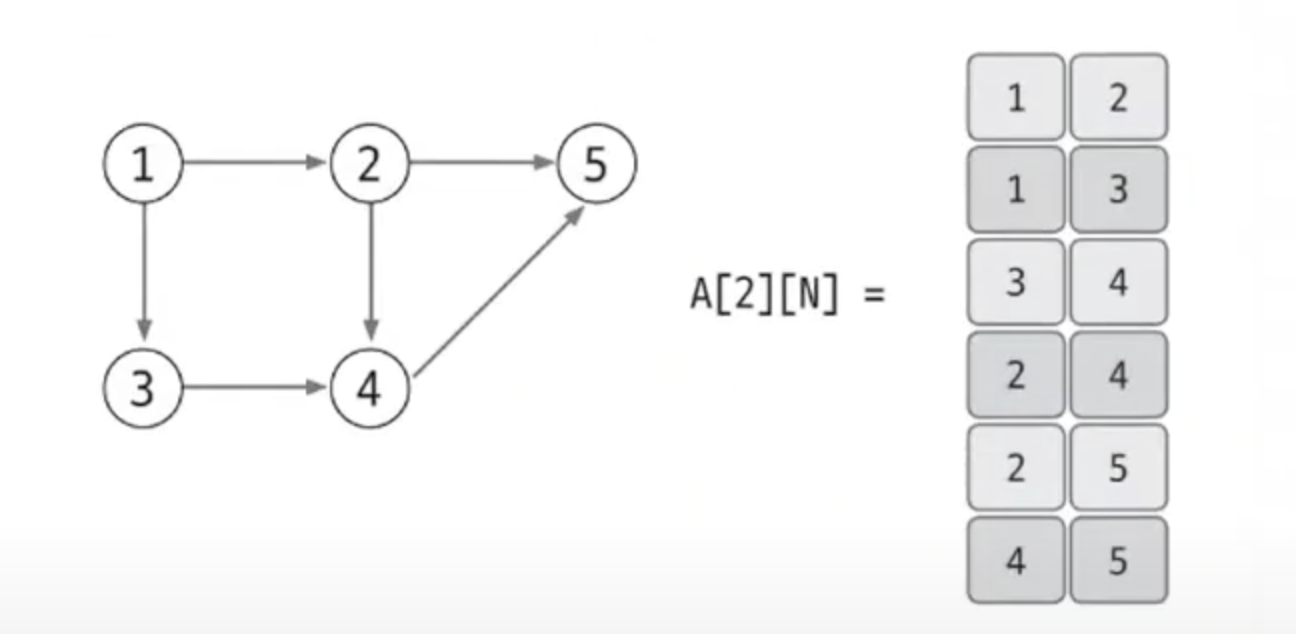
가중치가 있는 그래프
- 열을 하나 추가하여 가중치를 표현
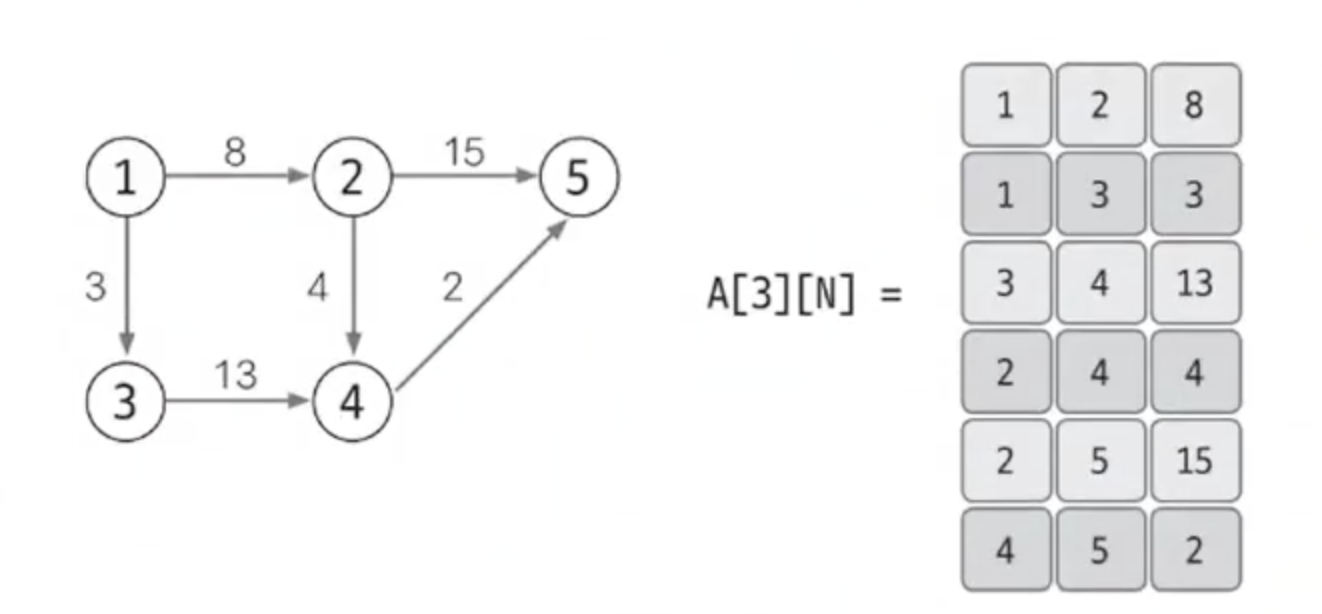
- 열을 하나 추가하여 가중치를 표현
-
엣지 리스트는 구현하기가 쉽지만 엣지를 중심으로 구현되어 있기 때문에 특정 노드와 관련있는 엣지를 구하는데 효율적이지 않다.
- ex) 2번 노드와 관련되어 있는 엣지를 찾으려면 모든 목록을 한번씩 확인해야한다.
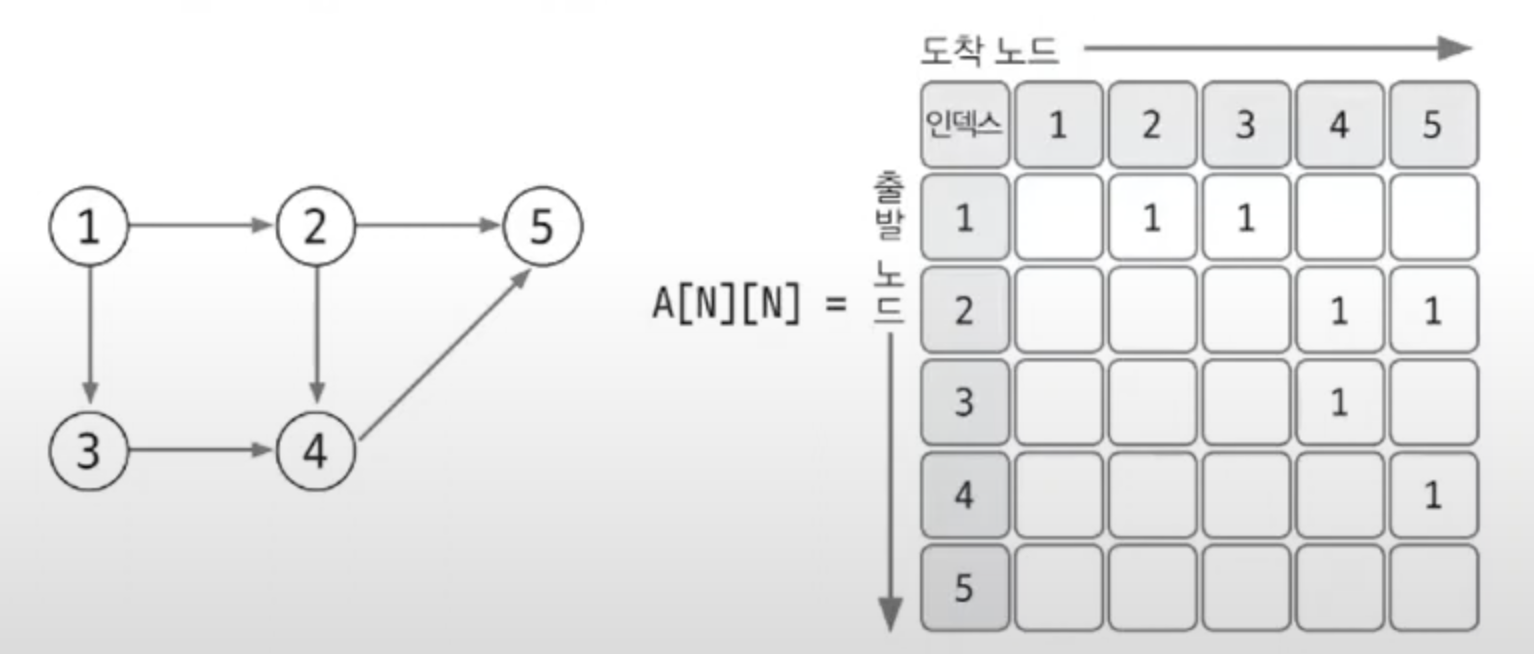
인접 행렬
- 2차원 배열을 자료구조로 이용하여 그래프를 표현
- 엣지 리스트와 다르게 노드 중심으로 그래프를 표현
- 노드의 수 X 노드의 수 행렬
- 가중치가 없는 그래프
- 가중치가 있는 그래프
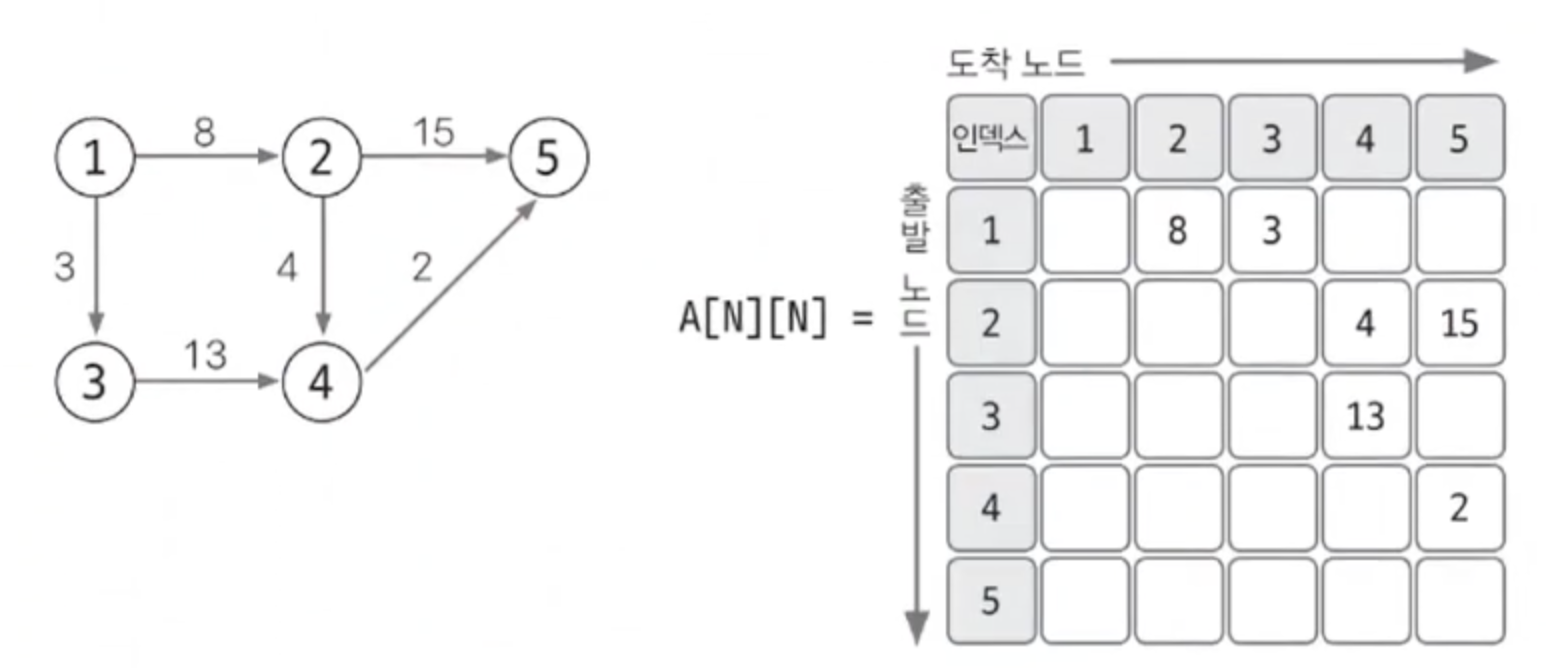
- 인접 행렬을 이용한 그래프 구현도 엣지리스트와 동일하게 구현이 쉽다. 하지만 노드와 관련되어 있는 엣지를 탐색하려면 노드의 개수만큼 접근해야하므로 노드 개수에 비해 엣지가 적을 때는 공간 효율성이 떨어진다.
- 예를 들어서, 노드가 1,000개인데 엣지는 10개밖에 없는 그래프의 경우를 생각해 보면, 이 경우 인접 행렬은 1,000 × 1,000 = 1,000,000개의 원소를 저장해야 하며, 대부분이 0으로 채워진다. 이렇게 엣지가 적은 경우, 인접 행렬에서는 불필요하게 많은 공간을 사용하게 된다. 따라서 인접 행렬은 노드 개수에 따라 사용 여부를 적절하게 판단하는 능력이 필요하다.
인접 리스트
-
인접 리스트는 ArrayList로 그래프를 표현. 노드 개수만큼 ArrayList를 선언
-
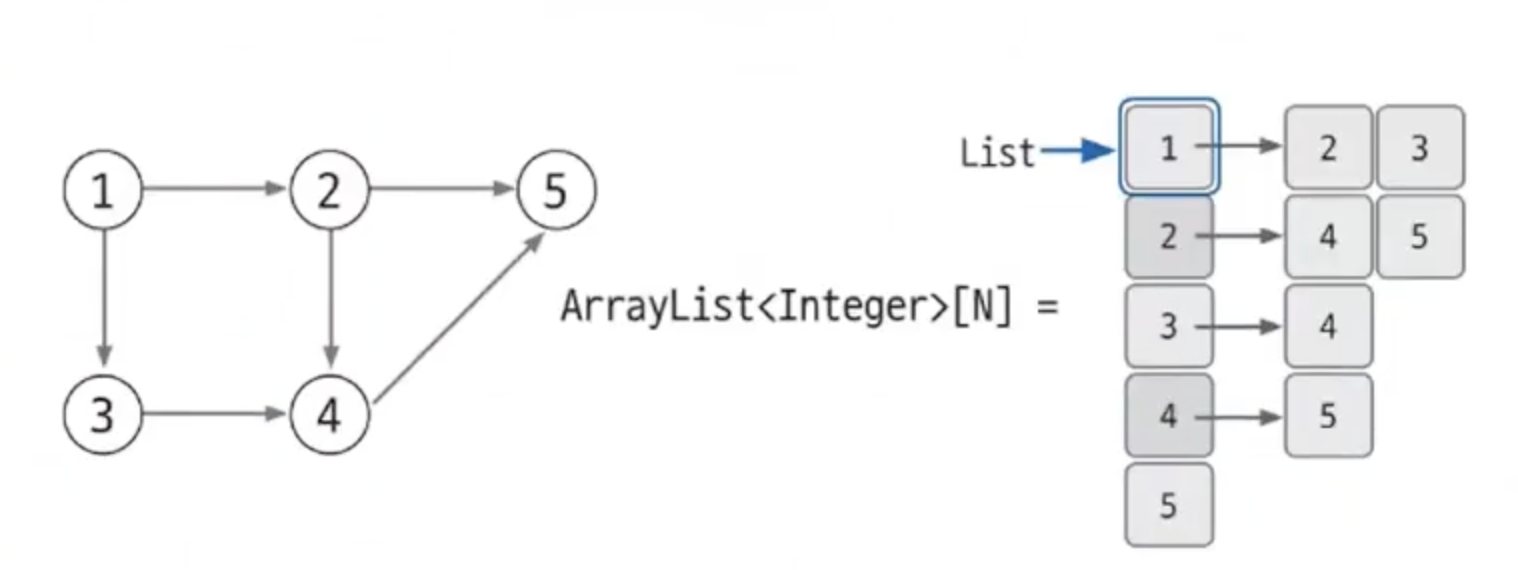
가중치가 없는 그래프
- 아래 그림의 경우 Integer형으로 표현하기 충분하므로
ArrayList<Integer>[5]로 선언한다.
- 아래 그림의 경우 Integer형으로 표현하기 충분하므로
-
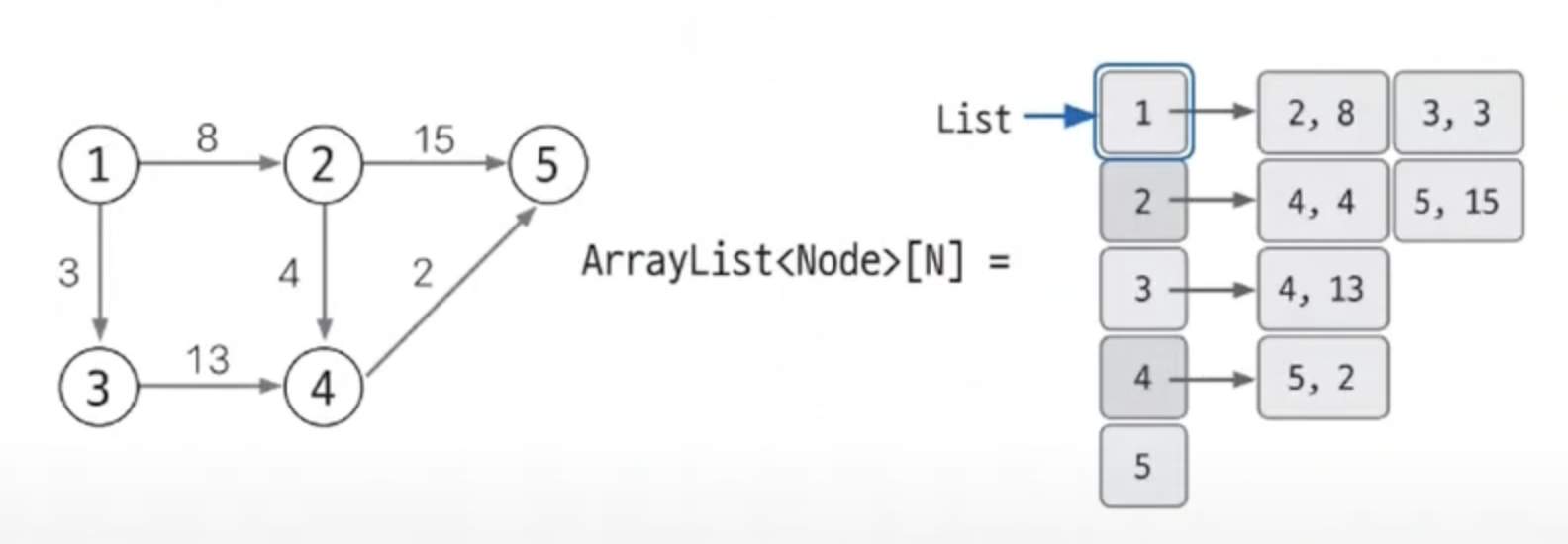
가중치가 있는 그래프
- 가중치가 없는 그래프와 다르게
ArrayList<Node>[5]와 같이 표현 - 여기서 Node는 사용자가 직접 만들어야 할 클래스이다.
- 아래와 같은 경우에는
class Node{ int (도착 노드); int (가중치); } - 가중치가 없는 그래프와 다르게
- 인접 리스트를 이용하여 그래프를 구현하는 것은 다른 방법들보다 복잡하지만, 노드와 연결되어 있는 엣지를 탐색하는 시간은 매우 뛰어나고, 공간 효율도 좋다.
- 따라서 대부분의 코딩테스트에서는 인접 리스트를 이용한 그래프 구현을 선호한다.
백준 1707
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Graph {
static boolean[] visited;
static boolean isEven;
static ArrayList<Integer>[] A;
static int[] check;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int K = input.nextInt();
for(int i=0; i<K; i++){
int V = input.nextInt();
int E = input.nextInt();
A = new ArrayList[V+1];
visited = new boolean[V+1];
isEven = true;
check = new int[V+1];
//노드 개수만큼 ArrayList생성
for(int j=1; j<=V; j++){
A[j] = new ArrayList<Integer>();
}
//엣지 데이터 저장
for(int j=0; j<E; j++){
int start = input.nextInt();
int end = input.nextInt();
A[start].add(end);
A[end].add(start);
}
//모든 노드에서 dfs실행
for(int j=1; j<=V; j++){
if(isEven){
dfs(j);
}else{
break;
}
}
if(isEven){
System.out.println("YES");
}else{
System.out.println("NO");
}
}
}
public static void dfs(int start){
visited[start] = true;
for(int i : A[start]){
if(!visited[i]){
//직전 노드와 다른 집합으로 분류
check[i] = (check[start] + 1) % 2;
dfs(i);
}else if(check[start]==check[i]){
isEven = false;
}
}
}
}
