개요

이전에 리뷰한 논문인 Image Inpainting for Irregular Holes Using Partial Convolutions 에서 사용한 모델과 손실함수를 구현하고 모델 학습까지 하는 코드를 포스팅 했다.
-
노트북 저장소 및 컴퓨터 사양으로 인한 시간 문제로 CelebA 데이터 만 사용하였다.
-
코드 양이 많아 아래 4개의 사용자 정의 모듈 (
.py)을 따로 작성했다.net.py: 모델 아키텍쳐 관련 모듈loss.py: 손실함수 관련 모듈util.py:MaskGernertor가 구현된 모듈train_utils.py: 모델 학습 관련 모듈
Code
환경
- python 3.8.16
- numpy 1.24.3
- pytorch 2.1.0
- torchvision 0.16.0
- torchinfo 1.8.0
- Pillow 10.1.0
- tqdm 4.66.1
구현
net.py
# net.py
# 모델 구현에 필요한 사용자 정의 class가 정의 된 모듈
# included:
# (class) PartialConv2d : User-defined Partial Convolutional layer
# (class) BasicPConv: PConv basic Unit (PConv layer - BN - Actvation)
# (class) EncoderLayer: Encoder PConv Unit
# (class) DecoderLayer: Decoder PConv Unit
# (class) PConvUNet: UNet architecture with only PConv
import torch
from torch import nn
class PartialConv2d(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride = 1, padding = 0, dilation = 1, groups = 1, bias = True):
super().__init__()
# Define Input Conv & Mask Conv
self.input_conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, padding, dilation, groups, bias)
self.mask_conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, padding, dilation, groups, False)
# Weight initialization
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode = "fan_in", nonlinearity = "relu")
nn.init.constant_(self.mask_conv.weight, 1.0)
# Mask is not updated
for param in self.mask_conv.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False
def forward(self, input, mask):
output = self.input_conv(input * mask)
if self.input_conv.bias is not None:
output_bias = self.input_conv.bias.reshape(1, -1, 1, 1).expand_as(output)
else:
output_bias = torch.zeros_like(output)
with torch.no_grad():
output_mask = self.mask_conv(mask)
# Mask -> 0: hole 1: non-hole
# 만약 conv 결과가 0 이라는 것은 해당 부분이 전부 hole 이라는 것임. -> sum(M)을 해줄 때 0으로 나눌 수 없으므로 mask_sum에서 해당 부분 보정을 해준다. (뒤에서 0으로 치환할 것임.)
mask_sum = torch.where(output_mask == 0, 1.0, output_mask)
# Calculate
output_pre = (output - output_bias) / mask_sum + output_bias
# 위에서 보정해준 값으로 1로 나눠졌기 때문에 Hole인 부분의 값이 0이 아닐 것임.
# 이 부분을 보정해서 hole인 부분을 0으로 채워준다.
output = torch.where(output_mask == 0, 0.0, output_pre)
new_mask = torch.where(output_mask != 0, 1.0, output_mask)
return output, new_mask
class BasicPconv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, activation, bn):
super().__init__()
assert activation in [None, "relu", "leaky", "sigmoid"]
assert stride < 3
assert kernel_size % 2 == 1
padding = kernel_size // 2 if stride == 2 else (kernel_size - 1) // 2
bias = False if bn else True
self.conv = PartialConv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, padding, bias = bias)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels) if bn else None
if activation is None:
self.activation = None
elif activation == "relu":
self.activation = nn.ReLU(inplace = True)
elif activation == "leaky":
self.activation = nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope = 0.2, inplace = True)
elif activation == "sigmoid":
self.activation = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x, mask):
x, mask = self.conv(x, mask)
if self.bn is not None:
x = self.bn(x)
if self.activation is not None:
x = self.activation(x)
return x, mask
class EncoderLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, activation = "relu", bn = True):
super().__init__()
self.pconv = BasicPconv(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, activation, bn)
def forward(self, x, mask):
x, mask = self.pconv(x, mask)
return x, mask
class DecoderLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size = 3, stride = 1, activation = "leaky", bn = True):
super().__init__()
self.up_img = nn.Upsample(scale_factor = 2, mode = "nearest")
self.up_mask = nn.Upsample(scale_factor = 2, mode = "nearest")
self.pconv = BasicPconv(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, activation, bn)
def forward(self, in_input, in_mask, enc_input, enc_mask):
up_input = self.up_img(in_input)
up_mask = self.up_mask(in_mask)
input = torch.concat([up_input, enc_input], axis = 1)
mask = torch.concat([up_mask, enc_mask], axis = 1)
input, mask = self.pconv(input, mask)
return input, mask
class PConvUNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_kernels = [7, 5, 5, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3], n_filters = [64, 128, 256, 512, 512, 512, 512, 512]):
super().__init__()
assert len(n_kernels) == len(n_filters)
self.freeze_enc_bn = False
# Encoder
down_stack = [EncoderLayer(3, n_filters[0], n_kernels[0], stride = 2, bn = False)]
in_channels = n_filters[0]
for kernel_size, out_channels in zip(n_kernels[1:], n_filters[1:]):
down_stack.append(EncoderLayer(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride = 2, bn = True))
in_channels = out_channels
self.encoder = nn.ModuleList(down_stack)
# Decoder
up_stack = [DecoderLayer(n_filters[0] + 3, 3, bn = False, activation = "sigmoid")]
out_channels = n_filters[0]
for in_channels in n_filters[1:]:
up_stack.append(DecoderLayer(in_channels + out_channels, out_channels))
out_channels = in_channels
self.decoder = nn.ModuleList(up_stack[::-1])
def forward(self, input, mask):
enc_input_list = [input]; enc_mask_list = [mask]
for down_layer in self.encoder:
input, mask = down_layer(input, mask)
enc_input_list.append(input)
enc_mask_list.append(mask)
enc_input_list = enc_input_list[::-1][1:]
enc_mask_list = enc_mask_list[::-1][1:]
assert len(self.decoder) == len(enc_input_list) == len(enc_mask_list)
for up_layer, enc_input, enc_mask in zip(self.decoder, enc_input_list, enc_mask_list):
input, mask = up_layer(input, mask, enc_input, enc_mask)
return input, mask
def train(self, mode = True):
super().train(mode)
if self.freeze_enc_bn:
for name, module in self.named_modules():
if isinstance(module, nn.BatchNorm2d) and "encoder" in name:
module.eval()- 모델은
PConvUNet이다. - class
PartialConv2d에서 mask 부분의 Conv layer는 bias가 없고 (bias = False), weight를 1.0으로 고정한 것을 볼 수 있다. (mask conv weight는 업데이트 하지 않는다.) - 이후 fine tuning을 할 때 encoder 쪽의 BN (BatchNormalization) layer의 weights를 고정하기 위해
PConvUNet을 구현할 때train함수에서 해당 부분을 따로 작성하였음.
util.py
# util.py
# 유틸리티 모듈
# included:
# (class) MaskGenerator : 데이터 준비 과정에서 이미지에 마스킹을 하기 위한 마스크 생성기
import os
import numpy as np
from random import randint, seed
import cv2
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw
class MaskGenerator():
def __init__(self, height, width, channels = 3, random_seed = None, filepath = None):
self.height = height
self.width = width
self.channels = channels
self.filepath = filepath
# If filepath supplied, load the list of masks within the directory
self.mask_files = []
if self.filepath:
filenames = [f for f in os.listdir(self.filepath)]
self.mask_files = [f for f in filenames if os.path.splitext(f)[1].lower() in [".jpeg", ".png", ".jpg"]]
print(f">> Found {len(self.mask_files)} masks in {self.filepath}")
# Seed for reproducibility
if random_seed:
np.random.seed(random_seed)
seed(random_seed)
def _generate_mask(self):
# Prepare mask
mask_array = np.full((self.height, self.width, self.channels), 0, np.uint8)
mask = Image.fromarray(mask_array)
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(mask)
# Set size scale
size = int((self.width + self.height) * 0.03)
if self.width < 64 or self.height < 64:
raise Exception("Width and Height of mask must be at lest 64!")
# Draw random lines
for _ in range(randint(1, 20)):
x1, x2 = randint(1, self.width), randint(1, self.width)
y1, y2 = randint(1, self.height), randint(1, self.height)
thickness = randint(3, size)
draw.line([(x1, y1) ,(x2, y2)], fill = "white", width = thickness)
# Draw random circles
for _ in range(randint(1, 20)):
x, y = randint(1, self.width), randint(1, self.height)
radius = randint(3, size)
draw.ellipse([(x - radius, y - radius), (x + radius, y + radius)], fill = "white")
# Draw random arc (a portion of a circle outline)
for _ in range(randint(1, 20)):
x1, y1 = randint(1, self.width), randint(1, self.height)
x2, y2 = randint(1, self.width), randint(1, self.height)
x1, x2 = (x2, x1) if x1 > x2 else (x1, x2)
y1, y2 = (y2, y1) if y1 > y2 else (y1, y2)
start_angle = randint(3, 180)
end_angle = start_angle + randint(3, 180)
thickness = randint(3, size)
draw.arc([(x1, y1), (x2, y2)], start = start_angle, end = end_angle, width = thickness)
return 255 - np.array(mask)
def _load_mask(self, rotation=True, dilation=True, cropping=True):
"""Loads a mask from disk, and optionally augments it"""
# Read image
mask = cv2.imread(os.path.join(self.filepath, np.random.choice(self.mask_files, 1, replace=False)[0]))
# Random rotation
if rotation:
rand = randint(-180, 180)
M = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D((mask.shape[1]/2, mask.shape[0]/2), rand, 1.5)
mask = cv2.warpAffine(mask, M, (mask.shape[1], mask.shape[0]))
# Random dilation
if dilation:
rand = randint(5, 47)
kernel = np.ones((rand, rand), np.uint8)
mask = cv2.erode(mask, kernel, iterations=1)
# Random cropping
if cropping:
x = randint(0, mask.shape[1] - self.width)
y = randint(0, mask.shape[0] - self.height)
mask = mask[y:y+self.height, x:x+self.width]
return (mask > 1).astype(np.uint8)
def sample(self, random_seed=None):
"""Retrieve a random mask"""
if random_seed:
seed(random_seed)
if self.filepath and len(self.mask_files) > 0:
return self._load_mask()
else:
return self._generate_mask()마스크를 생성하는 class인 MaskGenerator 가 포함된 모듈이다. 마스크 데이터가 존재한다면 그 데이터를 증강시키고 없다면 랜덤하게 생성한다.
loss.py
# loss.py
# loss function 모듈
# included:
# (class) VGG16FeatureExtractor: Loss function 계산을 위해 사용되는 Feature Extractor이다.
# ImageNet pretrained VGG 모델에서 일부 layer에 대해서만
# 통과시켜 feature를 얻기 위함.
#
# (class) InpaintingLoss: 논문에서 정의한 모델 학습을 위한 Loss 이다.
import torch
from torch import nn
from torchvision import models
class VGG16FeatureExtractor(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
vgg16 = models.vgg16(weights = models.VGG16_Weights.IMAGENET1K_V1)
vgg16_encoders = []
start_idx = 0
for idx, layer in enumerate(vgg16.features):
if isinstance(layer, nn.MaxPool2d):
encoder = vgg16.features[start_idx : idx + 1]
vgg16_encoders.append(encoder)
start_idx = idx + 1
if len(vgg16_encoders) == 3:
break
self.enc_1 = nn.Sequential(*vgg16_encoders[0])
self.enc_2 = nn.Sequential(*vgg16_encoders[1])
self.enc_3 = nn.Sequential(*vgg16_encoders[2])
for enc in [self.enc_1, self.enc_2, self.enc_3]:
for param in enc.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False
def forward(self, x):
x1 = self.enc_1(x)
x2 = self.enc_2(x1)
x3 = self.enc_3(x2)
return x1, x2, x3
class InpaintingLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vgg_extractor):
super().__init__()
self.l1 = nn.L1Loss()
self.vgg_extractor = vgg_extractor
def forward(self, input, mask, output, gt):
comp = mask * input + (1 - mask) * output
vgg_comp = self.vgg_extractor(comp)
vgg_output = self.vgg_extractor(output)
vgg_gt = self.vgg_extractor(gt)
hole_loss = self.loss_hole(mask, output, gt)
valid_loss = self.loss_valid(mask, output, gt)
perceptual_loss = self.loss_perceptual(vgg_output, vgg_comp, vgg_gt)
style_out_loss = self.loss_style(vgg_output, vgg_gt)
style_comp_loss = self.loss_style(vgg_comp, vgg_gt)
tv_loss = self.loss_tv(comp)
return valid_loss + 6*hole_loss + 0.05*perceptual_loss + 120*(style_out_loss + style_comp_loss) + 0.1*tv_loss
def loss_hole(self, mask, output, gt):
return self.l1((1 - mask) * output, (1 - mask) * gt)
def loss_valid(self, mask, output, gt):
return self.l1(mask * output, mask * gt)
def loss_perceptual(self, vgg_output, vgg_comp, vgg_gt):
perceptual_loss = 0
for i in range(3):
perceptual_loss += self.l1(vgg_output[i], vgg_gt[i])
perceptual_loss += self.l1(vgg_comp[i], vgg_gt[i])
return perceptual_loss
def loss_style(self, vgg_output_or_comp, vgg_gt):
style_loss = 0
for i in range(3):
style_loss += self.l1(self.gram_matrix(vgg_output_or_comp[i]), self.gram_matrix(vgg_gt[i]))
return style_loss
def loss_tv(self, comp):
loss = torch.mean(torch.abs(comp[:, :, :, :-1] - comp[:, :, :, 1:])) + \
torch.mean(torch.abs(comp[:, :, :-1, :] - comp[:, :, 1:, :]))
return loss
def gram_matrix(self, feat):
b, c, h, w = feat.shape
feat = feat.reshape(b, c, h * w)
feat_T = feat.transpose(1, 2)
gram = torch.bmm(feat, feat_T) / (c * h * w)
return gram학습 시 필요한 loss를 정의한 모듈이다.
Reference Code를 많이 참고하여 나만의 스타일로 재작성 하였다.
train_utils.py
# train_utils.py
# 모델 학습에 관련한 모듈
# included:
# (class) EarlyStopping: 일정 epoch이 지나고도 개선이 되지 않으면 모델 학습을 일찍 종료하기 위한 모듈
# (func) dice_coef: metric으로 사용할 다이스계수 함수
# (func) draw_history: 모델 학습 상황을 모니터링 하기 위한 함수
# (func) loss_epoch: 모델 학습 함수
# (func) vis: 모델 학습 상황을 시각화 하여 모니터링 하기 위한 함수
import numpy as np
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from tqdm import tqdm
class EarlyStopping:
def __init__(self, patience = 5, thresh = 0.0, mode = "min", verbose = True, print_flush = True):
self.early_stop = False
self.patience = patience
self.verbose = verbose
self.mode = mode
self.thresh = thresh
self.print_flush = print_flush
self.counter = 0
self.best_score = np.Inf if mode == "min" else 0 if mode == "max" else AssertionError
def step(self, score):
if self.mode == "min":
if score < (self.best_score - self.thresh):
self.counter = 0
self.best_score = score
else:
self.counter += 1
if self.verbose:
print(f"[EarlyStopping] (Patience) {self.counter}/{self.patience}. "\
f"Best score: {self.best_score:.5f}"\
f", Current: {score:.5f}", flush = self.print_flush)
elif self.mode == "max":
if score > (self.best_score + self.thresh):
self.counter = 0
self.best_score = score
if self.verbose:
print(f"[EarlyStopping] (Patience) {self.counter}/{self.patience}. "\
f"Best score: {self.best_score:.5f}"\
f", Current: {score:.5f}", flush = self.print_flush)
if self.counter >= self.patience:
if self.verbose:
print(f"[EarlyStop Triggered] Best Score: {self.best_score:.5f}", flush = self.print_flush)
#Early stop
self.early_stop = True
def dice_coef(y_true, y_pred):
y_true_f = torch.flatten(y_true)
y_pred_f = torch.flatten(y_pred)
intersection = torch.sum(y_true_f * y_pred_f)
return (2. * intersection) / (torch.sum(y_true_f + y_pred_f))
def draw_history(train_loss_list, val_loss_list, title):
assert len(train_loss_list) == len(val_loss_list)
if len(train_loss_list) < 2:
return None
train_loss_x_list = np.arange(0, len(train_loss_list), 1)
val_loss_x_list = np.arange(0, len(val_loss_list), 1)
plt.figure(figsize = (20, 10))
plt.plot(train_loss_x_list, train_loss_list, label = f"train {title}")
plt.plot(val_loss_x_list, val_loss_list, label = f"val {title}")
plt.title(title)
plt.show()
def loss_epoch(device, model, DL, criterion, metric, optimizer = None):
N = len(DL.dataset) # the number of data
r_loss = 0; r_score = 0
for x_input_batch, x_mask_batch, y_batch in tqdm(DL, leave=False):
x_input_batch = x_input_batch.to(device)
x_mask_batch = x_mask_batch.to(device)
y_batch = y_batch.to(device)
# inference
y_pred_batch, y_mask_pred_batch = model(x_input_batch, x_mask_batch)
# Loss
loss = criterion(x_input_batch, x_mask_batch, y_pred_batch, y_batch)
# update
if optimizer is not None:
optimizer.zero_grad() # gradient 누적을 막기 위한 초기화
loss.backward() # backpropagation
optimizer.step() # weight update
# loss accumulation
loss_b = loss.item() * x_input_batch.shape[0]
r_loss += loss_b # running loss
# metric
score_b = metric(y_batch, y_pred_batch).item() * x_input_batch.shape[0]
r_score += score_b
loss_e = r_loss / N
score_e = r_score / N
return loss_e, score_e
def vis(device, model, masked_img, mask, img):
masked_img = masked_img.to(device)
mask = mask.to(device)
prediction, _ = model(masked_img, mask)
prediction = prediction.detach()
masked_img = masked_img[0].to("cpu")
prediction = prediction[0].to("cpu")
img = img[0].to("cpu")
masked_img = torch.permute(masked_img, [1, 2, 0])
prediction = torch.permute(prediction, [1, 2, 0])
img = torch.permute(img, [1, 2, 0])
display_list = [masked_img, img, prediction]
title = ["Input image", "Original image","Predicted image"]
length = len(display_list)
plt.figure(figsize = (15, 15))
for i in range(length):
plt.subplot(1, length, i + 1)
plt.title(title[i])
plt.imshow(display_list[i])
plt.axis("off")
plt.show()모델 학습에 필요하거나 시각화를 하는데 필요한 함수들을 포함하는 모듈이다.
1. Import Dependecies
import os
import itertools
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from tqdm import tqdm
import time
from IPython import display
import torch
from torch import nn, optim
from torch.utils.data import random_split, Dataset, DataLoader
from torchinfo import summary
import torchvision
from torchvision import models
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
from mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1 import ImageGrid
from util import MaskGenerator
from net import *
from loss import VGG16FeatureExtractor, InpaintingLoss
from train_utils import *
PRINT_FLUSH = True
DEVICE = torch.device("mps")
DEVICE2. Set hyperparameters
SEED = 88
BATCH_SIZE = 3 # GPU 메모리 부족으로 3으로 지정 (논문에서는 BATCH_SIZE = 6)
TEST_RATIO = 0.20
EPOCHS = 30
LR = 0.0002
FINE_TUNING_LR = 0.000053. Prepare DataLoader
class CustomDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, data_directory, mask_generator, transform = None, resize_size = None):
self.imgs_path_list = [os.path.join(data_directory, basename) for basename in os.listdir(data_directory)]
self.transform = transform
self.mask_generator = mask_generator
self.resize_size = resize_size
def __len__(self):
return len(self.imgs_path_list)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
img_path = self.imgs_path_list[idx]
masked_img, mask, img = self.__load_masked_data(img_path)
mask_transformer = transforms.ToTensor()
mask = mask_transformer(mask)
if self.transform is not None:
masked_img = self.transform(masked_img)
img = self.transform(img)
return masked_img, mask, img
def __load_masked_data(self, img_path):
img = Image.open(img_path)
if self.resize_size is not None:
img = img.resize((self.resize_size, self.resize_size))
img = np.array(img)
mask = self.mask_generator.sample()
masked_img = img.copy()
masked_img[mask == 0] = 255
return masked_img, mask, img# Mask Generator
mask_generator = MaskGenerator(height = 512, width = 512, random_seed = SEED)
# Transform
transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
])
# Dataset
dataset = CustomDataset(data_directory = "./data/celeba_hq_1024",
mask_generator = mask_generator,
transform = transform,
resize_size = 512)
# Data split
generator = torch.Generator()
generator.manual_seed(SEED)
dataset_size = len(dataset)
train_size = int(dataset_size * (1 - TEST_RATIO))
val_size = int(train_size * TEST_RATIO)
test_size = int(dataset_size * TEST_RATIO)
train_size = train_size - val_size
train_dataset, val_dataset, test_dataset = random_split(dataset, [train_size, val_size, test_size], generator)
# Confirm
print(f"Training Data Size : {len(train_dataset)}") # Training Data Size : 19200
print(f"Validation Data Size : {len(val_dataset)}") # Validation Data Size : 4800
print(f"Testing Data Size : {len(test_dataset)}") # Testing Data Size : 6000
# DataLoader
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size = BATCH_SIZE, shuffle = True)
val_loader = DataLoader(val_dataset, batch_size = BATCH_SIZE, shuffle = True)
test_loader = DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size = BATCH_SIZE, shuffle = False)다운 받은 이미지를 목적에 맞게 재가공 (마스크 생성 및 적용) 하기 위해 CustomDataset을 정의했고 이후 재구성한 dataset으로 dataloader를 구성했다.
sample_masked_imgs, sample_masks, sample_imgs = next(iter(train_loader))
sample_imgs_batch = [None] * (len(sample_masked_imgs) + len(sample_masks) + len(sample_imgs))
sample_imgs_batch[::3] = sample_masked_imgs.permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
sample_imgs_batch[1::3] = sample_masks.permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
sample_imgs_batch[2::3] = sample_imgs.permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
fig = plt.figure(figsize = (16., 8.))
grid = ImageGrid(fig, 111, nrows_ncols = (3, 6), axes_pad = 0.3)
for ax, img in zip(grid, sample_imgs_batch):
ax.imshow(img)
plt.show()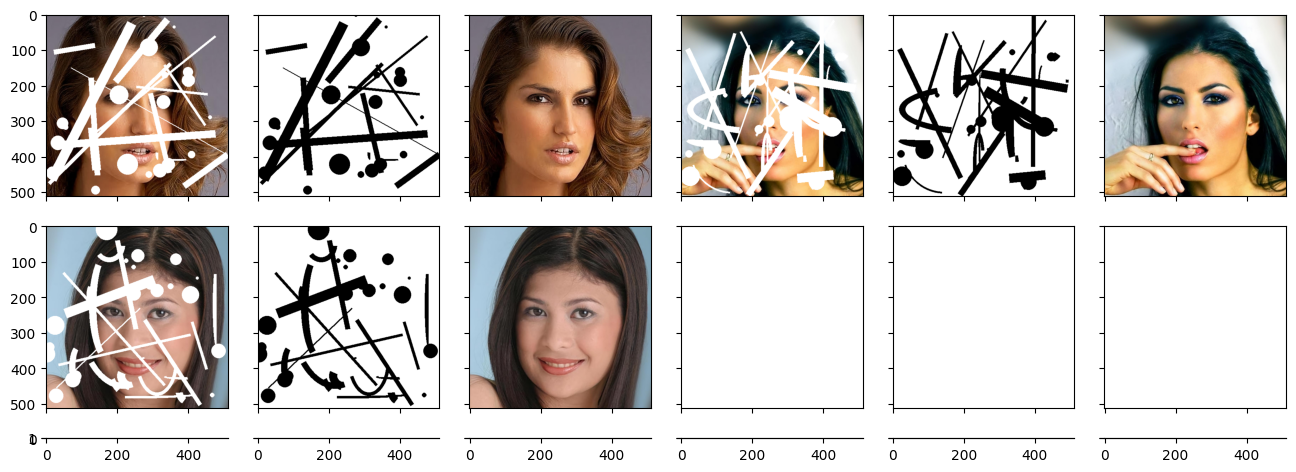
train_loader에서 임의로 하나의 배치를 뽑아 시각화 해보니 의도한대로 데이터 셋이 구성된 것을 확인할 수 있었다.
4. Model
model = PConvUNet(n_kernels = [7, 5, 5, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3],
n_filters = [64, 128, 256, 512, 512, 512, 512, 512])net.py 모듈에서 정의한 PConvUNet로 모델을 구성하였다.
summary(model, input_size = [(2, 3, 512, 512), (2, 3, 512, 512)])==========================================================================================
Layer (type:depth-idx) Output Shape Param #
==========================================================================================
PConvUNet [2, 3, 512, 512] --
├─ModuleList: 1-1 -- --
│ └─EncoderLayer: 2-1 [2, 64, 256, 256] --
│ │ └─BasicPconv: 3-1 [2, 64, 256, 256] 18,880
│ └─EncoderLayer: 2-2 [2, 128, 128, 128] --
│ │ └─BasicPconv: 3-2 [2, 128, 128, 128] 409,856
│ └─EncoderLayer: 2-3 [2, 256, 64, 64] --
│ │ └─BasicPconv: 3-3 [2, 256, 64, 64] 1,638,912
│ └─EncoderLayer: 2-4 [2, 512, 32, 32] --
│ │ └─BasicPconv: 3-4 [2, 512, 32, 32] 2,360,320
│ └─EncoderLayer: 2-5 [2, 512, 16, 16] --
│ │ └─BasicPconv: 3-5 [2, 512, 16, 16] 4,719,616
│ └─EncoderLayer: 2-6 [2, 512, 8, 8] --
│ │ └─BasicPconv: 3-6 [2, 512, 8, 8] 4,719,616
│ └─EncoderLayer: 2-7 [2, 512, 4, 4] --
│ │ └─BasicPconv: 3-7 [2, 512, 4, 4] 4,719,616
│ └─EncoderLayer: 2-8 [2, 512, 2, 2] --
│ │ └─BasicPconv: 3-8 [2, 512, 2, 2] 4,719,616
├─ModuleList: 1-2 -- --
│ └─DecoderLayer: 2-9 [2, 512, 4, 4] --
│ │ └─Upsample: 3-9 [2, 512, 4, 4] --
│ │ └─Upsample: 3-10 [2, 512, 4, 4] --
│ │ └─BasicPconv: 3-11 [2, 512, 4, 4] 9,438,208
│ └─DecoderLayer: 2-10 [2, 512, 8, 8] --
│ │ └─Upsample: 3-12 [2, 512, 8, 8] --
│ │ └─Upsample: 3-13 [2, 512, 8, 8] --
│ │ └─BasicPconv: 3-14 [2, 512, 8, 8] 9,438,208
│ └─DecoderLayer: 2-11 [2, 512, 16, 16] --
│ │ └─Upsample: 3-15 [2, 512, 16, 16] --
│ │ └─Upsample: 3-16 [2, 512, 16, 16] --
│ │ └─BasicPconv: 3-17 [2, 512, 16, 16] 9,438,208
│ └─DecoderLayer: 2-12 [2, 512, 32, 32] --
│ │ └─Upsample: 3-18 [2, 512, 32, 32] --
│ │ └─Upsample: 3-19 [2, 512, 32, 32] --
│ │ └─BasicPconv: 3-20 [2, 512, 32, 32] 9,438,208
│ └─DecoderLayer: 2-13 [2, 256, 64, 64] --
│ │ └─Upsample: 3-21 [2, 512, 64, 64] --
│ │ └─Upsample: 3-22 [2, 512, 64, 64] --
│ │ └─BasicPconv: 3-23 [2, 256, 64, 64] 3,539,456
│ └─DecoderLayer: 2-14 [2, 128, 128, 128] --
│ │ └─Upsample: 3-24 [2, 256, 128, 128] --
│ │ └─Upsample: 3-25 [2, 256, 128, 128] --
│ │ └─BasicPconv: 3-26 [2, 128, 128, 128] 884,992
│ └─DecoderLayer: 2-15 [2, 64, 256, 256] --
│ │ └─Upsample: 3-27 [2, 128, 256, 256] --
│ │ └─Upsample: 3-28 [2, 128, 256, 256] --
│ │ └─BasicPconv: 3-29 [2, 64, 256, 256] 221,312
│ └─DecoderLayer: 2-16 [2, 3, 512, 512] --
│ │ └─Upsample: 3-30 [2, 64, 512, 512] --
│ │ └─Upsample: 3-31 [2, 64, 512, 512] --
│ │ └─BasicPconv: 3-32 [2, 3, 512, 512] 3,621
==========================================================================================
Total params: 65,708,645
Trainable params: 32,859,796
Non-trainable params: 32,848,849
Total mult-adds (G): 151.90
==========================================================================================
Input size (MB): 12.58
Forward/backward pass size (MB): 729.65
Params size (MB): 262.83
Estimated Total Size (MB): 1005.06
==========================================================================================약 6570만 개의 파라미터를 갖는 모델이다. (이전에 포스팅 했던 약 776만 개의 파라미터를 갖는 튜토리얼 Autoencoder 모델에 비하면 큰 모델인 것을 알 수 있다.) 그러나 실질적으로 학습할 파라미터는 약 3280만 개이다. 학습에 참여하지 않는 Mask Conv layer 때문이다. (Non-trainable params : 32,848,849 Mask Conv layer는 bias가 없고, weight는 전부 1로 고정되어야 하기 때문에 Non trainable params에 속한다.)
5. Loss function & Metric
vgg_extractor = VGG16FeatureExtractor()
vgg_extractor.to(DEVICE)
criterion = InpaintingLoss(vgg_extractor)
metric = dice_coefloss.py 모듈에서 정의한 VGGFeatureExtractor와 InpaintingLoss를 불러온다.
VGGFeatureExtractor는 InpaintingLoss에서 Style loss, Perceptual loss를 계산하는데 필요하다.
metric은 간단하게 다이스 계수를 사용하였다.
6. Train
# Load model
model = PConvUNet()
model.to(DEVICE)
# Load object for training
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr = LR)
lr_scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.ReduceLROnPlateau(optimizer, mode = "min", factor = 0.1, patience = 5, cooldown = 2)
early_stopping = EarlyStopping(patience = 10, thresh = 0, mode = "min", print_flush = PRINT_FLUSH)
loss_history = {"train": [], "val" : []}
score_history = {"train": [], "val" : []}
best_loss = np.Inf; train_loss = np.Inf; val_loss = np.Inf
best_score = 0; train_score = 0; val_score = 0
# example image for visualization
example_masked_image, example_mask, example_image = next(iter(val_loader))
# Model Training
for epoch in range(EPOCHS):
display.clear_output(wait = True)
vis(DEVICE, model, example_masked_image, example_mask, example_image)
epochs_start = time.time()
current_lr = optimizer.param_groups[0]["lr"]
print(f"Epoch: {epoch + 1}, current_LR = {current_lr}", flush = PRINT_FLUSH)
print(f"Best val loss: {round(best_loss, 5)}, Best val score: {round(best_score, 5)}")
print(f"train loss: {round(train_loss, 5)}, val loss: {round(val_loss, 5)}", flush = PRINT_FLUSH)
print(f"train score: {round(train_score, 5)}, val score: {round(val_score, 5)} \n", flush = PRINT_FLUSH)
draw_history(loss_history["train"], loss_history["val"], title = "loss")
draw_history(score_history["train"], score_history["val"], title = "disc_coef")
# Train
model.train()
train_loss, train_score = loss_epoch(DEVICE, model, train_loader, criterion, metric, optimizer)
loss_history["train"].append(train_loss)
score_history["train"].append(train_score)
# Validation
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
val_loss, val_score = loss_epoch(DEVICE, model, val_loader, criterion, metric)
loss_history["val"].append(val_loss)
score_history["val"].append(val_score)
if val_loss < best_loss:
best_loss = val_loss
best_score = val_score
torch.save({
"model" : model,
"epoch" : epoch,
"optimizer" : optimizer,
"scheduler" : lr_scheduler,
}, f"./runs/pytorch_checkpoint/best.pt")
print("-" * 20, flush = PRINT_FLUSH)
lr_scheduler.step(val_loss)
early_stopping.step(val_loss)
if early_stopping.early_stop:
break
Epoch: 15, current_LR = 0.0002
Best val loss: 0.30284, Best val score: 0.61284
train loss: 0.31639, val loss: 0.30284
train score: 0.61463, val score: 0.61284 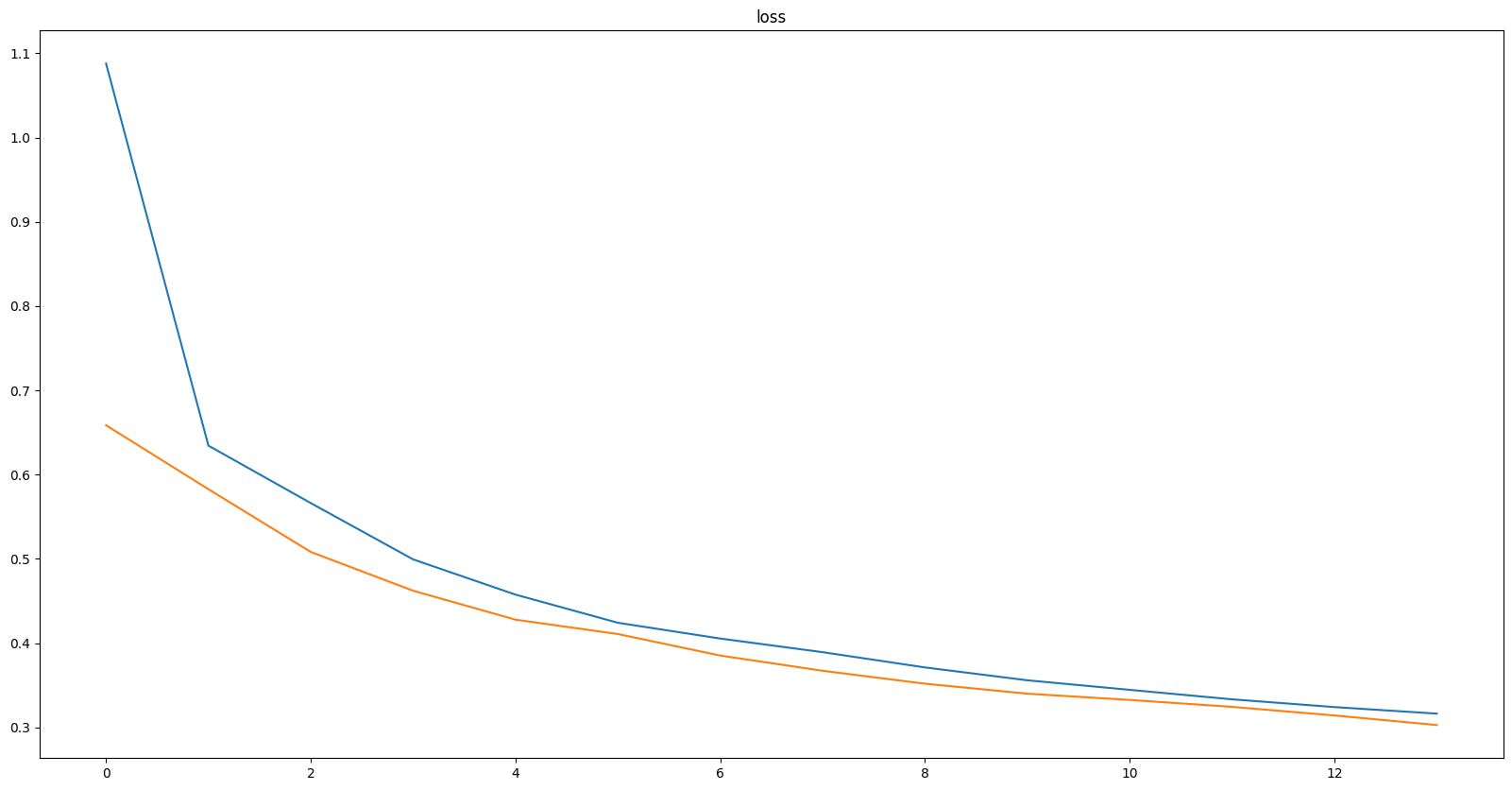
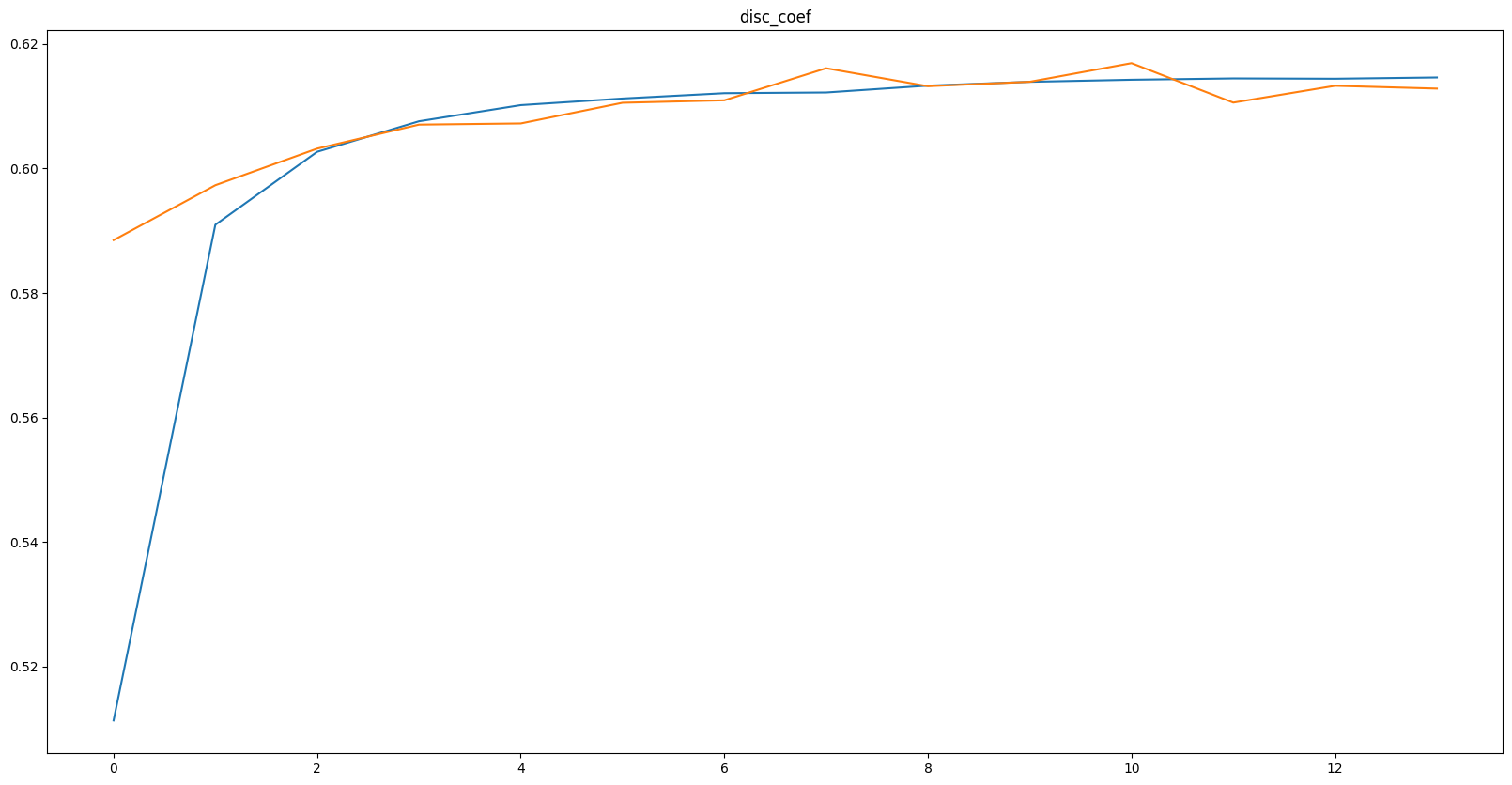
파란색이 train, 주황색이 val에 관한 지표이다.
과적합이 일어나지 않았지만, 노트북 사양이 좋지 않아 시간관계상 15 epochs에서 학습을 중단시켰다.
15 epochs이 끝난 모델이 만든 샘플 이미지를 보니 어느정도는 잘 inpainting 하지만 세밀한 묘사가 필요한 눈 부분과 치아 및 입술을 inpainting 하는데에는 약간 부자연스러운 것을 볼 수 있다.
7. Test (1)
test_model_dict = torch.load("./runs/pytorch_checkpoint/best.pt")
test_model_dict['epoch'] # 15test_model = test_model_dict["model"]
test_loss, test_score = loss_epoch(DEVICE, test_model, test_loader, criterion, metric)
print(test_score) # 0.613407697588205315 번째 epoch를 거친 모델의 val_loss 값이 가장 낮았다.
해당 모델을 이용해 Test 데이터의 다이스 계수를 구해보면 약 0.6134 가 나온 것을 볼 수 있다.
test_masked_imgs, test_masks, test_imgs = next(iter(test_loader))
for i in range(BATCH_SIZE):
vis(DEVICE, test_model, test_masked_imgs[i].unsqueeze(0), test_masks[i].unsqueeze(0), test_imgs[i].unsqueeze(0))


결과 이미지 일부를 보면 어느정도 잘 inpainting 한 것을 볼 수 있지만 눈, 코, 입 부분이 많이 부자연스럽다. 이는 논문과 비교했을 때 현저히 작은 데이터 양, 학습 횟수 (epoch)이 부족했기 때문이라고 추측된다.
8. Fine-tuning
# Load model
model = torch.load("./runs/pytorch_checkpoint/best.pt")["model"]
model.to(DEVICE)
model.freeze_enc_bn = True
# Load object for training
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr = FINE_TUNING_LR)
lr_scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.ReduceLROnPlateau(optimizer, mode = "min", factor = 0.1, patience = 5, cooldown = 2)
early_stopping = EarlyStopping(patience = 10, thresh = 0, mode = "min", print_flush = PRINT_FLUSH)
loss_history = {"train": [], "val" : []}
score_history = {"train": [], "val" : []}
best_loss = np.Inf; train_loss = np.Inf; val_loss = np.Inf
best_score = 0; train_score = 0; val_score = 0
# example image for visualization
example_masked_image, example_mask, example_image = next(iter(val_loader))
# Model Training
for epoch in range(EPOCHS):
display.clear_output(wait = True)
vis(DEVICE, model, example_masked_image, example_mask, example_image)
epochs_start = time.time()
current_lr = optimizer.param_groups[0]["lr"]
print(f"Epoch: {epoch + 1}, current_LR = {current_lr}", flush = PRINT_FLUSH)
print(f"Best val loss: {round(best_loss, 5)}, Best val score: {round(best_score, 5)}")
print(f"train loss: {round(train_loss, 5)}, val loss: {round(val_loss, 5)}", flush = PRINT_FLUSH)
print(f"train score: {round(train_score, 5)}, val score: {round(val_score, 5)} \n", flush = PRINT_FLUSH)
draw_history(loss_history["train"], loss_history["val"], title = "loss")
draw_history(score_history["train"], score_history["val"], title = "disc_coef")
# Train
model.train()
train_loss, train_score = loss_epoch(DEVICE, model, train_loader, criterion, metric, optimizer)
loss_history["train"].append(train_loss)
score_history["train"].append(train_score)
# Validation
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
val_loss, val_score = loss_epoch(DEVICE, model, val_loader, criterion, metric)
loss_history["val"].append(val_loss)
score_history["val"].append(val_score)
if val_loss < best_loss:
best_loss = val_loss
best_score = val_score
torch.save({
"model" : model,
"epoch" : epoch,
"optimizer" : optimizer,
"scheduler" : lr_scheduler,
}, f"./runs/pytorch_checkpoint/finetuned_best.pt")
print("-" * 20, flush = PRINT_FLUSH)
lr_scheduler.step(val_loss)
early_stopping.step(val_loss)
if early_stopping.early_stop:
break
Epoch: 7, current_LR = 5e-05
Best val loss: 0.29014, Best val score: 0.61596
train loss: 0.30082, val loss: 0.29014
train score: 0.61412, val score: 0.61596 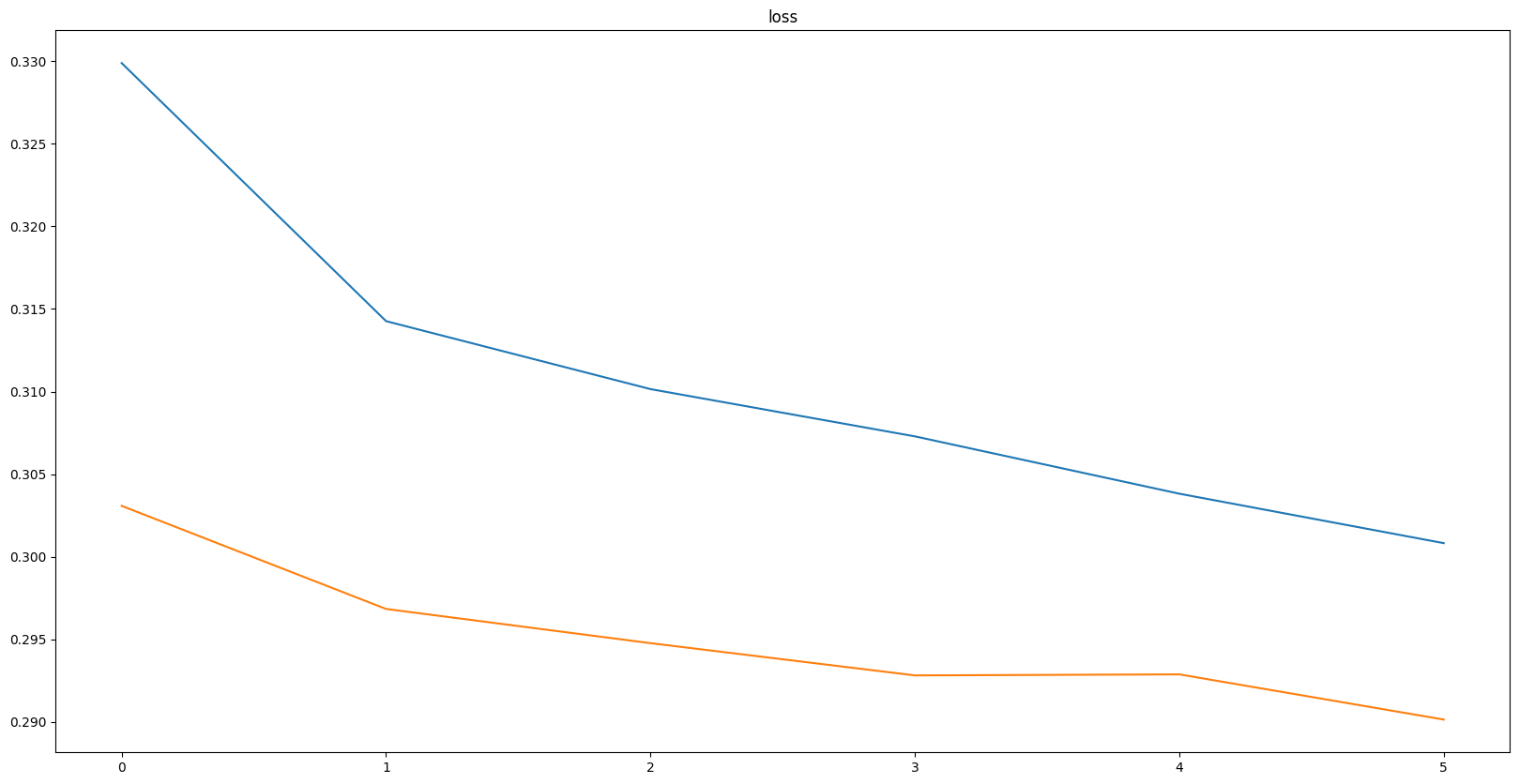
fine-tuning 코드도 위에서 작성한 train 코드와 상당히 유사하다. 특징은 다음과 같다.
- training 한 모델
best.pt를 로드해 fine-tuning - 더 작은 LR로 학습 (0.0002 0.00005)
- Encoder 쪽의 BN layer의 파라미터를 freeze
마찬가지로 시간관계상 학습 중단하였다. (epoch 7)
val_loss를 보면 fine-tuning에서 0.3 이하로 떨어진 것을 볼 수 있다. 과적합도 일어나지 않았고 학습시간이 더 확보가 되었다면 더 좋은 결과를 기대해볼 수 있었을 것 같다.
9. Test (2)
test_model_dict = torch.load("./runs/pytorch_checkpoint/finetuned_best.pt")
test_model_dict['epoch'] # 7test_model = test_model_dict["model"]
test_loss, test_score = loss_epoch(DEVICE, test_model, test_loader, criterion, metric)
print(test_score) # 0.6147270046323537score가 fine-tuning 전보다 약간 상승한 것을 볼 수 있다.
