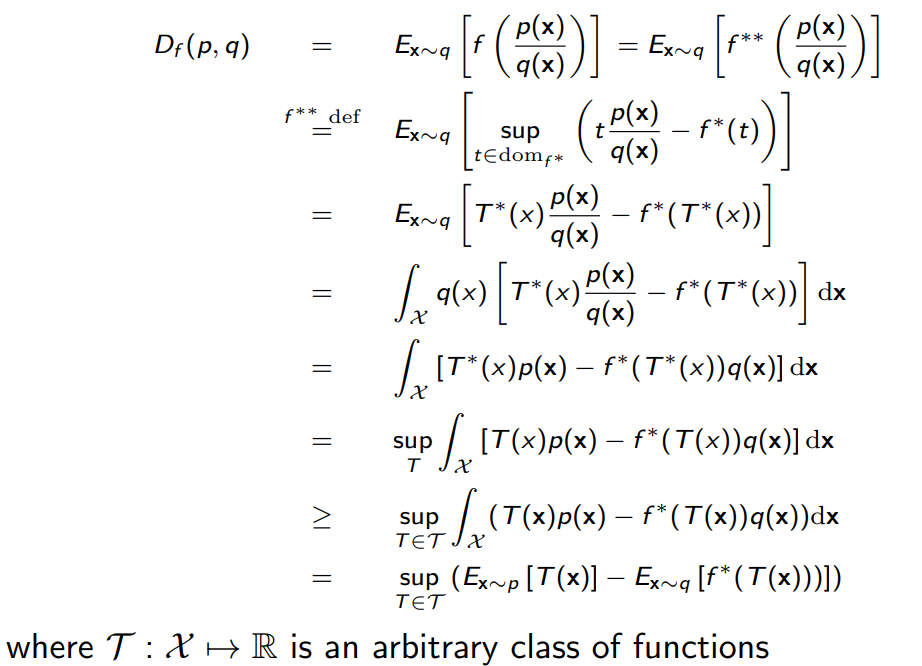F-Divergence
두 개의 distribution p,q가 주어졌을 때 f-divergence는 다음과 같이 정의 된다.
- Df(p,q)=Ex∼q[f(q(x)p(x))], f는 f(1)=0 인 convex, semicontinous function
f(1)=0 이기 때문에 jenson's inequality를 이용하면 f는 항상 non-negative function인 것을 알 수 있다. (증명은 생략) KL divergence도 f-divergece의 일종으로, f(u)=ulogu 인 f-divergence이다.
Train with F-Divergence
pdata,pθ가 주어졌을 때, f-divergece는 아래와 같을 수 있다.
- Df(pθ,pdata)=Ex∼pdata[f(pdata(x)pθ(x))]
- Df(pdata,pθ)=Ex∼pθ[f(pθ(x)pdata(x))]
두 경우 모두 두 distribution의 ratio 즉, probaility 계산을 요구한다. likelihood free 가 되려면, train objective는 오직 samples만 이용해서 구할 수 있어야한다.
Fenchel Conjugate
Fenchel conjugate를 이용하면 samples만 이용하여 구할수 있는 trainig objective를 만들 수 있다. 어떤 convex function의 conjugate는 다음과 같이 정의될 수 있다.
- f∗(t)=u∈domfsup(ut−f(u)), domf는 f의 정의역.
또한 conjugate의 conjugate는 다음과 같이 구할 수 있다.
- f∗∗(u)=t∈domf∗sup(tu−f∗(t))
f가 convex이면서 lower semicontinuos이면 f∗∗=f인 것이 알려져 있다. 이를 활용하면 아래와 같은 lower bound를 구할 수 있다.
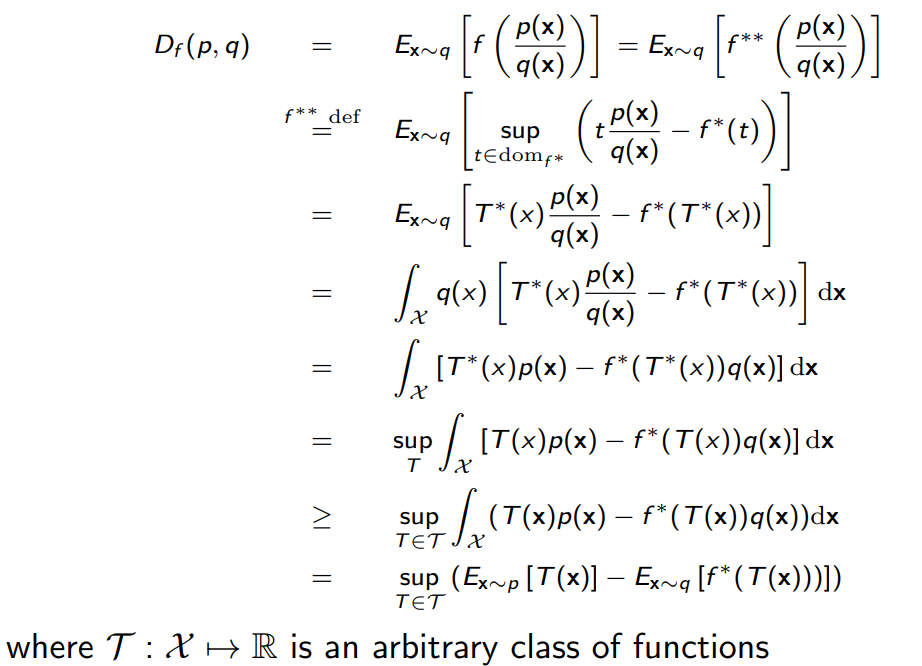
위 식 역시 likelihood free 인 것을 볼 수 있다.
F-GAN
이제 f-divergence를 이용한 GAN의 objective를 다음과 같은 lower bound를 이용하여 구할 수 있다.
- lower bound: Df(p,q)=≥T∈Tsup(Ex∼p[T(x)]−Ex∼q[f∗(T(x))])
- p=pdata, q=pG
- parameterize T by ϕ, G by θ
- f-GAN objective: θminϕmaxF(θ,ϕ)=Ex∼pdata[Tϕ(x)]−Ex∼pGθ[f∗(Tϕ(x))]
이제 아무 f-divergence를 가지고 GAN을 training 할 수 있다.
Wassertstein GAN(WGAN)
Wassertstein GAN의 핵심 아이디어는 p (true data distribution) 과 q (generative data distribution) 이 smoothly change 하며 닮도록 하자는 것이다. 아래는 wassertstein distance에 대한 정의이다.
- Dw(p,q)=γ∈Π(p,q)infE(x,y)∼γ[∣∣x−y∣∣1], Π(p,q)는 모든 x,y의 joint distribution을 갖고 있음.
위 식은 kantorovich-rubinstein duality로 다음과 같이 표현 가능하다.
- Dw(p,q)=∣∣f∣∣L≤1supEx∼p[f(x)]−Ex∼q[f(x)]
∣∣f∣∣L≤1은 f(x) 의 Lipschitz constant가 1이라는 것을 의미.
∀x,y:∣f(x)−f(y)∣≤∣∣x−y∣∣1
Lipschitz constant가 1 이하라는 것은 함수의 변화가 매우 빠르지 않다는 것을 의미한다.
Dϕ(x)를 discriminator, Gθ(x)를 generator로 한 WGAN의 objective function은 아래와 같다.
- θminϕmaxEx∼pdata[Dϕ(x)]−Ez∼p(z)[Dϕ(Gθ(z))]
보통 Dϕ(x)의 Lipschitzness는 weight clipping이나 ∇xDϕ(x)의 gradient penalty를 통해 이루어진다. WGAN은 더 stable한 training이 가능하며, mode collapse 가능성이 비교적 낮다.
Inferring Latent Representation in GNAs(BiGAN)
BiGAN은 x의 latent representation을 얻기 위해 encoder model을 추가한 형태의 GAN이다.

discriminator의 목표는 z,G(z)와 E(x),x 사이의 two-sample test objective를 최대화 하는 것이다. 즉 z,E(x)를 잘 구별하고, G(z),x를 잘 구별하는 것이다.
학습이 끝나고 나면 encoder model E를 가지고 data의 latent representation을 쉽게 얻을 수 있다.
Reference
cs236 Lecture 10