1. 3차원 물체의 표현
Object Modelling
Surface Representation : 물체 표면 표현
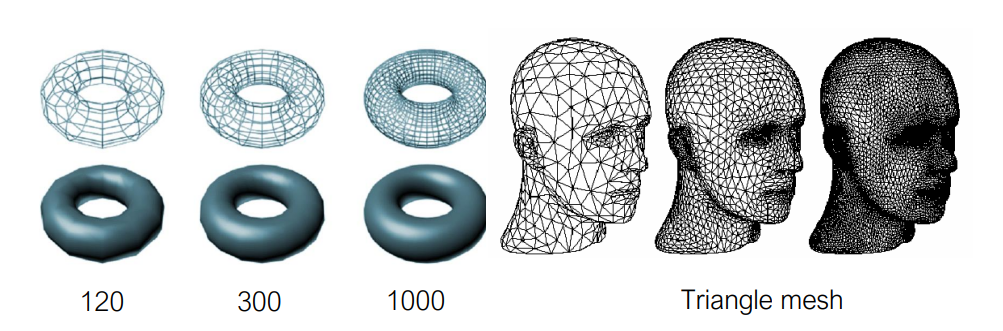
- Polygon, Mesh
- Rectangular mesh : 네 점이 한 평면 위에 있다는 것을 보장하지 못함
- Triangular mesh : 삼각형은 네 점이 한 평균 위에 있다는 것을 보장할 수 있음, 높은 정밀도, 삼각형 분할을 위한 두 배의 처리시간
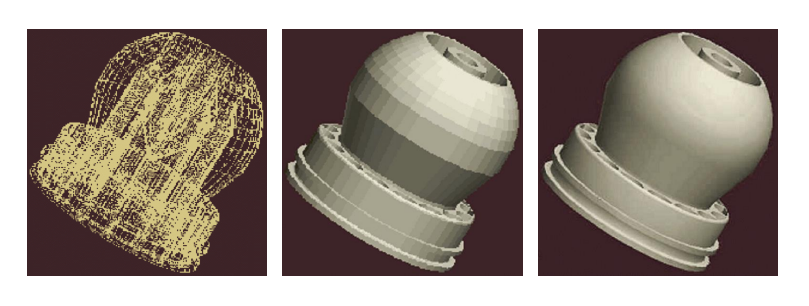
Rendering
- 조명, 음영, 질감, 가시성등과 같은 물리적 효과를 계산하여 객체 모델에서 실제 장면을 그림
- Wirwframe rendering : 빠름, 모델링 단계를 위함
- Solid rendering : 느림, 디자인 리뷰를 위함
2. 벡터 공간
Vector Sapce
Scalar
- 크기는 있지만 방향은 없음
- 실수
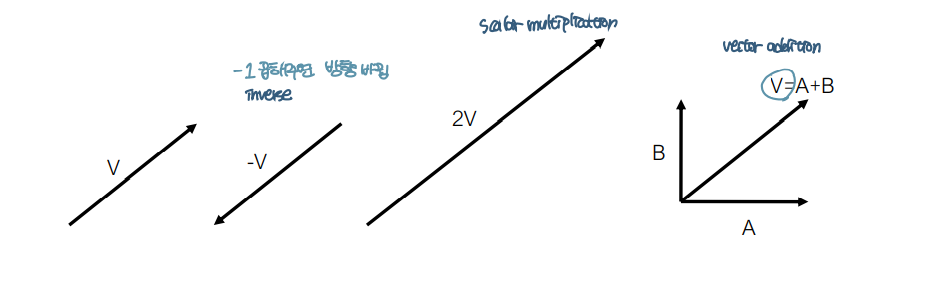
Vector
- 크기와 방향을 가지지만 origin(기원?)이 없음
- operations : 역, 스칼라 곱셈, 벡터 덧셈
- 객체 정점 정의 및 그래픽 렌더링 계산에 사용
3. 어파인 공간
Affine Space
- 동일한 크기 벡터는 시작점의 부재로 동일한 것으로 간주됨
- 크기와 방향이 같다면 같은 벡터로 인식
Affine Space
- 점의 개념에 의해 추가된 확장된 벡터 공간
- 벡터의 시작점도 나타낼 수 있음
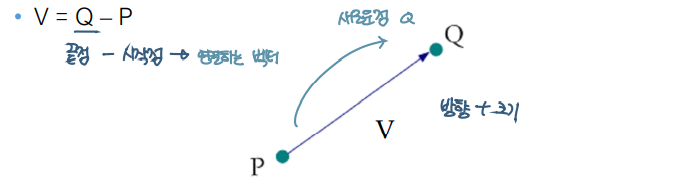
Affine operations
- V = A + B : 벡터 사이의 덧셈
- V' = 2V : 벡터와 스칼라 사이의 곱셈을 의미
- Q = V + P : 벡터 및 점은 새 점을 정의
4. 좌표축과 좌표계
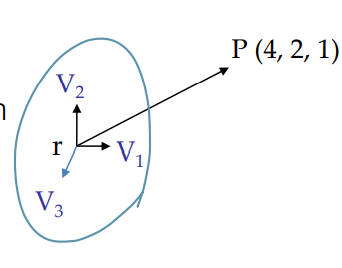
- 벡터는 primary aexes(x, y, z)에 대해 basic vectors(v1, v2, v3)로 나타내짐
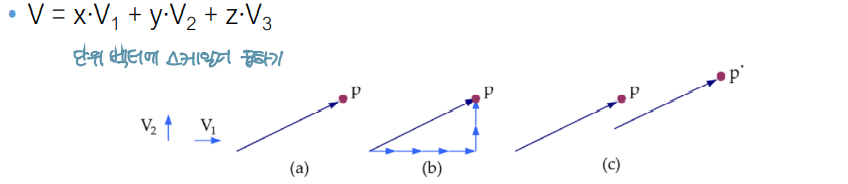
A Coordinate System (좌표 시스템)
- origin과 basic vector로 이루어진 프레임
- 있으면 임의의 점 정의 가능
➡ C = (r, v1, v2, v3)
점은 좌표계에 의해 표현
- P = r + 4V1 + 3V2 + v3
- r : 점
5. 동차 좌표
Homogeneous Coordinate System
- 동차 좌표계 : 차원이 같음
- 포인트 시작점 보존

- 벡터는 시작점이 없음
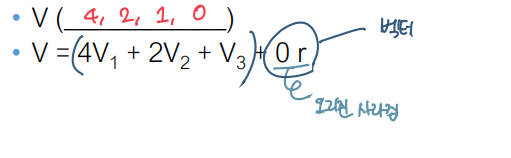
기하 변환
- Transformation 이동
- Rotation 회전
- Scaling 크기
- 객체를 변환하려면 객체 꼭짓점과 변환 matrix 사이의 곱셈에 의해 수행됨
1. 이동
2D Translation
- P(x, y) : Vertex point matrix (정점)
- P (Tx, Ty) : 이동 변환 matrix
- P' (x', y') T(Tx, Ty) * P (x, y) ⬅ 이동 변환 matrix
- x' = x + Tx
- y' = y + Ty
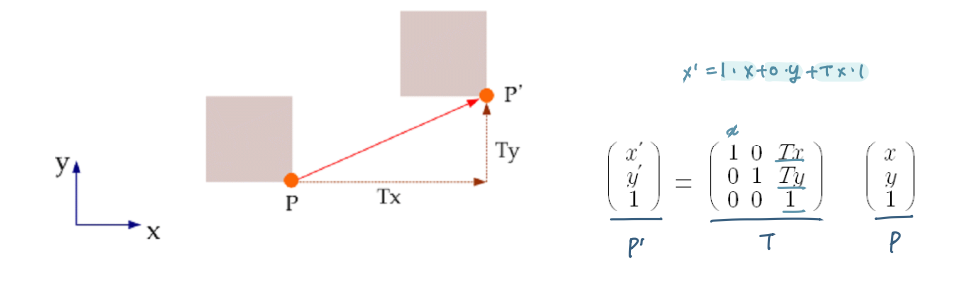
- 새로운 좌표점을 구하는 것
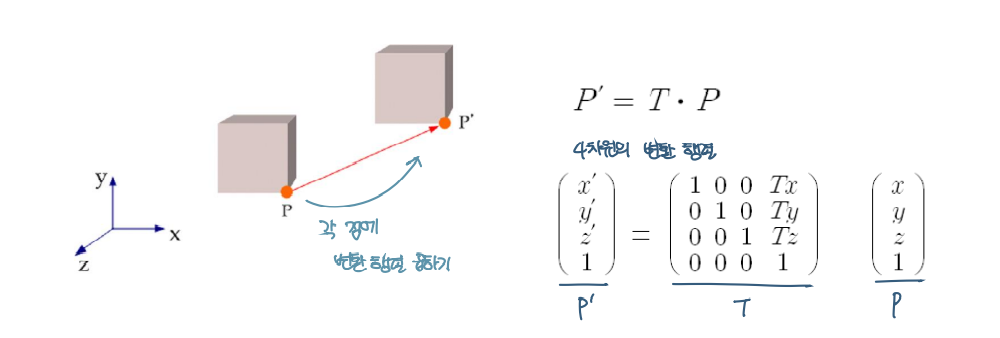
3D Translation
- P (x, y, z) : A vertex point matrix (정점)
- T (Tx, Ty, T2) : 이동 변환 matrix
- P' (x', y', z') = T * P : T의 이동변환 후의 점
x' = x + Tx, y' = y + Ty, z' = z + Tz
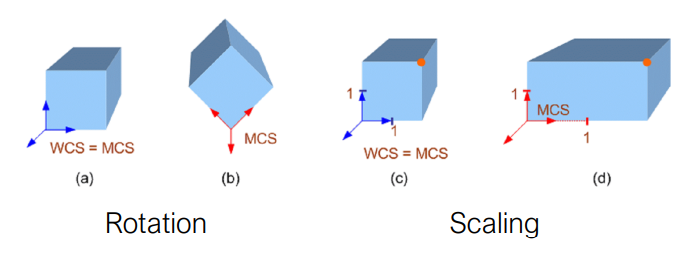
2. 회전
2D Rotation
- 원점 회전만 존재
- R : 원점 중심으로 회전
- P' = R * P
- Since x = rcosθ, and y = rsinθ

3D Rotation
- x, y, z axis rotation
- θ : 회전 각도
- Right-handed system : OpenGL
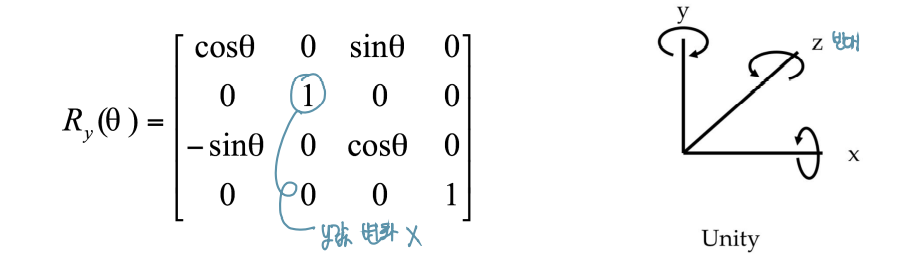
- Left-handed system : Unity, DirectX
- Rz : Z-rotation (z는 앞뒤이므로 변화 X)
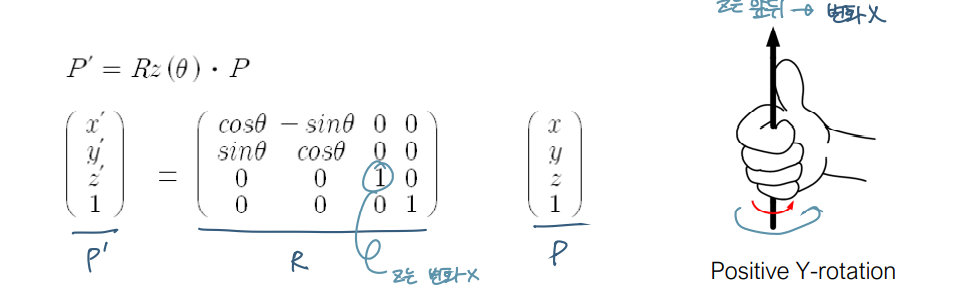
- X-axis rotation : OpenGL
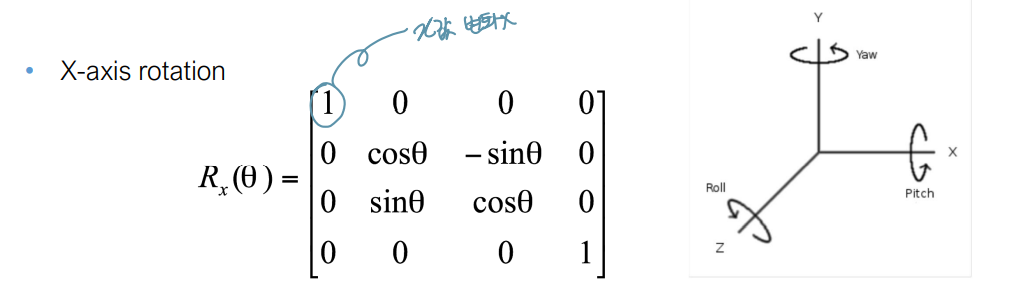
- Y-axis rotation : Unity
3. 크기 조절
Scaling
- Uniform vs Non-uniform scaling
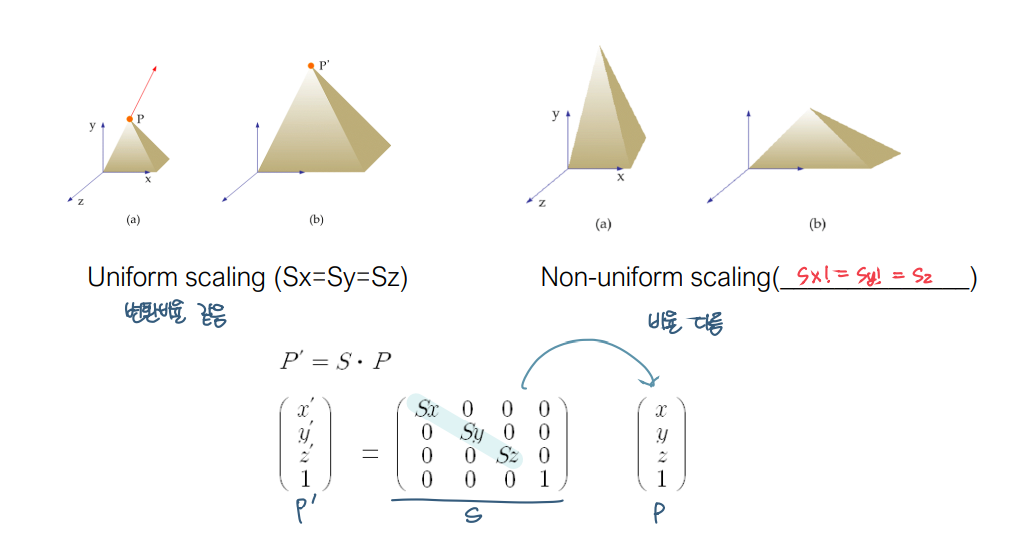
- 변환 비율에 따라 나뉨
4. 복합 변환
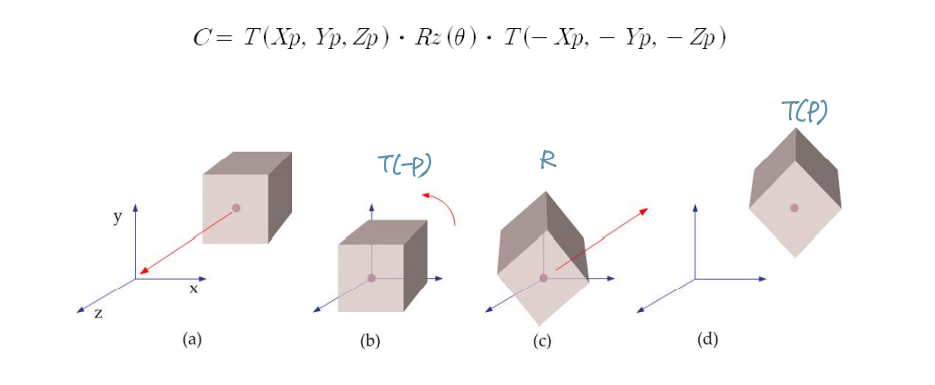
Composite Transformation
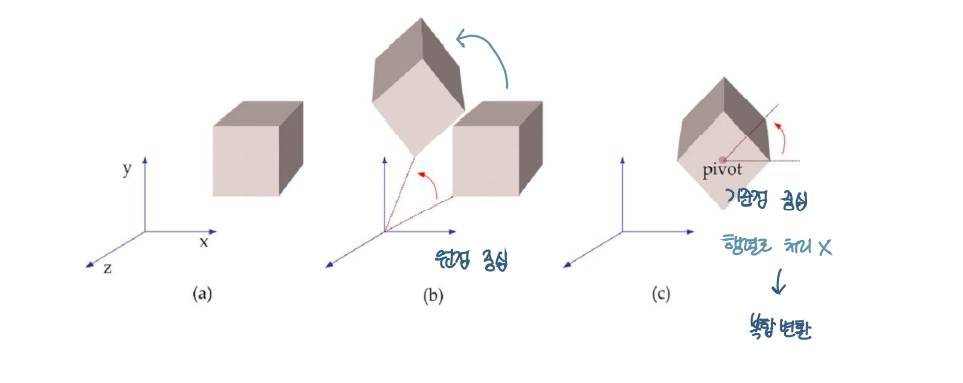
- (a) Original position of a cube
- (b) Origin-based rotation (원점 중심)
- (c) Pivot point rotation (큐브의 중심)
- 변환 순서는 T1 > Rotate > T2
Pivot Point Rotation
- pivot 지점이 원점과 겹치도록 개체를 이동 T(-P)
- 회전축에서 물체를 회전 : R
- 회전된 물체를 다시 원래의 위치로 이동 : T(P)
- 행렬은 변환의 역순으로 구함
Compose Transformation
변환은 WCS에 기반
- Translate(T1) > Rotate(R) > Translate(T2)
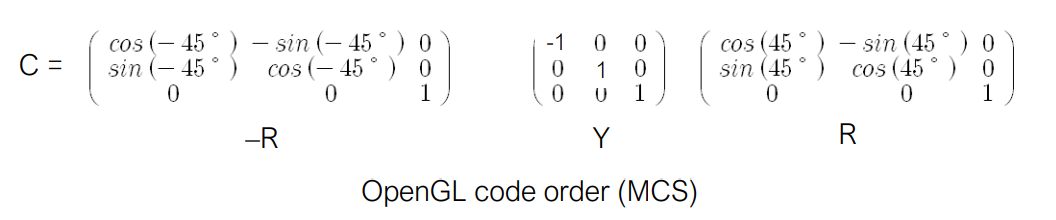
Matrix Multiplication in OpenGL (MCS에 기반)
- P' = T2 R T1 * P ⬅ 교환좌표 성립 X
- 복합 변환의 사전 컴퓨팅은 전체 처리 시간 절약 가능
- P' = C P // C = T2 R * T1
Transformation Order ⭐
matrix multiplication은 교환법칙 성립 X
- Translate ➡ Rotate(R2 * Tx) // left
- Rotate ➡ Translate(Tx * R2) // right
5. 반사
Reflection
- (a) X-reflection (b) Y-reflection (c) Origin reflection
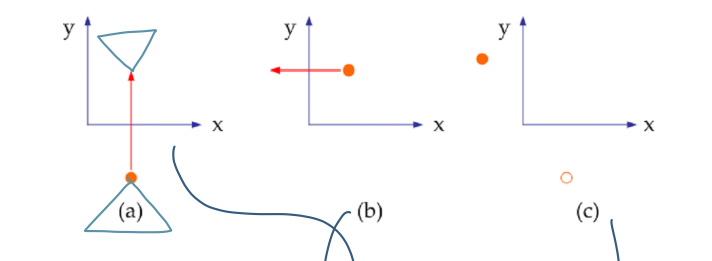
- Origin-Reflection Matrix
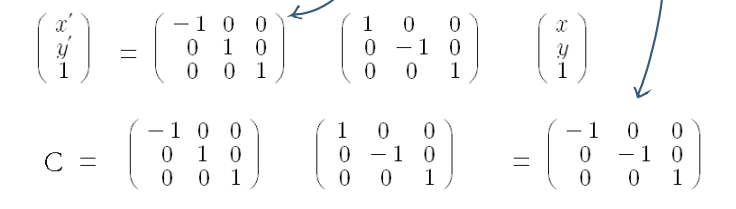
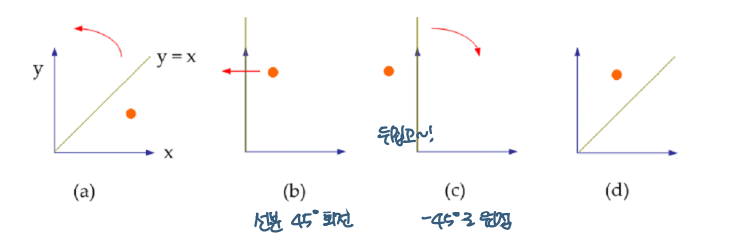
Composite Reflection
선 y = x에 대해 반사 (WCS 기반)
- 원점에서 점을 45도 회전 (R)
- 점의 y축 반사 (Y)
- 원점에서 점을 -45도 회전 (-R)
6. 구조 왜곡
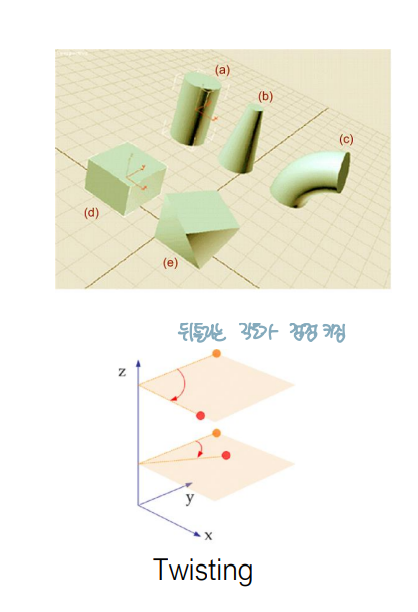
Structure-Deforming Transformation
Non-deforming transformation 구조변환
- 스케일링, 변환, 회전
Tapering : (a) > (b)
- Along z-axis, an object is scaled
Bendeing : (a) > (C)
- Along an axis, an object is bent (완전 형태 바뀜)
Twisting : (d) > (e) 뒤틀림
- Along z-axis, a rotational angle increases
7. 변환의 분류
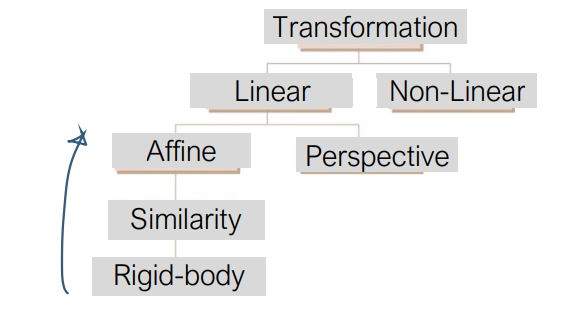
Transformation Classes
Rigid Body Transformation 감체
- 물체형태 보존
- ex) translation, rotation
Similarity Transformation 유사변환
- 폴리곤 사이의 각도와 vertex 유지
- ex) rigid-body transformation + uniform scaling, reflection
Affine Transformation Object 형태 유지
- 물체의 선, 다각형, 곡면, 평행선 등의 객체 항상 유지
- ex) Similarity transformation + non-uniform scaling, shearing
Perspective Transformation
- 평행선이 만남
- 직선 유지
Linear Transformation 선형 변환
- 선형 함수 x, y, z as x' = ax + by + cz로 구성
- 직선 유지
- ex) Affine + perspective trans
Non-linear transformation 비선형 변환
- x' = ayx + by2 + cz/x
- 상수 간의 곱셈, 1차 함수 x
- ex) structure-deforming trans > no guarantee of keeping straight lines
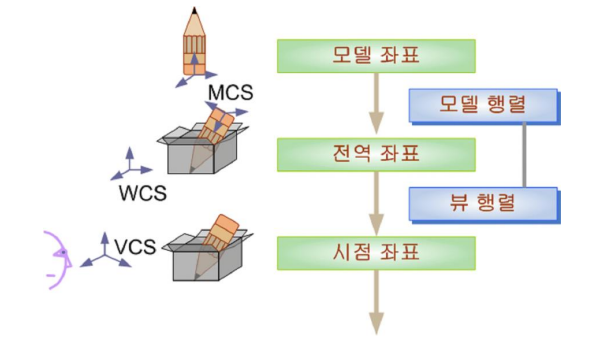
1. 모델 좌표계와 전역 좌표계
Modeling Coordinate System
MCS
- 모델링 단계에서 사용되는 객체별 좌표
- 임의의 좌표 원점 및 단위 보유
WCS, MCS and VCS
World Coordinate System
- 여러 MCS를 하나로 통합
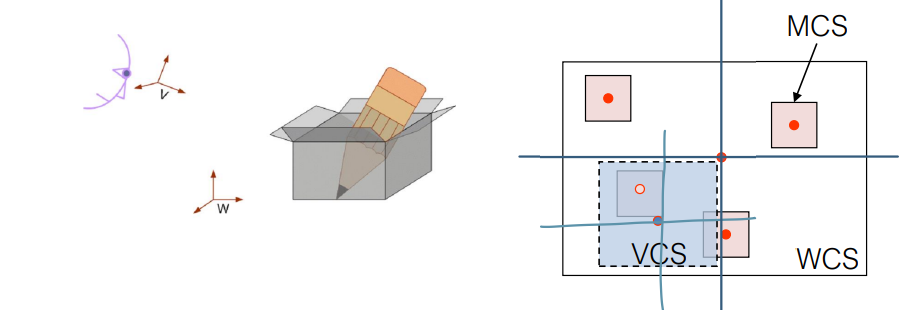
- 최종 스크린 ➡ VCS
View Coordinate System
- 카메라가 정의한 좌표계
- viewing space가 viewport로 이전
Matrix Multiplication
- 물체의 꼭짓점 좌표는 transformation으로부터 분류
- 물체가 변환될 때, vertex matrix에 변환 행렬을 곱해 WCS 위치를 얻음
- P'(WCS) = Translate * P(MCS)
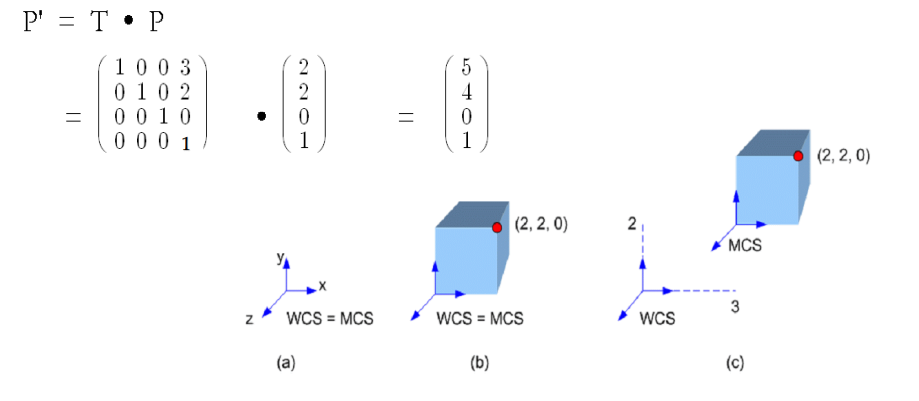
Rotation
- MCS가 물체와 회전
Scaling
- 스케일링으로 MCS와 WCS의 비율 변환
- Scaling by 2 on x-axis > WCS : MCS = 2 : 1
- P'(WCS) (4, 2, 0) = S(2, 1, 1) x P(MCS) (2, 2, 0)
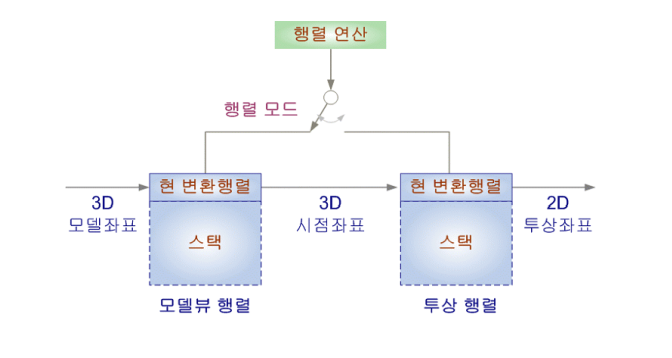
2. 지엘 파이프라인
ModelView Matrix
Modeling Transformation
- Translation, rotation, scaling of an object
Viewing Transformation
- 좌표계 보기 정의 방법
- 카메라의 위치 및 방향별
ModelView 시스템은 하나의 system matrix에서 관리
- 역변환 관계 (카메라 move - 모델 move)
3. 모델 변환
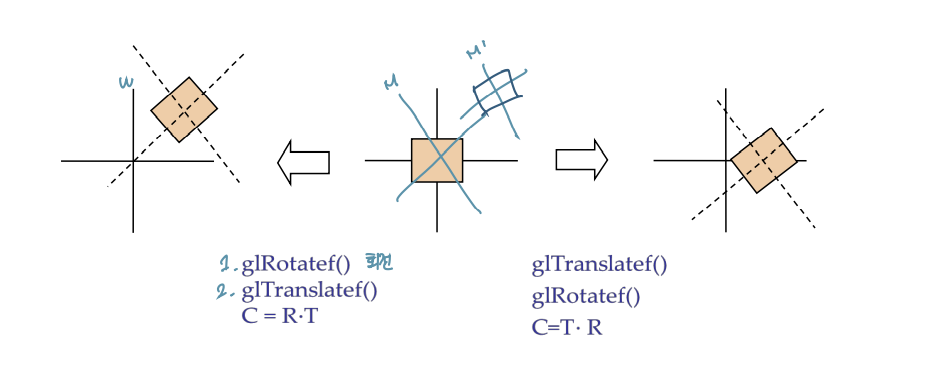
Matrix Stack
- 변형이 발생하면 변환 매트릭스 push
glMatrixMode (GLenum mode)
- GL_MODELVIEW
- GL_PROJECTION
- GL_TEXTURE
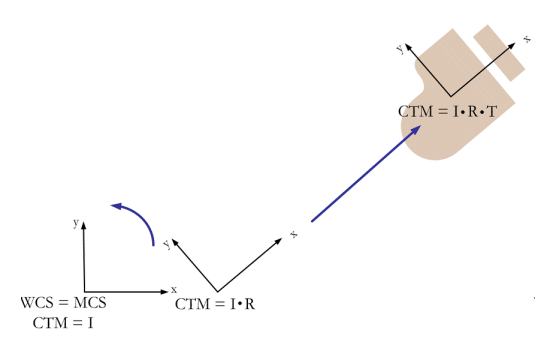
Object-based MCS
OpenGL
- glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW);
- glLoadIdentity();
- glRotatef(45, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
- glTranslatef(10.0, 0.0, 0.0);
- glVertex3f(x, y, z);
OpenGL Code-order
- object와 함께 MCS 회전
- Translate MCS on the lastest MCS
- 최종 MCS 원점에 object가 그려져 있음
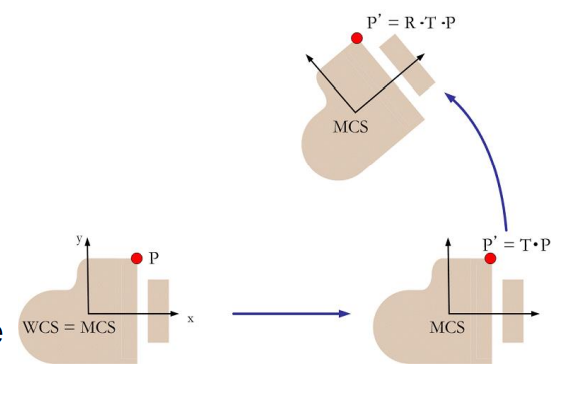
Origin-based WCS
OpenGL
- glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW);
- glLoadIdentity();
- glRotatef(45, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
- glTranslatef(10.0, 0.0, 0.0);
- glVertex3f(x, y, z);
Reverse order OpenGL code
- WCS 원점에서 MCS 번역
- WCS 원점에서 WCS 회전
- 지난 MCS의 origin에 object 그리기
CTM
Current Transformation Matrix
- 변환이 발생할때 그것은, system matrix stack의 최상위 요소인 CTM에 누적
- object vertex matrix는 CTM을 곱한 후 그림
4. 복합 변환에 의한 모델링
CTM Initialization
- glLoadIdentity()
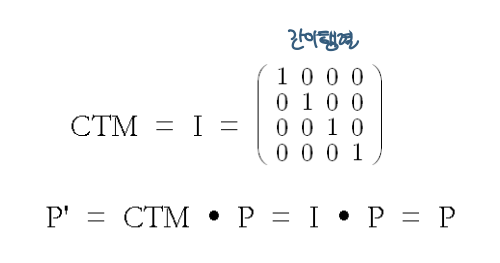
CTM accumulation
- 오른쪽부터 CTM의 변환이 쌓임
- CTM = CTM * M
- ex) glTranslatef(1, 2, 0)
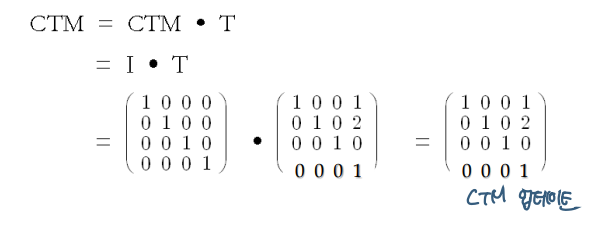
CTM
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW);
glLoadIdentity(); // CTM initialized
glScalef(sx, sy, sz);
glRotatef(theta, vx, vy, vz);
glBegin(GL_POINTS);
glVertex3f(x, y, z);
glEnd();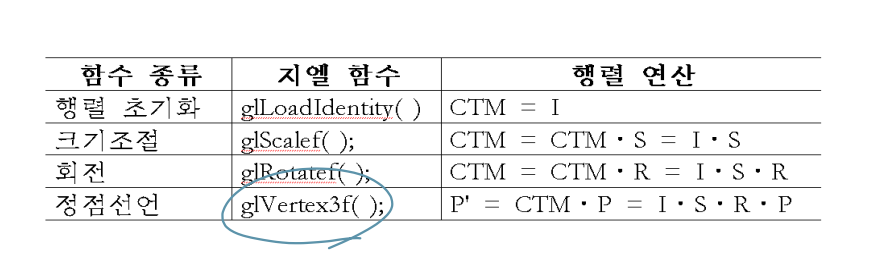
5. 행렬 스택 활용
Matrix Stack
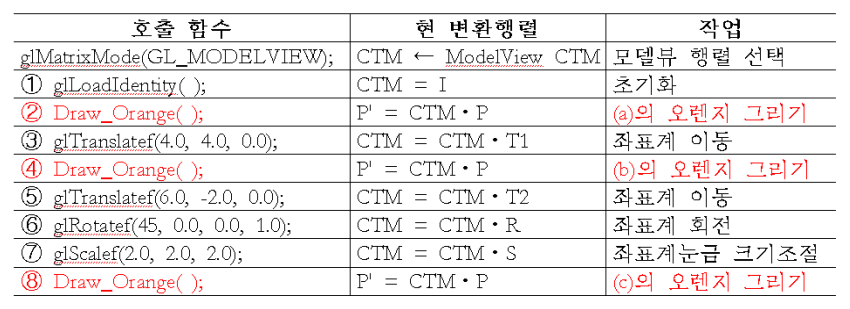
matrix stack에서 연속 변환 행렬 관리
- matrix stack의 top은 CTM 의미
- glPushMatrix() : 현재 CTM이 존재할 경우 CTM 복사해 push
- glPopMatrix() : top CTM pop ➡ 이전 CTM 위치로 돌아감
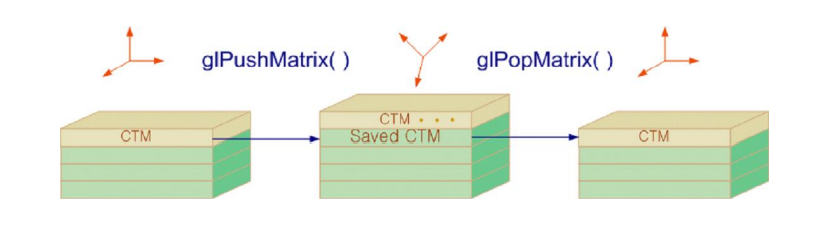
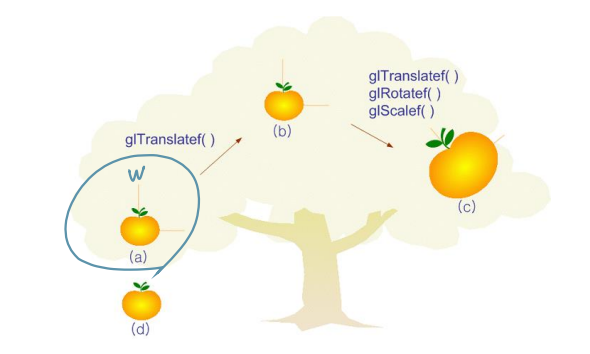
6. 계층 구조 모델링
Hierarchical Modelling
- 계층적 모델링

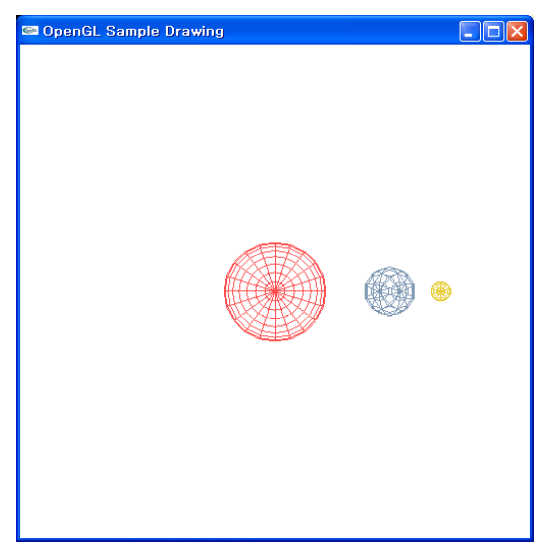
Solar System
- Scene tree 태양계
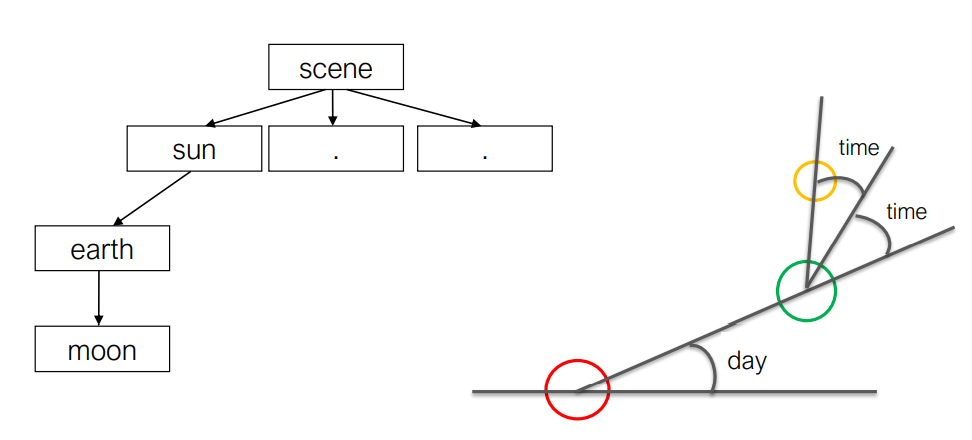

1. 시점 좌표계 설정
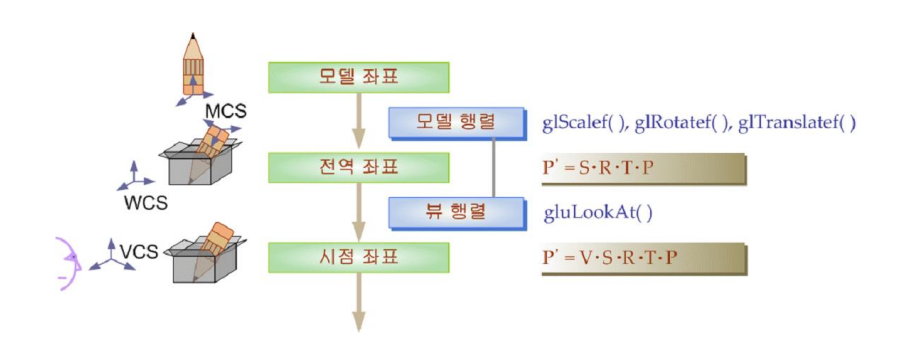
Viewing Transformation
Viewing Coordinate System VCS
- 뷰 볼륨 안에 있는 object만 출력
- 카메라 위치 및 방향에 의해 정의됨
- 보기는 모델링 변환과 반대
- model matrix + view matrix ➡ modelview matrix
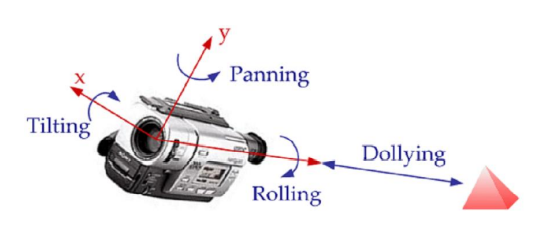
Camera Rotation
- Tilting : X-rotation
- Panning : Y-rotation
- Rolling : Z-rotation
- Dolling : Camera zoom-in/out
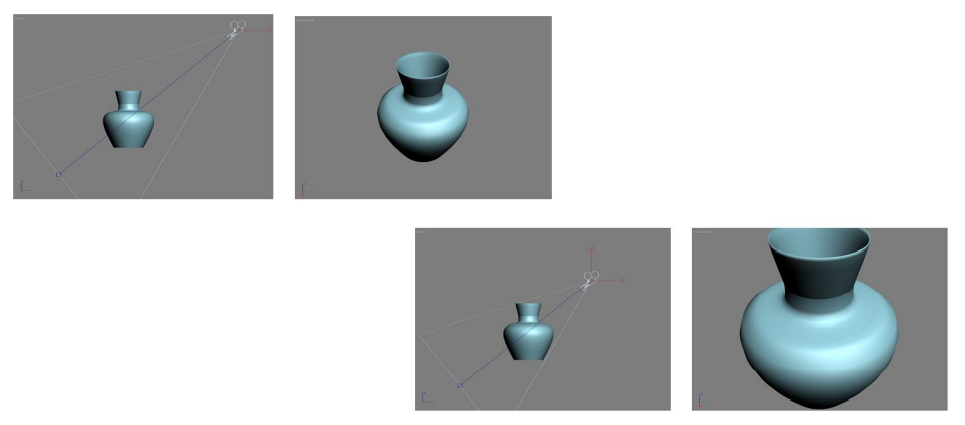
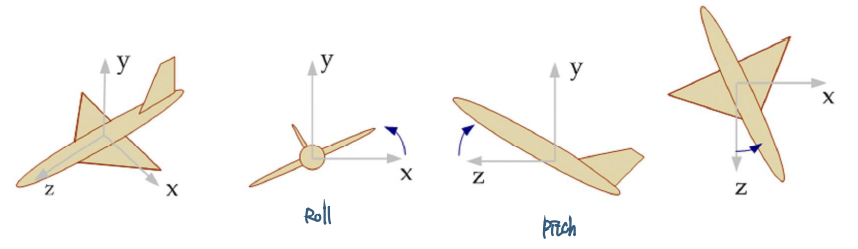
Flight Angels
- 평면의 방향은 세 각도로 정의됨
- Roll : Z-rotation angle (second)
- Pitch : X-rotation angle (third)
- Yaw : Y-rotation angle (last)
2. 지엘의 시점 좌표계
GL VCS

- glulookAt
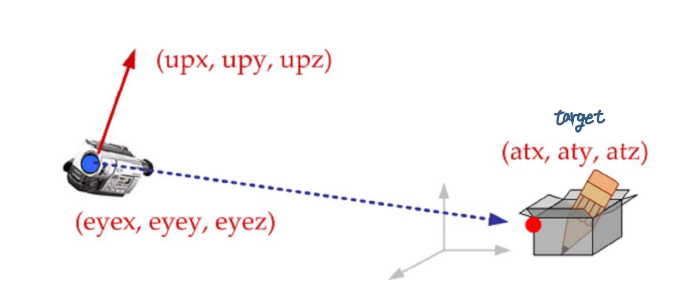
Viewing and Modelling Transformation
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW);
glLoadIdentity( ); // I
gluLookAt(0.0, 10.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, .0); // V
glTranslatef (5.0, 5.0, 0.0); // T1
glTranslatef (4.0, 2.0, 0.0); // T2
glRotatef (45, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0); // R
glutWireCube(1.0); // PMCS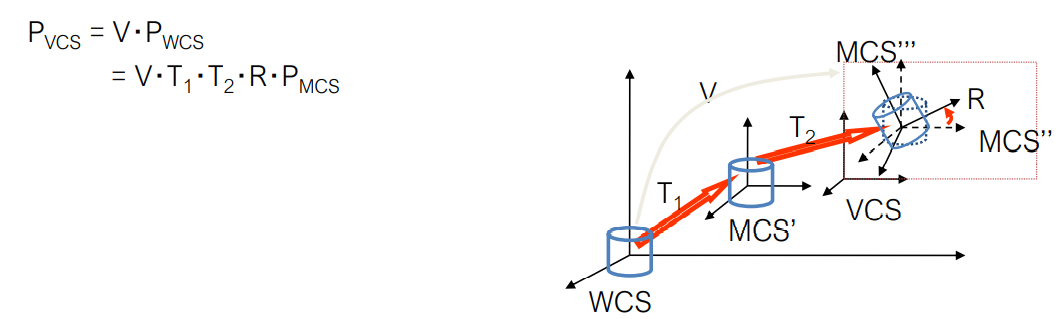
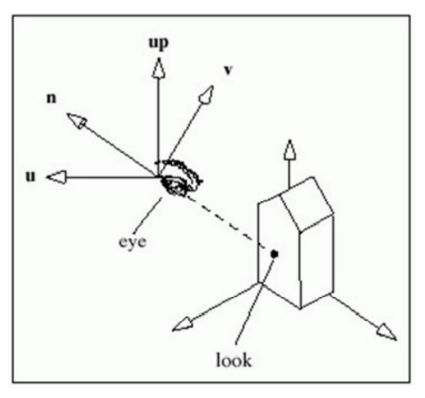
Camera Coordinate System
- gluLookAt(eyex, eyey, eyez, atx, aty, atz, upx, upy, upz);
- Axes : u, v, n
- n = eye - at
- u = up x n
- v = n x u
- origin : eye (looking in the direction -n)
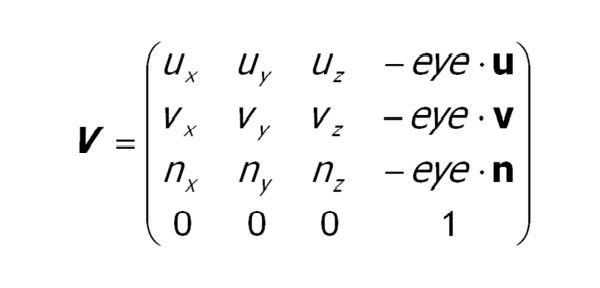
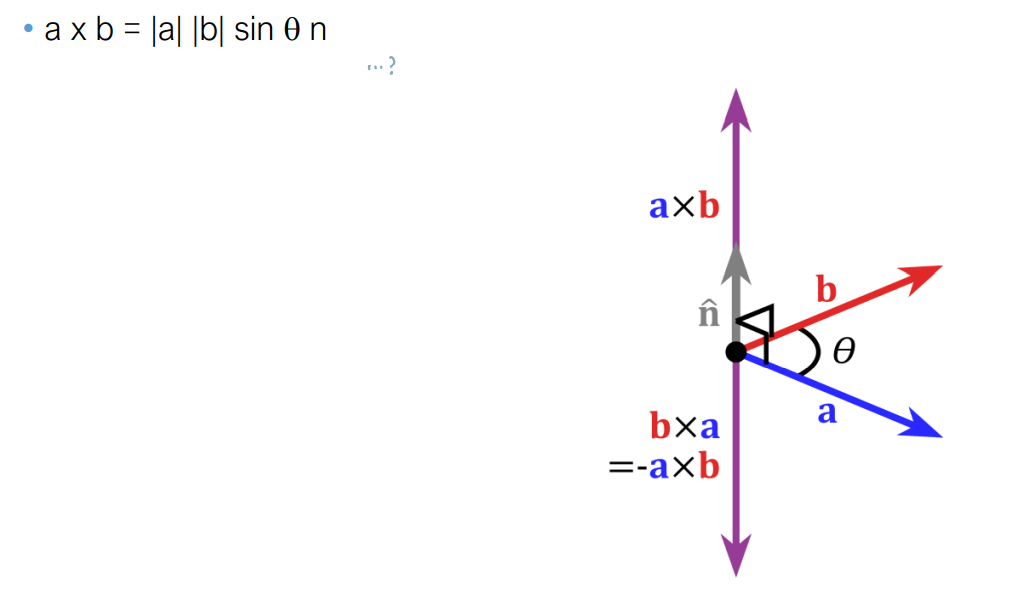
Cross Product