0. Abstraction
- 많은 연구에서 pretext taks들은 이미지가 변형됨에 따라 대표 특징들이 변형되었다.
- 이 논문에서는 이미지가 변형되어도 축출된 대표 특징들이 변화되지 않는 PIRL 진행
1. Introduction
- 기존의 이미지 인식 모델은 라벨링된 데이터나 바운딩 박스를 이용 -> long-tail에서 좋은 성능을 낼 수 없다(long-tail: 빈도가 적은 데이터)
- Self-supervised learning을통해 이 한계를 개선(미리 정해진 라벨을 통해 학습하는 것이 아닌 이미지 자체에서 representation을 학습)
- PIRL에서는 변형된 이미지&원본 이미지 사이의 유사성과 다른 이미지 사이의 차이를 이용하여 representation 학습
3. PIRL
3.1) Overview of the Approach
- 이미지 변형에도 변함없는 CNN을 만드는 것이 목적 , CNN with parameter theta: φ_θ(·)
- (1): 원본 이미지와 변형된 이미지에 대해서 똑같은 representation을 뽑아 내도록 CNN학습
- (2): represenation이 변형된 이미지에 대해서 변할 수 있도록 CNN학습
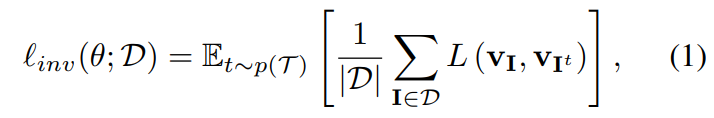

- Loss Function
1) 두 이미지의 representation 유사도 측정을 위해 cosine similarity 사용
2) 이 similarity를 NCE(noise contrastive estimator)에 적용
3) 각각의 positive sample(I, I_t)은 대응되는 negative sample이 있고 이 negative sample은 I가 아닌 I'에서 계산한다.
4) NCE는 (I, I_t)가 일어날 확률을 equation(3)과 같은 distribution에서 계산한다.

5) equation(4)는 I의 representation이 I_t의 representation과 비슷하도록 하고, I_t의 representation이 I'의 representation과 달라지도록 한다.

3.2) Using a Memory Bank of Negative Samples
- m_I: exponential moving average of feature representation that were computed in prior epochs
- memory bank를 사용하면 batch의 크기를 늘릴 필요 없이, negative sample(m_I')을 넣을 수 있다.
- Final Loss Function: 첫번째 부분은 equation(4)를 나타내고 두번째 요소는 m_I와 f(v_I)를 유사하게 하여 학습 속도를 늦추고, f(v_I)와 f(v_I')를 서로 유사하지 않게 한다.
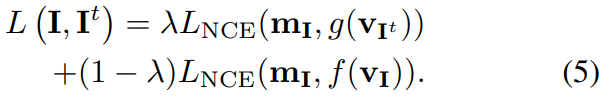
3.3) Implementation Details
- Jigsaw pretext task를 중점을 두고 실험을 진행
- ResNet 50 사용
- g(v_I_t)계산:
1) 이미지에서 9개의 패치 축출
2) 이미지의 representation 계산
3) 128차원인 패치의 특징을 얻기위해 projection
4) 패치의 특징을 랜덤하게 모으고, 다시 projection
5. Analysis
5.1.1) Does PIRL learn invariant representations?
- l_2: distance between the normalized representation of image & normalized representation of transformed image
- l_2가 Jigsaw에 비해 상당히 짧은 것은 관찰할 수 있다.

5.1.2) Which layer produces the best representations?
- res5 layer of PIRL

5.2.1) What is the effect of lambda in the PIRL loss function
-loss term 이 0.5 일 때 정확도가 최대인 것을 관찰할 수 있다.

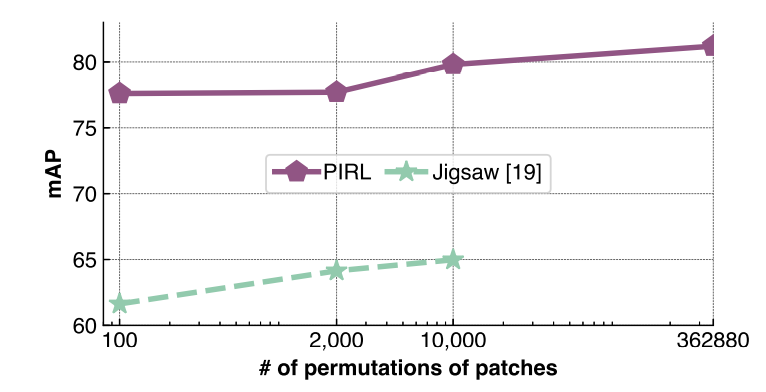
5.2.2) Effect of the number of image transforms
- PIRL의 경우 모델의 파라미터가 정해져 있어 많은 양의 patch조합을 학습할 수 있다.
5.2.3)Effect of the number of negative samples
- negative sample의 수가 모델 정확도에 긍정적인 영향을 미치는 것을 확인

