Next.js Streaming과 사용자 경험 개선 가이드
이전 Chapter에서는 대시보드 페이지를 동적으로 만드는 데 성공했지만, 데이터 Fetch 속도가 느린 경우 애플리케이션의 성능에 어떤 영향을 미칠 수 있는지 논의했습니다.
이번 코스에서는 느린 데이터 요청이 있을 때 사용자 경험을 어떻게 개선할 수 있는지에 대해 살펴보겠습니다.
1. 기존 SSR의 한계
기존 SSR의 flow를 생각해보면 다음과 같습니다:
- 백엔드 서버(API)로부터 Data를 가져온다
- 프론트엔드 서버(Next.js)에서 HTML을 렌더링한다
- 클라이언트(브라우저)에서 HTML을 받는다
- 클라이언트(브라우저)는 자바스크립트(bundle.js)를 다운로드 한 후, 상호작용성있는 웹을 만든다
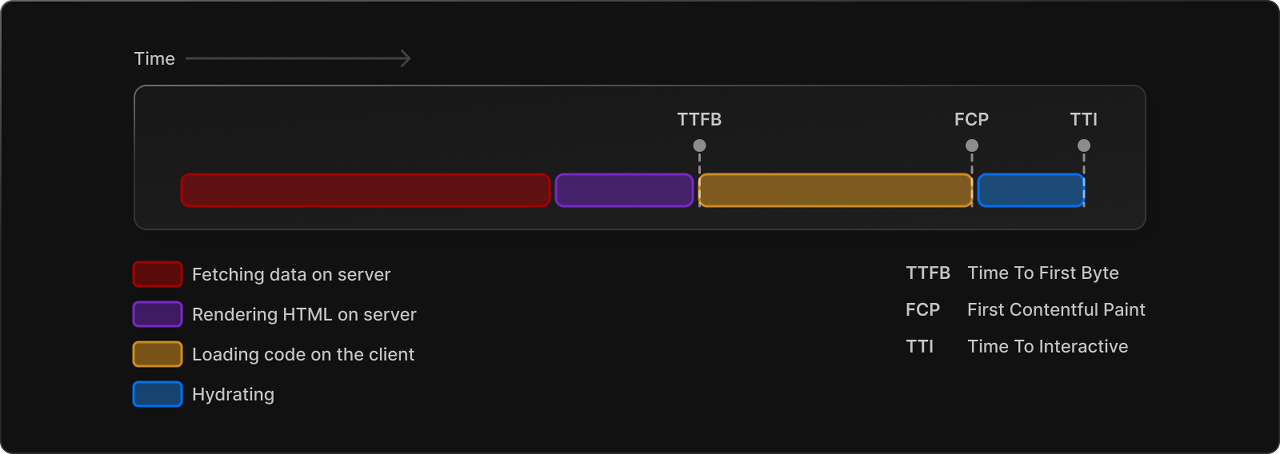
문제점: 위의 과정이 모두 끝나기 전까지는 사용자가 페이지와 상호작용을 할 수 없습니다. Next.js에서는 이 문제를 해결하기 위해 Streaming 기술을 도입했습니다.
2. Streaming이란?
2.1 Streaming의 정의
Next.js에서는 Streaming을 다음과 같이 정의합니다:
경로를 더 작은 "청크(chunk)"로 나누어 서버에서 클라이언트로 점진적으로 스트리밍하는 데이터 전송 기술
2.2 Streaming의 작동 원리
- HTML을 작은 단위로 나누어 모든 데이터가 로드되기 전에 준비된 컴포넌트는 미리 완성해 상호작용할 수 있게 합니다
- 우선순위가 높은 컴포넌트를 먼저 작동시킬 수 있습니다
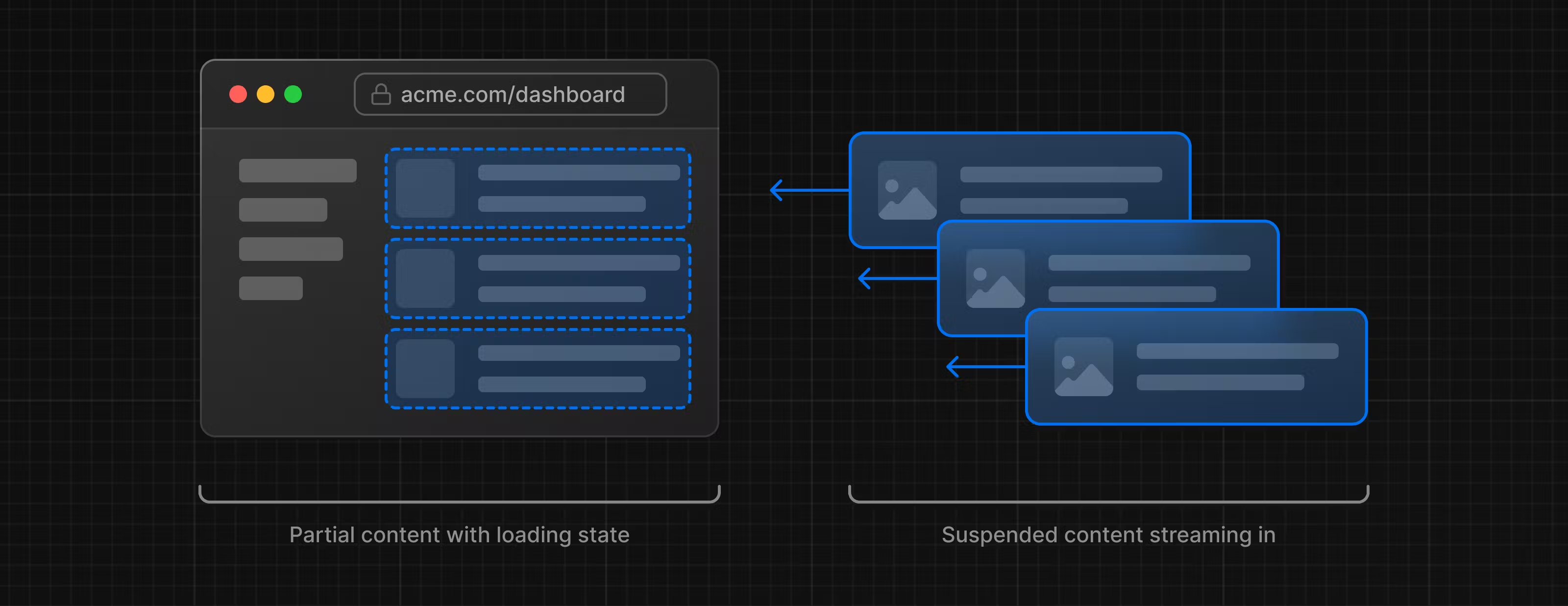
2.3 Streaming의 장점
- 느린 데이터 요청이 전체 페이지를 차단하는 것을 방지
- 사용자는 모든 데이터가 로드될 때까지 기다리지 않고 페이지의 일부를 보고 상호작용 가능
- 각 컴포넌트가 Hydrating되기까지의 시간(TTL)을 개별적으로 관리
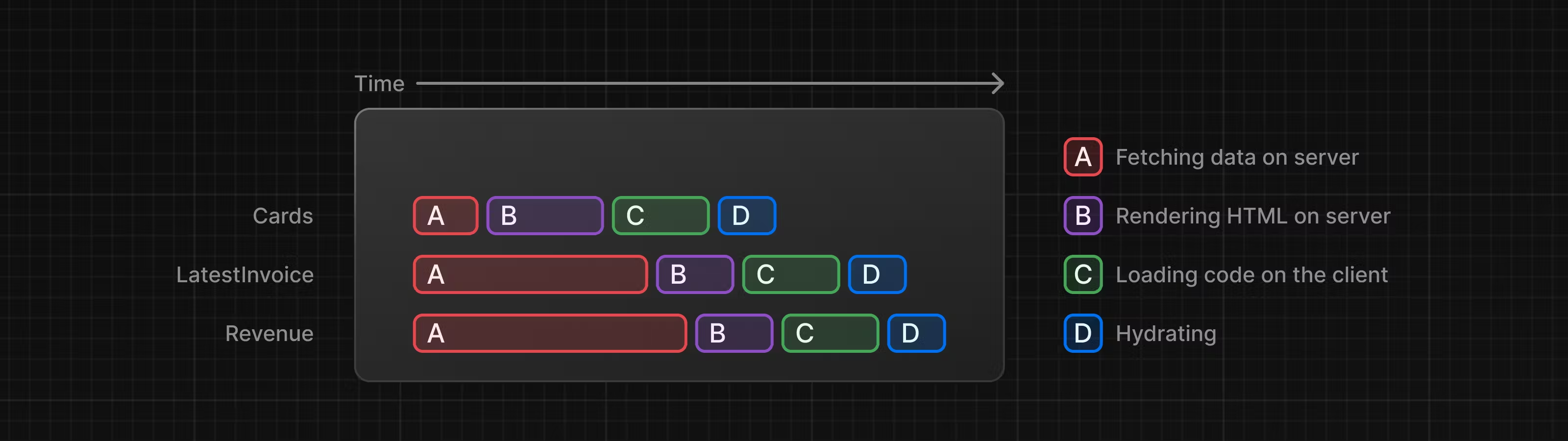
2.4 Hydrating이란?
Hydrating은 Next.js 서버가 Pre-Rendering된 웹 페이지를 클라이언트에게 보낸 뒤, React가 bundling된 Javascript 코드들을 chunk 단위로 클라이언트에게 전송하고, 이러한 Javascript 코드들이 이전에 전송된 HTML DOM 요소 위로 리렌더링되는 과정에서 자기 자리를 찾아 매칭되는 과정입니다.
Hydrating을 통해 초기 로딩 시 클라이언트에서 즉시 상호작용이 가능하고, 이후에는 일반적인 React 애플리케이션처럼 동작할 수 있습니다.
3. Next.js Streaming 구현 방법
Next.js에서 스트리밍을 구현하는 방법은 두 가지입니다:
- 페이지 수준에서
loading.tsx파일 사용 - 특정 컴포넌트에서
<Suspense>사용
4. 페이지 레벨 Streaming: loading.tsx
4.1 기본 Loading 컴포넌트 생성
/app/dashboard 디렉터리에 loading.tsx 파일을 생성합니다:
export default function Loading() {
return <div>Loading...</div>;
}4.2 Loading의 작동 원리
loading.tsx는 Suspense를 기반으로 한 Next.js의 특수 파일입니다- 페이지 콘텐츠가 로드되는 동안 대체 UI를 보여줍니다
<SideNav>같은 정적 컴포넌트는 즉시 표시되며, 사용자는 동적 콘텐츠가 로드되는 동안에도 상호작용할 수 있습니다- Interruptable navigation: 페이지가 완전히 로드되기를 기다릴 필요 없이 페이지를 떠날 수 있습니다
4.3 Loading Skeleton 추가
사용자 경험을 개선하기 위해 Loading Skeleton을 추가할 수 있습니다:
import DashboardSkeleton from "../ui/skeletons";
export default function Loading() {
return <DashboardSkeleton />;
}4.4 Skeleton UI의 장점
- 사용자에게 서비스가 원활히 작동 중임을 알림
- 하얀 백지 화면 대신 의미 있는 UI 제공
- 사용자 이탈 방지 효과
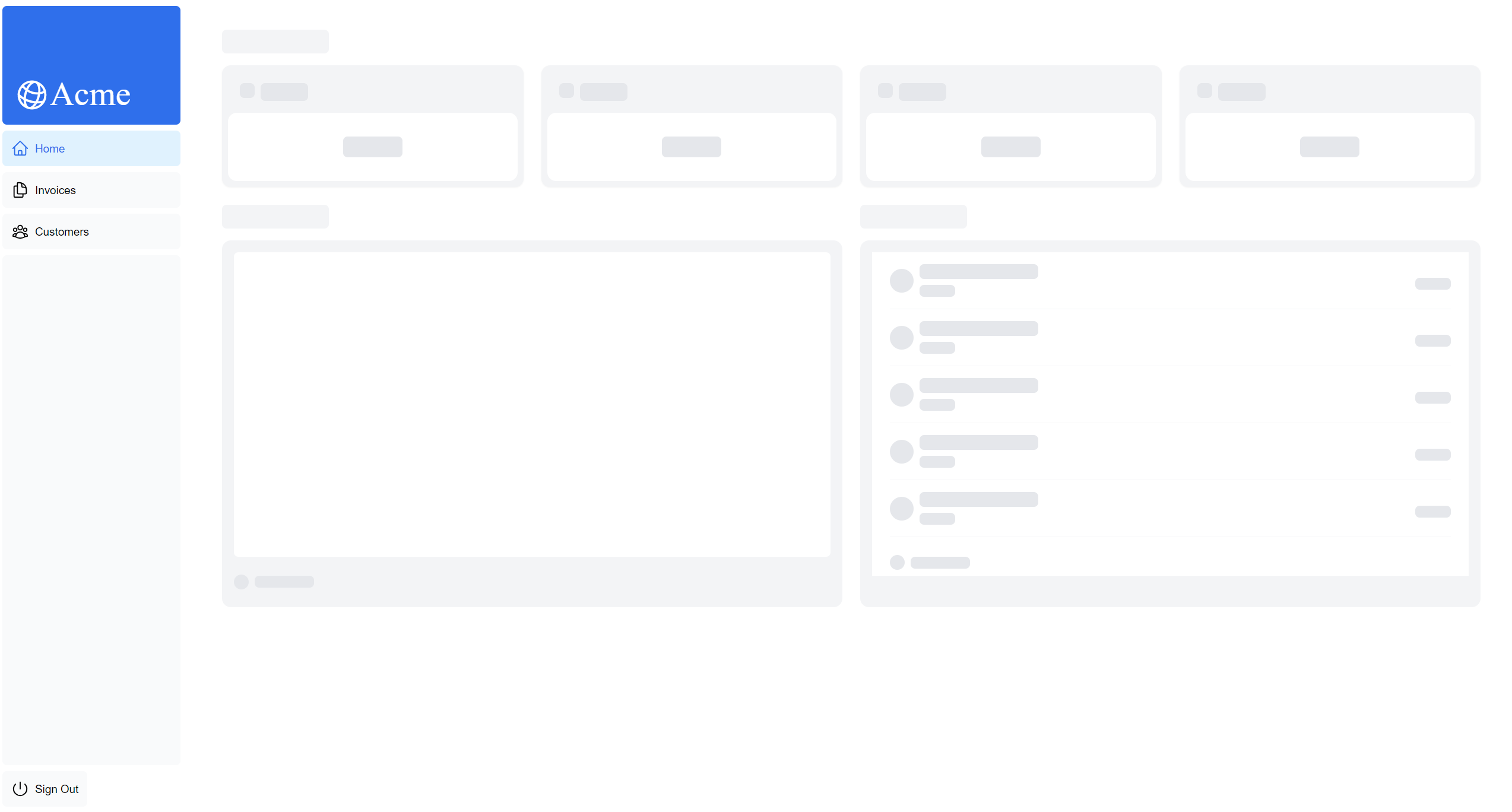
5. Route Groups를 활용한 Skeleton 버그 수정
5.1 문제 상황
현재 loading.tsx 파일의 대시보드 Skeleton UI가 송장 페이지와 고객 페이지에도 적용되는 문제가 발생합니다.
원인: /app/dashboard/loading.tsx가 /app/dashboard/invoices/page.tsx 및 /app/dashboard/customers/page.tsx보다 상위 레벨에 위치
5.2 Route Groups란?
Route Groups는 폴더를 경로의 URL 경로에 포함되지 않도록 표시할 수 있는 기능입니다.
- URL 경로 구조에 영향을 주지 않으면서 경로 세그먼트와 프로젝트 파일을 논리적인 그룹으로 구성
- 디렉터리명을 소괄호
()로 감싸서 생성
5.3 해결 방법
/app/dashboard 하위에 (overview) 폴더를 생성하고, page.tsx와 loading.tsx를 이동:
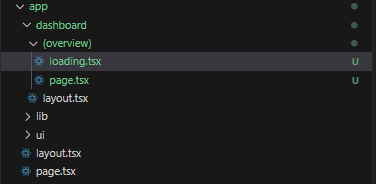
5.4 Route Groups 활용 방법
- URL 경로 구조에 영향을 주지 않고 파일을 논리적 그룹으로 구성
()로 감싼 디렉터리는 URL 경로에 포함되지 않음/dashboard/(overview)/page.tsx→ URL:/dashboard- 애플리케이션을 Section별
((marketing), (shop))또는 팀별로 분리 가능
6. 컴포넌트 레벨 Streaming: <Suspense>
6.1 컴포넌트별 세분화된 Streaming
전체 페이지가 아닌 특정 컴포넌트만 스트리밍하고 싶을 때 React Suspense를 사용합니다.
6.2 Suspense의 작동 원리
- 일부 조건(데이터 로드)을 충족할 때까지 애플리케이션 일부의 렌더링을 지연
- 동적 컴포넌트를 감싸고, 로드되는 동안 대체 컴포넌트(fallback) 표시
6.3 실습: RevenueChart 컴포넌트 스트리밍
Step 1: 기존 코드에서 데이터 fetch 제거
export default async function Page() {
// const revenue = await fetchRevenue(); // 삭제
const latestInvoices = await fetchLatestInvoices();
// ...
}Step 2: Suspense로 컴포넌트 감싸기
import { Suspense } from 'react';
return (
<main>
{/* 기존 코드 */}
<div className="mt-6 grid grid-cols-1 gap-6 md:grid-cols-4 lg:grid-cols-8">
<Suspense fallback={<RevenueChartSkeleton />}>
<RevenueChart />
</Suspense>
<LatestInvoices latestInvoices={latestInvoices} />
</div>
</main>
);Step 3: 컴포넌트 내부에서 데이터 fetch
import { fetchRevenue } from "@/app/lib/data";
export default async function RevenueChart() {
const chartHeight = 350;
const revenue = await fetchRevenue(); // 추가
const { yAxisLabels, topLabel } = generateYAxis(revenue);
if (!revenue || revenue.length === 0) {
return <p className="mt-4 text-gray-400">No data available.</p>;
}
// 컴포넌트 렌더링 로직...
}6.4 결과 비교
이전 코드 (Suspense 없음):
// 페이지 전체가 차단되고, 모든 데이터 fetch가 완료되어야 화면 표시
<RevenueChart />변경 코드 (Suspense 적용):
// 컴포넌트별 스트리밍으로 페이지 전체 차단 없음
// fetchRevenue() 완료 전까지 fallback 컴포넌트 표시
<Suspense fallback={<RevenueChartSkeleton />}>
<RevenueChart />
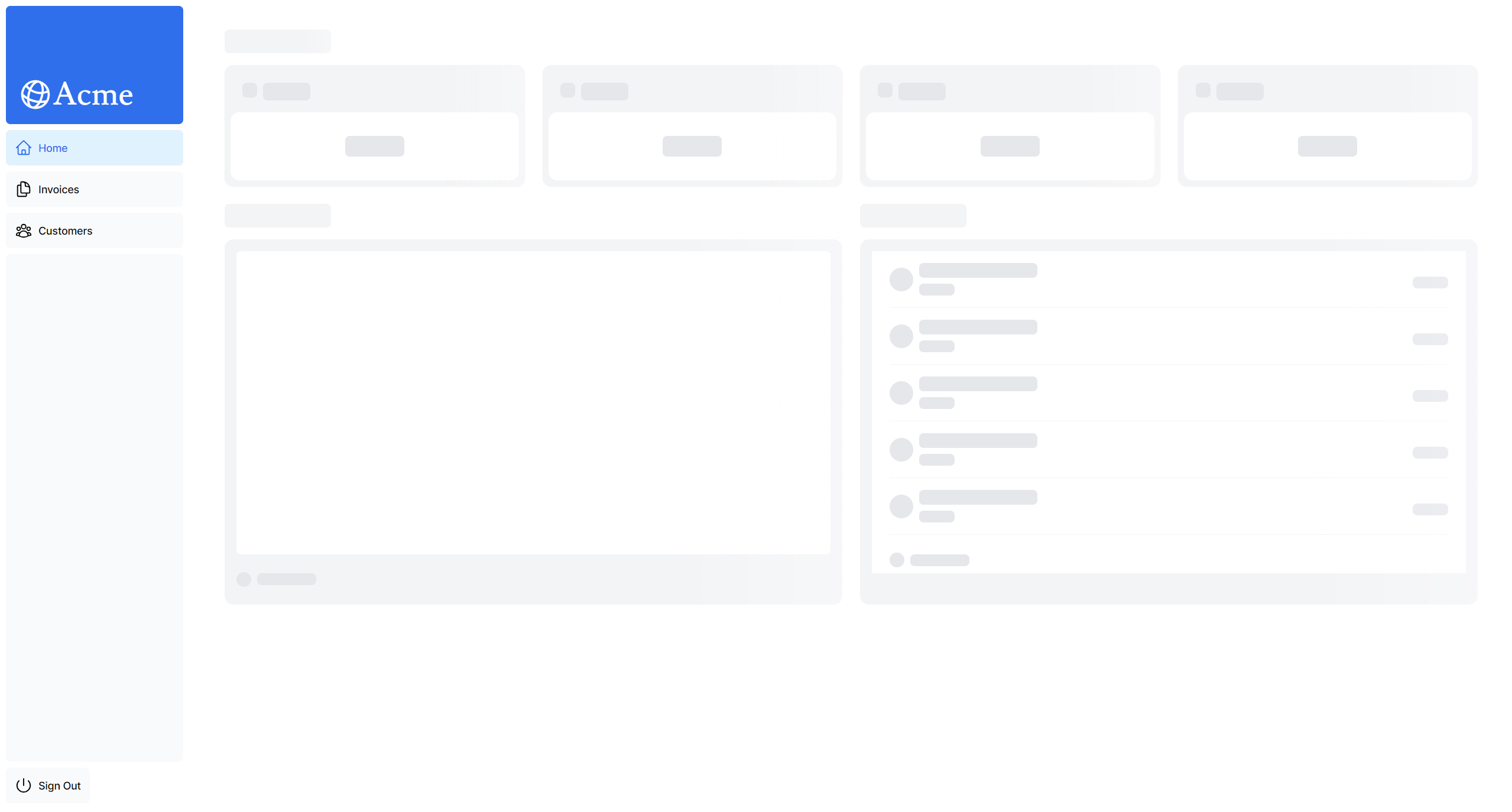
</Suspense>6.5 로딩 단계별 화면
1단계: fetchLatestInvoices(), fetchCardData() 진행 중
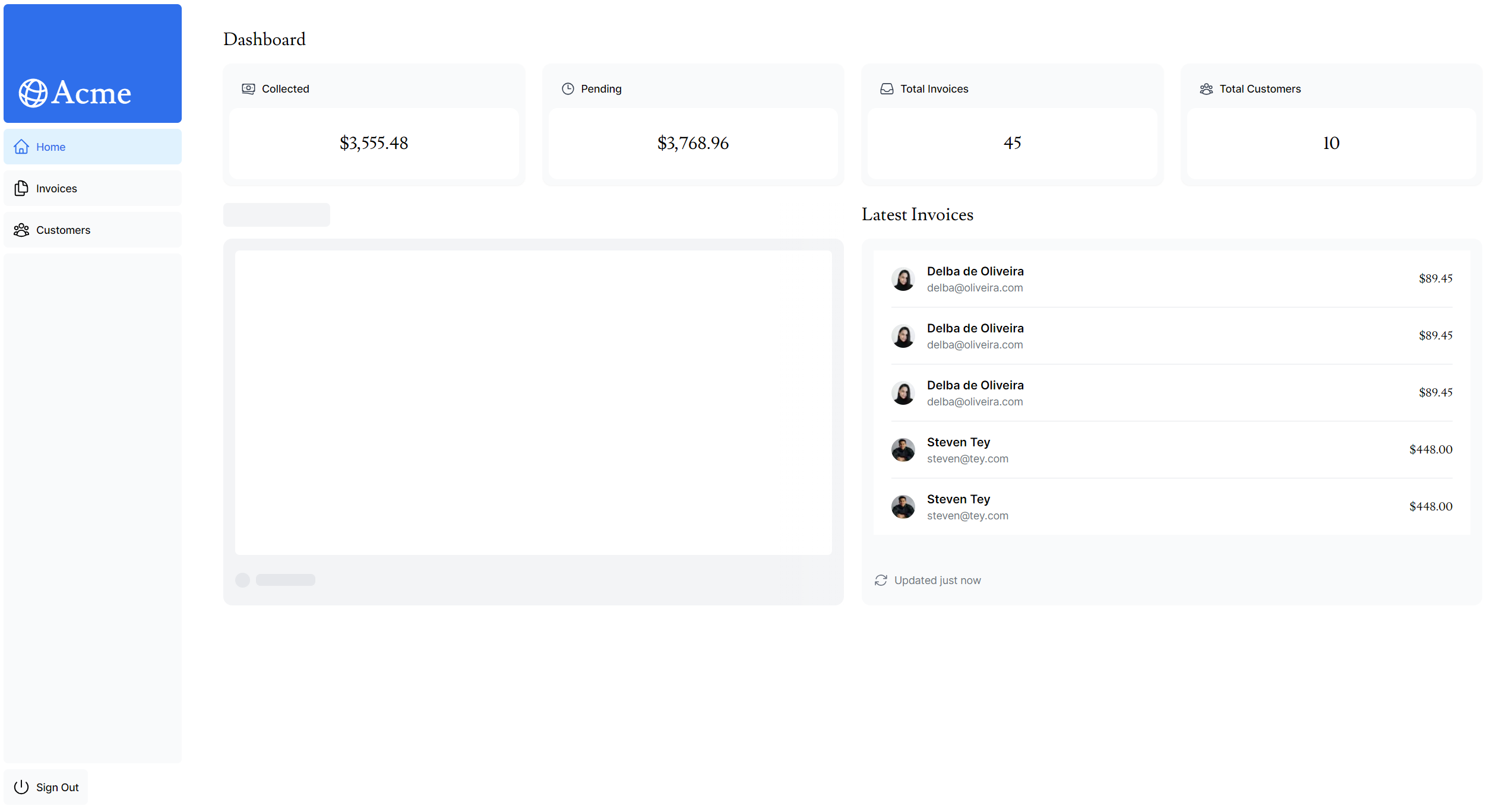
2단계: 위 함수들 완료 후, fetchRevenue() 수행 전
7. 컴포넌트 그룹핑: <Card/> 최적화
7.1 Popping 효과 문제
각 개별 카드에 대한 데이터를 따로 가져오면 Popping 효과(화면 요소가 갑자기 바뀌거나 나타나는 효과)가 발생하여 사용자에게 시각적으로 거슬릴 수 있습니다.
7.2 해결 방안: 컴포넌트 그룹화
카드들을 그룹화하여 종합된 지연 효과를 만들어 정적인 <SideNav/>가 먼저 표시되고 그 다음에 카드 데이터가 표시되도록 합니다.
7.3 구현 과정
Step 1: Page 컴포넌트 수정
import { Suspense } from "react";
import {
CardSkeleton,
LatestInvoicesSkeleton,
RevenueChartSkeleton,
} from "@/app/ui/skeletons";
import CardWrapper from "@/app/ui/dashboard/cards";
export default async function Page() {
return (
<main>
<h1 className={`${lusitana.className} mb-4 text-xl md:text-2xl`}>
Dashboard
</h1>
{/* 카드들을 그룹화하여 Suspense로 감싸기 */}
<div className="grid gap-6 sm:grid-cols-2 lg:grid-cols-4">
<Suspense fallback={<CardSkeleton />}>
<CardWrapper />
</Suspense>
</div>
<div className="mt-6 grid grid-cols-1 gap-6 md:grid-cols-4 lg:grid-cols-8">
<Suspense fallback={<RevenueChartSkeleton />}>
<RevenueChart />
</Suspense>
<Suspense fallback={<LatestInvoicesSkeleton />}>
<LatestInvoices />
</Suspense>
</div>
</main>
);
}Step 2: CardWrapper 컴포넌트 생성
export default async function CardWrapper() {
const {
numberOfCustomers,
numberOfInvoices,
totalPaidInvoices,
totalPendingInvoices,
} = await fetchCardData();
return (
<>
<Card title="Collected" value={totalPaidInvoices} type="collected" />
<Card title="Pending" value={totalPendingInvoices} type="pending" />
<Card title="Total Invoices" value={numberOfInvoices} type="invoices" />
<Card
title="Total Customers"
value={numberOfCustomers}
type="customers"
/>
</>
);
}7.4 최종 결과
8. Suspense 경계 설정 가이드
8.1 고려사항
Suspense 경계를 어디에 놓을지 결정할 때 고려해야 할 사항들:
- 사용자 경험: 페이지가 스트리밍되는 동안 사용자가 어떻게 경험하길 원하는가?
- 우선순위: 어떤 콘텐츠를 우선순위로 두길 원하는가?
- 데이터 의존성: 컴포넌트가 데이터 Fetch에 의존하는가?
8.2 Best Practices
✅ 권장사항
- 데이터를 필요로 하는 컴포넌트에 데이터를 불러오는 메소드를 이동
- 해당 컴포넌트를 Suspense로 래핑
- 컴포넌트별 독립적인 로딩 상태 관리
⚠️ 상황에 따른 선택
- Section 또는 전체 페이지 스트리밍도 애플리케이션 요구사항에 따라 적절할 수 있음
- 정답은 없으며, 프로젝트의 특성과 사용자 요구사항에 맞게 결정
8.3 실습에서 적용한 전략
- 처음: 전체 페이지를
loading.tsx로 스트리밍 - 개선: 느린 컴포넌트로 인한 전체 지연을 방지하기 위해 개별 컴포넌트 스트리밍
- 최적화:
<Card/>컴포넌트의 popping 효과 방지를 위한 그룹화
결론
Next.js의 Streaming 기능을 통해 사용자 경험을 크게 개선할 수 있습니다. 핵심은 데이터 로딩 상태를 세밀하게 관리하고, 사용자가 기다리는 시간을 최소화하면서도 시각적으로 안정적인 인터페이스를 제공하는 것입니다.
핵심 포인트
- 페이지 레벨:
loading.tsx로 전체 페이지 스트리밍 - 컴포넌트 레벨:
<Suspense>로 세밀한 제어 - Route Groups: 경로별 로딩 상태 분리
- 컴포넌트 그룹화: 시각적 안정성 확보
이러한 기법들을 적절히 조합하여 사용자가 만족할 수 있는 웹 애플리케이션을 구축할 수 있습니다.
