Next.js 정적 렌더링 vs 동적 렌더링 가이드 🚀
이전 Chapter에서 대시보드 개요 페이지에 대한 데이터 fetch를 구현했습니다. 이번에는 정적 렌더링과 관련된 제한 사항을 해결해보겠습니다.
📋 해결해야 할 제한 사항
현재 설정에서 존재하는 두 가지 주요 문제점:
- ⚡ Request Waterfalls 패턴 문제
- 🔒 정적 렌더링으로 인한 데이터 변경 미반영 문제
오늘은 두 번째 문제인 정적 렌더링에 집중하여 해결 방법을 알아보겠습니다.
🏗️ 1. What is Static Rendering? (정적 렌더링이란?)
정적 렌더링은 데이터 fetch 및 렌더링이 서버에서 미리 수행되는 렌더링 방식입니다.
정적 렌더링 발생 시점
- 빌드(배포) 시간
- Revalidation 발생 시
- 데이터를 새로고침하거나 다시 로드하여 최신 데이터를 가져오는 프로세스
정적 렌더링 동작 과정
렌더링 결과물은 콘텐츠 전달 네트워크(CDN)에 분배되고 캐시되어 성능이 향상됩니다.
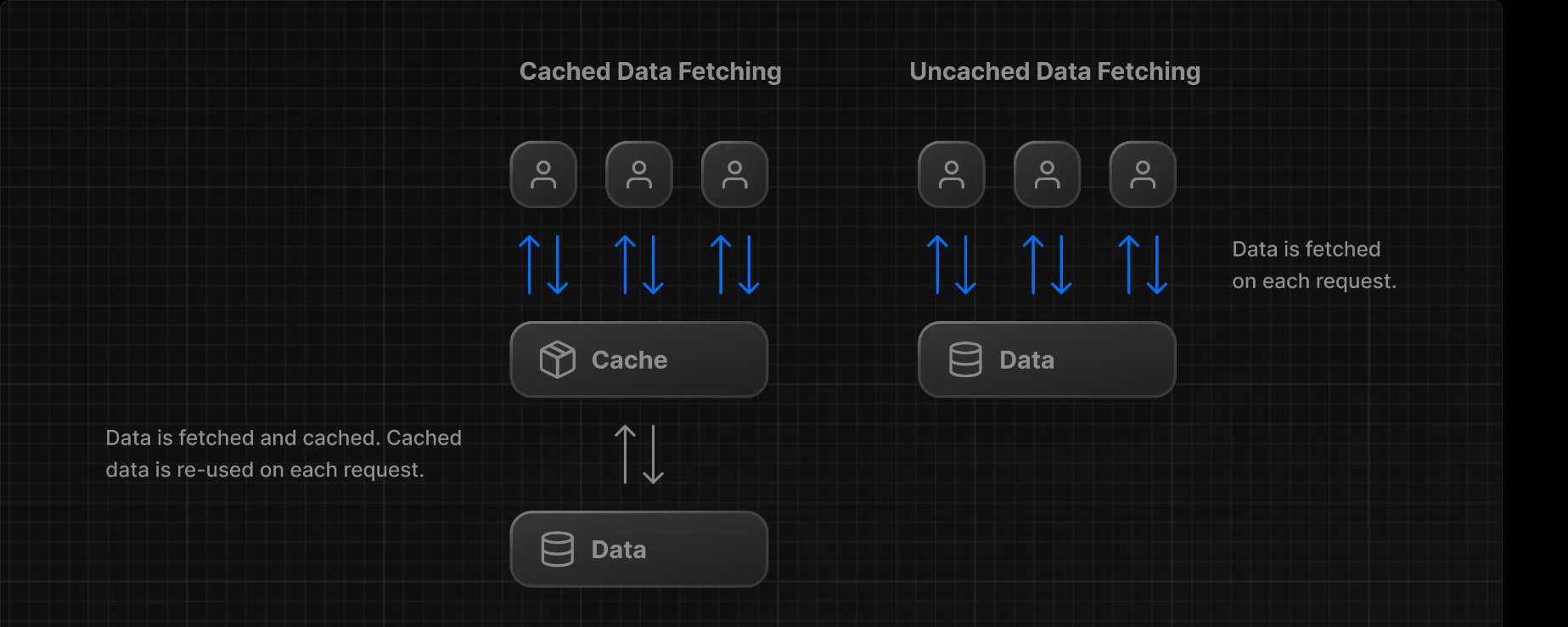
✅ 정적 렌더링의 장점
사용자가 페이지 방문 시마다 캐시된 결과가 제공되는 정적 렌더링의 주요 이점:
1. 🚀 더 빠른 웹사이트
- 미리 렌더링된 콘텐츠가 캐시됨
- 전 세계 사용자가 웹사이트 콘텐츠에 더 빠르고 신뢰성 있게 접근 가능
2. 💪 서버 부하 감소
- 콘텐츠가 캐시되어 서버가 각 사용자 요청에 동적으로 콘텐츠를 생성할 필요 없음
3. 🔍 SEO 최적화
- 미리 렌더링된 콘텐츠는 검색 엔진 크롤러가 쉽게 인덱싱 가능
- 검색 엔진 순위 향상에 유의미한 기여
⚡ 2. What is Dynamic Rendering? (동적 렌더링이란?)
동적 렌더링은 각 사용자의 요청 시점에서 서버에서 콘텐츠를 렌더링하는 방식입니다.
동적 렌더링 발생 시점
- 사용자가 페이지를 방문할 때
- 사용자의 요청이 발생할 때
💡 정적 vs 동적: 정적 렌더링은 빌드타임/revalidation 시, 동적 렌더링은 요청 시점에 발생
✅ 동적 렌더링의 장점
1. 📊 실시간 데이터 (Real-time Data)
- 애플리케이션이 실시간 혹은 자주 업데이트되는 데이터를 표시 가능
- 데이터가 자주 변경되는 애플리케이션에 이상적
2. 👤 사용자별 콘텐츠
- 대시보드나 사용자 프로필과 같은 개인화된 콘텐츠 제공
- 사용자 상호작용에 따른 데이터 업데이트가 정적 렌더링보다 유리
3. 🕐 요청 시간 정보
- 요청 시간에만 알 수 있는 정보에 액세스 가능
- 쿠키나 URL 검색 매개변수 등의 동적 정보 활용
🔧 3. Making the Dashboard Dynamic (대시보드를 동적으로 만들기)
Vercel Postgres의 캐싱 정책
기본적으로 @vercel/postgres는 자체 캐싱 의미론을 설정하지 않습니다. 이는 프레임워크가 자체 정적 및 동적 동작을 설정할 수 있도록 하기 위함입니다.
unstable_noStore 사용하기
Next.js API인 unstable_noStore를 사용하여 서버 컴포넌트나 데이터 Fetch 함수에서 정적 렌더링을 사용하지 않도록 설정할 수 있습니다.
구현 방법
/app/lib/data.ts 파일에서 next/cache 라이브러리의 unstable_noStore() 함수를 import하여 사용:
import { sql } from "@vercel/postgres";
import {
CustomerField,
CustomersTable,
InvoiceForm,
InvoicesTable,
LatestInvoiceRaw,
User,
Revenue,
} from "./definitions";
import { formatCurrency } from "./utils";
import { unstable_noStore as noStore } from "next/cache";
export async function fetchRevenue() {
// 🔥 응답이 캐시되지 않도록 설정
// fetch(..., {cache: 'no-store'})와 동일한 효과
noStore();
try {
const data = await sql<Revenue>`SELECT * FROM revenue`;
return data.rows;
} catch (error) {
console.error("Database Error:", error);
throw new Error("Failed to fetch revenue data.");
}
}
export async function fetchLatestInvoices() {
noStore();
try {
const data = await sql<LatestInvoiceRaw>`
SELECT invoices.amount, customers.name, customers.image_url, customers.email, invoices.id
FROM invoices
JOIN customers ON invoices.customer_id = customers.id
ORDER BY invoices.date DESC
LIMIT 5`;
const latestInvoices = data.rows.map((invoice) => ({
...invoice,
amount: formatCurrency(invoice.amount),
}));
return latestInvoices;
} catch (error) {
console.error("Database Error:", error);
throw new Error("Failed to fetch the latest invoices.");
}
}
export async function fetchCardData() {
noStore();
try {
const invoiceCountPromise = sql`SELECT COUNT(*) FROM invoices`;
const customerCountPromise = sql`SELECT COUNT(*) FROM customers`;
const invoiceStatusPromise = sql`SELECT
SUM(CASE WHEN status = 'paid' THEN amount ELSE 0 END) AS "paid",
SUM(CASE WHEN status = 'pending' THEN amount ELSE 0 END) AS "pending"
FROM invoices`;
const data = await Promise.all([
invoiceCountPromise,
customerCountPromise,
invoiceStatusPromise,
]);
const numberOfInvoices = Number(data[0].rows[0].count ?? "0");
const numberOfCustomers = Number(data[1].rows[0].count ?? "0");
const totalPaidInvoices = formatCurrency(data[2].rows[0].paid ?? "0");
const totalPendingInvoices = formatCurrency(data[2].rows[0].pending ?? "0");
return {
numberOfCustomers,
numberOfInvoices,
totalPaidInvoices,
totalPendingInvoices,
};
} catch (error) {
console.error("Database Error:", error);
throw new Error("Failed to card data.");
}
}
// 기타 함수들에도 noStore() 적용
const ITEMS_PER_PAGE = 6;
export async function fetchFilteredInvoices(
query: string,
currentPage: number
) {
noStore();
const offset = (currentPage - 1) * ITEMS_PER_PAGE;
try {
const invoices = await sql<InvoicesTable>`
SELECT
invoices.id,
invoices.amount,
invoices.date,
invoices.status,
customers.name,
customers.email,
customers.image_url
FROM invoices
JOIN customers ON invoices.customer_id = customers.id
WHERE
customers.name ILIKE ${`%${query}%`} OR
customers.email ILIKE ${`%${query}%`} OR
invoices.amount::text ILIKE ${`%${query}%`} OR
invoices.date::text ILIKE ${`%${query}%`} OR
invoices.status ILIKE ${`%${query}%`}
ORDER BY invoices.date DESC
LIMIT ${ITEMS_PER_PAGE} OFFSET ${offset}
`;
return invoices.rows;
} catch (error) {
console.error("Database Error:", error);
throw new Error("Failed to fetch invoices.");
}
}
export async function fetchInvoicesPages(query: string) {
noStore();
try {
const count = await sql`SELECT COUNT(*)
FROM invoices
JOIN customers ON invoices.customer_id = customers.id
WHERE
customers.name ILIKE ${`%${query}%`} OR
customers.email ILIKE ${`%${query}%`} OR
invoices.amount::text ILIKE ${`%${query}%`} OR
invoices.date::text ILIKE ${`%${query}%`} OR
invoices.status ILIKE ${`%${query}%`}
`;
const totalPages = Math.ceil(Number(count.rows[0].count) / ITEMS_PER_PAGE);
return totalPages;
} catch (error) {
console.error("Database Error:", error);
throw new Error("Failed to fetch total number of invoices.");
}
}
export async function fetchInvoiceById(id: string) {
noStore();
try {
const data = await sql<InvoiceForm>`
SELECT
invoices.id,
invoices.customer_id,
invoices.amount,
invoices.status
FROM invoices
WHERE invoices.id = ${id};
`;
const invoice = data.rows.map((invoice) => ({
...invoice,
amount: invoice.amount / 100,
}));
return invoice[0];
} catch (error) {
console.error("Database Error:", error);
}
}
export async function fetchCustomers() {
noStore();
try {
const data = await sql<CustomerField>`
SELECT
id,
name
FROM customers
ORDER BY name ASC
`;
const customers = data.rows;
return customers;
} catch (err) {
console.error("Database Error:", err);
throw new Error("Failed to fetch all customers.");
}
}
export async function fetchFilteredCustomers(query: string) {
noStore();
try {
const data = await sql<CustomersTable>`
SELECT
customers.id,
customers.name,
customers.email,
customers.image_url,
COUNT(invoices.id) AS total_invoices,
SUM(CASE WHEN invoices.status = 'pending' THEN invoices.amount ELSE 0 END) AS total_pending,
SUM(CASE WHEN invoices.status = 'paid' THEN invoices.amount ELSE 0 END) AS total_paid
FROM customers
LEFT JOIN invoices ON customers.id = invoices.customer_id
WHERE
customers.name ILIKE ${`%${query}%`} OR
customers.email ILIKE ${`%${query}%`}
GROUP BY customers.id, customers.name, customers.email, customers.image_url
ORDER BY customers.name ASC
`;
const customers = data.rows.map((customer) => ({
...customer,
total_pending: formatCurrency(customer.total_pending),
total_paid: formatCurrency(customer.total_paid),
}));
return customers;
} catch (err) {
console.error("Database Error:", err);
throw new Error("Failed to fetch customer table.");
}
}
export async function getUser(email: string) {
noStore();
try {
const user = await sql`SELECT * from USERS where email=${email}`;
return user.rows[0] as User;
} catch (error) {
console.error("Failed to fetch user:", error);
throw new Error("Failed to fetch user.");
}
}🎯 noStore() 함수의 효과
unstable_noStore() 함수를 사용함으로써:
- ❌ 응답이 캐시되지 않도록 설정
- ✅ 항상 최신 데이터를 가져올 수 있게 됨
- 🔄 동적 렌더링으로 전환
🐌 4. Simulating a Slow Data Fetch (느린 데이터 가져오기 시뮬레이션)
대시보드를 동적으로 만드는 것은 좋은 선택이지만, 여전히 해결되지 않은 문제가 있습니다:
❓ 핵심 문제: 다른 모든 데이터 요청보다 하나의 데이터 요청이 느리게 처리된다면?
시뮬레이션 구현
데이터를 느리게 가져오는 것을 시뮬레이션하기 위해 /app/lib/data.ts 파일에서 fetchRevenue() 함수를 수정합니다:
export async function fetchRevenue() {
try {
// 🚨 데모 목적으로 인위적인 지연 추가
// 실제 프로덕션에서는 사용하지 마세요!
console.log("Fetching revenue data...");
await new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, 3000));
const data = await sql<Revenue>`SELECT * FROM revenue`;
console.log("Data fetch complete after 3 seconds.");
return data.rows;
} catch (error) {
console.error("Database Error:", error);
throw new Error("Failed to fetch revenue data.");
}
}🔍 시뮬레이션 결과 확인
코드 변경 후 http://localhost:3000/dashboard 페이지를 새 탭에서 열면:
- 페이지 로드가 확실히 느려짐을 체감할 수 있습니다
- 터미널에서 로그 확인이 가능합니다:
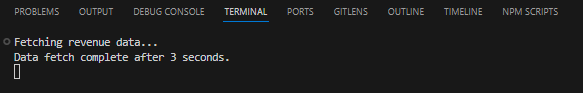
⚠️ 발견된 문제점
인위적인 3초 지연을 추가한 결과:
- 🚫 데이터를 가져오는 3초 동안 페이지가 완전히 차단됨
- 😞 사용자는 빈 화면을 보며 대기해야 함
- 📉 전체 애플리케이션 성능에 치명적 영향
🎯 해결해야 할 핵심 과제
개발자로서 해결해야 할 공통적인 문제들:
1. 🚀 성능 문제
- 페이지를 동적으로 만들었지만 느린 데이터 Fetch가 애플리케이션 성능에 큰 영향을 미침
2. 👤 사용자 경험 개선
- 데이터 요청이 느린 경우 사용자 경험을 개선할 수 있는 방법은 없을까?
3. 🔄 로딩 상태 관리
- 사용자에게 진행 상황을 알려줄 수 있는 방법이 필요
📝 다음 단계 미리보기
이러한 문제들을 해결하기 위한 방법들:
- 🔄 Streaming: 페이지의 일부분을 먼저 로드하고 나머지는 점진적으로 로드
- ⏳ Loading States: 사용자에게 로딩 상태를 명확히 표시
- 🎭 Suspense: React의 Suspense를 활용한 비동기 컴포넌트 처리
- 🧩 컴포넌트 분리: 독립적인 데이터 로딩으로 병목 현상 방지
다음 Chapter에서는 이러한 해결책들을 구체적으로 구현해보겠습니다! 🚀
