1. Hand Bone Image Dataset
1.1 Overview
목표 : X-ray 이미지에서 사람의 손 뼈를 Segmentation 하는 인공지능 만들기
Input : 손 뼈가 담긴 X-ray image
Output : 각 pixel 좌표에 따른 class 값
1.2 Data Format
Image file format
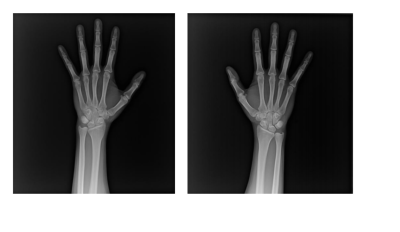
➢ 한 사람의 왼손, 오른손에 해당하는 X-ray 제공
➢ 2048 x 2048 size
➢ 3 channel
Annotation file format
➢ Segmentation mask가 points로 제공됨
➢ Polygon의 좌표는 .json의 ‘points’ 에 점으로 표시

2. EDA
2.1 Class 분석
Segmentation class 종류
손가락 / 손등/ 팔로 구성. 29개의 뼈 종류 존재
각 Class의 비율
- 클래스 별 Pixel 차지 비율
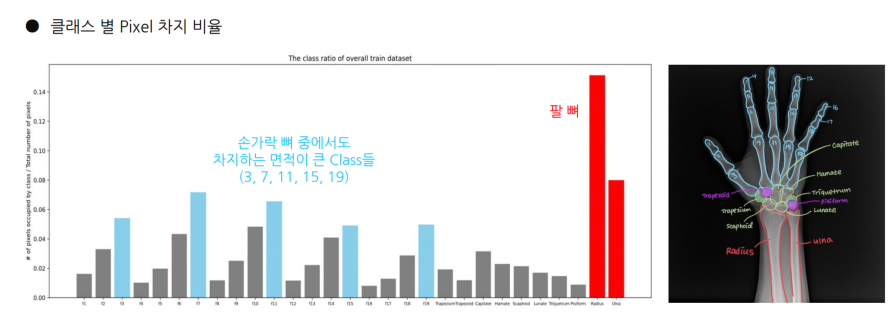
- Train dataset 내 주요 Class에 대한 분포
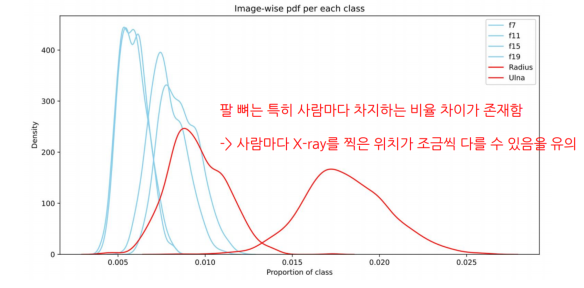
Multi-label 분석
한 pixel에 여러개의 class가 등장할 수 있음을 유의
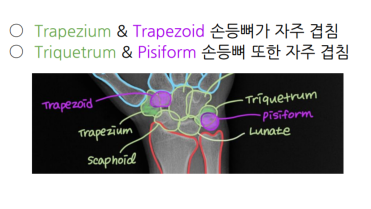
위 이미지는 어느 뼈들이 겹치는지를 보여주는 이미지.
어떤 뼈가 겹치는지를 보여주는 시각화
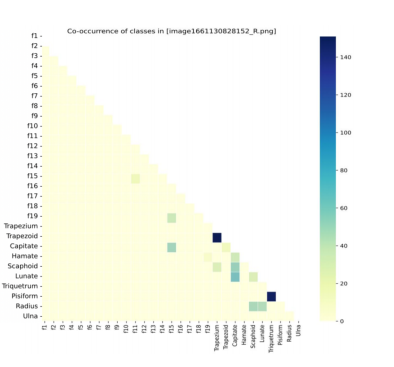
2.2 Meta 분석
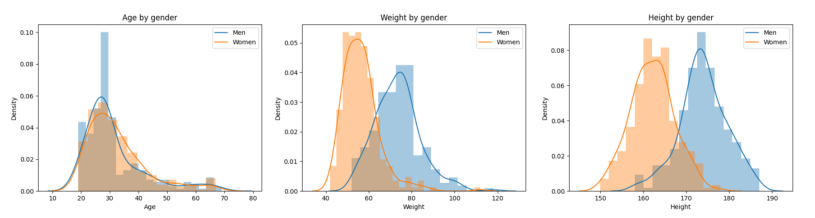
Meta data
550명에 대한 키/몸무게/성별/나이 Meta data 존재
-> 이를 이용해 Multi-modal을 설계하는 것을 고려해볼 수 있음
3. 평가 Metric
3.1 Dice
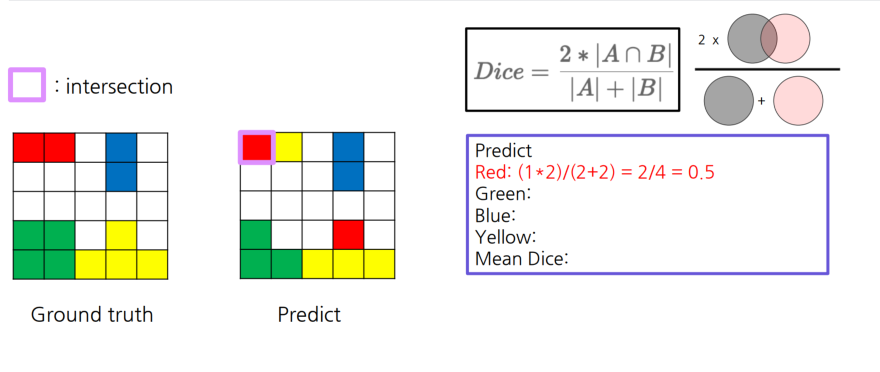
픽셀 겹친거를 계산
위 이미지를 예시로 들어보면 A= GT, B = Predicted
2*1/(2+2) 해서 2/4 = 1/2 임을 알 수 있다.
Dice Code
import torch
def dice_coef(y_true, y_pred):
# Flattening the spatial dimensions
y_true_f = y_true.flatten(2)
y_pred_f = y_pred.flatten(2)
# Calculating the intersection
intersection = torch.sum(y_true_f * y_pred_f, dim=-1)
# Small constant to avoid division by zero
eps = 0.0001
# Calculating the Dice coefficient
return (2. * intersection + eps) / (torch.sum(y_true_f, dim=-1) + torch.sum(y_pred_f, dim=-1) + eps)
4. Baseline Code
4.1 DataLoader
• init : Filenames, labelnames, is_train, transform 선언
• len : 총 dataset의 개수를 반환
• getitem : Image, label을 전처리 후 하나씩 load
class XRayDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, filenames, labelnames, transforms=None, is_train=False):
self.filenames = filenames # 각 이미지 경로가 담긴 list
self.labelnames = labelnames # 각 라벨 경로가 담긴 list
self.is_train = is_train # train 할지 말지
self.transforms = transforms # Transform 하고 싶은 작업
def __len__(self):
return len(self.filenames)
def __getitem__(self, item): # Dataloader에서 사용할 data를 반환하는 부분
image_name = self.filenames[item]
image_path = os.path.join(IMAGE_ROOT, image_name)
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
image = image / 255.
label_name = self.labelnames[item]
label_path = os.path.join(LABEL_ROOT, label_name)
# process a label of shape (H, W, NC)
label_shape = tuple(image.shape[:2]) + (len(CLASSES),)
label = np.zeros(label_shape, dtype=np.uint8)
# read label file
with open(label_path, "r") as f:
annotations = json.load(f)
annotations = annotations["annotations"]
# iterate each class
for ann in annotations:
c = ann["label"]
class_ind = CLASS2IND[c]
points = np.array(ann["points"])
# polygon to mask
class_label = np.zeros(image.shape[:2], dtype=np.uint8)
cv2.fillPoly(class_label, [points], 1) #cv2.fillpoly 함수 사용(point들을 mask로 변환하는 과정)
label[..., class_ind] = class_label
if self.transforms is not None:
inputs = {"image": image, "mask": label} if self.is_train else {"image": image} #train_mode일때 변환된 Image와 label data전환/ train_mode가 아닐때는 변환된 Image과 원본Label data 변환
result = self.transforms(**inputs)
image = result["image"]
label = result["mask"] if self.is_train else label
# to tensor will be done later
image = image.transpose(2, 0, 1) # make channel first
label = label.transpose(2, 0, 1)
image = torch.from_numpy(image).float()
label = torch.from_numpy(label).float()
return image, label
Train/valid split:Group K-fold 이용
동일 인물의 손이 train/valid에 같이 들어가는 걸 방지.
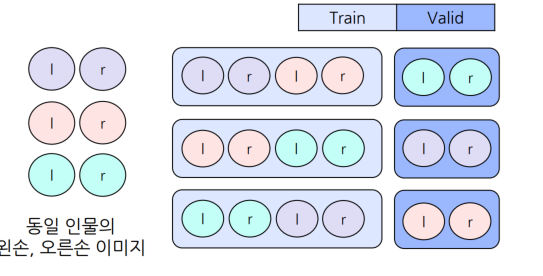
# 각 파일의 디렉토리 이름을 그룹으로 설정
groups = [os.path.dirname(fname) for fname in pngs]
ys = [0 for fname in pngs] # 타겟 값은 필요 없으므로 모두 0으로 설정
# 전체 데이터의 20%를 validation 데이터로 사용하기 위해 n_splits=5 설정
gkf = GroupKFold(n_splits=5)
train_filenames = []
train_labelnames = []
valid_filenames = []
valid_labelnames = []
# GroupKFold를 사용하여 데이터 분할
for i, (train_index, valid_index) in enumerate(gkf.split(pngs, ys, groups)):
# 0번을 validation dataset으로 사용
if i == 0:
valid_filenames += [pngs[idx] for idx in valid_index]
valid_labelnames += [jsons[idx] for idx in valid_index]
else:
train_filenames += [pngs[idx] for idx in train_index]
train_labelnames += [jsons[idx] for idx in train_index]Dataloader 정의
Train, valid에 사용할 torch dataloader를 정의
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
# 데이터셋 생성
train_dataset = XRayDataset(train_filenames, train_labelnames, transforms=tf, is_train=True)
valid_dataset = XRayDataset(valid_filenames, valid_labelnames, transforms=tf, is_train=False)
# 데이터로더 생성
train_loader = DataLoader(
dataset=train_dataset,
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
shuffle=True,
num_workers=8,
drop_last=True,
)
valid_loader = DataLoader(
dataset=valid_dataset,
batch_size=1,
shuffle=False,
num_workers=2,
drop_last=False,
)
4.2 Model
Torchvision을 이용한 Pretrained model 불러오기 및 output class 수정
from torchvision import models
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
# Pretrained FCN model with ResNet50 backbone
model = models.segmentation.fcn_resnet50(pretrained=True)
# Adjust the classifier's output layer to match the number of classes
model.classifier[4] = nn.Conv2d(512, len(CLASSES), kernel_size=1)
# Test the model with a sample input
input = torch.rand([1, 3, 512, 512])
output = model(input)["out"]
print(output.shape) # Expected output shape
4.3 Loss / optimizer 설정
Loss : BCEWithLogitsLoss( )//Optimizer : Adam( )
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
# Loss function 정의
criterion = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss() #Binary CrossEntropy 이진분류
# Optimizer 정의
optimizer = optim.Adam(params=model.parameters(), lr=LR, weight_decay=1e-6)- 멀티클래스 분류용 손실 함수
CrossEntropyLoss (nn.CrossEntropyLoss): 멀티클래스 분류에서 자주 사용하는 손실 함수로, 내부적으로 소프트맥스 처리를 포함하여 여러 클래스 간의 확률 분포를 비교합니다. - 이진 분류용 손실 함수
BCEWithLogitsLoss (nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss): 이진 분류에서 사용하며, 내부적으로 시그모이드를 적용하여 0과 1 사이의 확률로 변환한 후, 이진 크로스 엔트로피를 계산합니다.
4.4 Train / validation 함수 정의
Train
def train(model, data_loader, val_loader, criterion, optimizer):
print(f'Start training..')
model = model.cuda()
n_class = len(CLASSES)
best_dice = 0.
for epoch in range(NUM_EPOCHS):
model.train()
for step, (images, masks) in enumerate(data_loader):
# gpu 연산을 위해 device 할당
images, masks = images.cuda(), masks.cuda()
# inference
outputs = model(images)['out']
# loss 계산
loss = criterion(outputs, masks)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
- 정해진 epoch만큼 model을 이용해 forward 수행
- 앞서 정의한 loss와 optimizer로 backward 수행
Validation
def dice_coef(y_true, y_pred):
y_true_f = y_true.flatten(2)
y_pred_f = y_pred.flatten(2)
intersection = torch.sum(y_true_f * y_pred_f, -1)
eps = 0.0001
return (2. * intersection + eps) / (torch.sum(y_true_f, -1) + torch.sum(y_pred_f, -1) + eps)
def validation(epoch, model, data_loader, criterion, thr=0.5):
print(f'Start validation #{epoch:2d}')
model.eval()
dices = []
with torch.no_grad():
n_class = len(CLASSES)
total_loss = 0
cnt = 0
for step, (images, masks) in tqdm(enumerate(data_loader), total=len(data_loader)):
images, masks = images.cuda(), masks.cuda()
model = model.cuda()
outputs = model(images)['out']
output_h, output_w = outputs.size(-2), outputs.size(-1)
mask_h, mask_w = masks.size(-2), masks.size(-1)
# Restore original size
if output_h != mask_h or output_w != mask_w:
outputs = F.interpolate(outputs, size=(mask_h, mask_w), mode="bilinear")
loss = criterion(outputs, masks)
total_loss += loss
cnt += 1
outputs = torch.sigmoid(outputs)
outputs = (outputs > thr).detach().cpu()
masks = masks.detach().cpu()
dice = dice_coef(outputs, masks)
dices.append(dice)
dices = torch.cat(dices, 0)
dices_per_class = torch.mean(dices, 0)
dice_str = [
f"{c:12}: {d.item():.4f}"
for c, d in zip(CLASSES, dices_per_class)
]
dice_str = "\n".join(dice_str)
print(dice_str)
avg_dice = torch.mean(dices_per_class).item()
return avg_dice
- Sigmoid 함수를 사용해 predict된 값을 0~1 범위로 변환이 후, threshold(=0.5) 초과의 prediction 값은 1로, 나머지는 0으로 설정
4.5 학습 시키기
train(model, train_loader, valid_loader, criterion, optimizer)4.6 Best model 불러오기
저장된 모델 불러오기
def save_model(model, file_name='fcn_resnet50_best_model.pt'):
output_path = os.path.join(SAVED_DIR, file_name)
torch.save(model, output_path)
# Training loop
if (epoch + 1) % VAL_EVERY == 0:
dice = validation(epoch + 1, model, val_loader, criterion)
if best_dice < dice: #여기서 best_dice model 를 저장하는것.
print(f"Best performance at epoch: {epoch + 1}, {best_dice:.4f} -> {dice:.4f}")
print(f"Save model in {SAVED_DIR}")
best_dice = dice
save_model(model)
4.7 Test (Inference)
Test dataloader
class XRayInferenceDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, filenames, transforms=None):
_filenames = np.array(sorted(filenames))
self.filenames = _filenames
self.transforms = transforms
def __len__(self):
return len(self.filenames)
def __getitem__(self, item):
image_name = self.filenames[item]
image_path = os.path.join(IMAGE_ROOT, image_name)
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
image = image / 255.
if self.transforms is not None:
inputs = {"image": image}
result = self.transforms(**inputs)
image = result["image"]
# to tensor will be done later
image = image.transpose(2, 0, 1) # make channel first
image = torch.from_numpy(image).float()
return image, image_name
Test function
import torch.nn.functional as F
def test(model, data_loader, thr=0.5):
model = model.cuda()
model.eval()
rles = []
filename_and_class = []
with torch.no_grad():
n_class = len(CLASSES)
for step, (images, image_names) in tqdm(enumerate(data_loader), total=len(data_loader)):
images = images.cuda()
outputs = model(images)['out']
# Restore original size
outputs = F.interpolate(outputs, size=(2048, 2048), mode="bilinear") # .interpolate는 주어진 텐서를 특정 크기로 보간(크기 조정)하는 함수입니다. 여기서는 모델의 출력인 outputs 텐서를 (2048, 2048) 크기로 보간하여 원본 이미지 크기에 맞추고 있습니다
outputs = torch.sigmoid(outputs)
outputs = (outputs > thr).detach().cpu().numpy()
for output, image_name in zip(outputs, image_names):
for c, segm in enumerate(output):
rle = encode_mask_to_rle(segm)
rles.append(rle)
filename_and_class.append(f"{IND2CLASS[c]}_{image_name}")
return rles, filename_and_class
RLE(Run-Length-Encoding)
Submission file size를 줄이기 위해 각 pixel 값 대신 ‘start position, total length’로 output을 저장
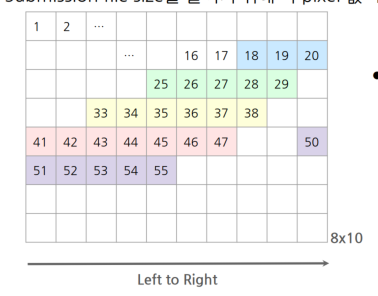

4.8 Submission
RLE적용코드
for output, image_name in zip(outputs, image_names):
for c, segm in enumerate(output):
rle = encode_mask_to_rle(segm)
rles.append(rle)
filename_and_class.append(f"{IND2CLASS[c]}_{image_name}")
대회는 RLE 인코딩을 이용해 csv 파일로 저장해 제출하는 형식이다.
