AD CA Setup & Sign intune PowerShell Script
0. Overview
One of my clients has decided to change their PowerShell execution policy to AllSigned.
As a result, any PowerShell scripts executed through Intune are now required to be digitally signed, and script signature validation must be enforced at runtime.
We initially considered signing the scripts with a public certificate, but due to the associated cost and the short renewal cycle, we decided instead to deploy an internal Active Directory Certificate Authority (AD CA) to handle the code signing ourselves.
-
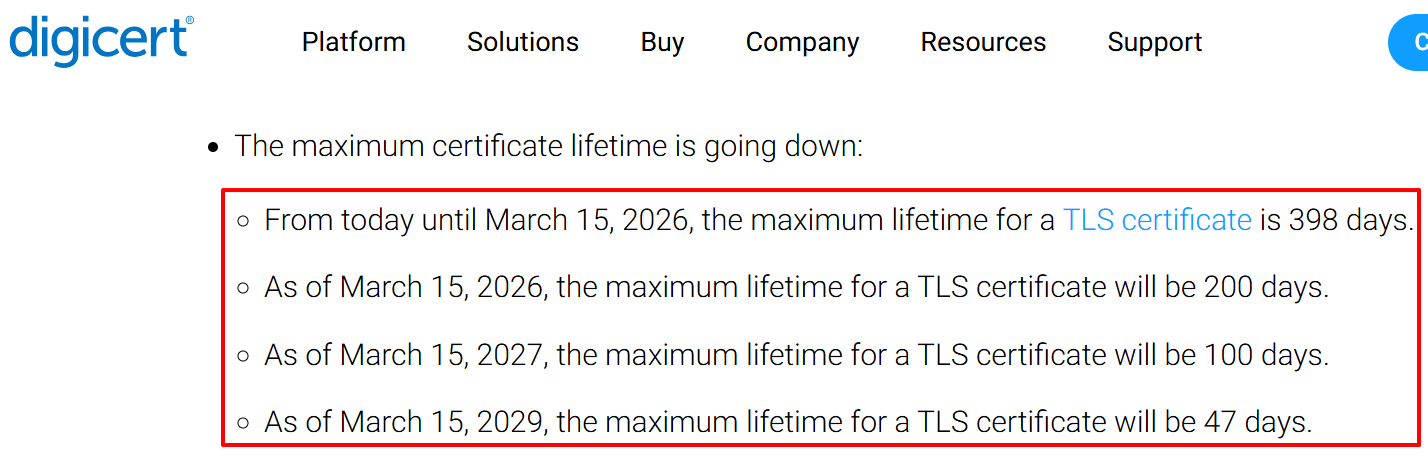
ref) https://www.digicert.com/blog/tls-certificate-lifetimes-will-officially-reduce-to-47-days
-
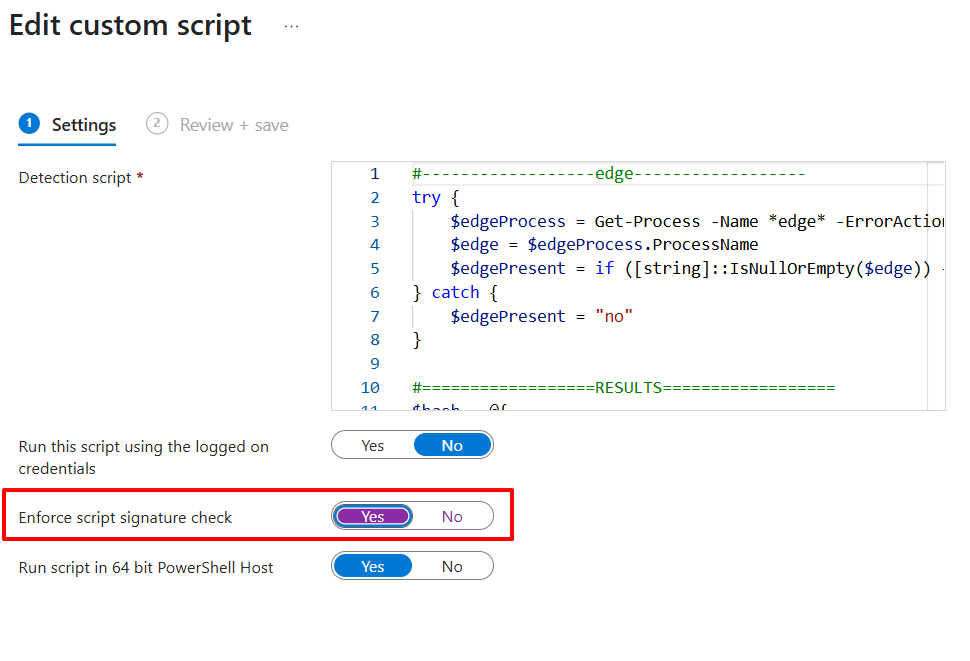
ref) 'Enforce script signature check' from Intune
1. AD CA Configuration
1. Install CA feature
Check Active directory Certificate Services
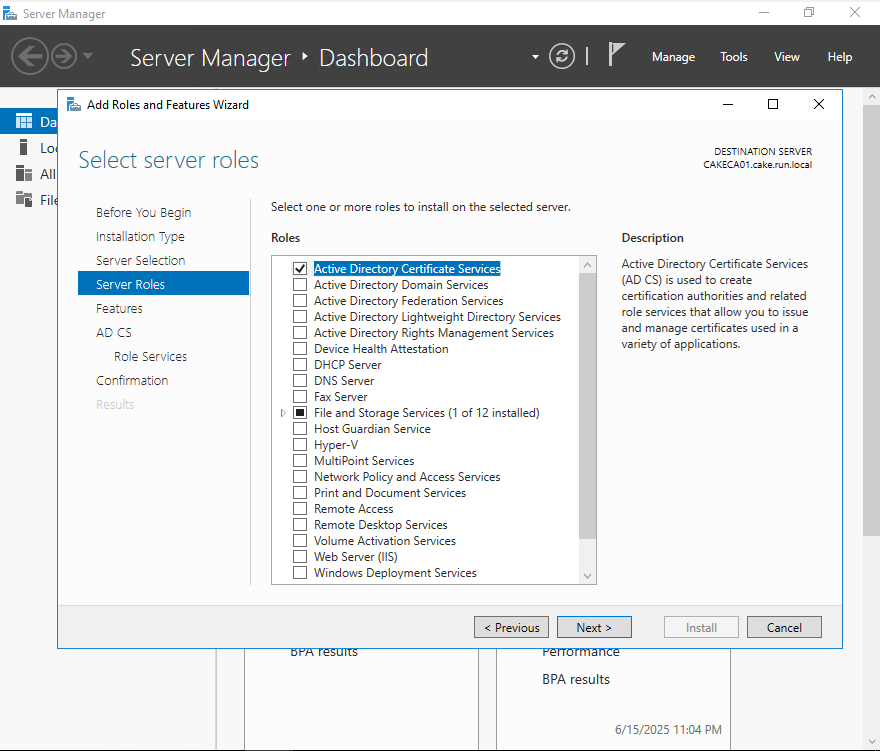
Check 'Certificate Authority' and 'Certificate Authority Web Enrollment'
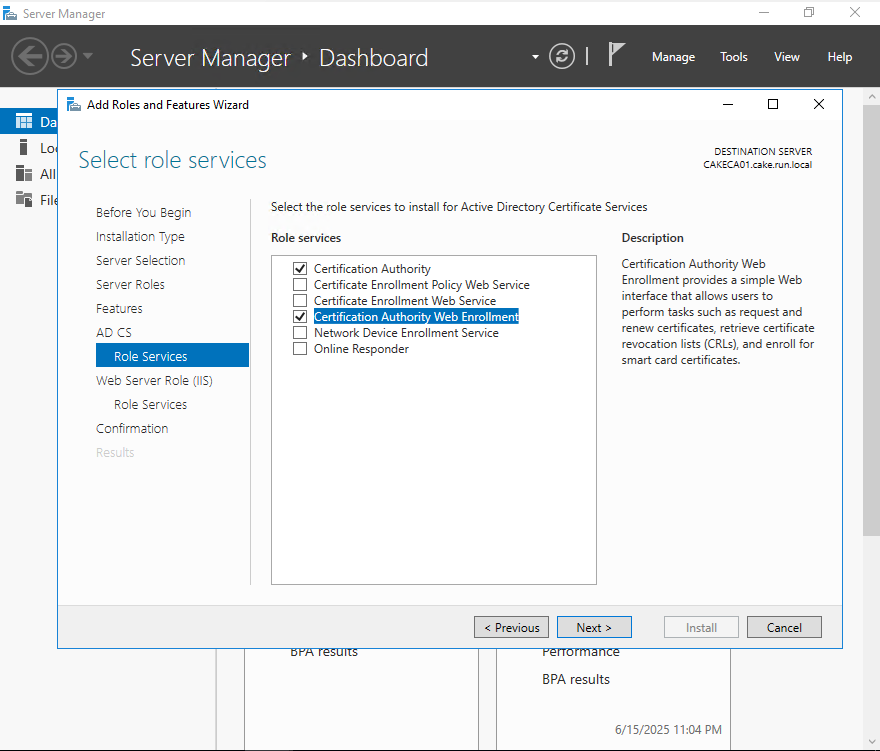
Check 'Certificate Authority' and 'Certification Authority Web Enrollment'
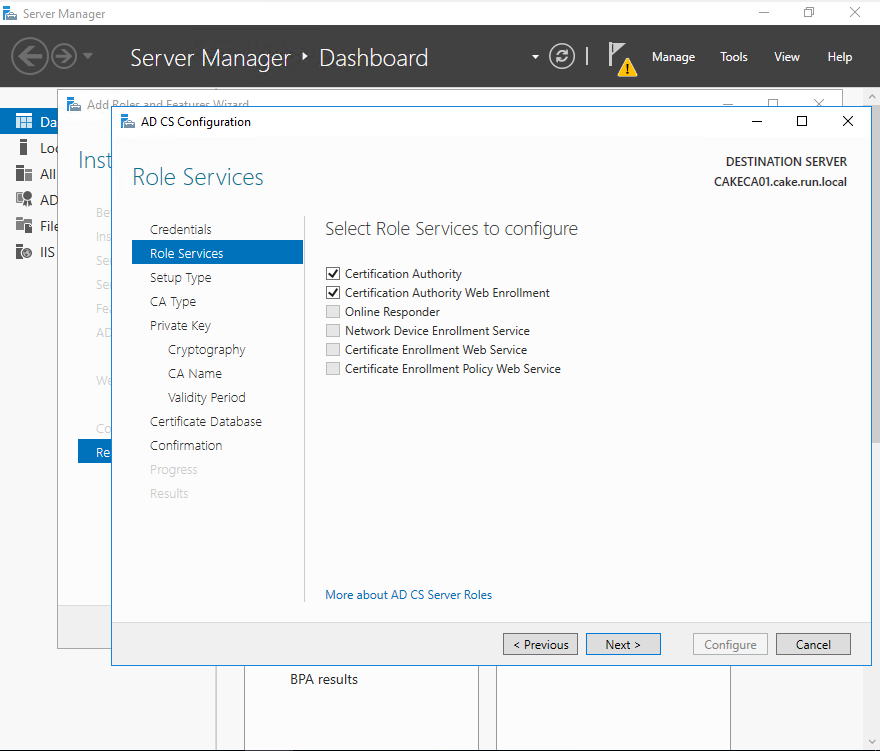
Make sure to select Enterprise CA!!
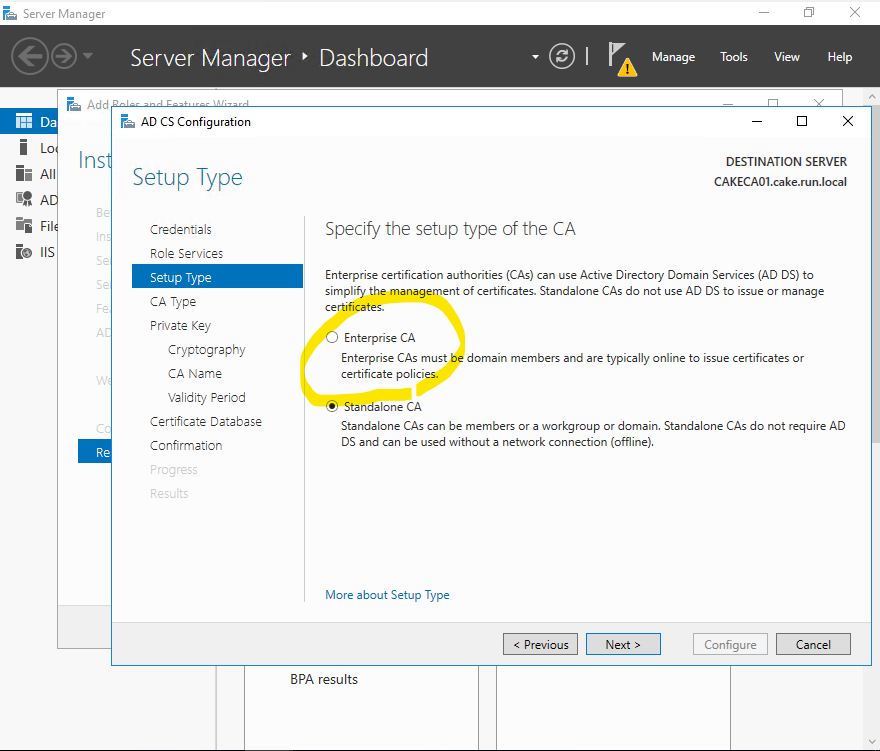
Click Next
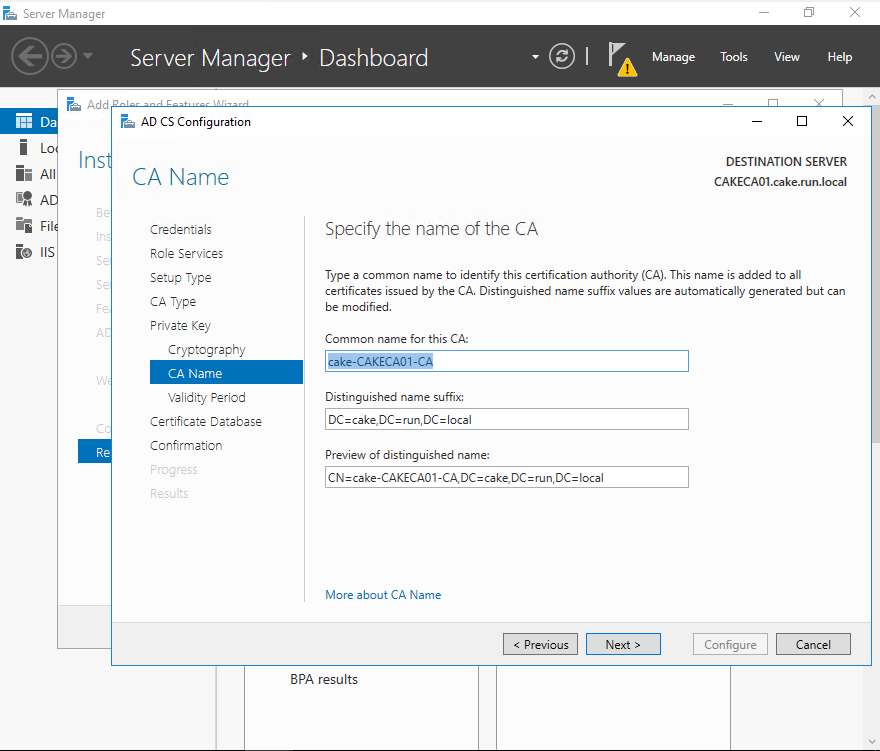
Set CN of CA
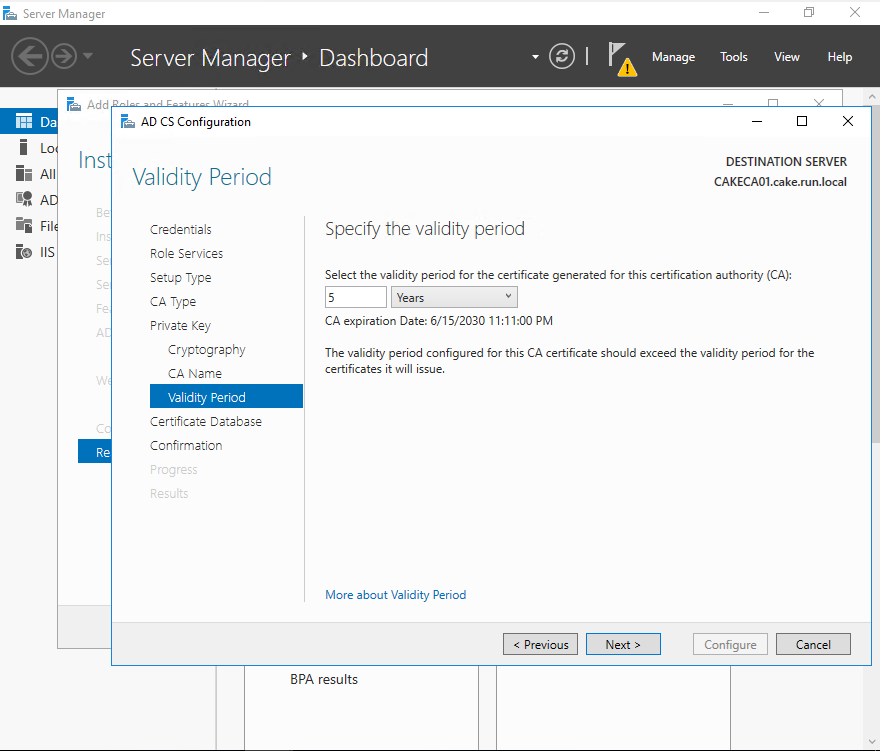
Select the validity period of the CA.
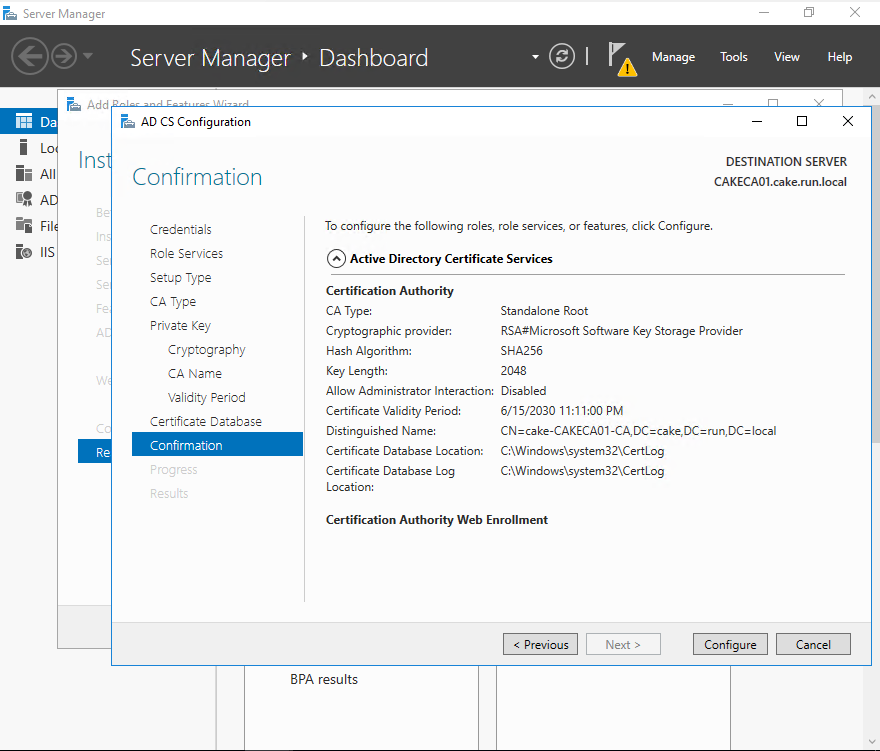
It's finished and close the window.
2. Create the code signing certificate template
Once the installation has finished successfully, go servermanager > Tools > Certificate Authority.
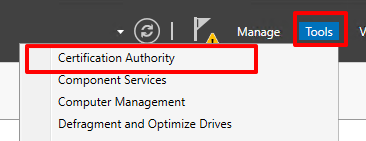
Go Certificate Template > Manage under the CN of the CA drop down list.
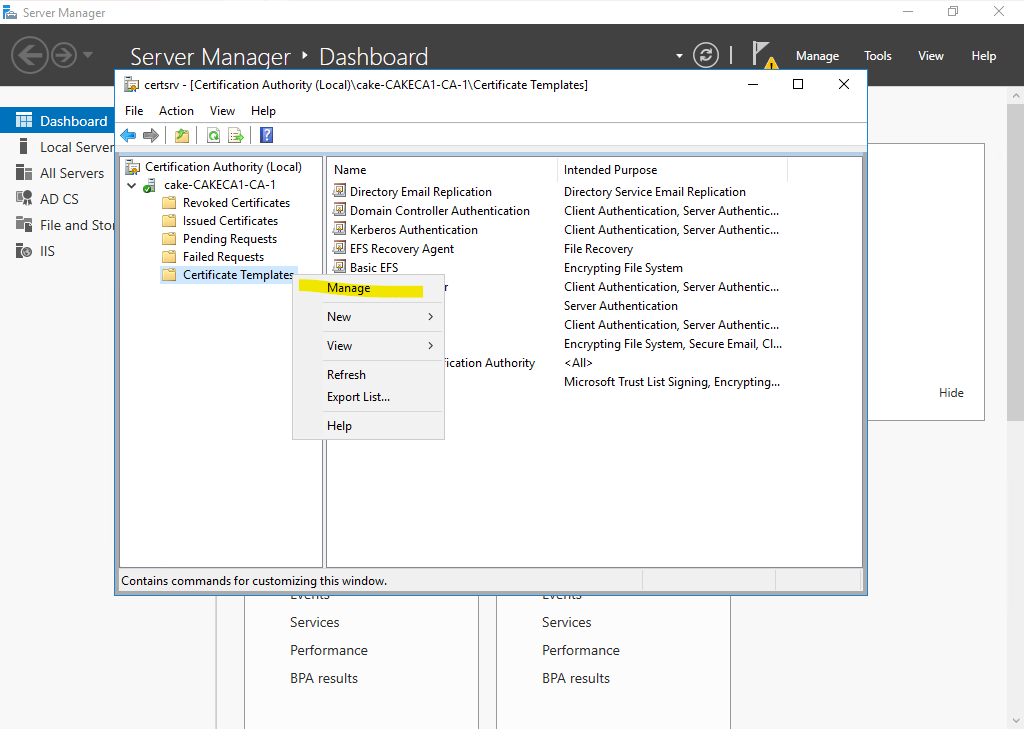
And Code Signing > (Right Click) Duplicate Template. Well, you can use this template directly but you can create your own template with duplicate from this one.
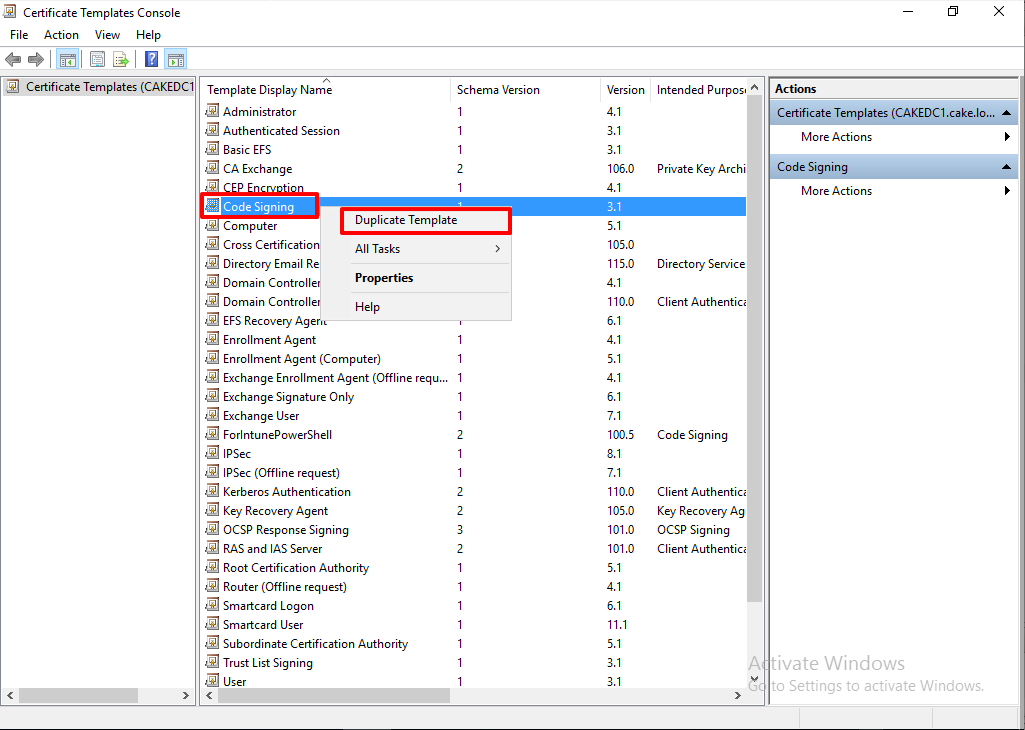
In General tab, set Template name and the validity of the certificate.
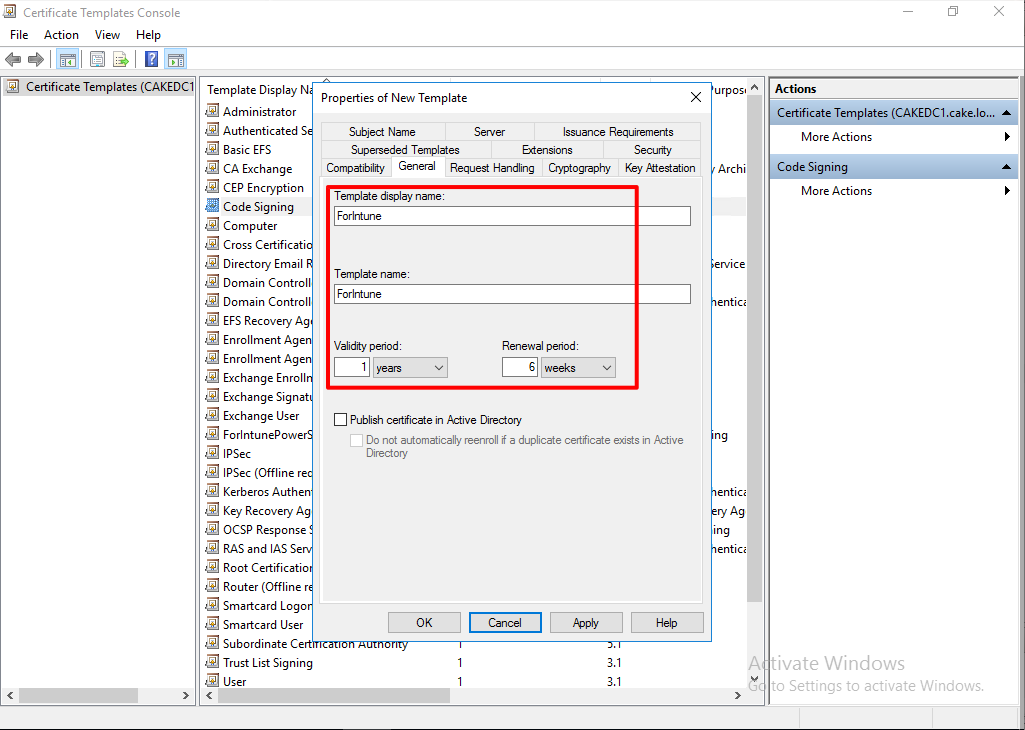
In Request Handling tab, select the options.
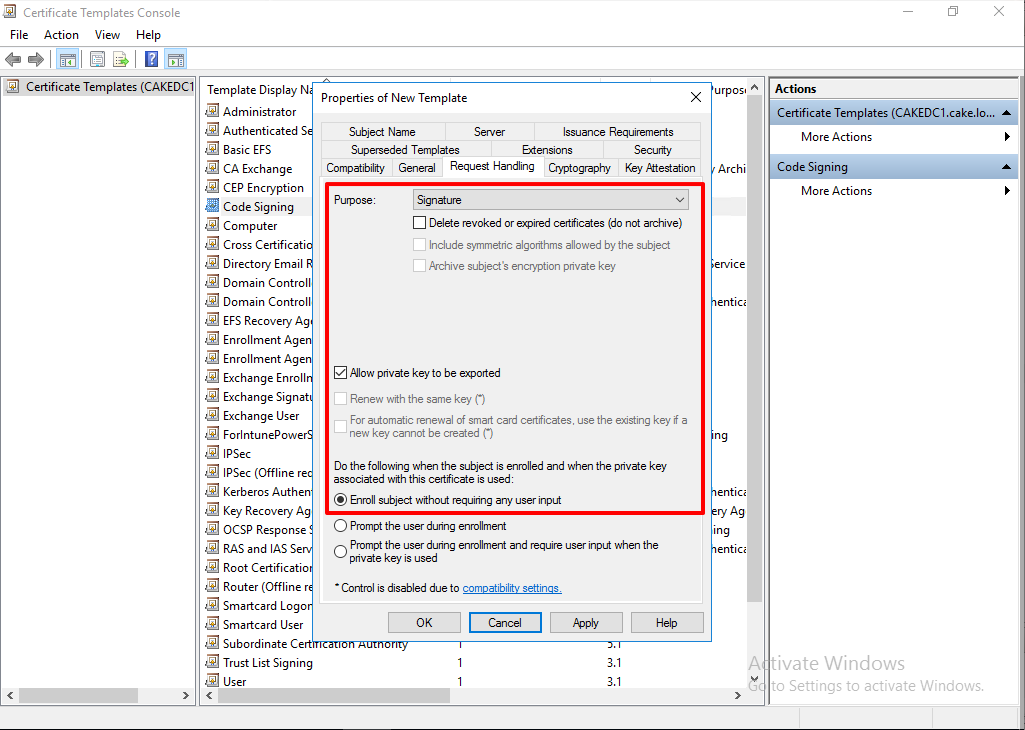
In Subject Name, Select CN as Subject name format.
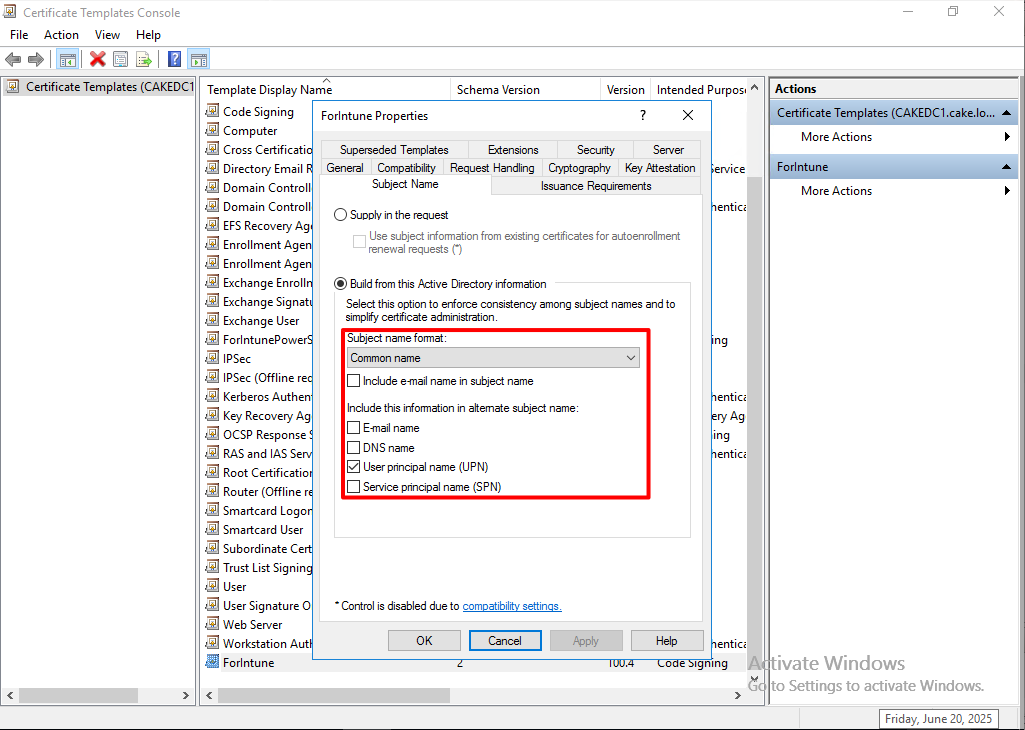
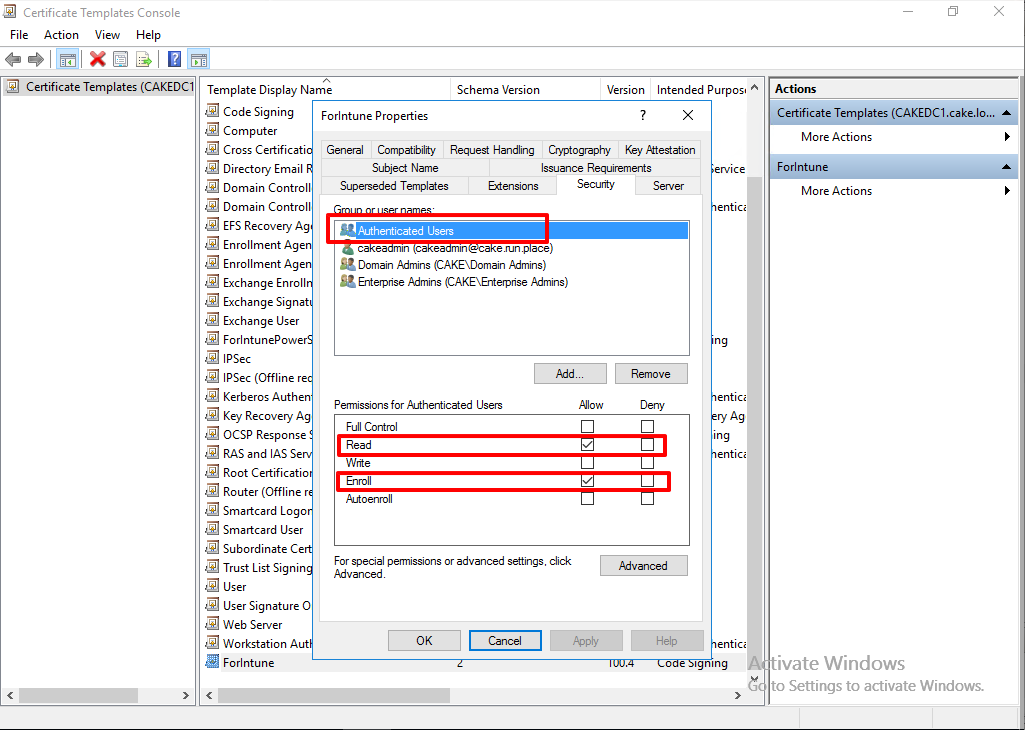
In Security tab, I allow read and write permissions to Authenticated Users.
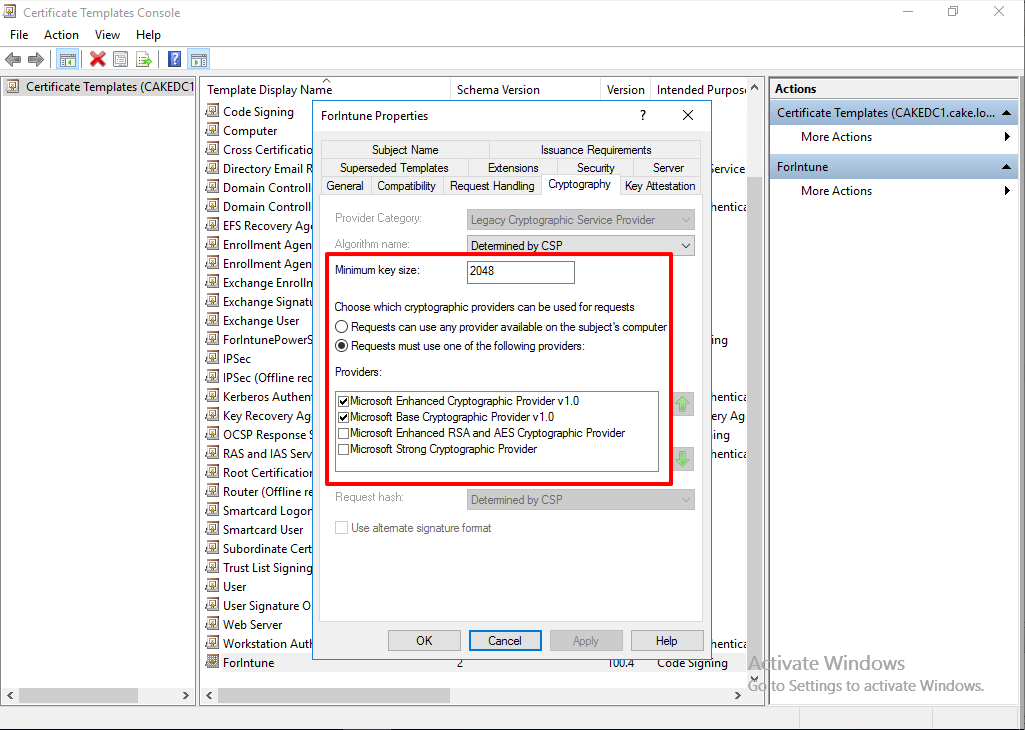
Lastly, In Cryptography tab, I just let them as default. Click 'Apply' and 'OK' for save.
So here is the our customed certificate for the Code Signing.
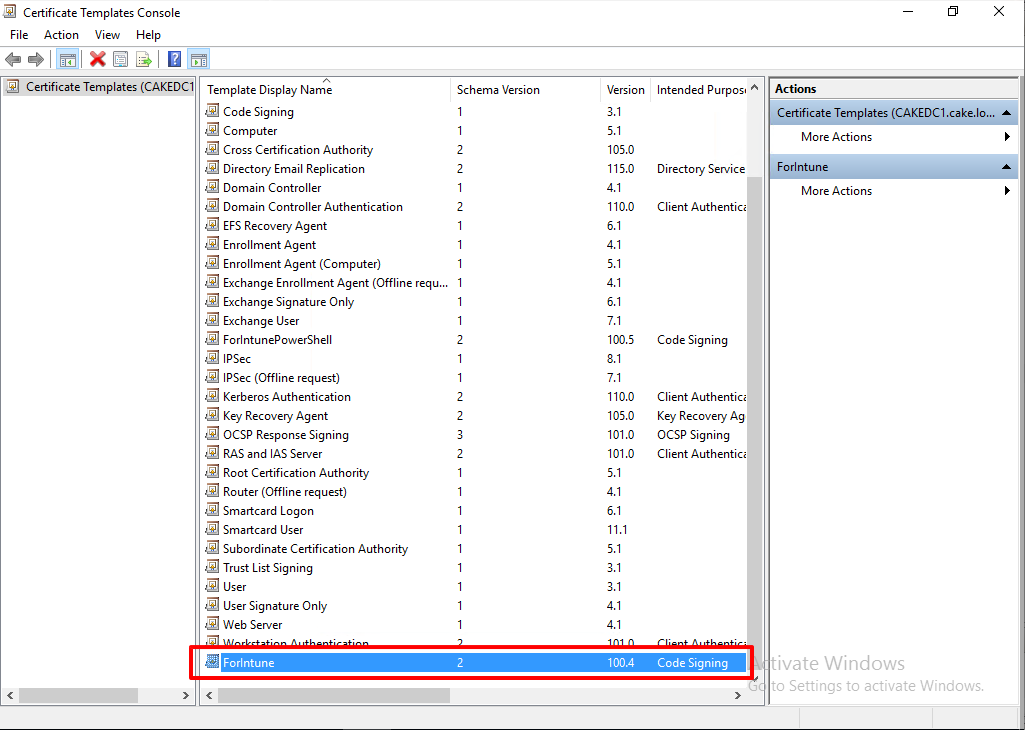
3. Adding to the Certificate Templates
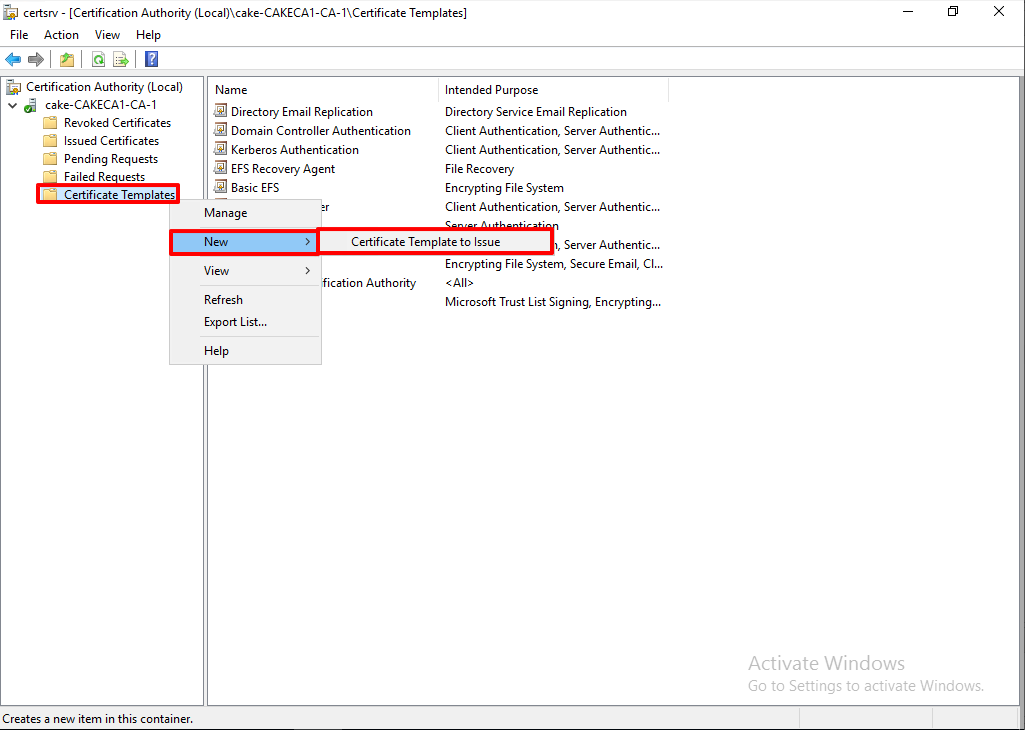
Now we have created the customed template, we have to issue the template to issue.
Go Certificate Template > (Right Click) New > Certificate Template to Issue.
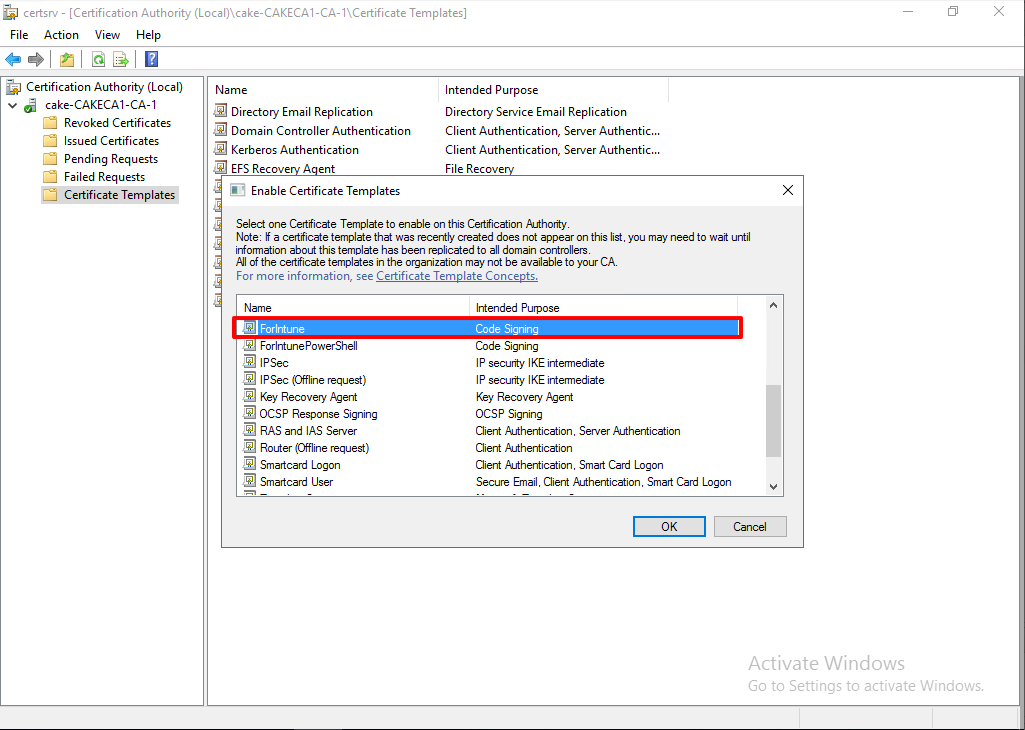
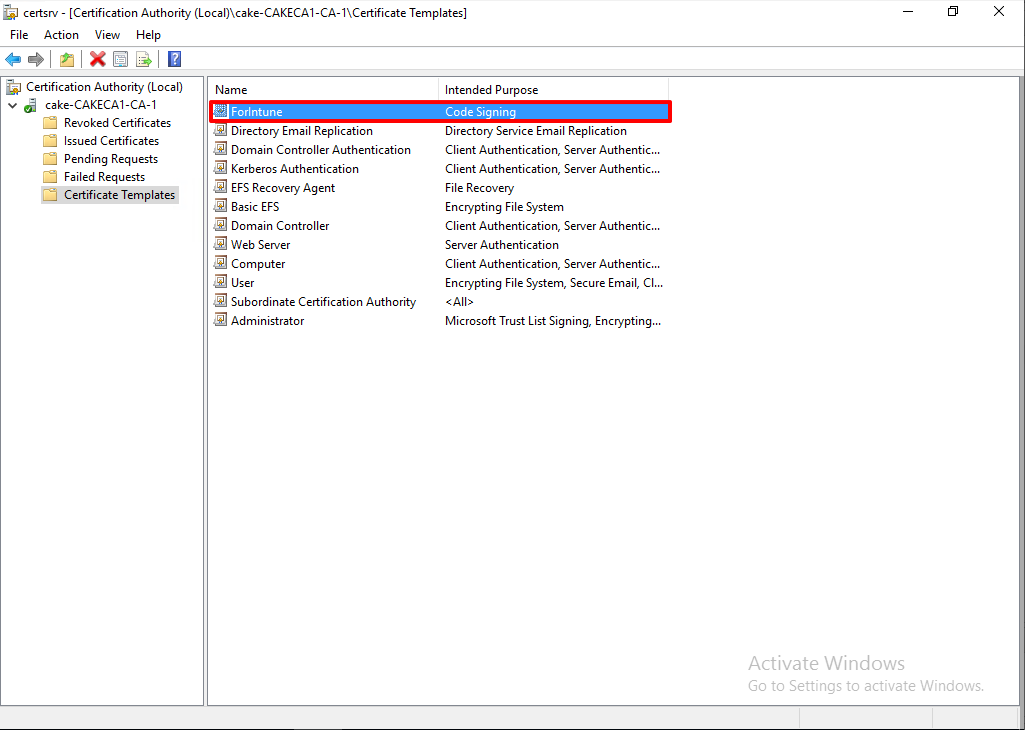
Find the 'ForIntune' from the list and click 'OK' to add the Certificate Templates.
2. From AD DC, Request Certificate
Go to AD DC, and add snap in certificate with Current User. Go (Right Click) Personal > All Tasks > Request new Certificate.
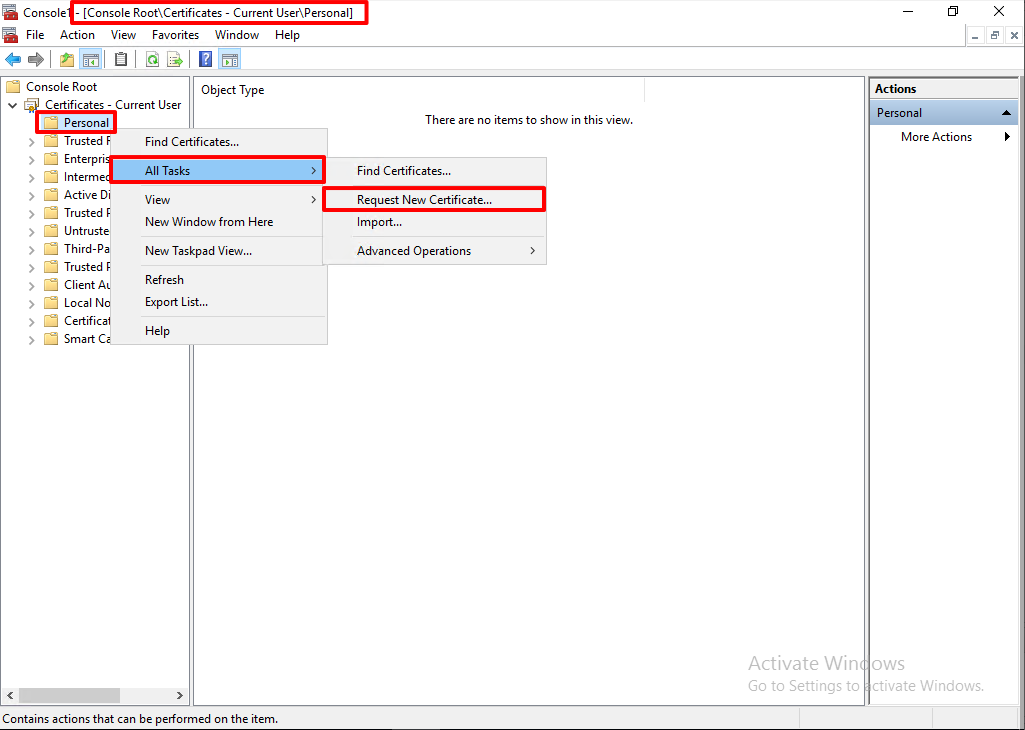
Next
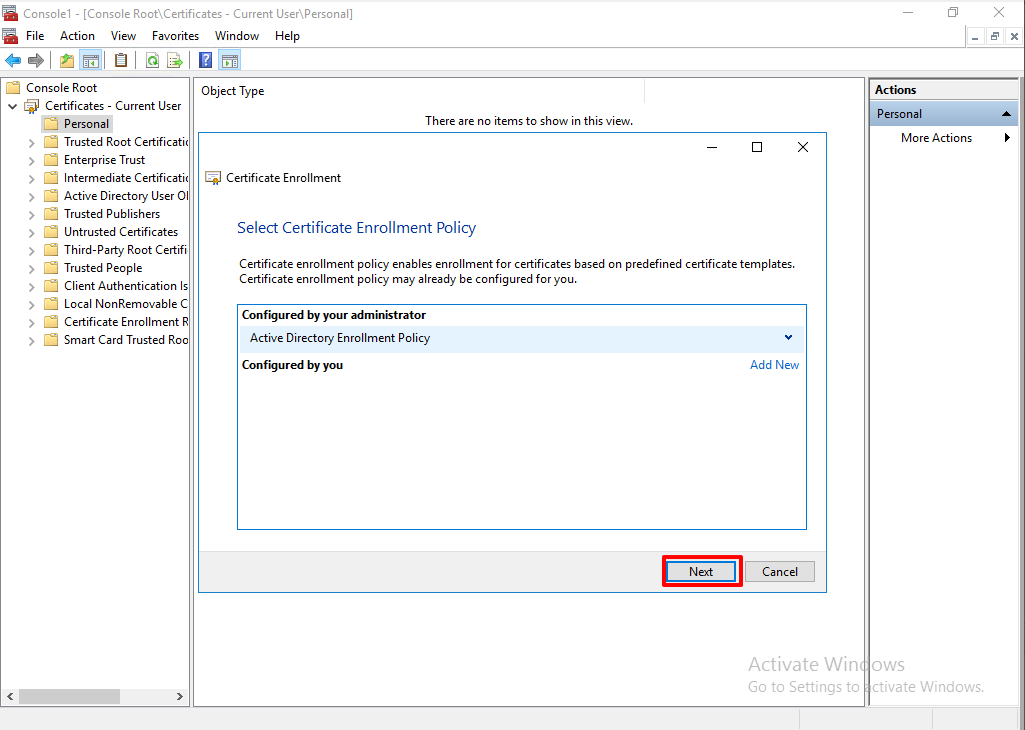
Select 'ForIntune' and Click 'Enroll'
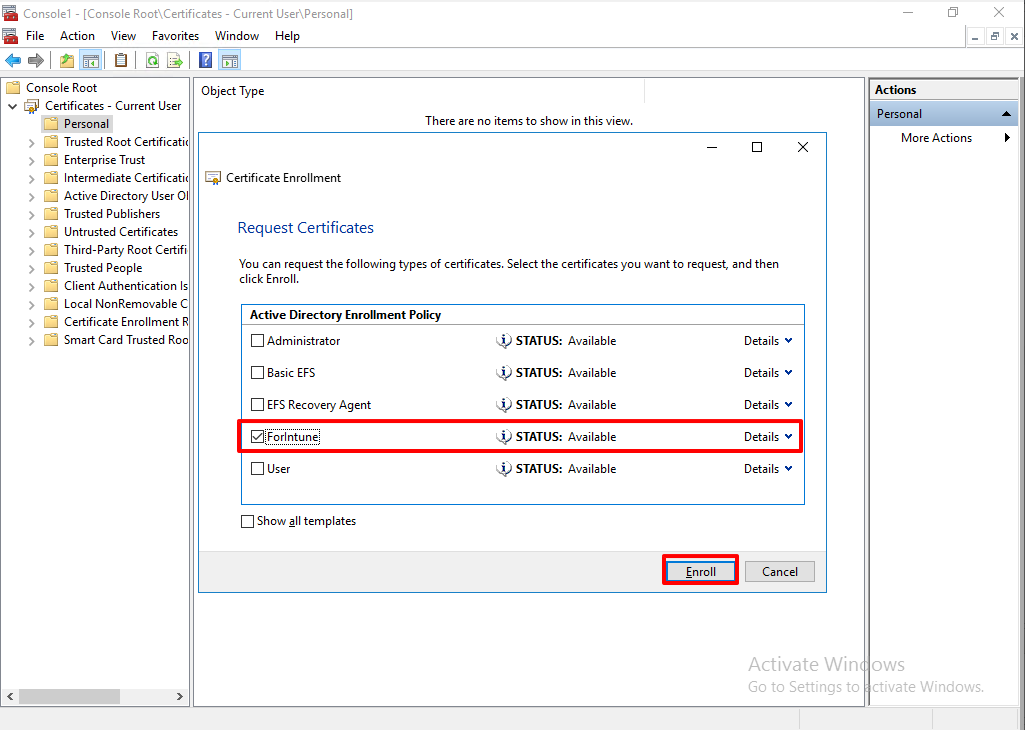
Certificate installation Enrollment has been succeed from AD CA.
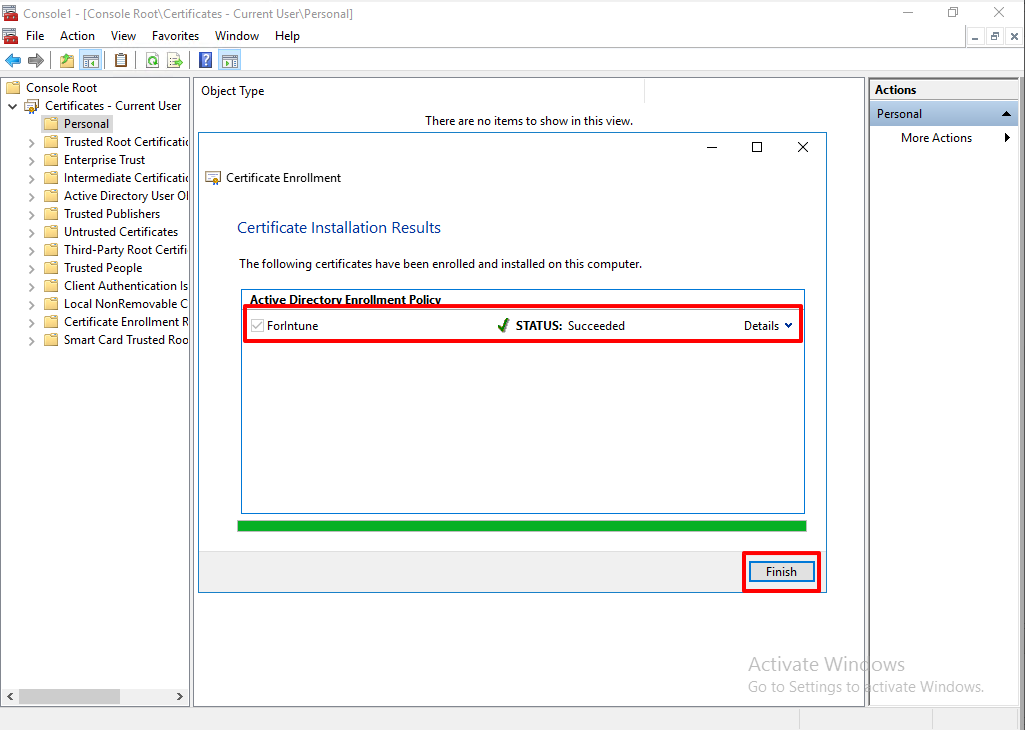
So, we got a new directory under the 'Personal' and the Cod Signing certificate as well.
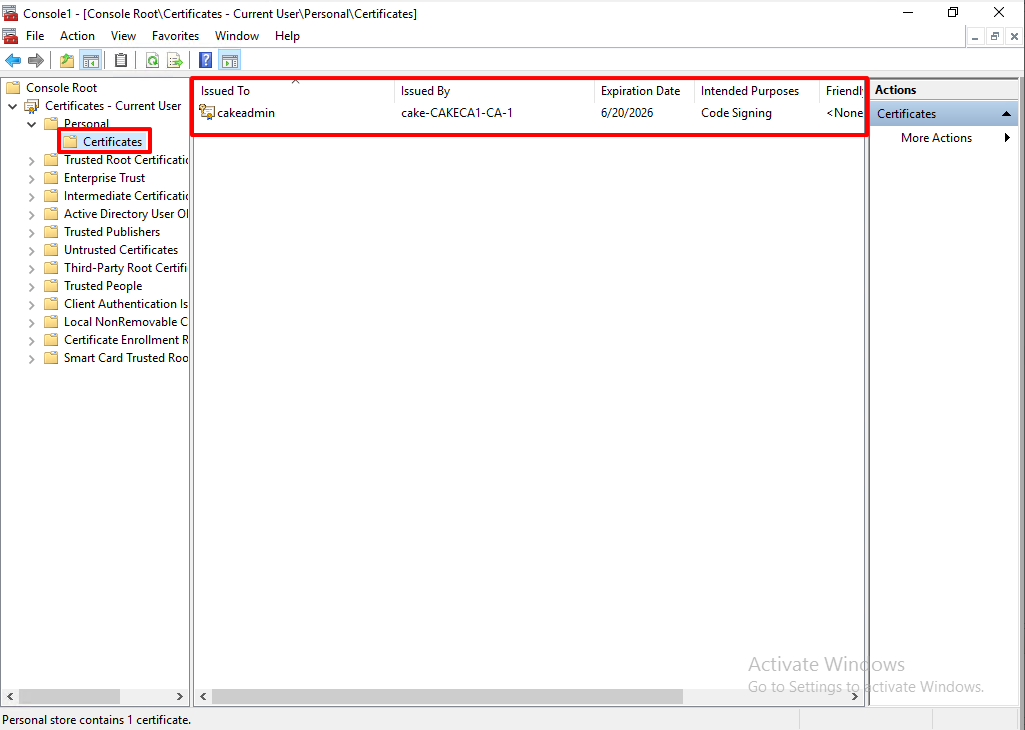
I just add friendly name to the certificate.
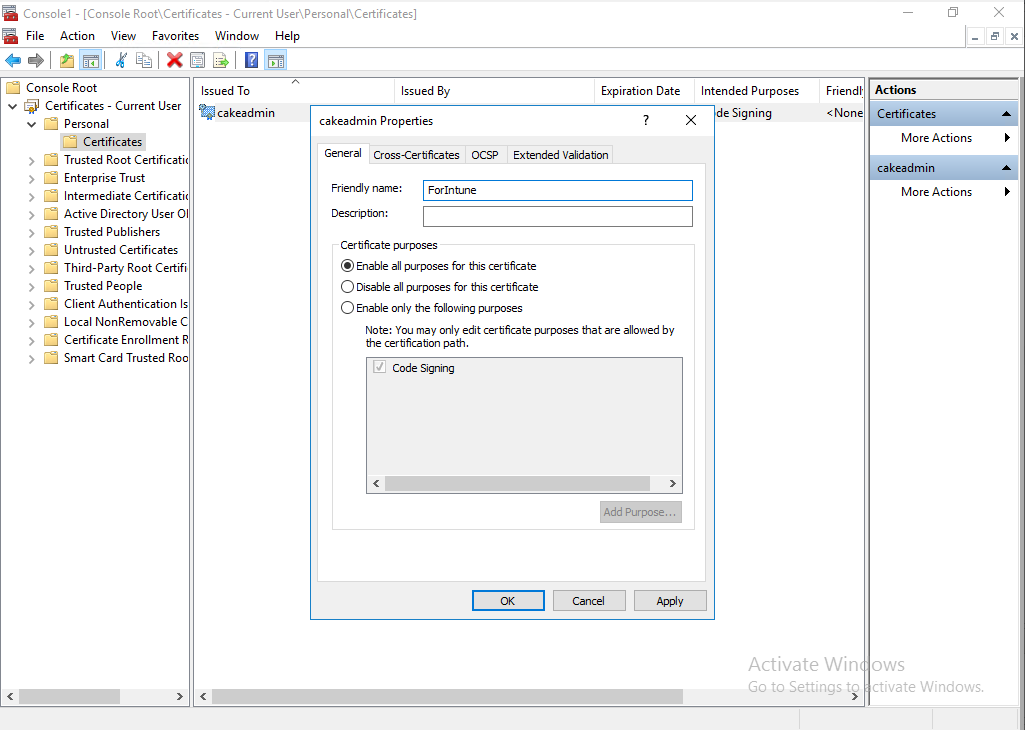
3. Signing the script
1. Signing
Now let's sign the script. First of all, we must identify the script. Use this command.
'Cert:\CurrentUser\My" is the path in the command where we issed the certificate under the personal.
Get-ChildItem "Cert:\CurrentUser\My" | fl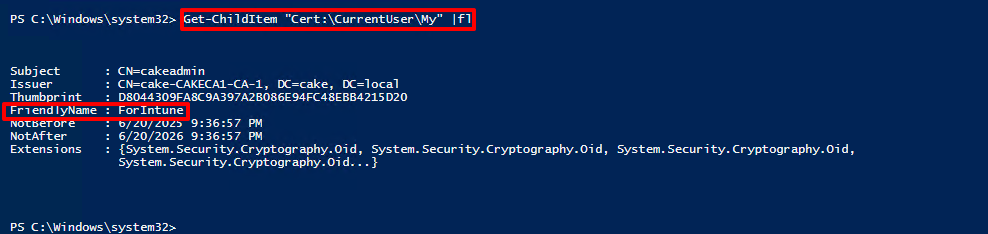
Assign the certificate to a variable. Refer following command.
$certificate = Get-ChildItem "Cert:\CurrentUser\My" | Where-Object {$_.Thumbprint -eq "Thumbprint"}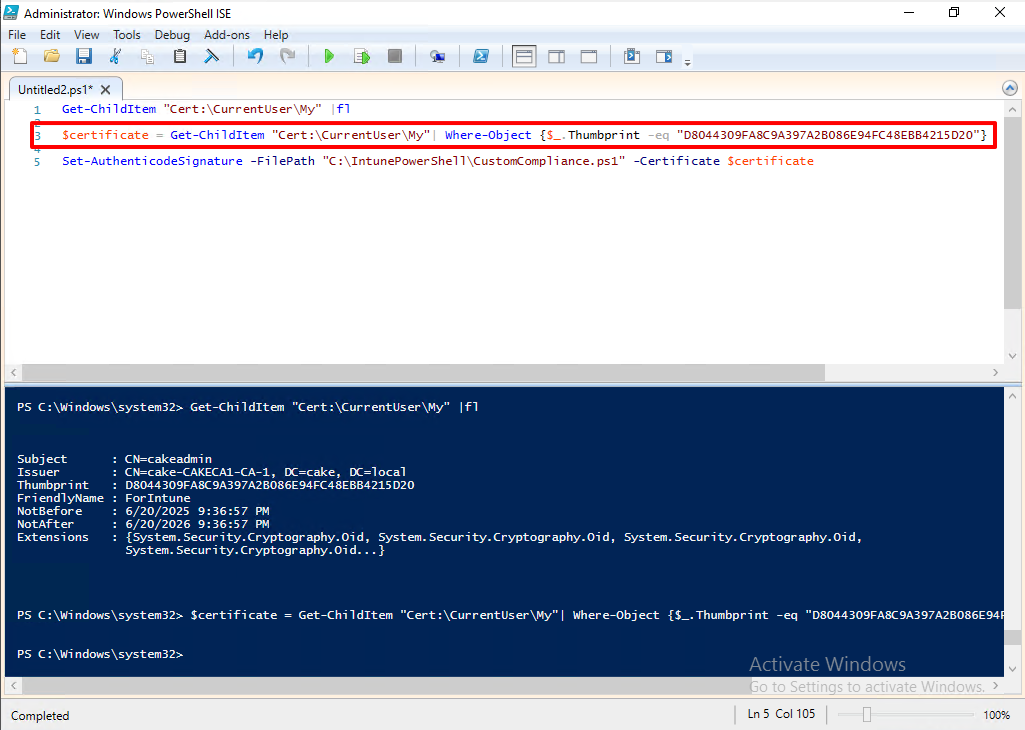
We are ready to go. Execute following command to sign the PowerShell script.
Set-AuthenticodeSignature -FilePath "C:\IntunePowerShell\CustomCompliance.ps1 -Certificate $certificate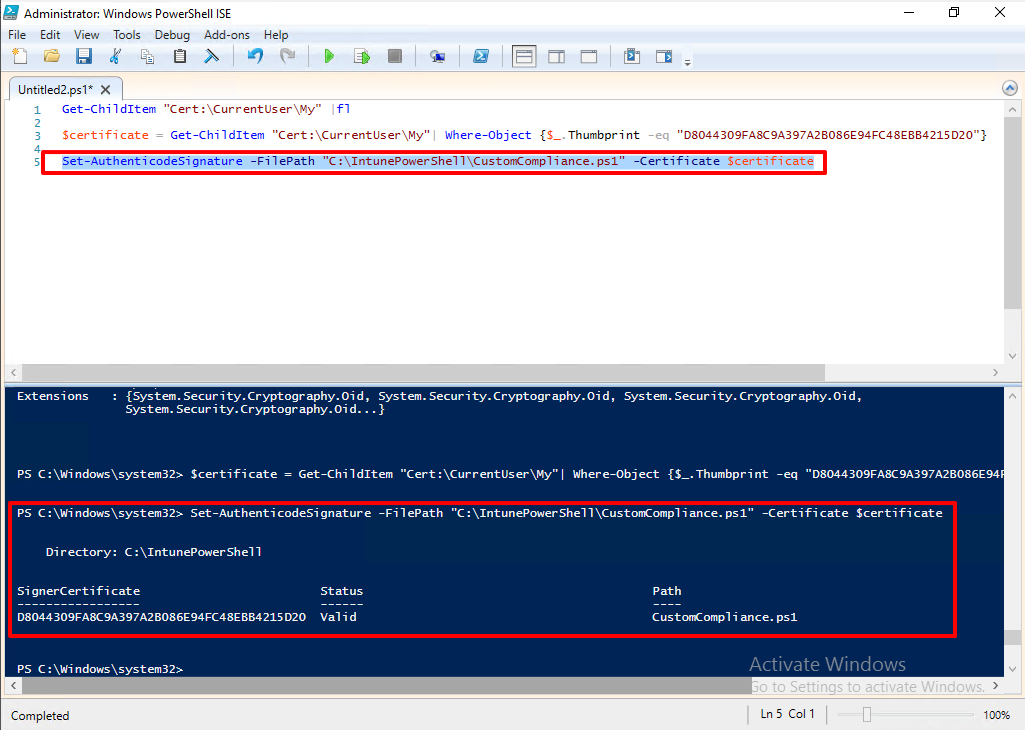
2. Validating
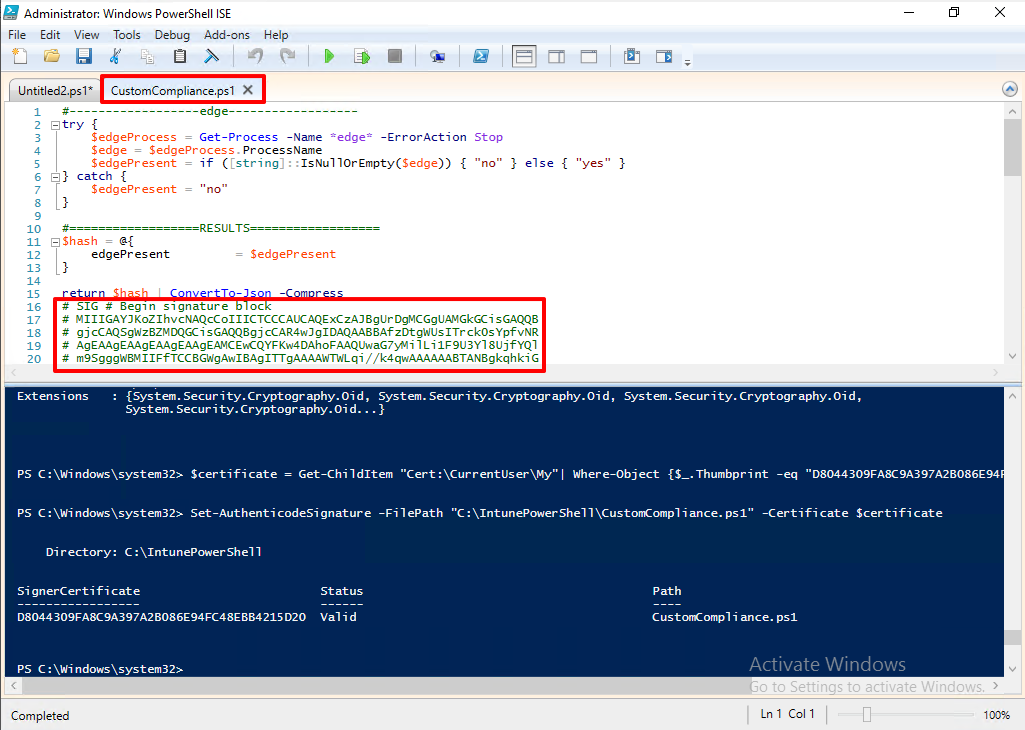
Once the script is signed, you will see the signature information as a commented section within the script.
The script will only run if this information and the certificate details on the device match exactly. If even a single character in the script is modified, it must be signed again.
3. Deploying the Certificate with GPO
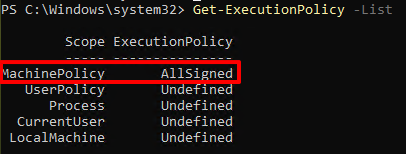
1. Current PowerShell Policy
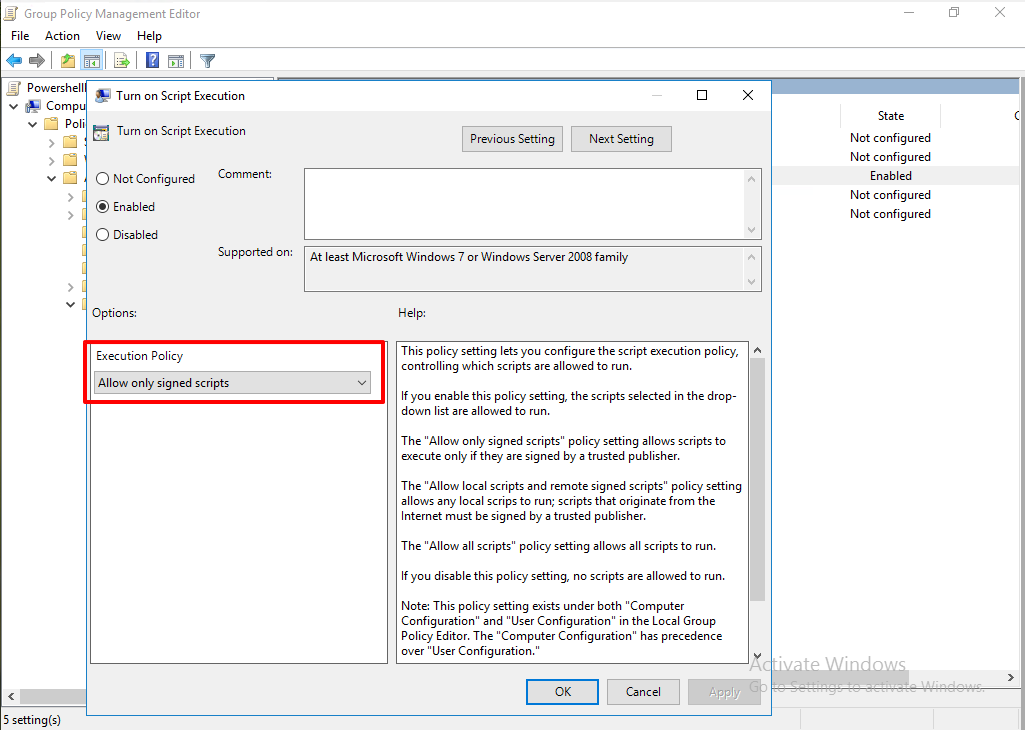
From Group policy, MachinePolicy is Allsign which means only allow to execute digitally signed script.
2. if not signed script..
So at the moment, if the script is not digitally signed, it can't be executed.
Here is the test.ps1 which is not signed.
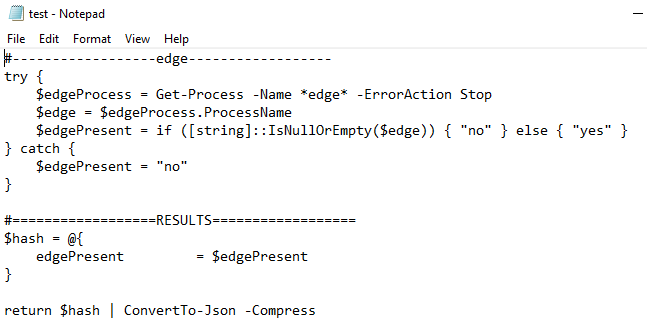
If I execute the test.ps1 in the AD joined device used user cake1, the execution is blocked.
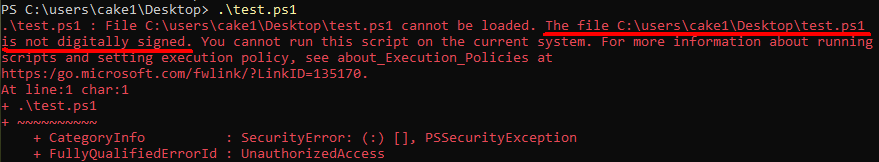
3. if signed script but the certificate is not installed in the device..
The script is signed but the device can't identify the signature in the script. This is why we have to install the certificate to the devices. From intune, we selected that we will run the script as a system context which means automatically executed without any prompt. Let's deployment the certificate from AD GPO.
4. Create GPO
Before create GPO, we need to export the certificate
From mmc, export the certificate.
Next
Select export PK or not. Next.
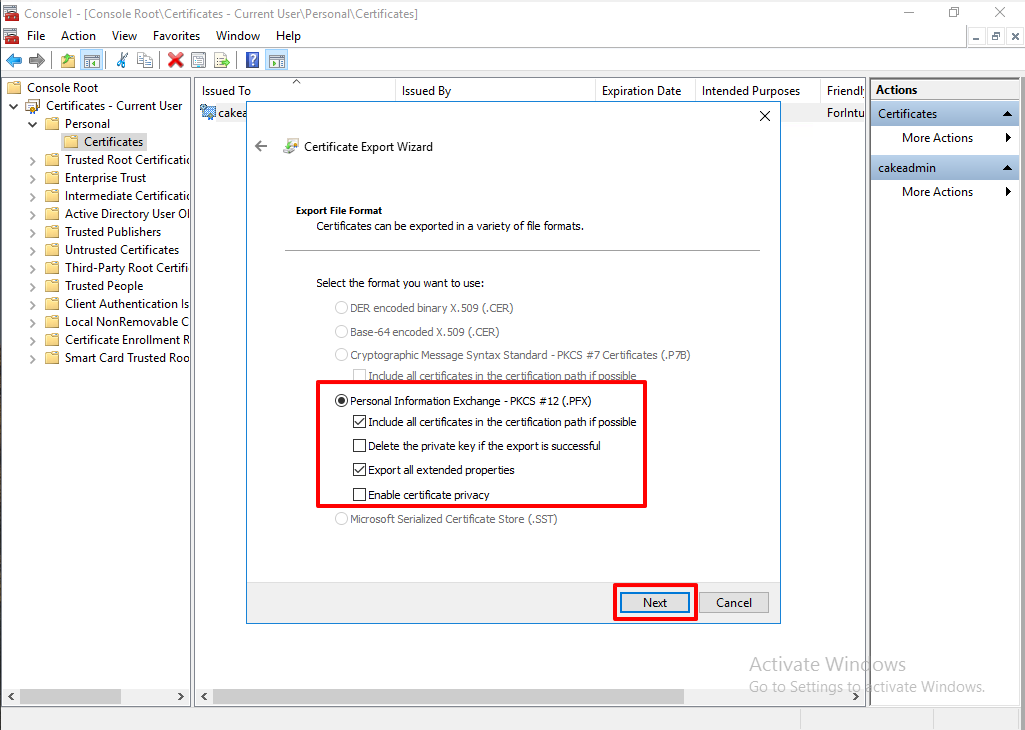
Select the options you want. Next.
Select the security principals. Next.
Browse and select where you want to export.
Finish.
This is it.
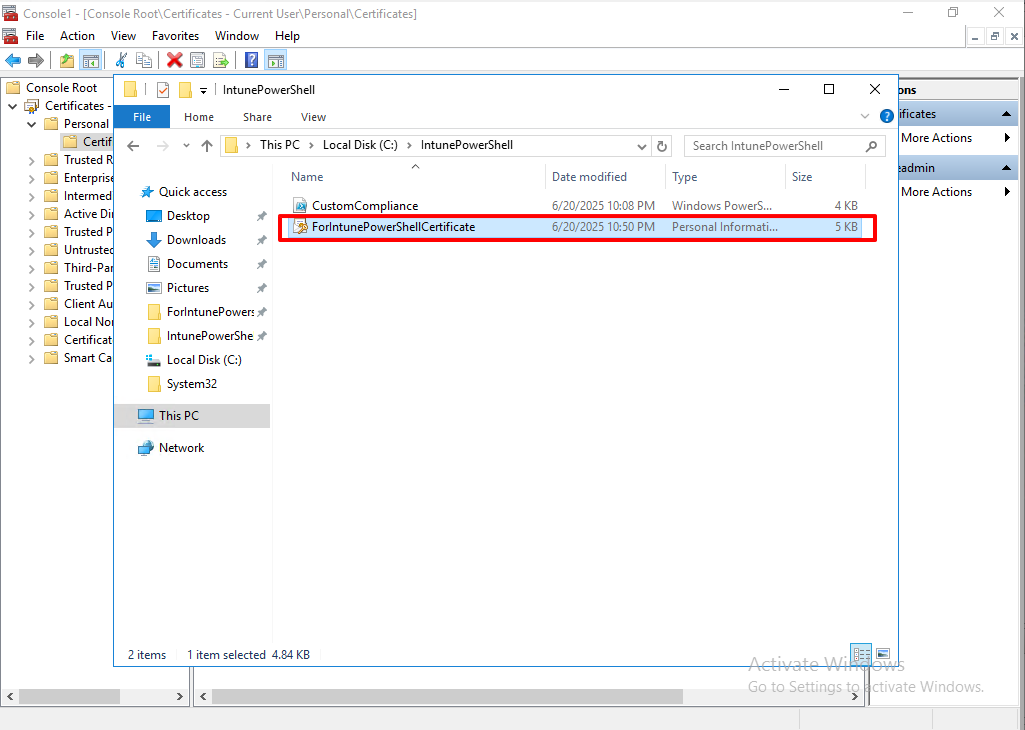
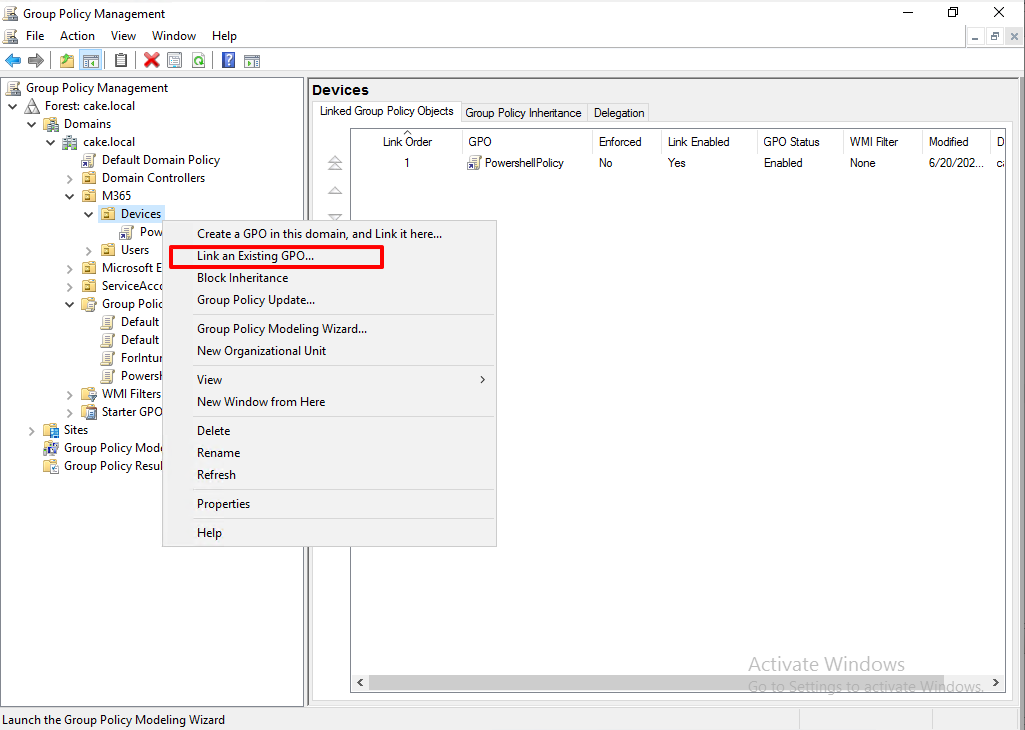
Create GPO(Trusted Root Certificate Authorities & Trusted Publishers!!)
So, we will create a new Group Policy Object to deploy our certificate.
(Right Click)Group Policy Objects > New
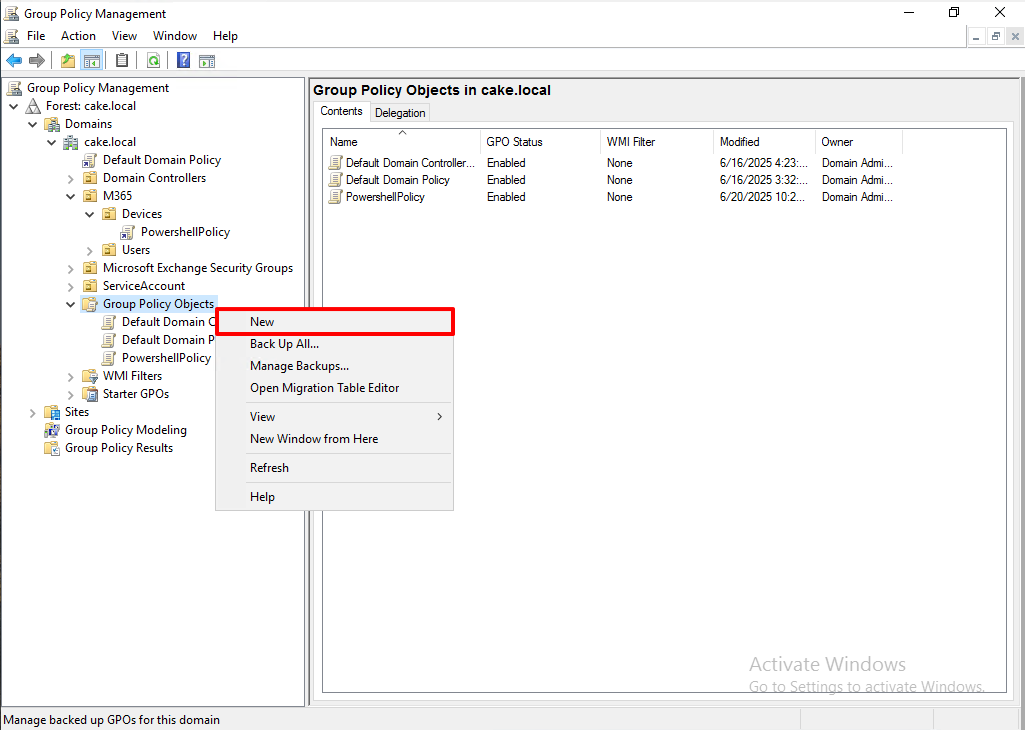
Give it a name.
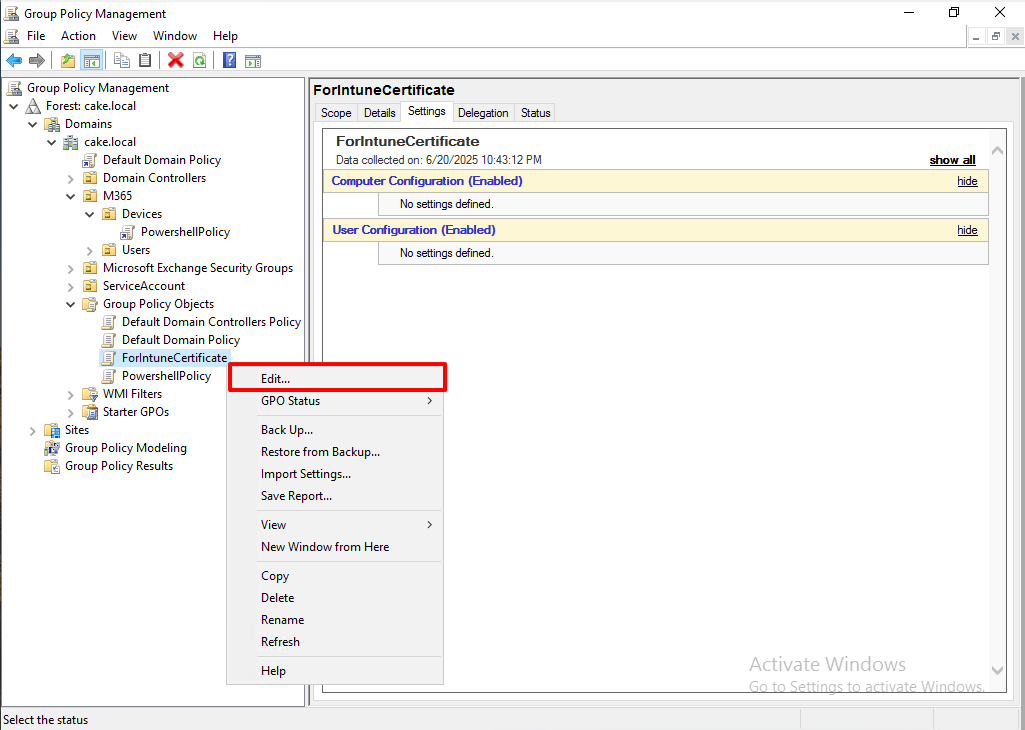
Right click and edit.
Go to the 'Public Key Policies' and import the certificate.
YOU SHOULD DO THE SAME PROCESS TO TRUSTED PUBLISHERS!!!!
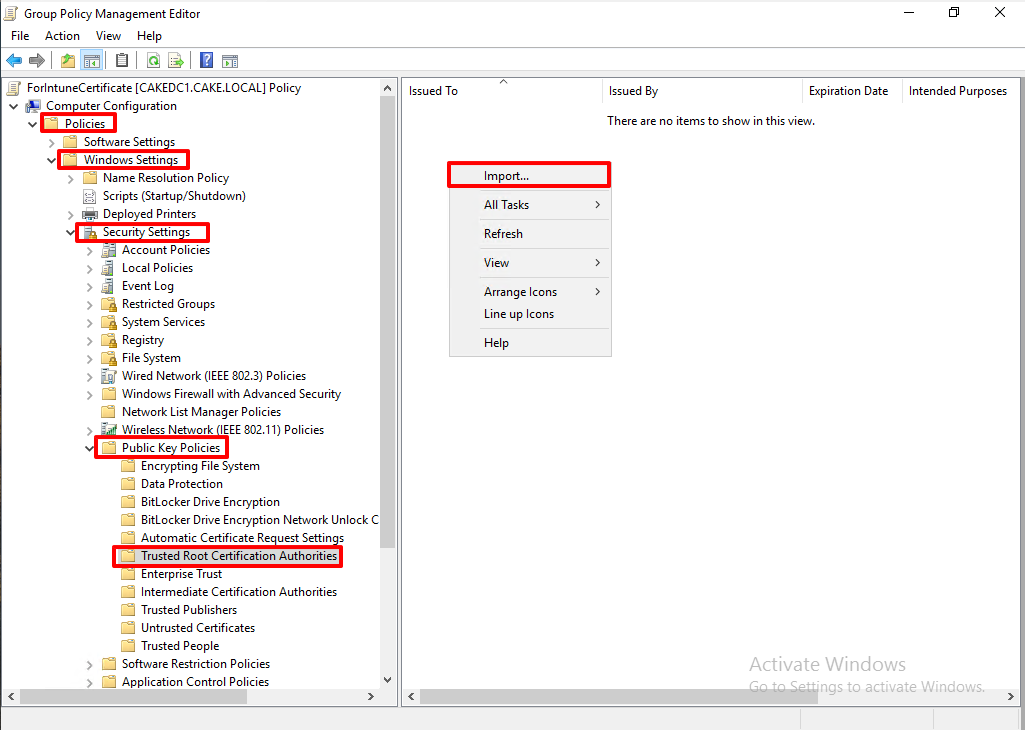
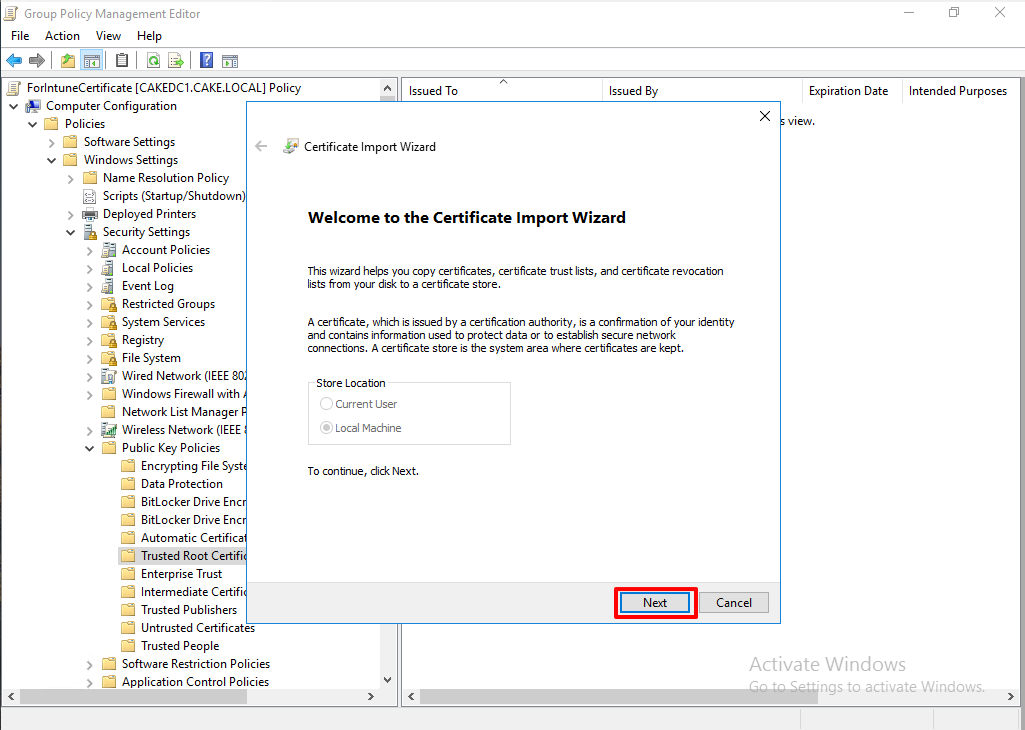
Browse the location where we export the certificate.
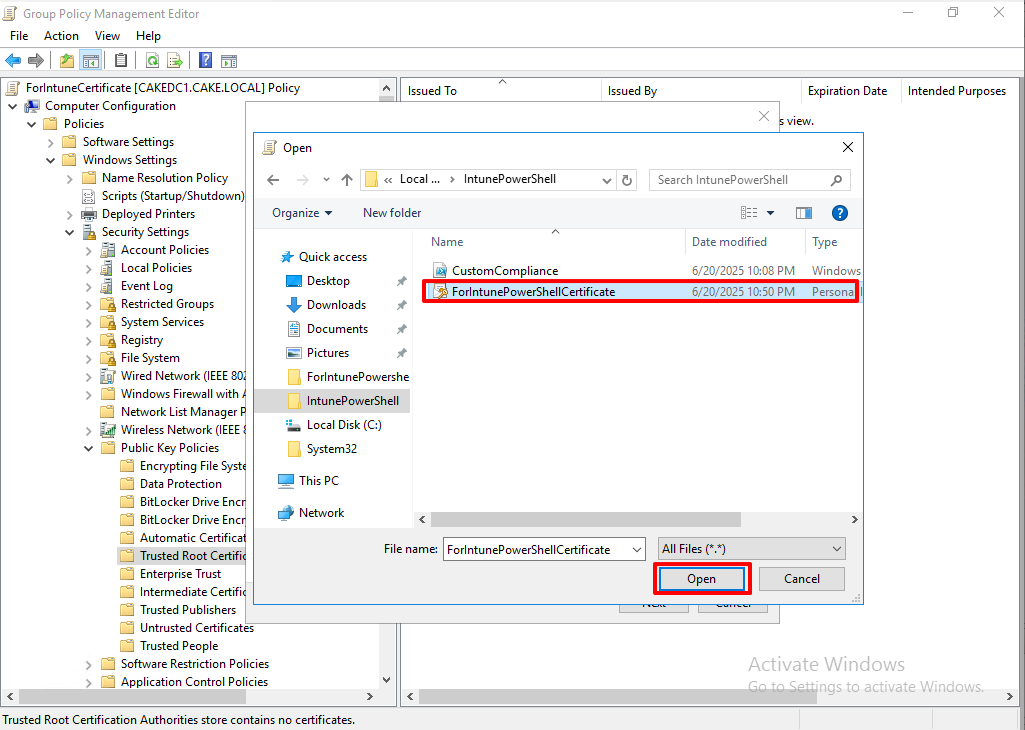
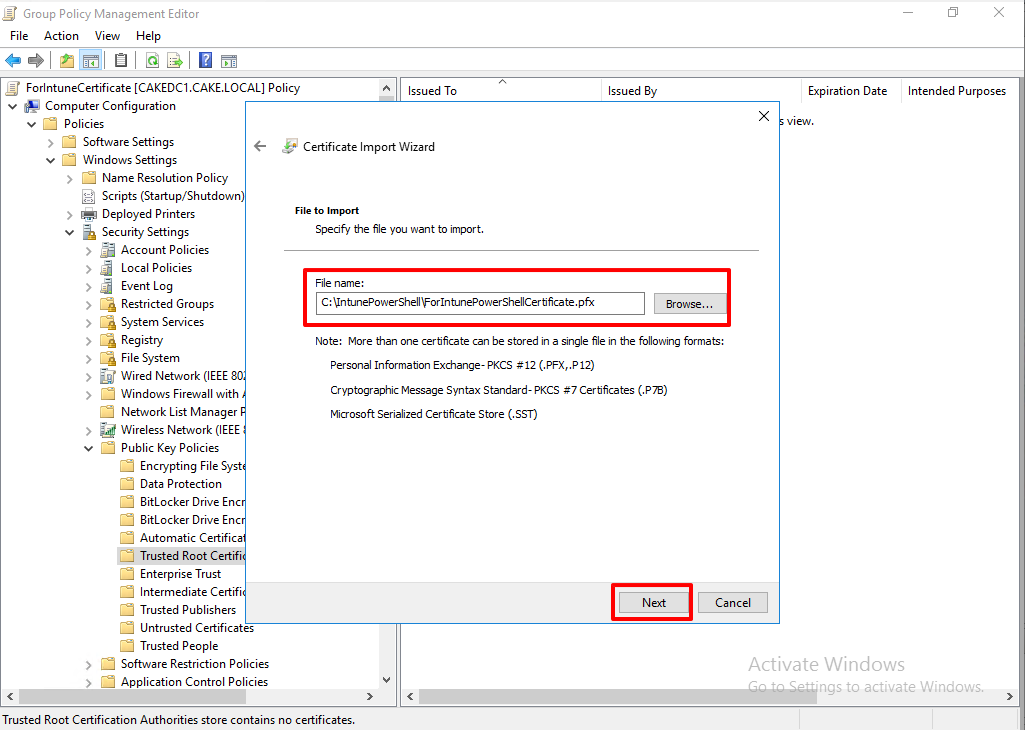
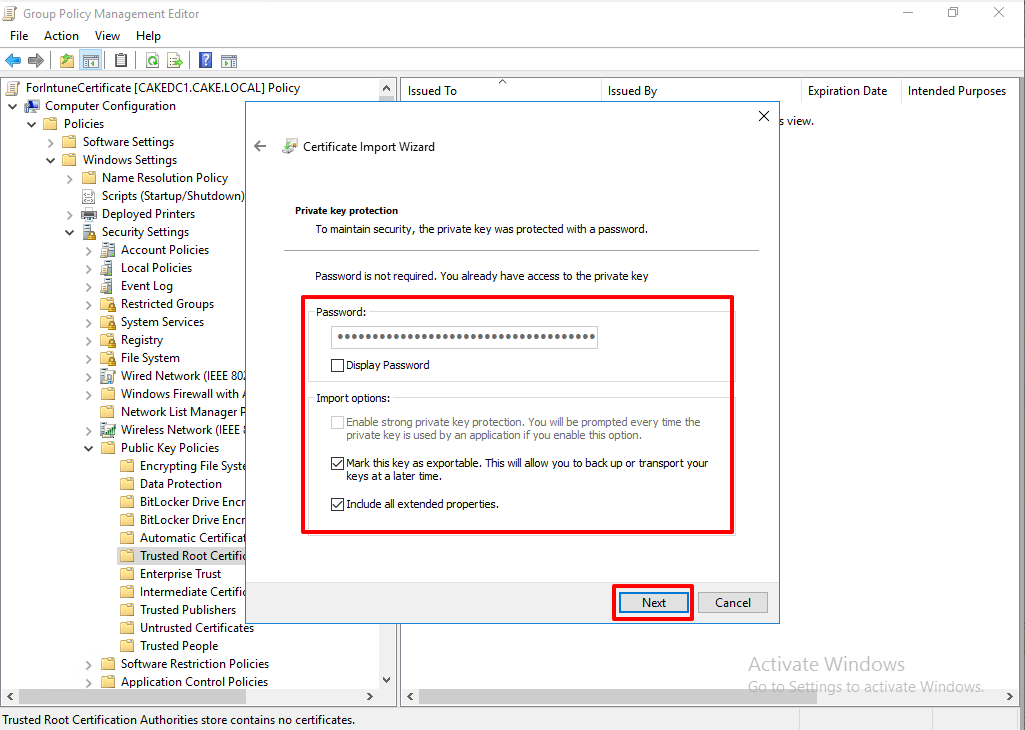
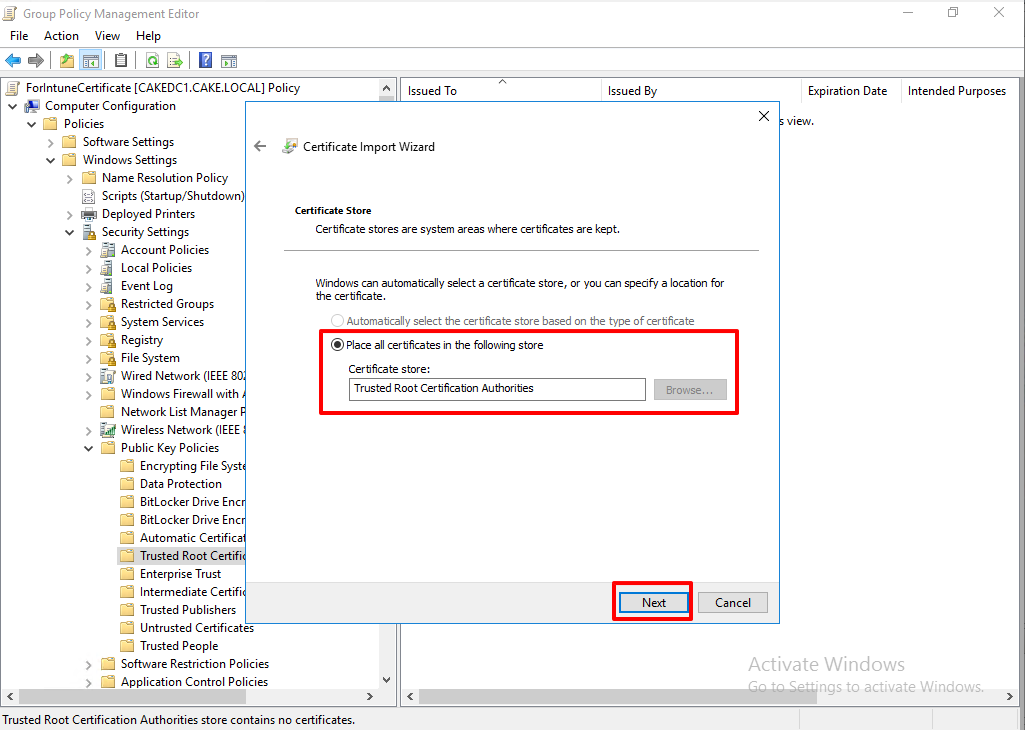
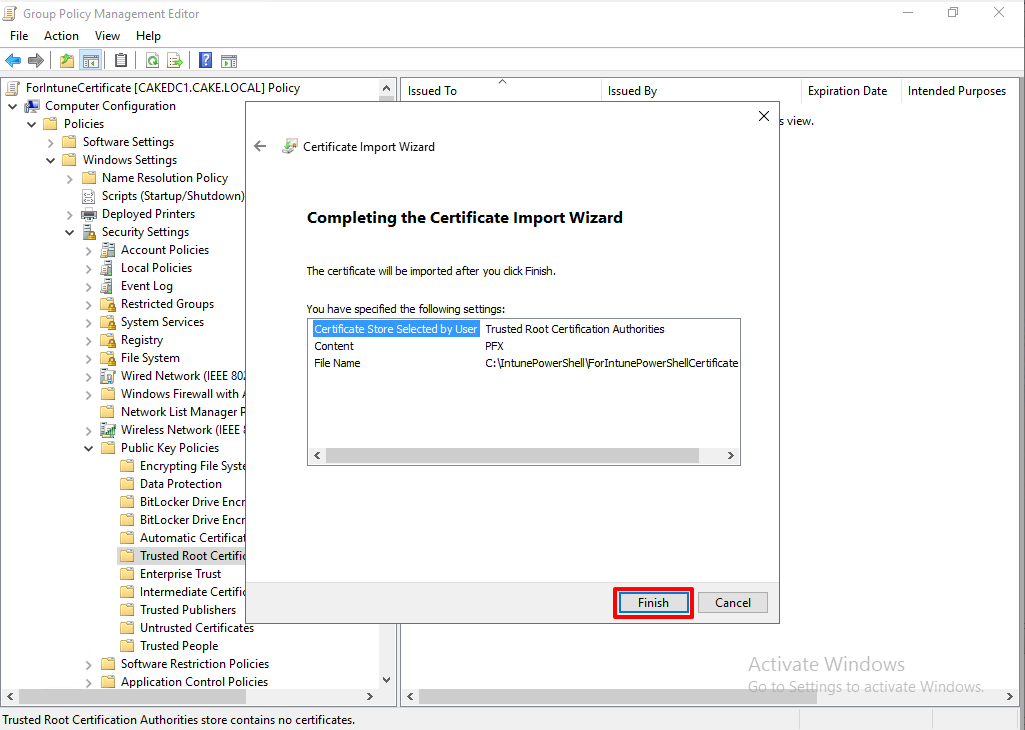
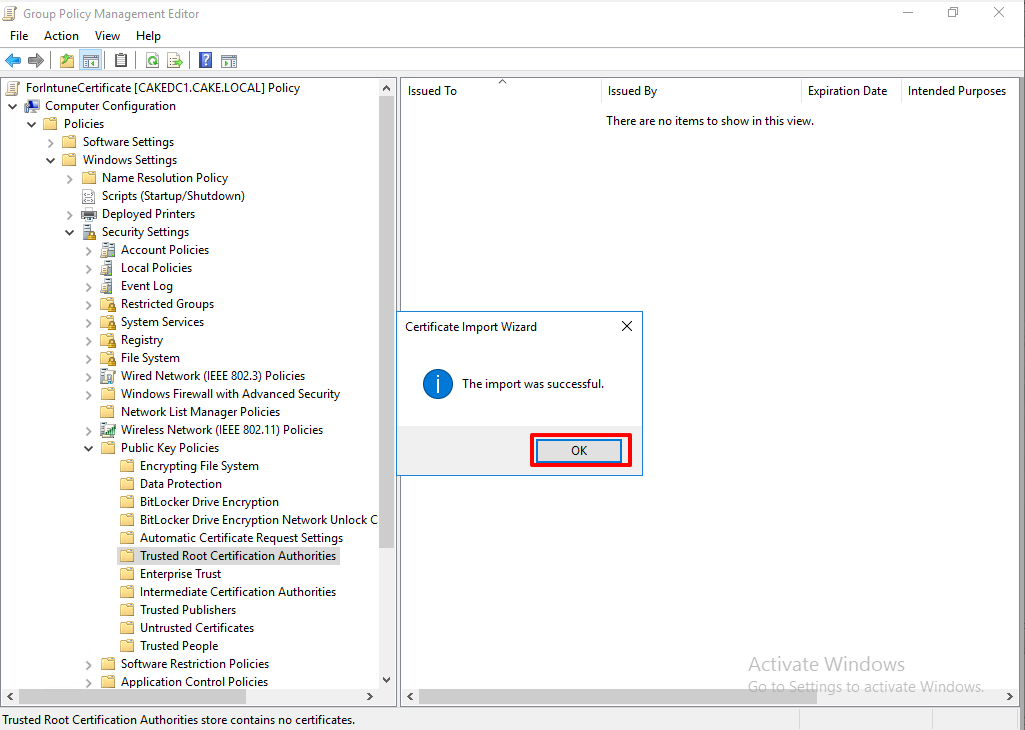
The certificate is imported to the GPO.
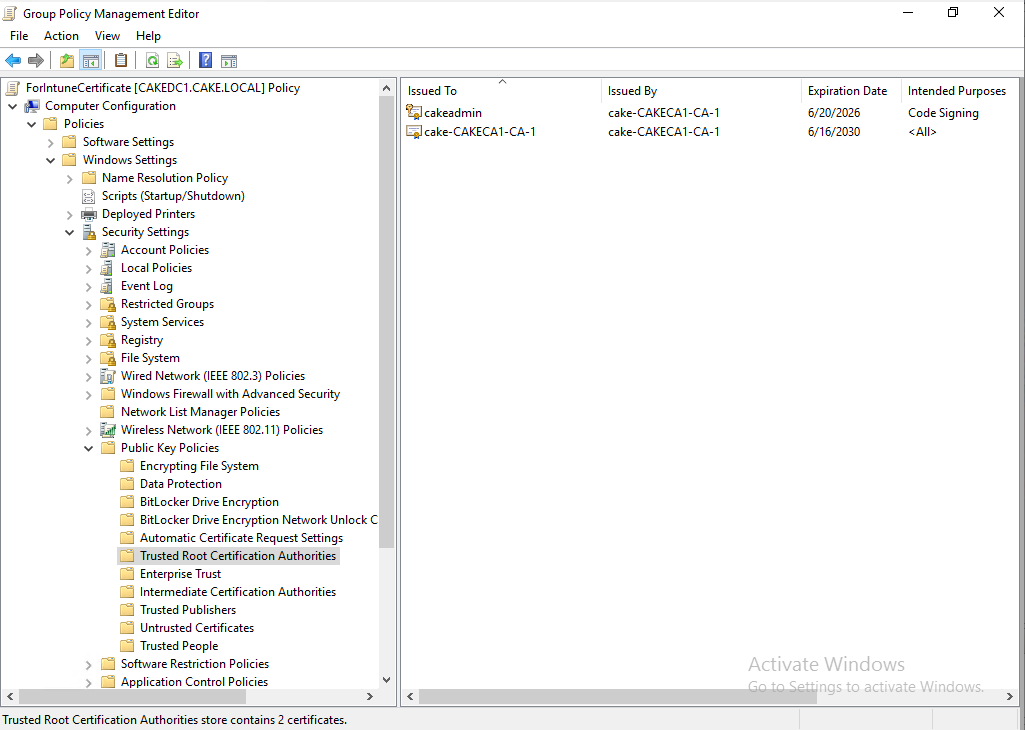
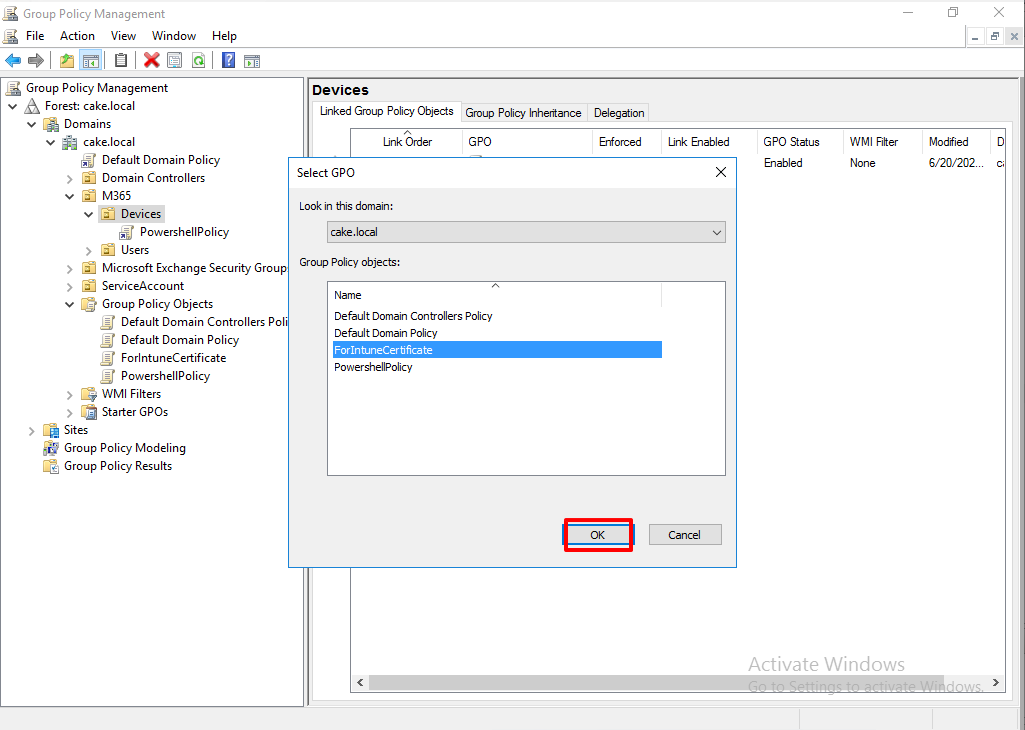
Link the GPO to the OU where the domain joined devices exist.
Click OK.
5. Validating
Moving on one of the domain joined devices. Run cmd as administrator and execute the command 'gpupdate /force' or you can take some time, the certificate will be installed automatically.
Trusted Root Certification Authorities and Trusted Publishers.
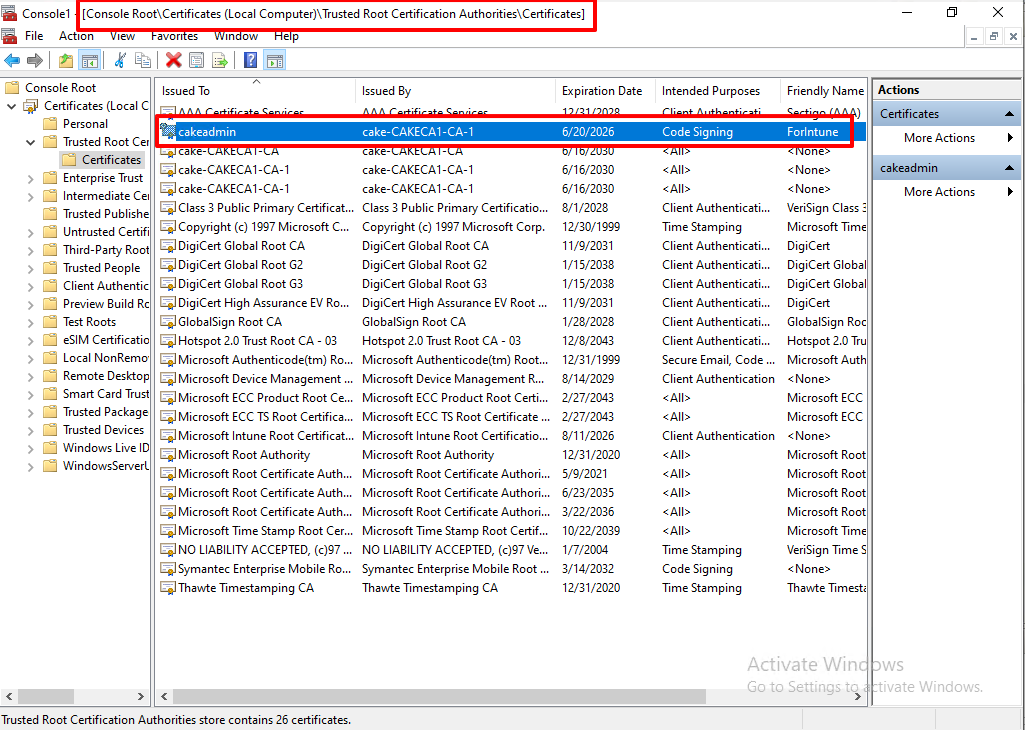
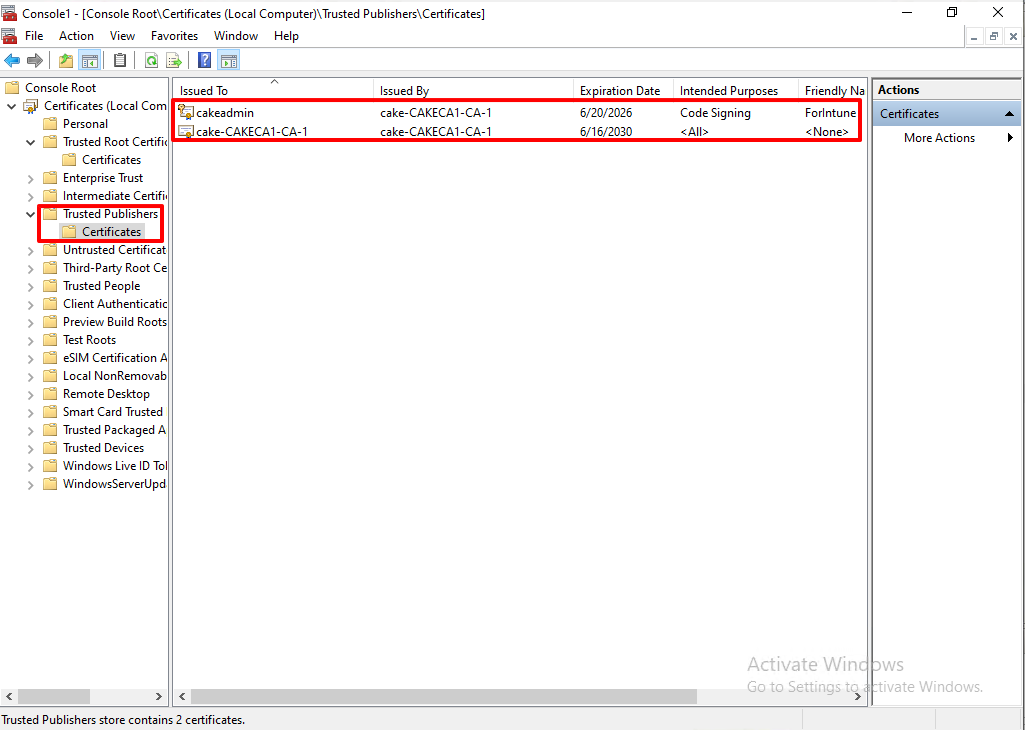
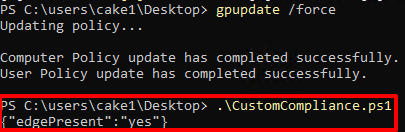
After that, the script will be executed very well without any prompt.
So, we are good to go to move on Intune for the last step.
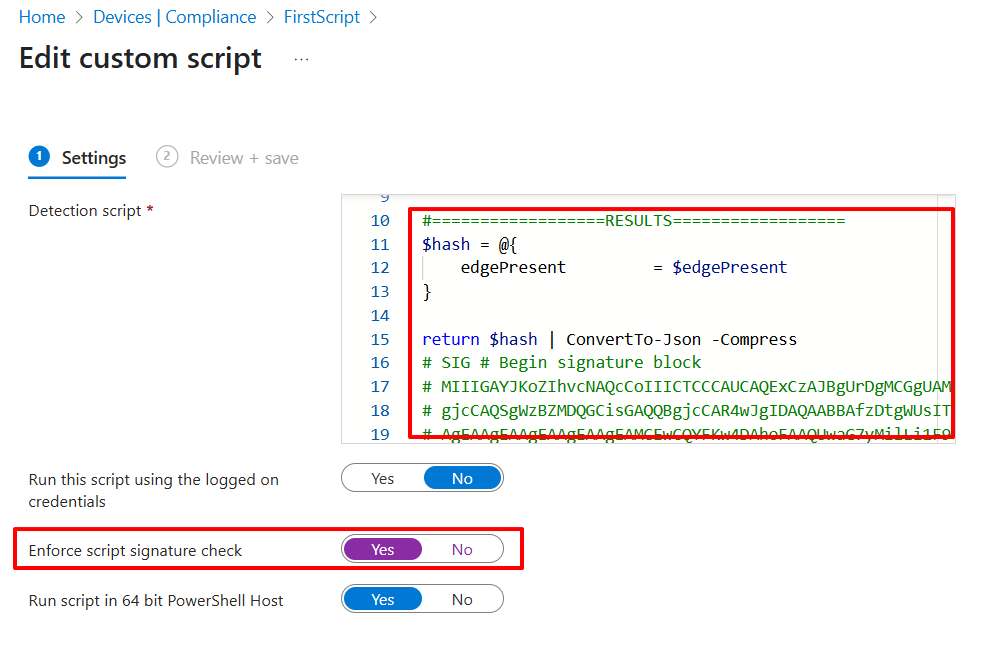
4. Intune Configuration
All you have to do in intune is update the script and select 'Yes' to 'Enforce script signature check'.
5. Result
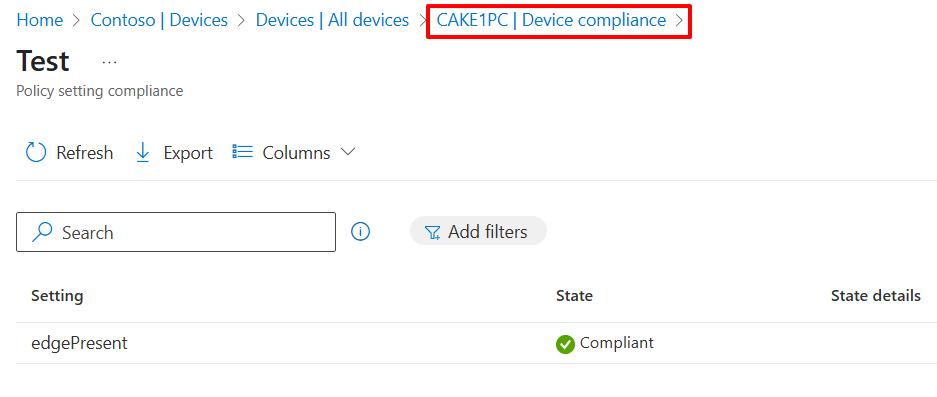
Here is the result. Only domain joined device which is CAKE1PC is marked as 'Compliant'.
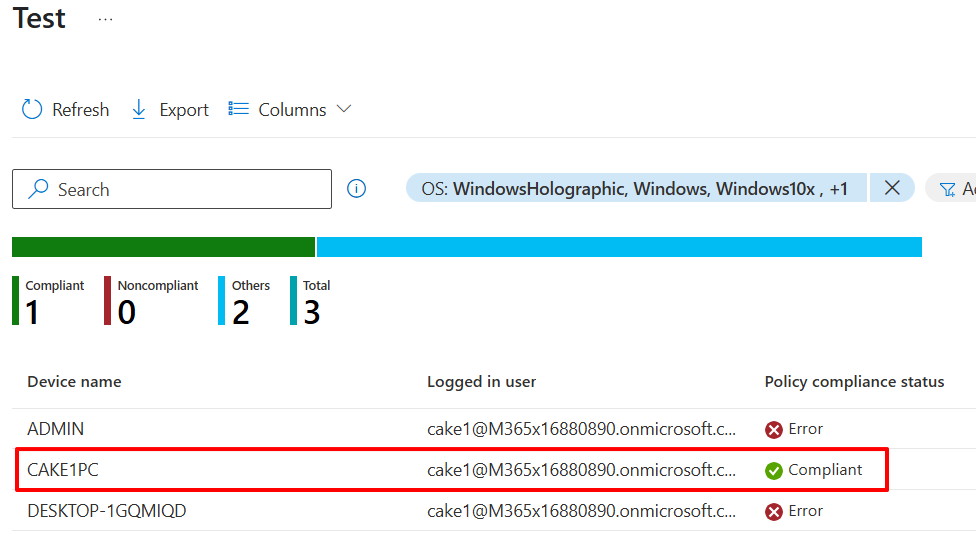
Let's check in azure portal. The CAKE1PC is Compliant which means the signed intune script is well executed.
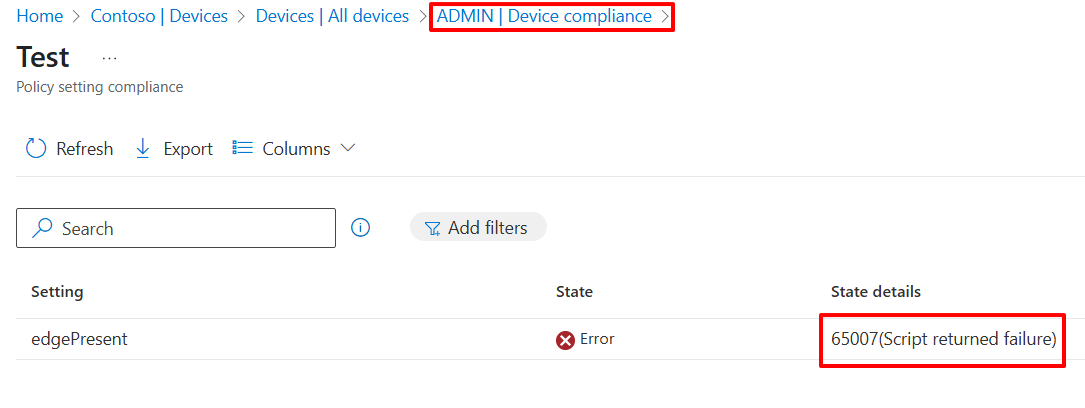
But the other devices which is not domain joined PC and only registered in intune so that the device is not installed certificate from the GPO.
We configured Intune to allow scripts to run only if they are signed. However, when the signed script was executed on the device, it failed to run properly because the required certificate was not installed on the device. As a result, the script couldn't return JSON data, which led Intune to throw the following error.
6. Ref)
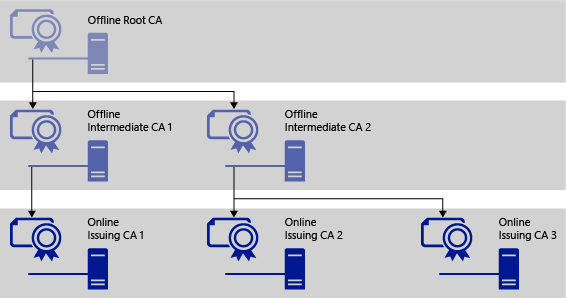
If you are planning to implement CA to your production environment, It's highly recommaneded to select the 3-tier certificate authorities. Please refer following document.
7. Note
In this post, I select web enrollment but it's not recommended. Please check the following link.