최적화 (Optimize)
- 모델을 학습하는 과정이 최적화 과정이다.
- 모델의 예측값과 실제 값의 차이 즉 오차를 계산하는 함수를 만들고 그 오차를 가장 적게 만드는 파라미터를 찾는 작업을 한다.
최적화 문제
- 어떤 함수가 반환할 수 있는 가장 작은 또는 가장 큰 값을 반환하도록 하는 파라미터 값을 찾는 문제를 최적화 문제라고 한다.
- 머신러닝은 Loss 함수(오차계산함수)가 반환하는 값(오차)를 최소화 할 수 있는 파라미터를 찾는 작업을 학습 과정에서 진행한다.
손실함수(Loss Function), 비용함수(Cost Function), 목적함수(Object Function), 오차함수(Error Function)
- 모델의 예측한 값과 정답값 간의 차이(오차)를 계산하는 함수.
- 모델을 학습시키는 것은 이 함수의 반환값(Loss)을 최소화 하는 파라미터을 찾는 과정이다.
- 문제 유형에 따라 Loss를 계산하는 방법이 다르다.
- Classification(분류)의 경우 log loss(cross entropy)를 사용한다.
- Regression(회귀)의 경우 MSE(Mean Squared Error)를 사용한다.
최적화 문제를 해결하는 방법
- Loss 함수 최적화 함수를 찾는다.
- Loss를 최소화하는 weight들을 찾는 함수(공식)을 찾는다.
- Feature와 sample 수가 많아 질 수록 계산량이 급증한다.
- 최적화 함수가 없는 Loss함수도 있다.
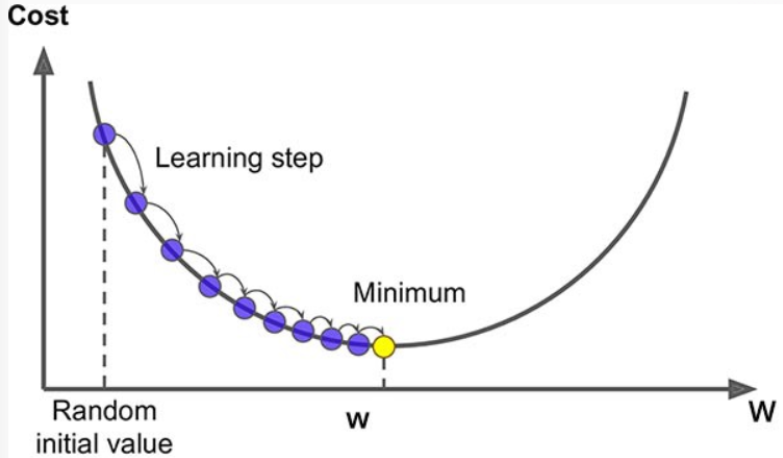
- 경사하강법 (Gradient Descent)
- 값을 조금씩 조금씩 조정해나가면서 최소값을 찾는다.
경사하강법 (Gradient Descent)
- 다양한 종류의 문제에서 최적의 해법을 찾을 수 있는 일반적인 최적화 알고리즘. 특히 최적화 함수가 없는 모델의 경우 경사하강법을 사용한다.
- 손실함수를 최소화하는 파라미터를 찾기위해 반복해서 조정해 나간다.
- 파라미터 에 대해 손실함수의 현재 gradient(경사,기울기,순간변화율)를 계산한다.
- gradient는 파라미터에 대한 손실함수의 순간변화율 즉 미분해서 구한다.
- gradient가 감소하는 방향으로 파라미터 를 변경한다.
- gradient가 0이 될때 까지 반복 1,2 를 반복한다.
- 파라미터 에 대해 손실함수의 현재 gradient(경사,기울기,순간변화율)를 계산한다.
- Gradient의 부호에 따른 새로운 파라미터값 계산
- gradient가 양수이면 loss와 weight가 비례관계란 의미이므로 loss를 더 작게 하려면 weight가 작아져야 한다.
- gradient가 음수이면 loss와 weight가 반비례관계란 의미이므로 loss를 더 작게 하려면 weight가 커져야 한다.
파라미터 조정
$W$: 파라미터
$\alpha$:학습률
- 현재 파라미터에 대해 Loss를 미분 한다.
- 1의 값에 Learning rate를 곱한 뒤 현재 파라미터값에서 뺀다.
- 학습률 (Learning rate)
- 기울기에 따라 이동할 step의 크기. 경사하강법 알고리즘에서 지정해야하는 하이퍼 파라미터이다.
- 학습률을 너무 작게 잡으면 최소값에 수렴하기 위해 많은 반복을 진행해야해 시간이 오래걸린다.
- 학습률을 너무 크게 잡으면 왔다 갔다 하다가 오히려 더 큰 값으로 발산하여 최소값에 수렴하지 못하게 된다.
# 가상의 loss 함수 def loss(weight): return (weight-1)**2 + 2 # 위의 loss함수의 도함수 def derived_loss(weight): return 2*(weight-1) # 기울기 print('w=1, 오차:', loss(1)) print('w=1, 기울기:', derived_loss(1))w=1, 오차: 2
w=1, 기울기: 0loss(5-8*0.01), derived_loss(5-8*0.01)(17.3664, 7.84)
#초기 weight weight = 5 # 학습율 lr = 0.1 new_weight = weight - lr*derived_loss(weight) new_weight반복문을 이용해 gradient가 0이 되는 지점의 weight 찾기
import numpy as np np.random.seed(0) # learning_rate = 0.001 # learning_rate = 10 learning_rate=0.4 # 죄적의 weight를 찾기 위한 최대 반복횟수. max_iter = 100 # 첫번째(시작) weight => random하게 잡는다. weight = np.random.randint(-2, 3) weight_list = [weight] # 새로 계산된 weight들을 저장할 리스트 iter_cnt = 0 # 반복회수를 저장할 변수 while True : # loss함수에 대한 미분값(기울기)을 구해서 0(최소지점)이면 반복을 멈춘다. if derived_loss(weight) == 0 : break if iter_cnt == max_iter : # 현재 반복수가 max_iter이면 멈춘다. break # 새로운 weight값을 계산 weight = weight - learning_rate * derived_loss(weight) weight_list.append(weight) iter_cnt += 1iter_cnt23
weight1.0
loss(weight)2.0
weight_list[2,
1.2,
1.04,
1.008,
1.0016,
1.00032,
1.000064,
1.0000128,
1.00000256,
1.000000512,
1.0000001024,
1.00000002048,
1.000000004096,
1.0000000008192,
1.00000000016384,
1.000000000032768,
1.0000000000065536,
1.0000000000013107,
1.0000000000002622,
1.0000000000000524,
1.0000000000000104,
1.000000000000002,
1.0000000000000004,
1.0]