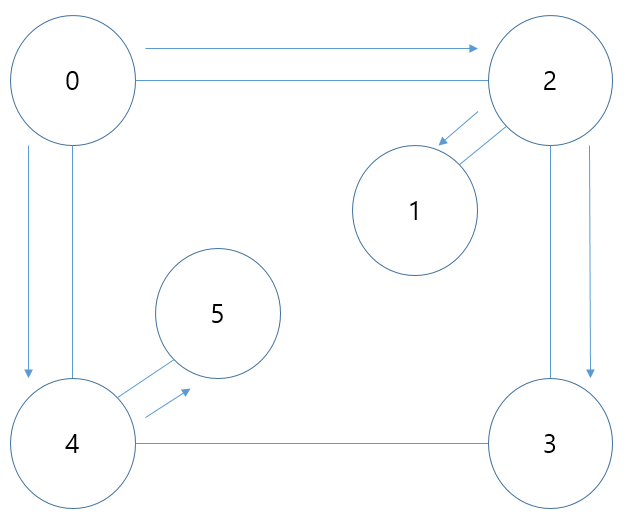
그래프는 객체 사이의 연결 관계를 표현할 수 있는 자료구조.
대표적인 예시 : 지하철 노선도, 전기 소자를 그래프로 표현하게 되면 어떻게 연결되어있는지를 표현해야 회로가 제대로 동작하는지 분석할 수 있고, 운영 체제에서는 프로세스와 자원들이 어떻게 연관되는지를 그래프로 분석하여 시스템의 효율이나 교착상태 유무등을 알아낼 수 있다.
그래프로 표현할 수 있는 것들 : 도로, 미로, 선수과목(위상정렬)
그래프의 정의
정점과 간선들의 유한 집합. 정점은 node라고도 불리고, 간선은 link라고 불린다.
용어 정리
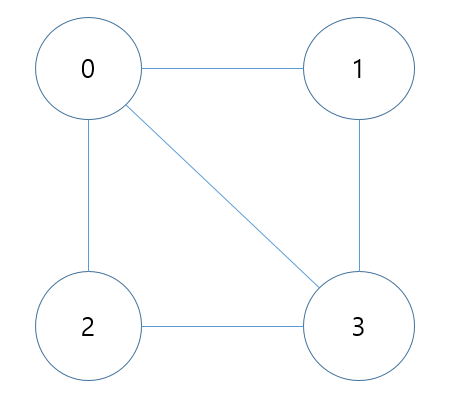
예시 : 0의 차수->3, 0의 진입 차수->3, 0의 진출 차수->3
무방향 그래프에서 한 정점의 진입차수와 진출차수는 같다.(양방향이므로)
그래프의 탐색
깊이 우선 탐색(Depth First Search)
탐색 순서
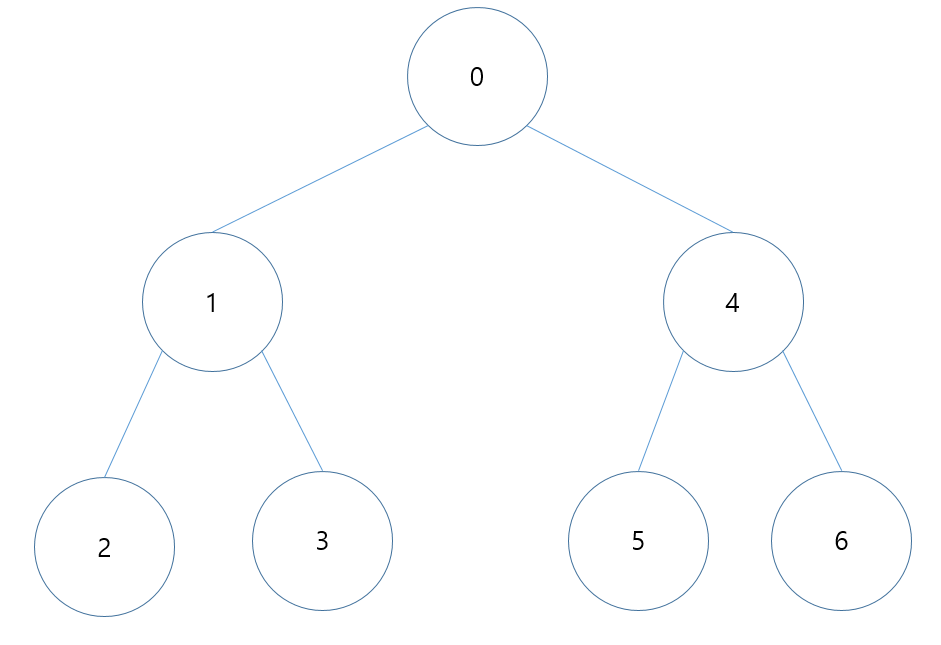
코드(행렬)
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX_VERTICES 50
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
int visited[MAX_VERTICES];
typedef struct {
int n;
int adj_mat[MAX_VERTICES][MAX_VERTICES];
}GraphType;
void graph_init(GraphType* g)
{
int r, c;
g->n = 0;
for (r = 0;r < MAX_VERTICES;r++)
for (c = 0;c < MAX_VERTICES;c++)
g->adj_mat[r][c] = 0;
}
void insert_vertex(GraphType* g, int v)
{
if (((g->n) + 1) > MAX_VERTICES) {
printf("그래프:정점의 개수 초과");
return;
}
g->n++;
}
void delete_vertex(GraphType* g, int v)
{
if (v >= g->n || v < 0) {
printf("error\n");
return;
}
g->n--;
}
//insert edge in undirected graph(무방향 그래프)
void insert_edge(GraphType* g, int start, int end)
{
if (start >= g->n || end >= g->n) {
printf("그래프 :정점 번호 오류");
}
g->adj_mat[start][end] = 1;
g->adj_mat[end][start] = 1;
}
void delete_edge(GraphType* g, int start, int end)
{
if (start >= g->n || end >= g->n) {
printf("그래프 :정점 번호 오류");
}
g->adj_mat[start][end] = 0;
g->adj_mat[end][start] = 0;
}
void print_graph(GraphType* g)
{
int r, c;
for (r = 0;r < g->n;r++)
for (c = 0;c < g->n;c++) {
if (g->adj_mat[r][c])
printf("<%d , %d>", r, c);
}
printf("\n");
}
void dfs_mat(GraphType* g, int v)
{
int w;
visited[v] = TRUE;
printf("%d ", v);
for (w = 0;w < g->n;w++)
if (g->adj_mat[v][w] && !visited[w])
dfs_mat(g, w);
}
void main()
{
int i;
GraphType g;
graph_init(&g);
for (i = 0;i < 4;i++)
insert_vertex(&g, i);
insert_edge(&g, 0, 1);
// insert_edge(&g,1,0);
insert_edge(&g, 0, 3);
insert_edge(&g, 1, 2);
insert_edge(&g, 1, 3);
insert_edge(&g, 2, 3);
print_graph(&g);
//dfs_mat(&g,0);
printf("\n");
delete_edge(&g, 0, 1);
dfs_mat(&g, 0);
printf("\n");
print_graph(&g);
}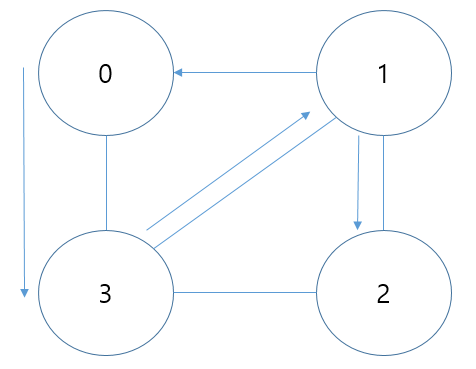
너비 우선 탐색(Breath First Search)
탐색 순서
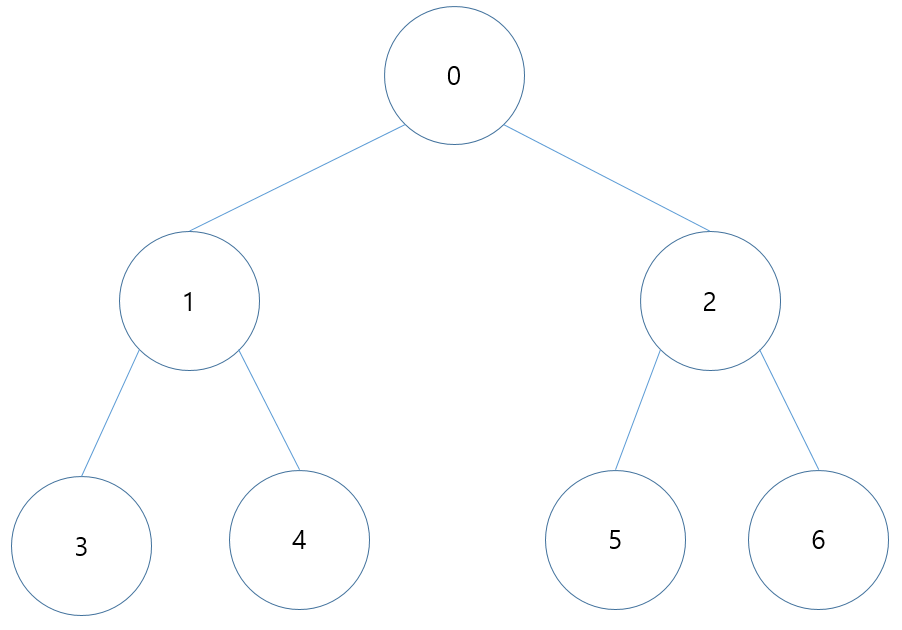
코드(행렬)
include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define MAX_QUEUE_SIZE 10
typedef int element;
typedef struct { // 큐 타입
element queue[MAX_QUEUE_SIZE];
int front, rear;
} QueueType;
// 오류 함수
void error(char* message)
{
fprintf(stderr, "%s\n", message);
exit(1);
}
// 공백 상태 검출 함수
void queue_init(QueueType* q)
{
q->front = q->rear = 0;
}
// 공백 상태 검출 함수
int is_empty(QueueType* q)
{
return (q->front == q->rear);
}
// 포화 상태 검출 함수
int is_full(QueueType* q)
{
return ((q->rear + 1) % MAX_QUEUE_SIZE == q->front);
}
// 삽입 함수
void enqueue(QueueType* q, element item)
{
if (is_full(q))
error("큐가 포화상태입니다");
q->rear = (q->rear + 1) % MAX_QUEUE_SIZE;
q->queue[q->rear] = item;
}
// 삭제 함수
element dequeue(QueueType* q)
{
if (is_empty(q))
error("큐가 공백상태입니다");
q->front = (q->front + 1) % MAX_QUEUE_SIZE;
return q->queue[q->front];
}
#define MAX_VERTICES 50
typedef struct GraphType {
int n; // 정점의 개수
int adj_mat[MAX_VERTICES][MAX_VERTICES];
} GraphType;
int visited[MAX_VERTICES];
// 그래프 초기화
void graph_init(GraphType* g)
{
int r, c;
g->n = 0;
for (r = 0; r < MAX_VERTICES; r++)
for (c = 0; c < MAX_VERTICES; c++)
g->adj_mat[r][c] = 0;
}
// 정점 삽입 연산
void insert_vertex(GraphType* g, int v)
{
if (((g->n) + 1) > MAX_VERTICES) {
fprintf(stderr, "그래프: 정점의 개수 초과");
return;
}
g->n++;
}
// 간선 삽입 연산
void insert_edge(GraphType* g, int start, int end)
{
if (start >= g->n || end >= g->n) {
fprintf(stderr, "그래프: 정점 번호 오류");
return;
}
g->adj_mat[start][end] = 1;
g->adj_mat[end][start] = 1;
}
void bfs_mat(GraphType* g, int v)
{
int w;
QueueType q;
queue_init(&q); // 큐 초기화
visited[v] = TRUE; // 정점 v 방문 표시
printf("%d 방문 -> ", v);
enqueue(&q, v); // 시작 정점을 큐에 저장
while (!is_empty(&q)) {
v = dequeue(&q); // 큐에 정점 추출
for (w = 0; w < g->n; w++) // 인접 정점 탐색
if (g->adj_mat[v][w] && !visited[w]) {
visited[w] = TRUE; // 방문 표시
printf("%d 방문 -> ", w);
enqueue(&q, w); // 방문한 정점을 큐에 저장
}
}
}
int main(void)
{
GraphType* g;
g = (GraphType*)malloc(sizeof(GraphType));
graph_init(g);
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
insert_vertex(g, i);
insert_edge(g, 0, 2);
insert_edge(g, 2, 1);
insert_edge(g, 2, 3);
insert_edge(g, 0, 4);
insert_edge(g, 4, 5);
insert_edge(g, 1, 5);
printf("너비 우선 탐색\n");
bfs_mat(g, 0);
printf("\n");
free(g);
return 0;
}