Review ISA
-
Definition
Interface between what the software commands and the what the hardware carries out.
-
ISA specifies
-
The memory orgniazion
- Address space ( RV32I : bytes = 4GB )
- Addressability ( RV32I : 8bits = 1byte )
-
The register set
- 32 registers ( x0~x31 ) in RV32I
-
The instruction set
- Opcodes (6+ opcode type = 6 format of RV32I )
- Data types
- Addressing modes
- Length and format of instructions (32 bits size and aligned)
-
Terminology Review
-
Immediate
- A constant value directly encoded in the instruction.
- Usually shorter than 32 bits, such as 12 bits or 20 bits, so sign-extension is required.
-
Sign-Extension
- When extending an immediate value to 32 bits, the following steps occur:
- Identify the leftmost bit of the immediate (the sign bit).
- Replicate the sign bit into the upper bits of the 32-bit value.
- Copy the original immediate into the lower bits.
Example:
Immediate (12 bits):1011 1111 1111
Sign bit = 1
After sign-extension (32 bits):
1111 1111 1111 1011 1111 1111 1111
- When extending an immediate value to 32 bits, the following steps occur:
6 Instruction Formats
-
Four core formats (R/I/S/U/B/J),

Figure 1: RV32I의 6가지 format 정보
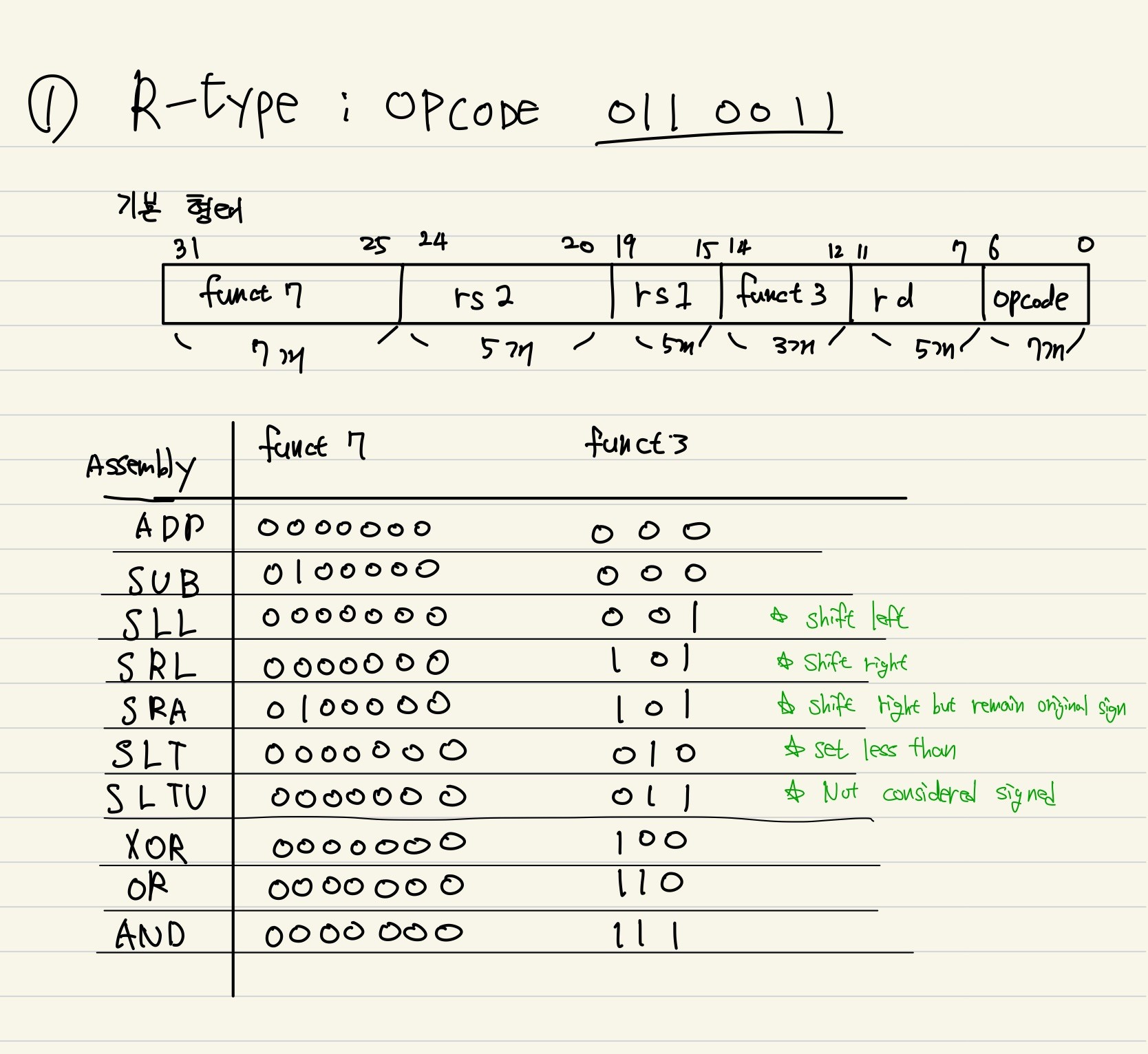
1. R-type (r1와 r2 연산 -> rd)
R-type introduction
- Opcode = 0110011
- rs1 & rs2 = source register
- rd = destination register
- fucnt7, funct3 = 이들의 조합에 따라 R-type 명령어 나뉨
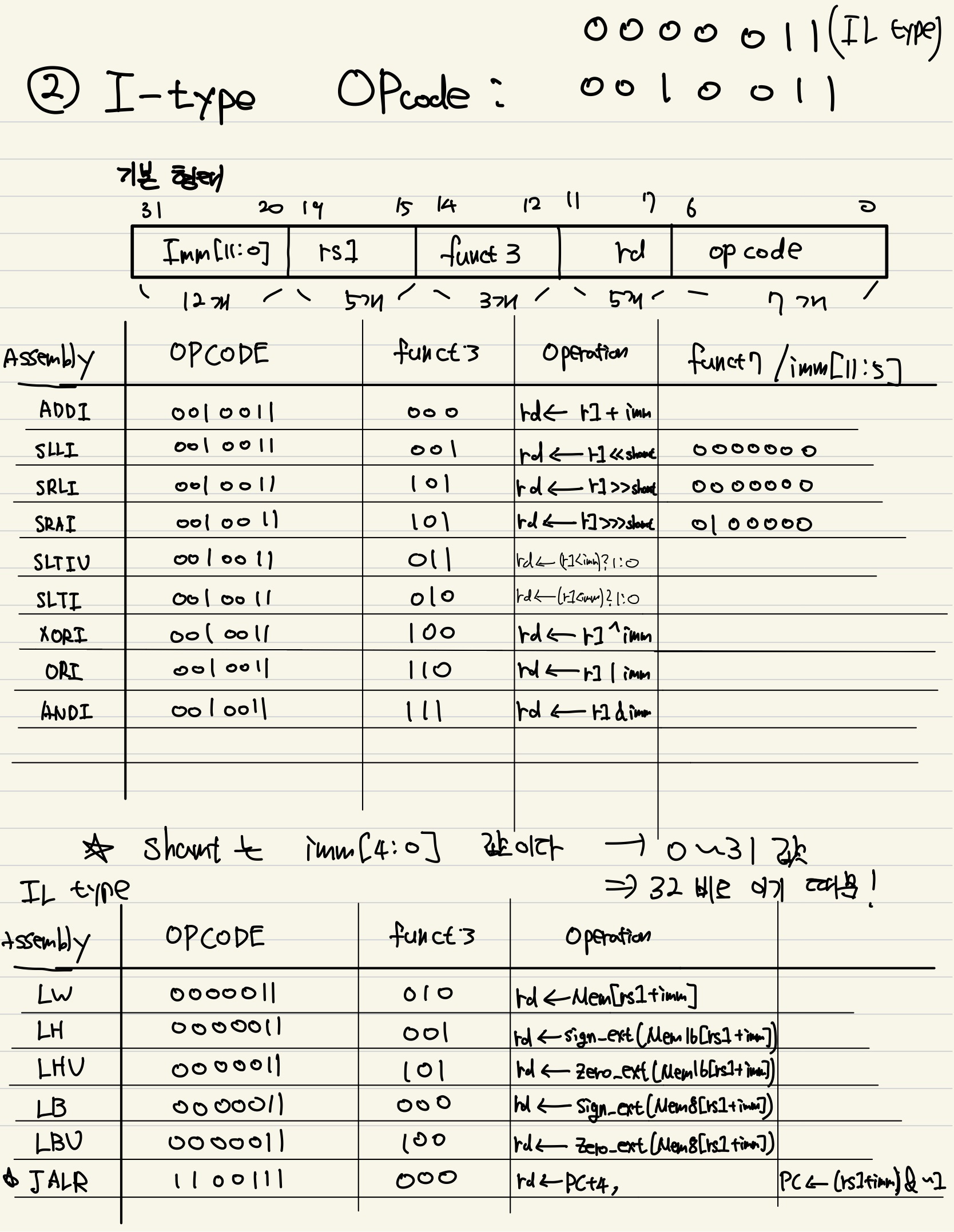
2. I-type (r1와 imm 연산 -> rd)
내가 표를 생각없이 그려놓았는데..
I type은 크게 3 종류로 나뉜다!!!!
1. 연산 목적 (R-type 과 유사 그러나 레지스터 값 하나와 Imm을 연산)
2. 메모리에서 레지스터로 load! (나는 편하게 IL type이라 명칭)
3. Branch 명령어 같은 JARL (정확히는 control-flow instr)
I-type opcode (ALU형): 0010011
I-type opcode (Load형): 0000011
I-type opcode (JALR형): 1100111- Opcode = 위 표 참고!
- rs1 = source register
- rd = destination register
- funct3 = 이들의 조합에 따라 I-type 명령어 나뉨
2-1 연산 목적 I-type
- Source Reg 값 하나와 Imm (즉시값)의 연산
- Imm(즉시값)은 ImmGen에서 32 bit로 sign-extension 된다.
Shamt 란?
shift 연산시 사용되는 수로 총 5bit가 필요하다. 왜? reg bit 수는 총 32 bit 이기 때문이다. 따라서 일부 shift 연산 assembly 명령어는 Imm[11:5] 를 funct7로 사용하고 Imm[4:0]만 shamt로 사용한다.
2-2 로딩 목적 I-type (IL type)
- 메모리에서 레지스터로 값을 로딩할 때 쓰는 명령어들이다.
2-3 Branch 목적 I-type (JARL)
- 여기서 특이한 친구가 있는데, 바로 명령어는
JALR이다.4JALR
왜 쓰냐? branch 명령어의 일종이다.
opcode도 기존 I type과 차이가 있다. 기작은 다음과 같다.- rs1과 imm의 합을 jump할 address로 생각한다. 그리고 alignment를 위해 LSB를 0으로 만든다.
PC <-(rs1+imm) & ~1. - 그리고 rd에는 PC+4 즉 복귀할 명령어를 저장한다!
- rs1과 imm의 합을 jump할 address로 생각한다. 그리고 alignment를 위해 LSB를 0으로 만든다.
3. S-type (레지스터 -> 메모리에 저장!)
- 위에 그림에 다 써놓았다
- assembly 명령어로
sw만 구현할 것인데, 32 bit 정보를 그대로 저장하는 sw
4. B-type
명령어 구조
- Opcode : 1100011
- funct3 로 분기 조건 구분
- Immediate(즉시값) 비트가 분산배치 되어 있음!
왜 즉시값 비트가 분산배치?
B-type은 S-type 변형으로 생각하자.
1. PC는 4의 배수만큼 읽어야 한다. PC 주소하나는 1 Byte를 읽으니 4 Byte Instruction을 읽기 위해선 4의 배수만큼 읽어야 한다.
2. RISC-V는 C-extension(16 bit instr.) 도 고려해 PC는 최소 2 byte 씩 읽기로 약속되어 있다.
3. 따라서 imm[0]은 항상 0일 것이니 저장하지 않는다.
+물론 RV32I는 4 byte 씩 읽어서 imm[1]도 항상 0일테지만 호환성을 위해 B-type을 위와 같이 설계한다.
+남은 Imm[0] 자리에는 가장 높은 비트 만만한거 하나 가지고 온 것이다! Imm[12]는 sign bit이니 가져오기 애매해서 그 다음 것인 Imm[11]을 가져온 것!
분기 조건 (funct 3 정보)
| funct3 | assembly | condition |
|---|---|---|
| 000 | BEQ | rs1 == rs2 |
| 001 | BNE | rs1 != rs2 |
| 100 | BLT | (signed) rs1 < rs2 |
| 101 | BGE | (signed) rs1 > = rs2 |
| 110 | BLTU | (unsigned) rs1 < rs2 |
| 111 | BGEU | (unsigned) rs1 >= rs2 |
명령어 예시
BEQ x1 x2 offset- x1 == x2 이면
PC <- PC + offset
5. J-type (JAL)
목적
- 무조건 점프 + 복귀 주소 저장 목적
- 함수 호출이나 루프 점프에서 사용
대표 명령어 : JAL rd imm
rd <- PC +4andPC <- PC +imm- 보통
rd = x1(return address, RA) 로 사용한다.
명령어 구조
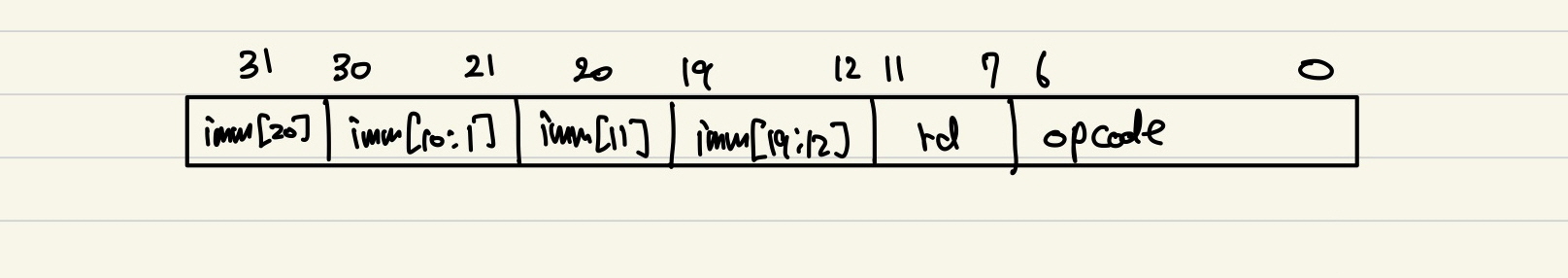
- Opcode = 1101111
- funct3 / funct7 가 없다!!
- Imm 값이 찍어져 저장된다! 마치 B-type
얜 왜 찢어져 저장?
상위 비트는 U-type처럼 instr[31:20] 근처에, 하위 비트는 rd, opcode 근처에 다른 명령어들과 비슷하게 저장
-> 하드웨어가 공통 경로로 해석하기 쉽게 만듬
-> 즉 결국 잘 보면 대부분 형태나 위치를 비슷하게 만드려고 노력한게 보인다.
명령어 예시
JAL x2 16
` 설명
----------------------------------------
Current PC : 0x1000 |현재 명령 주소
imm : 16 |16 byte 떨어진 곳으로 점프
stored imm : 16 >> 1 = 8 | imm[0]은 버리고 상위 비트만 저장
Restore : 8 << 1 = 16 | 분기 주소 계산을 위한 복원
Excute : PC_next = 0x1000+16 | 점프
= 0x1010
rd(x1) : 0x1004 | 복귀 주소 저장
- 점프 가능한 범위 : 즉시값 비트 수 : 21 bit (imm[20:0])
6. U-type
목적
-
상위 20 bit 즉시값 사용 명령어
-
하위 12 bit는 0으로 채워서 큰 상수를 만들거나, PC-relative 주소 계산에 사용
-
RISC-V에는 두가지 U-type 명령이 있다!!
1. LUI (Load Upper Immedate)
2. AUIPC ( Add Upper Immediate to PC)
| 명령어 | Opcode | 설명 |
|---|---|---|
| LUI | 0110111 | 상위 20 bit를 rd에 load |
| AUPIC | 0010111 | (PC+상위 20 bit) 값을 rd 에 저장 |
명령어 포맷
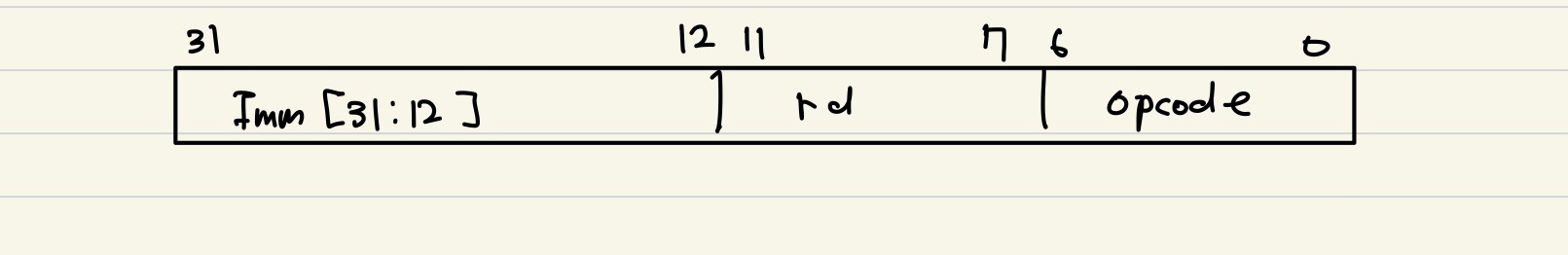
명령어 예시
| 명령어 | 수행 연산 | 설명 |
LUI rd Imm | rd <- imm << 12 | 상위 20 bit load (하위 0)
AUIPC rd imm | rd <- PC + (imm << 12) | PC-relative 주소 계산계속 수정하기..