
참고 사이트
드림코딩 엘리 JS수업
엘리 수업을 정리해준 Notion 사이트
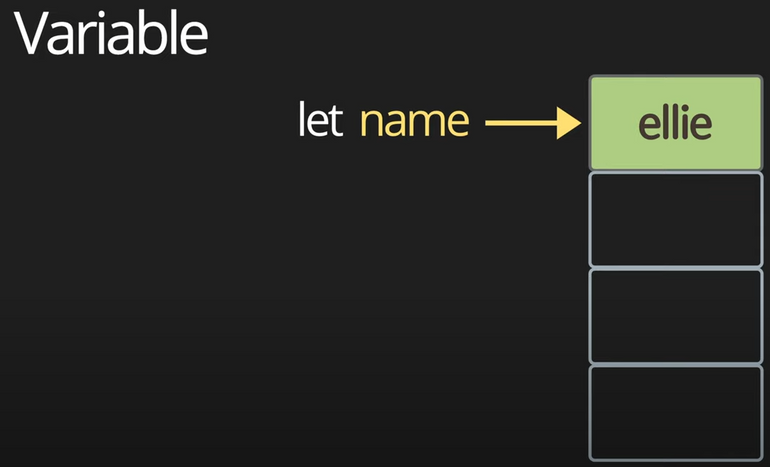
1. let
// 1. Use strict
// added in ES 5
// use this ffor Valina Javascript.
'use strict'
// 2. Variable
// let (added in ES6)
let globalName = 'global name';
{
let name = 'ellie';
console.log(name);
name = 'hello';
console.log(name);
}
console.log(name);
console.log(globalName);- let은 ES6부터 생겨났다.
- scope를 가지고 있다.
- 변경(값의 재 할당)이 가능하다.
2. var
// var (don't ever use this!)
// var hoisting (move declaration from bottom to top)
// has no block scope
{
age = 4;
var age;
}
console.log(age);- let 이전부터 사용가능한 변수 였다.
- scope가 없다.(엄청 안에 사용되었어도 어디서든 사용 가능하다. --> 에러의 주요 원인이 될 수 있다.)
- hoisting된다.(가장 아래에 선언 되었어도 사용이 가능하다 --> 역시 에러의 원인이 된다.)
3. const

// 3. Contants
// favor immutable data type always for a few reasons:
// - security
// - thread safety
// - reduce human mistakes
// Immutable
const daysInWeek = 7;
const maxNumber = 5;- let과 같이 나왔으며 차이점은 재할당이 불가능 하다는 점이다.
- 코드의 안전성을 위해서라도 const를 쓸만한 상황이라면(재할당이 필요없는 변수)const를 쓰는 게 실수를 줄여줄 수 있다.(버릇을 들이기 위해 우선 const로 쓰고 let이 필요한가를 생각해보자.)
4. Variable types
// 4. Varialbe types
// primitive, single item: number, string, boolean, nul, undifiendm symbol
// object, box container
// function, first-class function1. primitive

1. 변수에 값(참조가 아닌)이 들어간다.
1. number
const count = 17; // integer
const size = 17.1; //decimal number
console.log(`value: ${count}, type: ${typeof count}`);
console.log(`value: ${size}, type: ${typeof size}`);
// number - speical numeric values:
const infinity = 1 / 0;
const negativeInfinity = -1 / 0;
const nAn = 'not a number' / 2;
console.log(infinity);
console.log(negativeInfinity);
console.log(nAn);
// 중요한 이유 나중에 dom요소를 연산하게 될 테인데 낮누고자 하는 값이 0인지 확인도 하지 않으면 안되고
// 숫자가 아닌 값을 연산할 수 있기 때문에
// bigInt (fairly new, don't use it yet)
const bigInt = 1234567890123456789012345678901234567890n; // over (-2**53) ~ 2**53
console.log(`value: ${bigInt}, type: ${typeof bigInt}`);
console.log(Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER);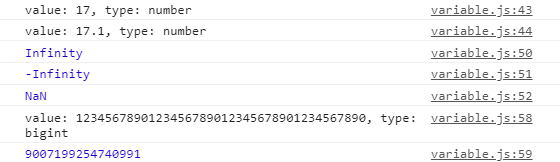
1. JS에선 다른 언어와 다르게 숫자는 모두 number이다.
(Java나 C경우 int, float double, long등의 차이가 있다)
2. 무한대, -무한대, 숫자가 아님을 뜻하는 타입이 있다.
(이는 후에 조건을 검사할 때 유요하게 쓸 수 있다고 한다.)
3. 최근 문법으로 숫자뒤에 'n'을 붙여 bigint타입을 지정할 수 있다고 나온다.
2. string
// string
const char = 'c';
const brendan = 'brendan';
const greeting = 'hello' + brendan;
console.log(`value: ${greeting}, type: ${typeof greeting}`);
const helloBob = `hi ${brendan}!`; // template literals (string)
console.log(`value: ${helloBob}, type: ${typeof helloBob}`);- 역시 다른 언어(Java, C)와 다르게 한 문자든 문장이든 string이라는 하나의 타입이다
- template literal이라는 문법으로 편리하게 문자열을 만들 수 있다.
3. boolean
// boolean
// false: 0, null, undefined, NaN, ''
// true: any other value
const canRead = true;
const test = 3 < 1; // false
console.log(`value: ${canRead}, type: ${typeof canRead}`);
console.log(`value: ${test}, type: ${typeof test}`);- false값으로 0, null, undefined, NaN, ''
'' 빈 문자열 역시 false로 취급한다는걸 명심했으면 좋겠다.
4. null, undefined
// null
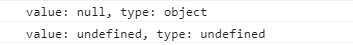
let nothing = null;
console.log(`value: ${nothing}, type: ${typeof nothing}`);
// undefined
let x;
console.log(`value: ${x}, type: ${typeof x}`);- 둘의 차이는 헷갈릴 수 있는데, null은 null이라고 명시해줘야 하고(null이라는 값이 지정되어 있다는 말), undefiend는 아직 아무 값도 지정되어 있지 않기 때문에 undefined이다.
- 특이하게 null의 type은 Object이다.
5. Symbol
// symbol, create unique identifiers for objects
const symbol1 = Symbol('id');
const symbol2 = Symbol('id');
console.log(symbol1 === symbol2); // false
// 맵이나 다른 자료구조에서 고유한 식별자가 필요하거나 동시에 다발적으로 컨커런트하게 실행될 수 잇는 코드에서 우선순위를 주고 싶을 때 정말 고유한 식별자가 필요할 때 사용
// string은 다른 모듈에서 동이란 string의 경우 동일한 식별자로 취급받는데
// Symbol은 동일한 string으로 만들어 져도, 다른 값을 가질 수 있는 것을 볼 수 있다.
// 반대로 필요에 따라 동일한 string이면 같은 Symbol을 만들 수 도 있다
const gSymbol1 = Symbol.for('id');
const gSymbol2 = Symbol.for('id');
console.log(gSymbol1 === gSymbol2); // true
console.log(`value: ${symbol1.description}, type: ${typeof symbol1}`);- 객체나 맵의 id값을 고유하게 식별할 때 string대신 사용할 수 있는 값이다.
- Symbol은 stirng을 매개로 만들어지는데, string이 같아도 다른 심볼로 취급된다.
console.log(symbol1 === symbol2); // false - 필요시 같은 심볼로 만드는 방법이 존재한다.(
Symbol.for('id'))
console.log(gSymbol1 === gSymbol2); // true - 출력할 때 그냥은 출력이 안되고 .description을 해야 한다.
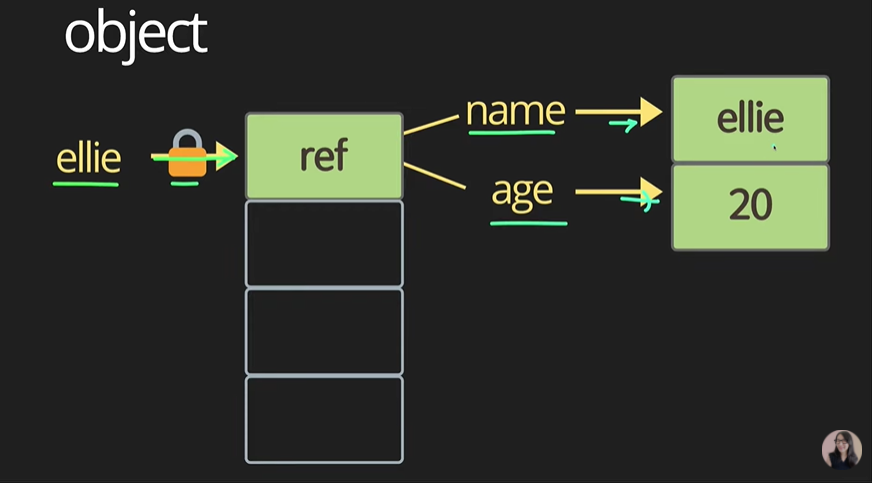
2. object
// object, real-life object, data structure
const ellie = {name: 'ellie', age: 20};
ellie.age = 21;- 변수에 참조(
값 자체가 아닌)가 들어간다. - 자세한 내용은 3부에
3. Dynamic typing
// 5. Dynamic typing: dynamically typed langauge
let text = 'hello';
console.log(text.charAt(0)); // h
console.log(`value: ${text}, type: ${typeof text}`);
text = 1;
console.log(`value: ${text}, type: ${typeof text}`);
text = '7' + 5;
console.log(`value: ${text}, type: ${typeof text}`);
text = '8' / 2
console.log(`value: ${text}, type: ${typeof text}`);
console.log(text.charAt(0)); // error!!- js는 중간에 변수의 형 변환이 드라마틱하게 가능하다
- 이는 수 많은 에러를 불러 일을 킬 수 있다.
- 이를 해결하기 위해 나온 문법이 타입스크립트이다.
