✒️ 테라폼으로 ArcoCD 설치 & 트러블 슈팅 과정 기록
테라폼으로 ALB Controller 설치 & 트러블슈팅 과정 기록에 이어서 ArgoCD를 설치하고 트러블 슈팅하면서 배운 것들에 대해 기록해보려 한다.
원래 ALB Controller랑 같이 적으려 했는데 ACM 인증서 적용해서 만드는 것까지 포함해서 적으려니 글이 너무 길어질 것 같아서 나누었다.
설치 개요
처음에는 ArgoCD를 따로 도메인 없이 ALB DNS로 접근하는 방식으로 사용하려 했는데 전에 가비아에서 사놓은 도메인이 있어서 그걸 활용하기로 했다.
그래서 전체적인 큰 흐름은 아래와 같다
1. Route53 콘솔에서 호스팅 영역 생성
2. 가비아에 Route53에서 생성된 NS 레코드 등록
3. 테라폼으로 ACM 발급
4. ACM ARN 받아서 ArgoCD 설치1번, 2번은 생략하고 테라폼을 통해 ACM을 발급하는 것부터 시작하겠다.
설치 과정
🧾 ACM 발급
1. ACM 인증서 요청
사용자가 aws_acm_certificate 리소스를 생성하면서 도메인 이름과 함께 인증서 발급을 요청한다.
resource "aws_acm_certificate" "cert" {
domain_name = "*.${var.domain_name}" # 와일드카드 도메인
subject_alternative_names = [var.domain_name] # 루트 도메인 추가
validation_method = "DNS"
}여기서 ACM이 인증용 CNAME 레코드 정보를 생성한다. 하지만 이를 실제 DNS(Route53)에 등록하지는 않아서 테라폼을 통해 등록해주어야 한다.
2. Route53 호스팅 영역 조회
data "aws_route53_zone" "zone" {
name = var.domain_name
private_zone = false
}전에 만들어둔 호스팅 영역 정보를 가져온다.
3. CNAME 레코드를 Route53에 생성
resource "aws_route53_record" "validation" {
for_each = {
for dvo in aws_acm_certificate.cert.domain_validation_options : dvo.domain_name => {
name = dvo.resource_record_name
type = dvo.resource_record_type
record = dvo.resource_record_value
}
}
zone_id = data.aws_route53_zone.zone.zone_id
name = each.value.name
type = each.value.type
ttl = 60
records = [each.value.record]
}domain_validation_options 에서 ACM이 요구한 CNAME 레코드 리스트를 추출하고, 이를 기반으로 해당 도메인의 검증용 CNAME 레코드를 Route53에 등록한다.
4. ACM에서 최종 검증 수행
resource "aws_acm_certificate_validation" "cert_validation" {
certificate_arn = aws_acm_certificate.cert.arn
validation_record_fqdns = [for r in aws_route53_record.validation : r.fqdn]
depends_on = [ aws_route53_record.validation ]
}DNS에 필요한 CNAME을 동록했으므로, ACM에 CNAME 레코드에 대한 검증을 트리거한다. depends_on = [ aws_route53_record.validation ]을 명시해서 레코드가 먼저 완전히 생성된 후에만 이 리소스가 실행되도록 강제했다.
레코드에 대한 검증이 완료되면 인증서의 상태가 '발급됨(Issued)'으로 변경된다.
🐙 ArgoCD 설치
ArgoCD를 생성하기 위해 네임스페이스를 먼저 생성하고, Helm 차트로 설치했다.
# modules/eks-argocd/main.tf
resource "kubernetes_namespace" "argocd" {
metadata {
name = "argocd"
}
}
resource "helm_release" "argocd" {
name = "argocd"
repository = "https://argoproj.github.io/argo-helm"
chart = "argo-cd"
version = "6.7.11"
namespace = kubernetes_namespace.argocd.metadata[0].name
create_namespace = false
values = [
templatefile("${path.module}/values/argocd-values.yaml.tpl", {
domain_name = var.domain_name
cert_arn = var.cert_arn
})
]
}values 템플릿 파일에 도메인 이름과 ACM 인증서 ARN을 전달하여 ArgoCD Ingress 구성을 동적으로 주입한다.
# modules/eks-argocd/values/argocd-values.yaml.tpl
global:
domain: argocd.${domain_name}
configs:
params:
server.insecure: true
controller:
metrics:
enabled: true
serviceMonitor:
enabled: true
server:
ingress:
enabled: true
ingressClassName: alb
hostname: "argocd.${domain_name}"
annotations:
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/scheme: internet-facing
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/target-type: ip
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol: HTTP
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/listen-ports: '[{"HTTP":80}, {"HTTPS":443}]'
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/certificate-arn: ${cert_arn}
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: '443'
aws:
serviceType: ClusterIP
backendProtocolVersion: GRPC
metrics:
enabled: true
serviceMonitor:
enabled: true
repoServer:
metrics:
enabled: true
serviceMonitor:
enabled: true
applicationSet:
metrics:
enabled: true
serviceMonitor:
enabled: true
notifications:
metrics:
enabled: true
serviceMonitor:
enabled: true
위 values 설정을 기반으로 Helm Chart가 설치되면, ALB Controller가 다음과 같이 동작한다.
ingressClassName: alb를 통해 ALB Controller가 해당 Ingress 리소스를 감지하고 ALB를 프로비저닝한다.certificate-arn: ${cert_arn}을 통해 ACM 인증서를 바인딩하고, HTTPS 리스너를 구성한다.ssl-redirect: '443'설정으로 HTTP 요청은 자동으로 HTTPS로 리다이렉션된다.
결과적으로 https://argocd.${domain.name} 도메인으로 ArgoCD에 접근할 수 있게 된다.
🔥 트러블 슈팅
1. 레코드 중복 에러
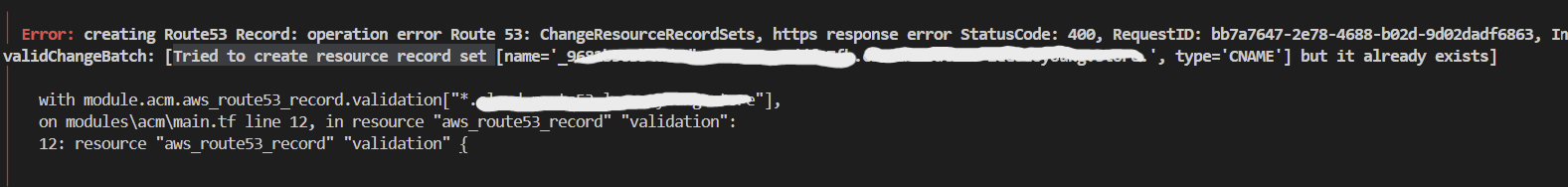
아래 CNAME 레코드를 생성하는 코드에서 동일한 레코드를 생성하려 하는 것이 원인으로 보였다.
원인을 좀 더 정확히 이해하기 위해 코드를 좀 더 자세히 살펴보았다.
resource "aws_route53_record" "validation" {
for_each = {
for dvo in aws_acm_certificate.cert.domain_validation_options : dvo.domain_name => {
name = dvo.resource_record_name
type = dvo.resource_record_type
record = dvo.resource_record_value
}
}
zone_id = data.aws_route53_zone.zone.zone_id
name = each.value.name
type = each.value.type
ttl = 60
records = [each.value.record]
}이 코드는 aws_acm_certificate 리소스가 발급 요청한 모든 도메인(domain_name, subject_alternative_names)에 대해 ACM이 반환한 CNAME 검증 레코드를 Route 53에 등록하는 구조이다.
aws_acm_certificate 리소스가 와일드카드(*.~)와 루트 도메인 두 개의 도메인을 포함하고 있으므로, aws_acm_certificate.cert.domain_validation_options는 예를 들자면 다음과 같은 리스트를 반환한다.
[
{
"domain_name": "*.example.com",
"resource_record_name": "_abc.example.com",
"resource_record_value": "abc-validation.aws"
},
{
"domain_name": "example.com",
"resource_record_name": "_def.example.com",
"resource_record_value": "def-validation.aws"
}
]
그래서 결과적으로 두 개의 CNAME 레코드를 생성하려고 시도한다.
그런데 여기서 문제가 있다. 이 AWS Certificate Manager DNS 검증 공식문서를 보면, 기본적으로 각 도메인의 레코드 이름-값 페어는 고유하지만, 와일드카드 도메인의 경우 ACM에서 생성한 문자열이 기본 도메인에 대해 생성된 문자열과 동일하다는 것이다.
그래서 테라폼에서 두 개의 동일한 CNAME 레코드를 생성하려고 하면서 에러가 발생한 것이었다.
따라서 이미 같은 동일한 레코드가 존재하더라도 덮어쓰기를 허용하도록 allow_overwrite = true 를 넣어준다.
resource "aws_route53_record" "validation" {
for_each = {
...
}
allow_overwrite = true
zone_id = data.aws_route53_zone.zone.zone_id
...
}이렇게 하면 두 번째 루프가 첫 번째 레코드를 덮어쓰면서 Route53에 하나의 CNAME 레코드만 존재하게 되지만, 이는 ACM이 요구한 검증 조건(CNAME)을 만족하므로 인증에는 전혀 문제가 없다.
2. ALB Controller 의존성 에러
failed calling webhook "mservice.elbv2.k8s.aws":
no endpoints available for service "aws-load-balancer-webhook-service"ALB Controller가 설치되기 전에 ArgoCD를 먼저 설치하려 해서 발생한 에러이다.
당연히 ALB Controller가 설치되어야 ArgoCD Ingress에서 설정한 ALB가 프로비저닝될 수 있으므로, 의존성을 명시해줘야 한다.
module "eks_argocd" {
source = "./modules/eks-argocd"
domain_name = var.domain_name
cert_arn = module.acm.acm_certificate_arn
providers = {
helm = helm.eks
kubernetes = kubernetes.eks
}
depends_on = [module.eks_addons_alb] # ALB Controller 설치 이후에 실행되도록
}성공~~~!
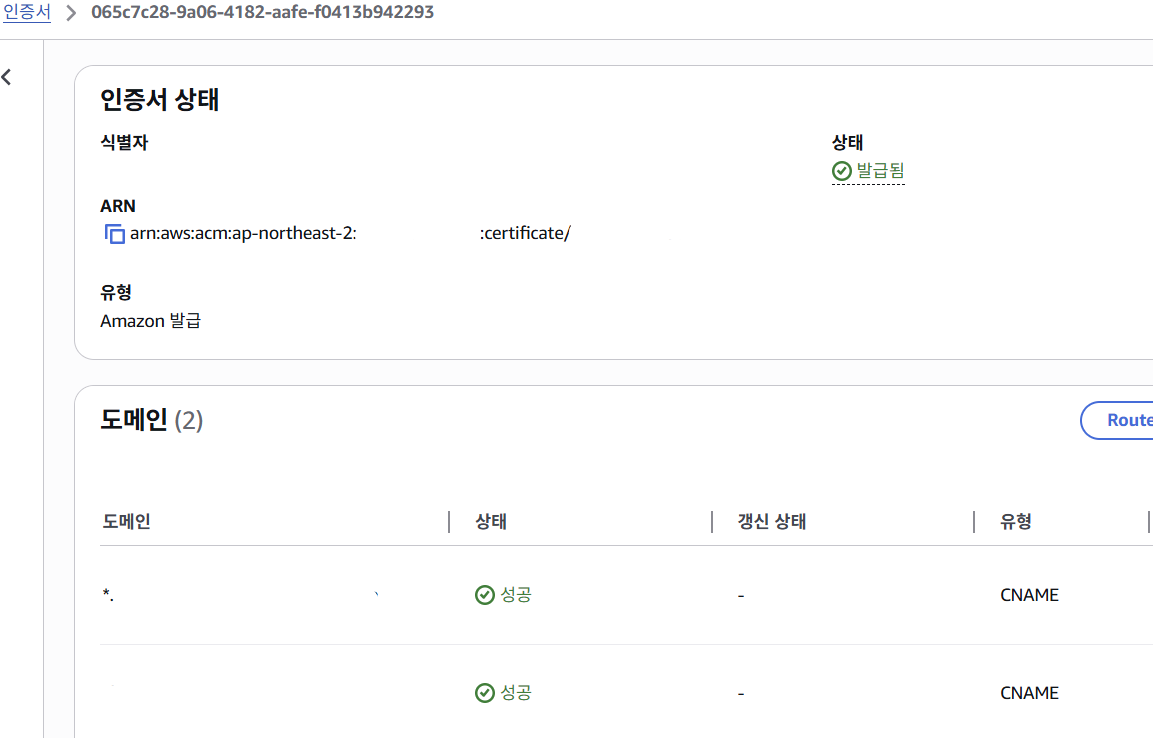
두 도메인에 대한 인증서도 잘 생성되었고,
 ArgoCD에 ALB의 주소와 호스트 주소도 잘 붙었다.
ArgoCD에 ALB의 주소와 호스트 주소도 잘 붙었다.
이때, 이전에 Helm Chart 설치 시 Ingress 리소스에 host 기반 라우팅으로 설정했기 때문에, 도메인을 ALB DNS 이름과 연결하기 위해 Route53에 alias 타입 A 레코드를 생성하였다.
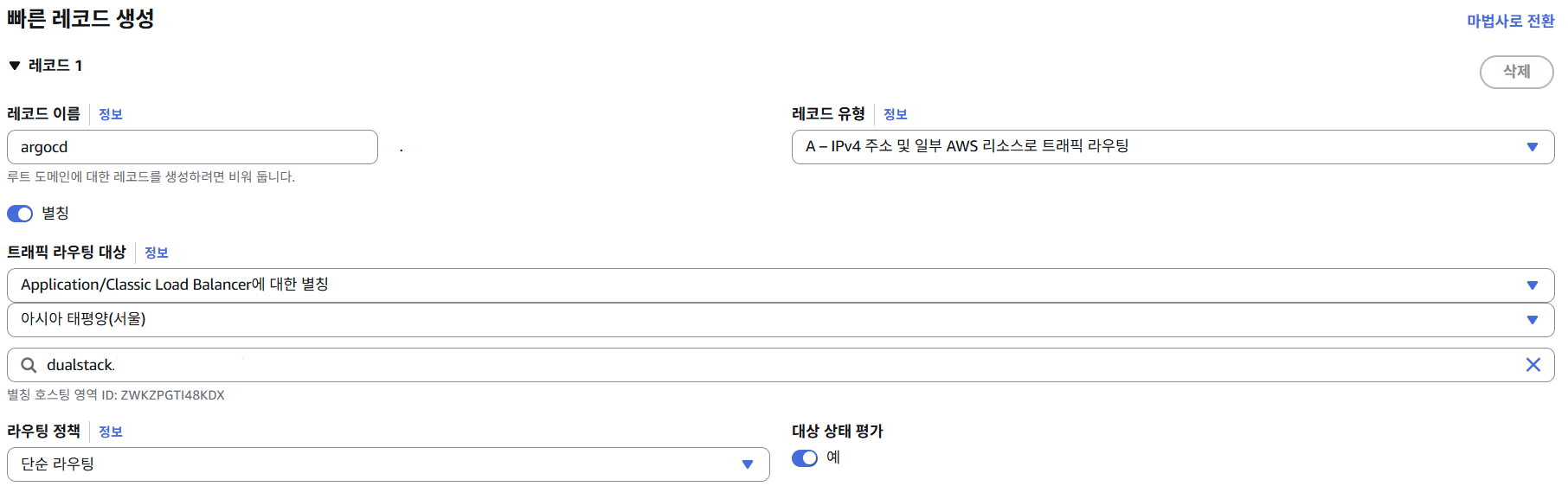
이렇게 하면 도메인 주소로 접근이 가능하다.
‼️ 삭제 시 주의할 점
ArgoCD까지 정상적으로 실행되는 것을 확인하고 terraform destroy를 실행했지만, 아래와 같은 에러 메시지가 뜨면서 일부 리소스를 삭제하지 못했고, 수동으로 콘솔에서 삭제해야 했다.
│ Error: deleting EC2 Subnet (subnet-05d483b7cb32e3393): operation error EC2: DeleteSubnet, https response error StatusCode: 400 : The subnet 'subnet-05d483b7cb32e3393' has dependencies and cannot be deleted.
│
│
╵
╷
│ Error: context deadline exceeded
│
│
╵
╷
│ Error: deleting EC2 Internet Gateway (igw-00c41fe770ae2cc13): detaching EC2 Internet Gateway (igw-00c41fe770ae2cc13) from VPC (vpc-078e0ca9f6807dcf7): operation error EC2: DetachInternetGateway, https response error StatusCode: 400, api error DependencyViolation: Network vpc-078e0ca9f6807dcf7 has some mapped public address(es). Please unmap those public address(es) before detaching the gateway.
│
│
╵
╷
│ Error: deleting EC2 Subnet (subnet-099dd712e01539633): operation error EC2: DeleteSubnet, https response error StatusCode: 400, api error DependencyViolation: The subnet 'subnet-099dd712e01539633' has dependencies and cannot be deleted.
│
│
╵
╷
│ Error: deleting ACM Certificate : operation error ACM: DeleteCertificate, https response error StatusCode: 400, ResourceInUseException: Certificate arn:certificate/a6fd938d-2367-4e4a-9f6b-c3b9b0fc5e39 in account 123456789 is in use.
│
│
╵
╷의존성 때문에 이러나... 의존성 고려해서 알아서 삭제하는 줄 알았는데 갑자기 왜 이러나... 고민하다 원인을 알게 되었다.
ALB Controller가 ArgoCD Ingress 리소스를 감지해서 생성한 ALB가 문제였다. 이 ALB는 Terraform이 직접 생성한 것이 아니므로 Terraform이 관리하지 않는다. 따라서 이 리소스가 VPC, Subnet, ACM 등과 연결되어 있지만 의존성을 인지하지 못하고 삭제를 시도해서 에러가 발생한 것이다.
다음과 같은 순서로 리소스를 삭제하면 이전처럼 모든 리소스를 깔끔하게 정리할 수 있다!
1. ArgoCD Helm 릴리스 수동 삭제
helm uninstall argocd -n argocdArgoCD Ingress가 삭제되면, ALB Controller가 이를 감지하고 ALB 및 관련 리소스도 함께 정리된다.
2. Terraform 상태에서 Helm 릴리스 제거
terraform state rm module.eks_argocd.helm_release.argocd이 Helm은 테라폼에서 설치한 것이다. 테라폼은 아무것도 모르고 Helm이 잘 설치된 것으로 알고 있을 것이므로, 상태에서 수동으로 제거해 Terraform의 인식과 실제 상태를 맞춰준다.
3. Terraform destroy 실행
terraform destroy이제 AWS 리소스들 간 의존성이 정리되어, 나머지 리소스들이 정상적으로 삭제된다.
테라폼으로 EKS 구조를 구축하면서, 초기에 어디까지 인프라를 자동화하는 것이 좋을까 하는 고민을 많이 했다. 직접 운영해본 경험이 없다보니 확신이 없어서 여기저기 찾아보다 레딧에도 질문 글을 올렸다. (생각보다 많은 사람들이 댓글을 달아줘서 감동 받음ㅎㅎ)
흠 결론은 당연히 상황에 따라 다르겠지만, 테라폼으로 쿠버네티스까지 배포하는 경우에는 ArgoCD까지 설치해서 GitOps로 연결하는 게 좋을 것 같다고 생각됐다. 그래서 ArgoCD까지 설치해봤으니 테라폼으로 EKS 배포하기 프로젝트는 여기서 마무리 지으려고 한다. 생각보다 오래 걸렸고, 비용도 많이 들었지만, 테라폼으로 배포하면서 내가 이전에 구축했던 아키텍처의 전체적인 흐름을 좀 더 깊이 이해하게 된 것 같다.

