brain Segmentation ] GAN_1
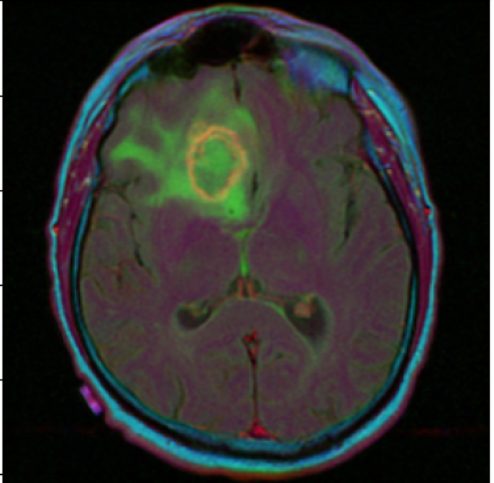
원본이미지
brain tumor
로스 설명

E : cross entropy
1. loss : W loss
input : gray scale + normalization(mean = 0, std=1)로 1, 128,128 size
로스: W loss
critic_real = critic(real_images)
critic_fake = critic(generator(noise))
loss_critic = -(torch.mean(critic_real) - torch.mean(critic_fake))
1, 128,128 size
-> 로스 마이너스값...
W loss보다는 BCE 사용으로 보기 + 중간 사진 저장하게
2. Loss BCE
input , output : 1, 128, 128
loss : BCE
D_loss가 0.00 되면서 학습 안이뤄짐
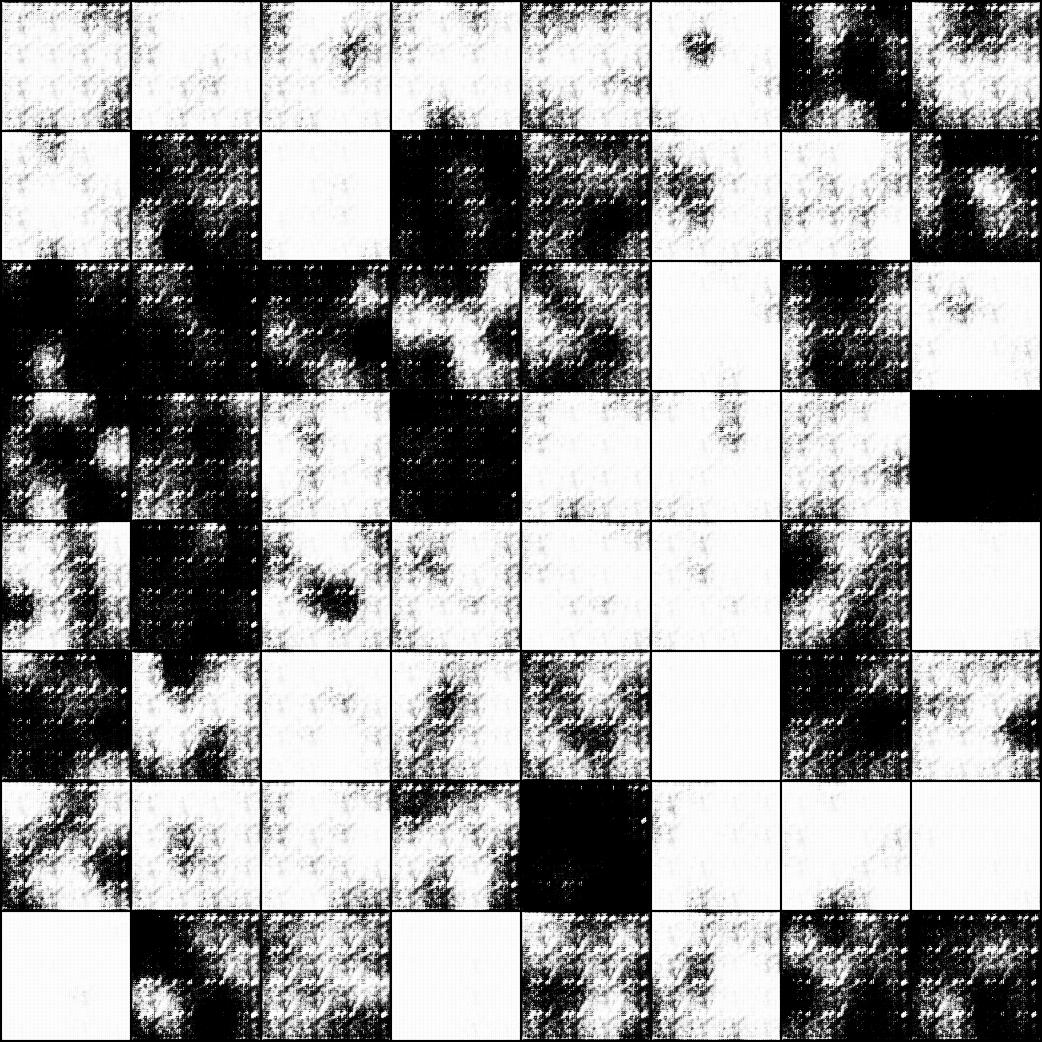

epoch 100 때에 생성된 이미지..
D가 0이되면 G가 더 이상 더 좋은 이미지 생성 못함
3.
- 흑백이 잘못인가, 더 시각화로 볼수 있게 color 3channel 쓰기로함
가우시안 노이즈 추가하면 좋다고해서 추가 - 또한 D 로스 0으로 확 주는거 방지하려고 parameter clamp추가함
-0.1 ~ 0,1 사이 값으로 parameter 조절 - 후에 G 학습할 때 D 파라미터 require grade =False 추가.
그런데 어차피 G optimizer에 넘어가는게 G param이어서 굳이 고정 안해도 되지않나,,?
3-1
cv로 읽을 수 /255.로 0~1맞춘 후 가우시안 노이즈 추가
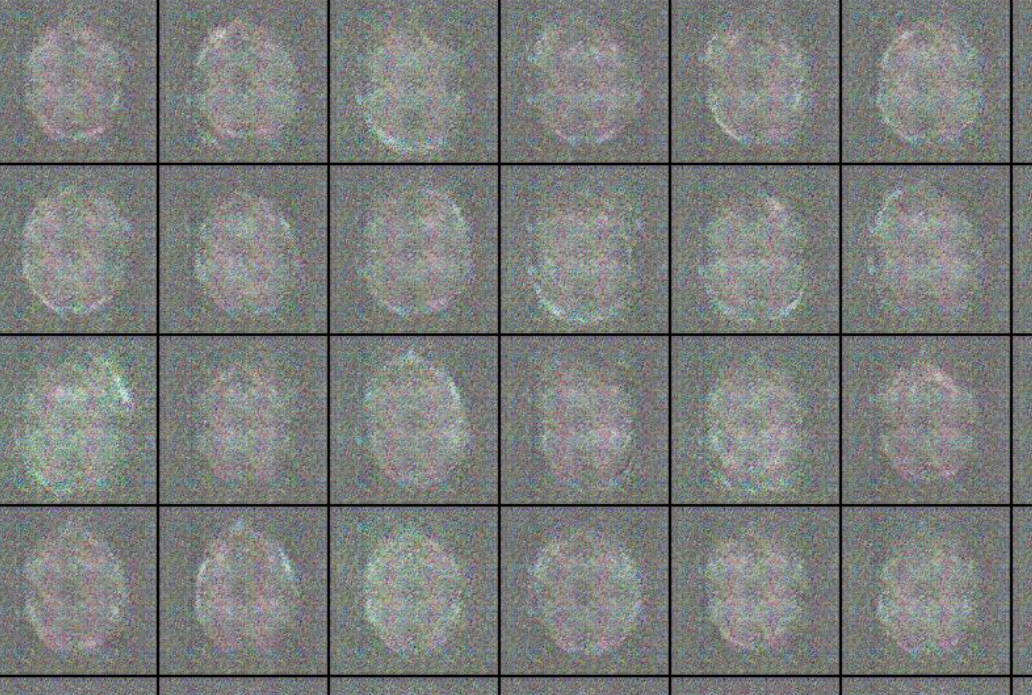
epoch 10때의 현상
그런데 노이즈 255 나눈 후 0~1 된 상태 이미지 너무 치직거려서
노이즈 추가 후에 255로 나눔
에포크 10 때의 이미지
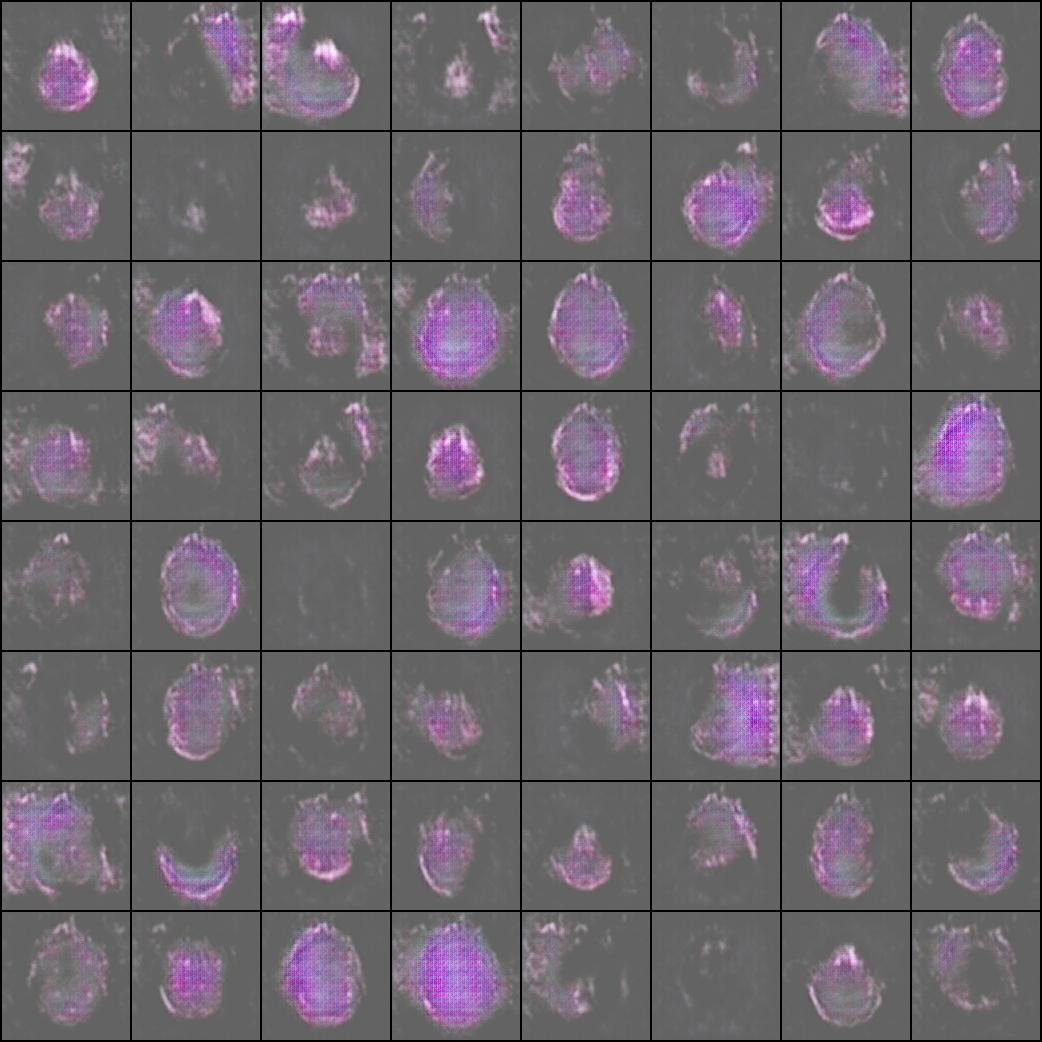
에포크 300 때의 이미지
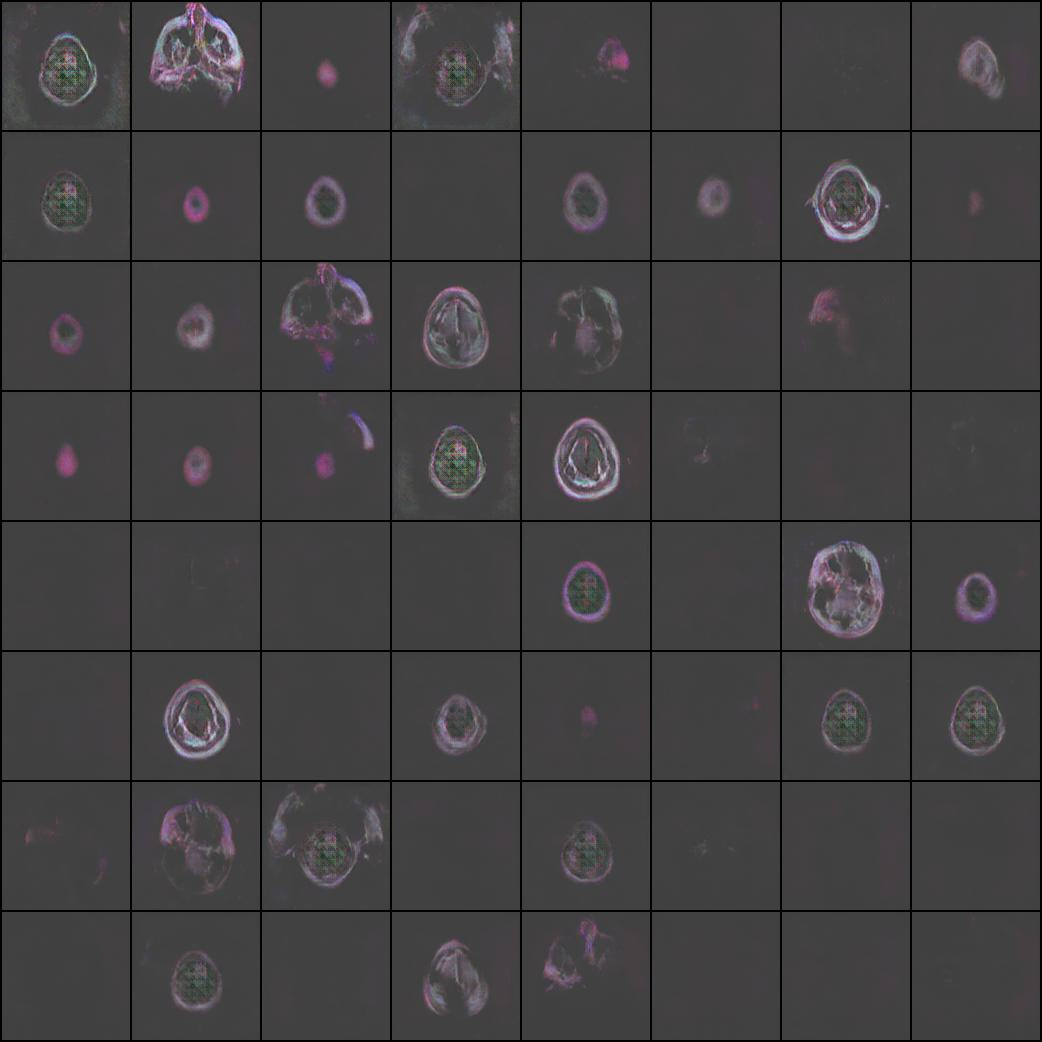
학습이 잘 되나 싶었으나 되지 않음을 확인했다.
하루동안 돌려놓고 다음날 와서 확인했는데 저모양...

학습 그래프는 위와같다.
3-2
노이즈에 W loss 다시적용해보기.............+ Gradient panelty 적용
data normalization 은 그냥 /255.로
epoch는 최대 100정도만 보고 확인하는게 나을듯
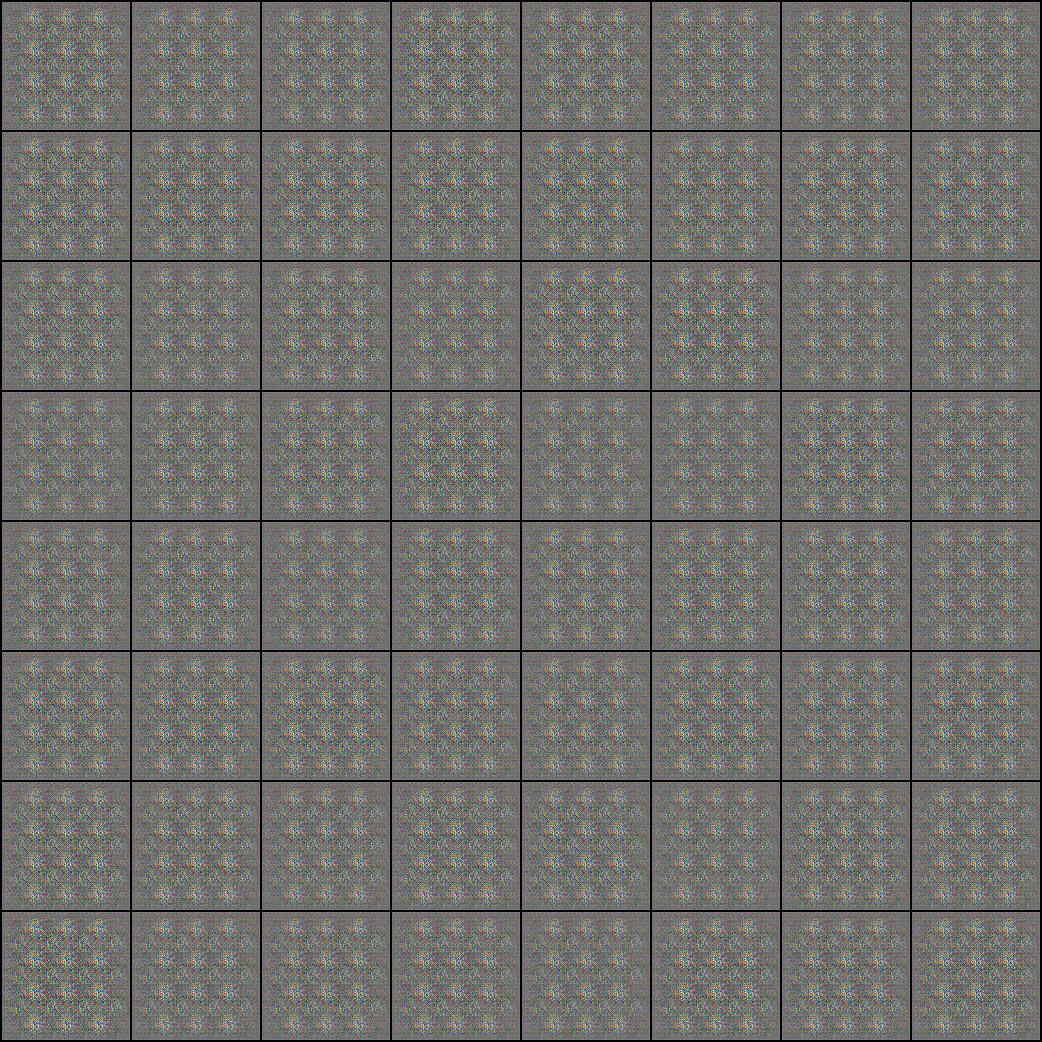
epoch 20 때... 저렇게 나와버려서
3-3
혹시 G loss : -mean(D(fake))가 잘못인가 싶어서 부호를 바꿔 트레이닝 시켰다가 중단.
모델을 DC gan에서 바꿈
latent vec 받아서 (1, nz, 1,1) 바로 trans conv2d (nz -> nc*16) 해줬는데 linear로..
WGAN 에서 그렇게 쓰는거 같길래,,

EPOCH [31/100] Loss_D: 10.0000 Loss_G: -0.0000 D(x): 0.0000 D(G(z)): 0.0000 / 0.0000
Loss G가 0이 되면서 학습 안일어남
3-4
Wloss 이용.
netD에 들어가기전 real image, fake image에 가우사안 노이즈 추가하기.
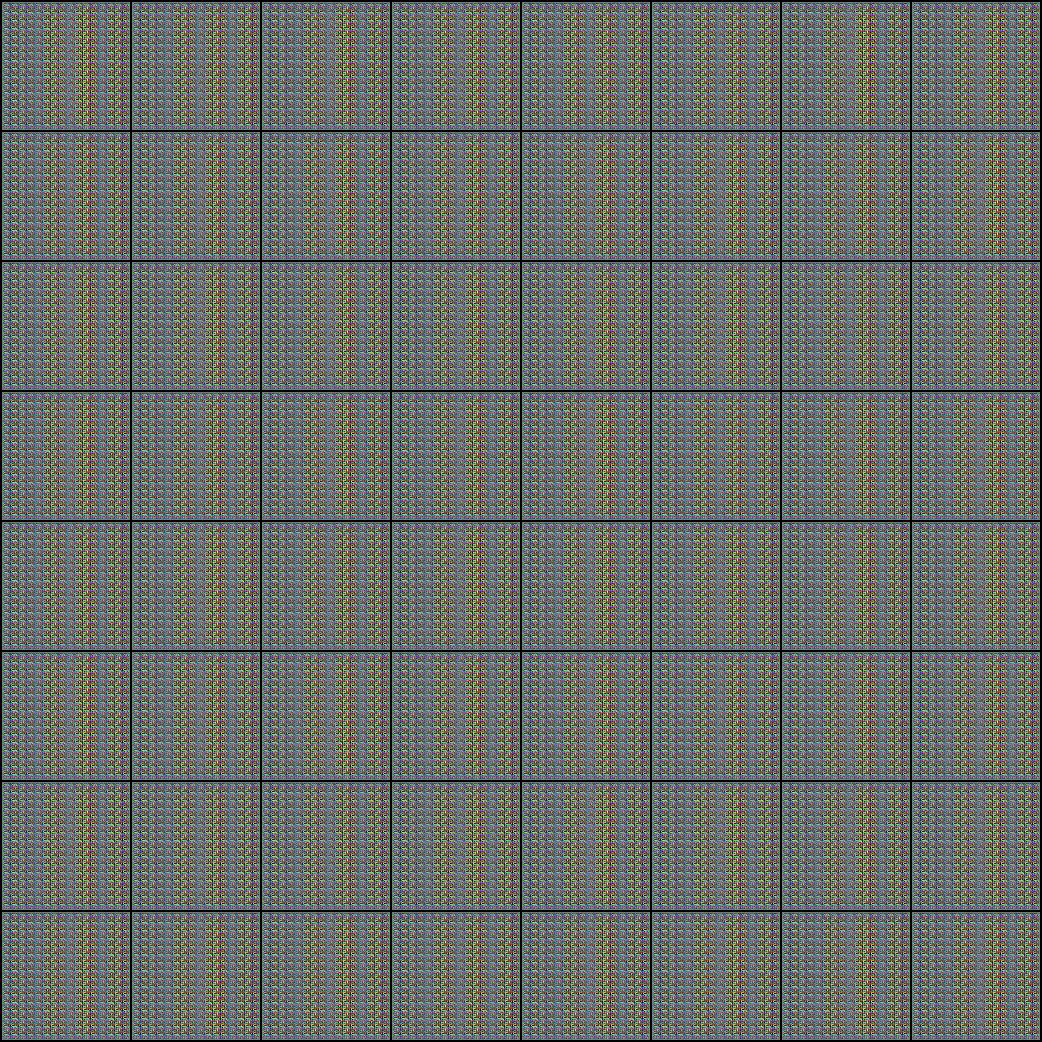
왜안되지
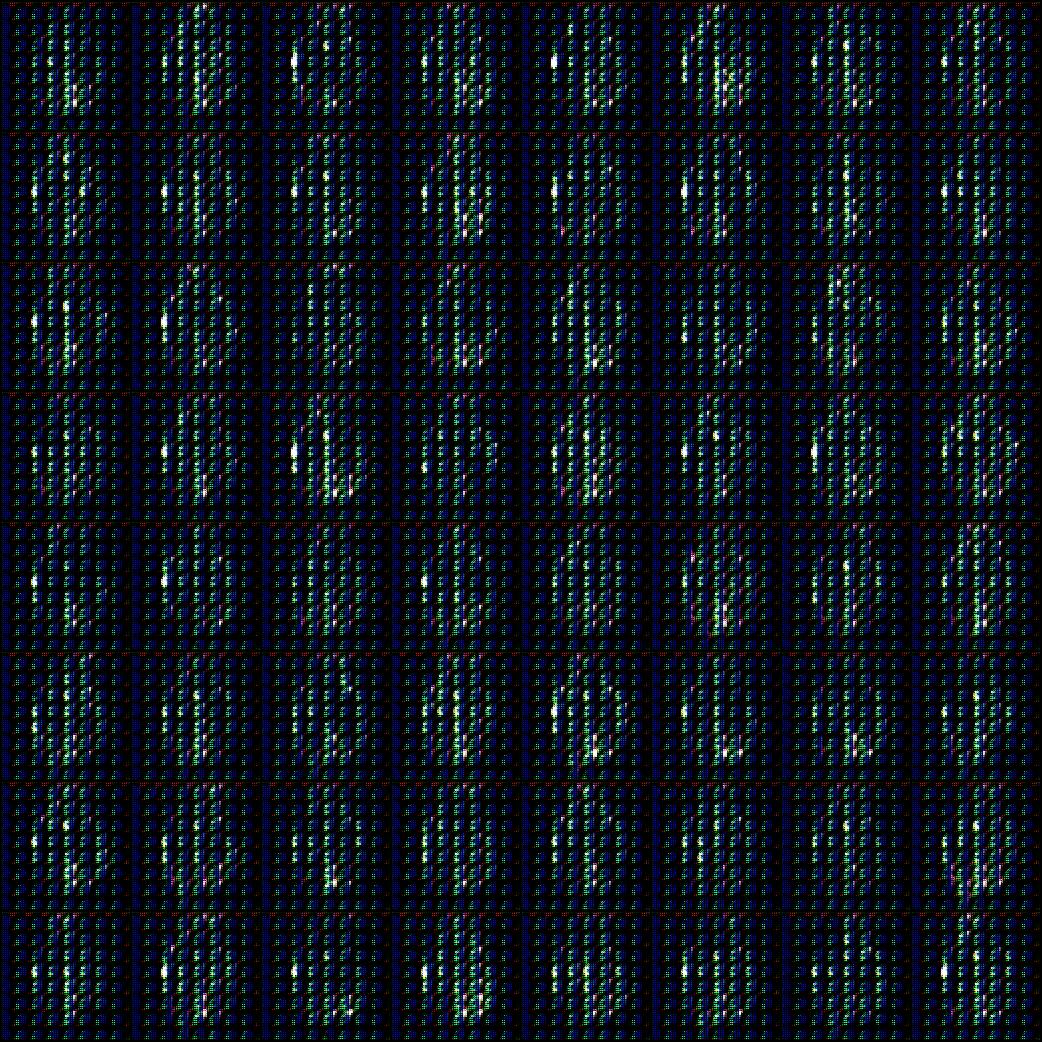
3-5
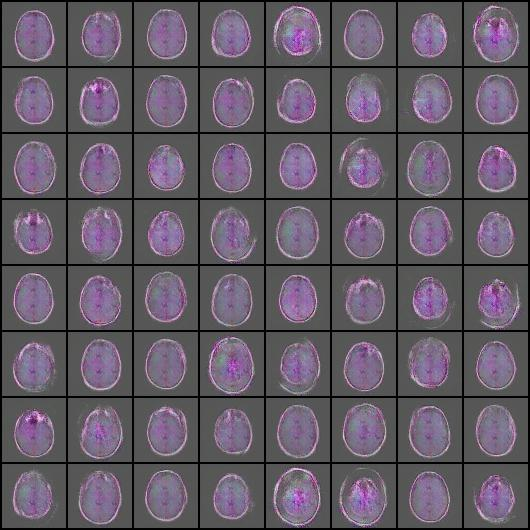
epoch 191 때
image 64
DC GAN 이용
class Dataset()
def __getitem__(self, index)
image = self.image_file[index]
data = cv2.imread(image)
#data = noisy("gauss", data)
data =data/255.
dataransform=transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Resize(64),
])
data = dataransform(data).type(torch.float64)
return data # torch.Size([1, 128, 128])
class Generator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Generator, self).__init__()
self.main = nn.Sequential(
nn.ConvTranspose2d( nz, ngf * 8, 4, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ngf * 8),
nn.ReLU(True),
#(ngf*8) x 4 x 4
nn.ConvTranspose2d(ngf * 8, ngf * 4, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ngf * 4),
nn.ReLU(True),
#(ngf*4) x 8 x 8
nn.ConvTranspose2d( ngf * 4, ngf * 2, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ngf * 2),
nn.ReLU(True),
# (ngf*2) x 16 x 16
nn.ConvTranspose2d( ngf * 2, ngf, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ngf),
nn.ReLU(True),
# (ngf) x 32 x 32
nn.ConvTranspose2d( ngf, nc, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.Tanh()
# (nc) x 64 x 64
)
def forward(self, input):
return self.main(input)
class Discriminator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Discriminator, self).__init__()
self.main = nn.Sequential(
# (nc) x 64 x 64
nn.Conv2d(nc, ndf, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
# (ndf) x 32 x 32
nn.Conv2d(ndf, ndf * 2, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ndf * 2),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
# (ndf*2) x 16 x 16
nn.Conv2d(ndf * 2, ndf * 4, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ndf * 4),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
# (ndf*4) x 8 x 8
nn.Conv2d(ndf * 4, ndf * 8, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ndf * 8),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
# (ndf*8) x 4 x 4
nn.Conv2d(ndf * 8, 1, 4, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def forward(self, input):
return self.main(input)