7.1 큰 DataFrame 살펴보기
pandas에는 큰 dataframe을 다룰 수 있는 기능들도 있다 !!
import pandas as pd
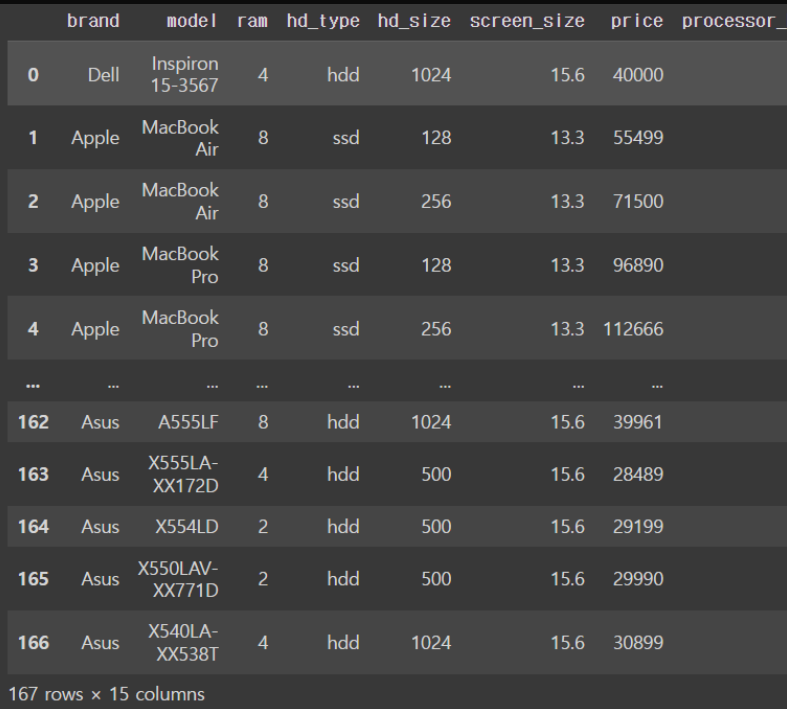
laptops_df=pd.read_csv('drive/MyDrive/dataScience/data/laptops.csv')
laptops_dfoutput
ㄴ 167 rows x 15 columns 로 큰 데이터 !
큰 데이터프레임에서 몇 줄만 가져오게 할 수도 있는데 슬라이싱 하듯이 윗줄 부터 가져오고 싶으면 .head()를 쓰면 된다
laptops_df.head(3)output
laptops_df.head(7)output
아랫줄 부터 가져오고 싶다면 .tail()을 쓰자
laptops_df.tail(6)output
dataframe이 어떻게 생겼는지 알아보고자 하면 .shape()를 쓰면 된당
laptops_df.shapeoutput
(167, 15)column에 무슨 요소들이 있는지 알아보고 싶다면
laptops_df.columnsoutput
Index(['brand', 'model', 'ram', 'hd_type', 'hd_size', 'screen_size', 'price',
'processor_brand', 'processor_model', 'clock_speed',
'graphic_card_brand', 'graphic_card_size', 'os', 'weight', 'comments'],
dtype='object')row에 무슨 요소들이 있는지 알아보고 싶다면
laptops_df.indexoutput
Int64Index([ 5, 90, 96, 31, 154, 122, 151, 34, 44, 6,
...
119, 9, 14, 158, 143, 73, 100, 108, 83, 148],
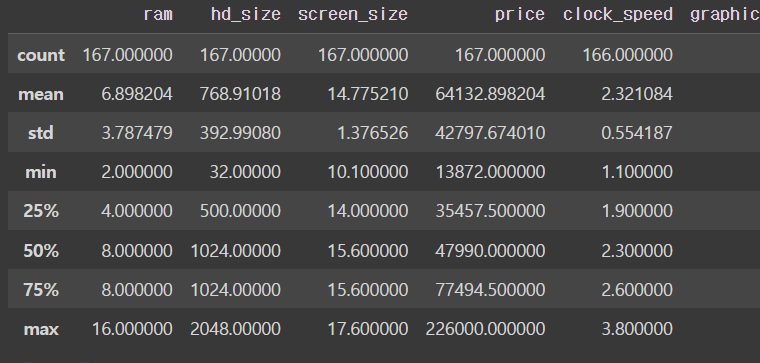
dtype='int64', length=167)dataFrame에 대한 간단한 통계적 요약정보를 제공하는 함수를 .describe()라고 한다. 이는 dataFrame에 숫자형 컬럼들이 있을 때, 해당 컬럼들의 기술 통계 정보를 보여줌
laptops_df.describe()output
정렬을 하고싶다면 sort_values()를 이용하면 된다 !
오름차순 정렬은 그냥 쓰면 되고
laptops_df.sort_values(by='price')output
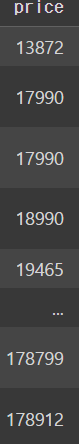
ㄴ 이렇게 되면 price만 sorting 할 수 있다
내림차순으로 정렬하고자 하면 ascending=False를 넣어주면 된다
laptops_df.sort_values(by='price',ascending=False)output
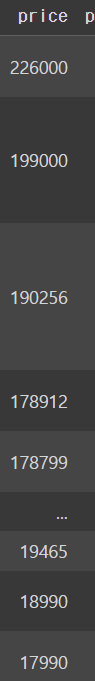
이렇게 정렬을 하고 나서 다시 laptops_df로 선언을 하면
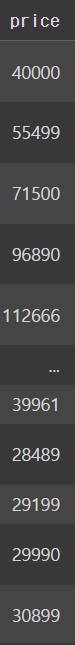
원 상태와 그대로인 것을 볼 수 있음 !!
이때도 역시 inplace = True를 쓰도록 하자
laptops_df.sort_values(by='price',ascending=False,inplace=True)
laptops_dfoutput
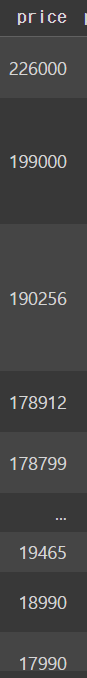
원본이 수정되는 것을 확인할 수 있당
7.2 큰 Series 살펴보기
Series는 1차원이기 때문에 dataFrame보다는 간단하다 ! 살펴보장
(아까와 같은 dataFrame)
한 column만 뽑아내고자 하면 []안에 입력해주면 된다
laptops_df['brand']output
5 Apple
90 Alienware
96 Alienware
31 Acer
154 Microsoft
...
73 Acer
100 Acer
108 Acer
83 Acer
148 Acer
Name: brand, Length: 167, dtype: object중복 되는 것들을 무시하고 하나로 취급해서 추출하고 싶을 때는 df['~~'].unique()를 쓰자
laptops_df['brand'].unique()output
array(['Apple', 'Alienware', 'Acer', 'Microsoft', 'HP', 'Dell', 'Lenovo',
'Asus'], dtype=object)몇 번 나오는지 알고 싶으면 .value_counts()라고 쓰면 된다
laptops_df['brand'].value_counts()output
HP 55
Acer 35
Dell 31
Lenovo 18
Asus 9
Apple 7
Alienware 6
Microsoft 6
Name: brand, dtype: int64.describe()로 요약도 가능하다
laptops_df['brand'].describe()output
count 167
unique 8
top HP
freq 55
Name: brand, dtype: object7.3 (실습) 여행지 선정하기 I
1.여행을 좋아하는 익중이는 여행지를 알아보고 있습니다. 주어진 데이터에는 총 몇 개의 도시와 몇 개의 나라가 있는지 알아맞혀 보세요.
code
-cities
df['City / Urban area'].value_counts().shapeoutput
(249,)-countries
df['Country'].value_counts().shapeoutput
(61,)2.사람 만나기를 좋아하는 익중이는 가장 사람이 붐비는 도시로 여행을 가기로 마음 먹었습니다. 주어진 데이터에서, 인구 밀도(명/sqKm) 가 10000 이 넘는 도시는 총 몇 개인지 알아보세요.
참고로 인구 밀도는 인구 수 / 땅의 면적 (in sqKm) 로 구할 수 있습니다.
code
density = cities_df['Population'] / cities_df['Land area (in sqKm)']
density>10000
cities_df[density>10000].value_counts().shape3.이번에는 인구 밀도가 가장 높은 도시를 찾아봅시다.
답안은 데이터에 적힌 이름을 그대로 입력해 주세요. (예시: Seoul)
code
density = cities_df['Population'] / cities_df['Land area (in sqKm)']
cities_df['density']=density
cities_df.sort_values(by='density',ascending=False)7.4 (실습) 여행지 선정하기 II
익중이는 누나에게 여행지를 추천 받으려고 합니다.
그런데 나라 이름이 기억나지 않고, 이 데이터에 4개의 도시가 나왔다는 것만 기억이 난다고 하네요.
이 나라는 무엇일까요?
code
countries=cities_df['Country'].value_counts() # 어떤 국가가 얼마나 등장하는지 세기
countries[countries == 4] # 빈도 확인하기output
Italy 4
Name: Country, dtype: int647.5 (실습) 코드잇 대학교 : 수강신청 준비하기
2,000명의 코드잇 대학교 학생들이 수강신청을 했습니다.
수강신청에는 다음 3개의 조건이 있습니다.
“information technology” 과목은 심화과목이라 1학년은 수강할 수 없습니다.
“commerce” 과목은 기초과목이고 많은 학생들이 듣는 수업이라 4학년은 수강할 수 없습니다.
수강생이 5명이 되지 않으면 강의는 폐강되어 수강할 수 없습니다.
기존 DataFrame에 “status”라는 이름의 column을 추가하고, 학생이 수강 가능한 상태이면 “allowed”, 수강 불가능한 상태이면 “not allowed”를 넣어주세요.
code
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv('data/enrolment_1.csv')
df["status"] = "allowed"
# 조건 1
boolean1 = df["course name"] == "information technology"
boolean2 = df["year"] == 1
df.loc[boolean1 & boolean2, "status"] = "not allowed"
# 조건 2
boolean3= df["course name"] == "commerce"
boolean4= df["year"] == 4
df.loc[boolean3 & boolean4, "status"] = "not allowed"
# 조건 3
allowed = df["status"] == "allowed"
course_counts = df.loc[allowed, "course name"].value_counts()
closed_courses = list(course_counts[course_counts < 5].index)
for course in closed_courses:
df.loc[df["course name"] == course, "status"] = "not allowed"
# 테스트 코드
df내가 다시 정리했는데 왜 안된다는지 모르겠는 코드
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv('data/enrolment_1.csv')
df['status'] ='allowed' #status 열 추가 하고 allowed 로 바꿔놓기
boolean1 = df['course name']=='information technology'
boolean2 = df['year']== 1
df.loc[boolean1 & boolean2,'status']='not allowed' # it 과목을 1학년이 들으면 not allowed가 나오게
boolean3 = df['course name'] == 'commerce'
boolean4 = df['year']== 4
df.loc[boolean3 & boolean4,'status']=='not allowed' #commerce 과목을 4학년이 들으면 not allowed가 나오게
allowed = df['status']=='allowed' #allowed인 데이터 변수에 담기
course_counts = df.loc[allowed,'course name'].value_counts() # allowed인 과목의 count 확인
closed_courses = list(course_counts[course_counts < 5].index) # count가 5 이하인 course_counts의 인덱스들을 리스트에 담기
for course in closed_courses: #5이하인 closed_courses 리스트에 course들을 not allowed로 바꾸기
df.loc[df['course name']==course, 'status']='not allowed'
df7.6 (실습) 코드잇 대학교 : 강의실 배정하기 I
수강 신청이 완료되었습니다. 이제 각 과목을 수강하는 학생수에 따라 크기가 다른 강의실을 배치하려고 합니다.
강의실은 규모에 따라 “Auditorium”, “Large room”, “Medium room”, “Small room” 총 4가지 종류가 있습니다.
aud
아래 조건에 따라 강의실 종류를 지정해 주세요.
- 80명 이상의 학생이 수강하는 과목은 “Auditorium”에서 진행됩니다.
- 40명 이상, 80명 미만의 학생이 수강하는 과목은 “Large room”에서 진행됩니다.
- 15명 이상, 40명 미만의 학생이 수강하는 과목은 “Medium room”에서 진행됩니다.
- 5명 이상, 15명 미만의 학생이 수강하는 과목은 “Small room”에서 진행됩니다.
- 폐강 등의 이유로 status가 “not allowed”인 수강생은 room assignment 또한 “not assigned”가 되어야 합니다.
모범답안
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv('data/enrolment_2.csv')
# 과목별 인원 가져오기
allowed = df["status"] == "allowed"
course_counts = df.loc[allowed, "course name"].value_counts()
# 각 강의실 규모에 해당되는 과목 리스트 만들기
auditorium_list = list(course_counts[course_counts >= 80].index)
large_room_list = list(course_counts[(80 > course_counts) & (course_counts >= 40)].index)
medium_room_list = list(course_counts[(40 > course_counts) & (course_counts >= 15)].index)
small_room_list = list(course_counts[(15 > course_counts) & (course_counts > 4)].index)
# not allowed 과목에 대해 값 지정해주기
not_allowed = df["status"] == "not allowed"
df.loc[not_allowed, "room assignment"] = "not assigned"
# allowed 과목에 대해 값 지정해주기
for course in auditorium_list:
df.loc[(df["course name"] == course) & allowed, "room assignment"] = "Auditorium"
for course in large_room_list:
df.loc[(df["course name"] == course) & allowed, "room assignment"] = "Large room"
for course in medium_room_list:
df.loc[(df["course name"] == course) & allowed, "room assignment"] = "Medium room"
for course in small_room_list:
df.loc[(df["course name"] == course) & allowed, "room assignment"] = "Small room"
# 정답 출력
dfㄴ & allowed는 굳이 왜 붙여야할까?
& allowed를 사용해서 해당 과목이 allowed상태인지 확인하고 그 조건이 만족되는 경우에만 변경 작업을 할 수 있음
7.7 (실습) 코드잇 대학교 : 강의실 배정하기 II
이전 과제에서 강의실 크기에 따라 room assignment column을 만들어 주었습니다.
이제 이 room assignment에 따라 강의실 이름을 붙여주려고 합니다.
아래 세 가지 조건을 만족하도록 코드를 작성하세요.
같은 크기의 강의실이 필요한 과목에 대해 알파벳 순서대로 방 번호를 배정하세요.
예를 들어 "Auditorium"이 필요한 과목으로 “arts”, “commerce”, “science” 세 과목이 있다면, “arts”는 “Auditorium-1”, “commerce”는 “Auditorium-2”, “science”는 “Auditorium-3” 순서로 방 배정이 되어야 합니다.
방 번호에 room 은 포함되지 않습니다. 아래 스크린샷을 참고하여 작성해주세요.
status column이 “not allowed”인 수강생은 room assignment column을 그대로 “not assigned”로 남겨둡니다. "not allowed" 인 수강생의 room assignment 상태가 변경되지 않도록 유의해주세요.
room assignment column의 이름을 room number로 바꿔주세요.
code
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv('data/enrolment_3.csv')
# 과목별 인원 가져오기
allowed = df["status"] == "allowed"
course_counts = df.loc[allowed, "course name"].value_counts()
# 각 강의실 규모에 해당되는 과목 리스트 만들기
auditorium_list = list(course_counts[course_counts >= 80].index)
large_room_list = list(course_counts[(80 > course_counts) & (course_counts >= 40)].index)
medium_room_list = list(course_counts[(40 > course_counts) & (course_counts >= 15)].index)
small_room_list = list(course_counts[(15 > course_counts) & (course_counts > 4)].index)
# 강의실 이름 붙이기
for i in range(len(auditorium_list)):
df.loc[(df["course name"] == sorted(auditorium_list)[i]) & allowed, "room assignment"] = "Auditorium-" + str(i + 1)
for i in range(len(large_room_list)):
df.loc[(df["course name"] == sorted(large_room_list)[i]) & allowed, "room assignment"] = "Large-" + str(i + 1)
for i in range(len(medium_room_list)):
df.loc[(df["course name"] == sorted(medium_room_list)[i]) & allowed, "room assignment"] = "Medium-" + str(i + 1)
for i in range(len(small_room_list)):
df.loc[(df["course name"] == sorted(small_room_list)[i]) & allowed, "room assignment"] = "Small-" + str(i + 1)
# column 이름 바꾸기
df.rename(columns={"room assignment": "room number"}, inplace = True)
# 테스트 코드
df