CLIP Text Encoder (Prompt)
다음 Prompt를 구현할 차례입니다.
먼저 load_checkpoint의 아웃풋을 보면 아래와 같습니다.
return model, clip, vae여기에서 clip과 text(prompt)를 입력값으로 받아 임베딩을 변환해주는 PromptEncoder 함수를 제작해보겠습니다.
전에 말했듯이, SDXL는 인코더가 2개 이고, SD15는 인코더가 하나 여서 각각 구현해줘야합니다.
Tokenizer
대부분의 SDXL는 동일한 토크나이저를 사용합니다, 이는 SD15도 마찬가지여서 Huggingface에서 어렵지 않게 모델 토크나이저 파일들(merges.txt, special_tokens_map.json, tokenizer_config.json, vocab.json)을 찾을 수 있습니다.
이 파일들을 transformers의 CLIPTokenizer 클래스로 불러올 수 있습니다.
def load_tokenizer(model_type : Literal['sd15', 'sdxl']):
sd_tok1_dir = os.path.join(env.get_tokenizer_dir(), 'sd15_tokenizer')
xl_tok1_dir = os.path.join(env.get_tokenizer_dir(), 'sdxl_tokenizer')
xl_tok2_dir = os.path.join(env.get_tokenizer_dir(), 'sdxl_tokenizer_2')
cache_dir = env.get_tokenizer_dir()
if model_type == 'sd15':
tokenizer = CLIPTokenizer.from_pretrained(sd_tok1_dir, cache_dir=cache_dir)
return tokenizer
elif model_type == 'sdxl':
tokenizer1 = CLIPTokenizer.from_pretrained(xl_tok1_dir, cache_dir=cache_dir)
tokenizer2 = CLIPTokenizer.from_pretrained(xl_tok2_dir, cache_dir=cache_dir)
return (tokenizer1, tokenizer2)SDXL Encoder
class PromptEncoder(TextualInversionLoaderMixin):
def sdxl_text_conditioning(
self,
prompt : str,
clip : Tuple[CLIPTextModel, CLIPTextModelWithProjection],
dtype : torch.dtype = torch.float16,
clip_skip : Optional[int] = None,
lora_scale : Optional[float] = None,
):PromptEncoder 함수는 diffusers의 TextualInversionLoaderMixin 클래스를 상속받습니다. 상속받는 클래스에서 maybe_convert_prompt 함수를 사용하는데, 이는 프롬프트의 각 토큰을 Multi vector 형식으로 변환하는데 사용됩니다.
이 클래스는 아래와 같이 Import 합니다.
from diffusers.loaders.textual_inversion import TextualInversionLoaderMixin전체 함수는 아래와 같습니다.
def sdxl_text_conditioning(
self,
prompt : str,
clip : Tuple[CLIPTextModel, CLIPTextModelWithProjection],
dtype : torch.dtype = torch.float16,
clip_skip : Optional[int] = None,
lora_scale : Optional[float] = None,
):
tokenizer1, tokenizer2 = load_tokenizer("sdxl")
text_encoder1 = clip[0].to(dtype=dtype)
text_encoder2 = clip[1].to(dtype=dtype)
device = next(text_encoder1.parameters()).device
if lora_scale is not None:
scale_lora_layers(text_encoder1, lora_scale)
scale_lora_layers(text_encoder2, lora_scale)
prompt2 = prompt
prompt2 = [prompt2] if isinstance(prompt2, str) else prompt
prompt_embeds_list = []
prompts = [prompt, prompt2]
tokenizers = [tokenizer1, tokenizer2]
text_encoders = [text_encoder1, text_encoder2]
for prompt, tokenizer, text_encoder in zip(prompts ,tokenizers, text_encoders):
prompt = self.maybe_convert_prompt(prompt, tokenizer)
text_inputs = tokenizer(
prompt,
padding="max_length",
max_length = tokenizer.model_max_length,
truncation = True,
return_tensors = "pt"
)
text_input_ids = text_inputs.input_ids
untruncated_ids = tokenizer(prompt, padding="longest", return_tensors="pt").input_ids
if untruncated_ids.shape[-1] >= text_input_ids.shape[-1] and not torch.equal(
text_input_ids, untruncated_ids
):
removed_text = tokenizer.batch_decode(untruncated_ids[:, tokenizer.model_max_length - 1 : -1])
print(
"The following part of your input was truncated because CLIP can only handle sequences up to"
f" {tokenizer.model_max_length} tokens: {removed_text}"
)
with torch.no_grad():
prompt_embeds = text_encoder(text_input_ids.to(device), output_hidden_states=True)
pooled_prompt_embeds = prompt_embeds[0]
if clip_skip is None:
prompt_embeds = prompt_embeds.hidden_states[-2]
else:
# "2" because SDXL always indexes from the penultimate layer.
prompt_embeds = prompt_embeds.hidden_states[-(clip_skip + 2)]
prompt_embeds_list.append(prompt_embeds)
prompt_embeds = torch.concat(prompt_embeds_list, dim=-1)
if text_encoder1 is not None:
unscale_lora_layers(text_encoder1, lora_scale)
unscale_lora_layers(text_encoder2, lora_scale)
return (prompt_embeds, pooled_prompt_embeds)여기서 보이는
lora_scale : Optional[float] = None,
if lora_scale is not None:
scale_lora_layers(text_encoder1, lora_scale)
scale_lora_layers(text_encoder2, lora_scale)
if text_encoder1 is not None:
unscale_lora_layers(text_encoder1, lora_scale)
unscale_lora_layers(text_encoder2, lora_scale)이 구문은 LoRA를 적용할때 필요한 함수지만 Default workflow에서는 LoRA가 없으니 삭제해도 됩니다.
또한 입력값으로 받는 clip_skip : Optional[int] = None, 역시 A1111에서는 입력값으로 사용하지만, ComfyUI에서는 사용하지 않을 예정입니다.
위 과정을 통해 임베딩하면 벡터의 차원은 다음과 같이 변하게 됩니다.
예를 들어, default workflow에서도 사용된
beautiful scenery nature glass bottle landscape, purple galaxy bottle이 구문을 예시로 든다면
# 토크나이저 1------------------------------------
Tokenized shape: torch.Size([1, 77])
Text encoder output shape: torch.Size([1, 77, 768])
Pooled embeddings shape: torch.Size([1, 77, 768])
# ------------------------------------------------
# 토크나이저 2------------------------------------
Tokenized shape: torch.Size([1, 77])
Text encoder output shape: torch.Size([1, 1280])
Pooled embeddings shape: torch.Size([1, 1280])
# ------------------------------------------------
Final layer embeddings shape: torch.Size([1, 77, 1280]) # 풀링된 임베딩
Final concatenated embeddings shape: torch.Size([1, 77, 2048])
Final pooled embeddings shape: torch.Size([1, 1280])
이런식으로 변하게 되며, 토크나이저가 1개인 SD15 역시
def sd15_text_conditioning(
self,
prompt : str,
clip : CLIPTextModel,
dtype : torch.dtype = torch.float16,
clip_skip : Optional[int] = None,
lora_scale : Optional[float] = None,
):
tokenizer = load_tokenizer("sd15")
text_encoder = clip.to(dtype=dtype)
device = next(text_encoder.parameters()).device
if lora_scale is not None:
scale_lora_layers(clip, lora_scale)
prompt = self.maybe_convert_prompt(prompt, tokenizer)
text_inputs = tokenizer(prompt, padding="max_length", max_length=tokenizer.model_max_length, truncation=True, return_tensors="pt")
text_input_ids = text_inputs.input_ids
untruncated_ids = tokenizer(prompt, padding="longest", return_tensors='pt').input_ids
if untruncated_ids.shape[-1] >= text_input_ids.shape[-1] and not torch.equal(
text_input_ids, untruncated_ids
):
removed_text = self.tokenizer.batch_decode(
untruncated_ids[:, self.tokenizer.model_max_length - 1 : -1]
)
print(
"The following part of your input was truncated because CLIP can only handle sequences up to"
f" {self.tokenizer.model_max_length} tokens: {removed_text}"
)
if hasattr(text_encoder.config, "use_attention_mask") and text_encoder.config.use_attention_mask:
attention_mask = text_inputs.attention_mask.to(device)
else:
attention_mask = None
with torch.no_grad():
if clip_skip is None:
prompt_embeds = text_encoder(text_input_ids.to(device), attention_mask = attention_mask)
prompt_embeds = prompt_embeds[0]
else:
# Skip the output of Transformer layers
# if the parameter `clip_skip` is set to k. CLIP model's output will be (final_layer - k)
prompt_embeds = text_encoder(text_input_ids.to(device), attention_mask = attention_mask, output_hidden_states = True)
prompt_embeds = prompt_embeds[-1][-(clip_skip + 1)]
# normalization
prompt_embeds = text_encoder.text_model.final_layer_norm(prompt_embeds)
prompt_embeds.to(dtype=text_encoder.dtype, device=device)
if text_encoder is not None:
# Retrieve the original scale by scaling back the LoRA layers
unscale_lora_layers(text_encoder, lora_scale)
# bs_embed, seq_len, _ = prompt_embeds.shape
# # duplicate text embeddings for each generation per prompt, using mps friendly method
# prompt_embeds = prompt_embeds.repeat(1, num_images_per_prompt, 1)
# prompt_embeds = prompt_embeds.view(bs_embed * num_images_per_prompt, seq_len, -1)
return prompt_embeds이렇게 구현됩니다. 차이점은 SDXL와는 다르게 풀링된 임베딩이 없다는 것 정도입니다.
마지막에 주석처리된
# bs_embed, seq_len, _ = prompt_embeds.shape
# # duplicate text embeddings for each generation per prompt, using mps friendly method
# prompt_embeds = prompt_embeds.repeat(1, num_images_per_prompt, 1)
# prompt_embeds = prompt_embeds.view(bs_embed * num_images_per_prompt, seq_len, -1)이 부분은 원본 소스인 Diffusers에서는 pipeline에서 모든 파라미터를 받아 한번에 진행해야하지만, 저희는 각 과정을 Nodes 단위로 나누는 ComfyUI를 구현하는게 목적입니다.
따라서 num_images_per_prompt (batch size) 는 EmptyLatentImage에서 입력을 받기때문에 이 입력을 통해 디노이징을 진행하는 KSampler 노드에서 따로 후처리할 예정입니다.
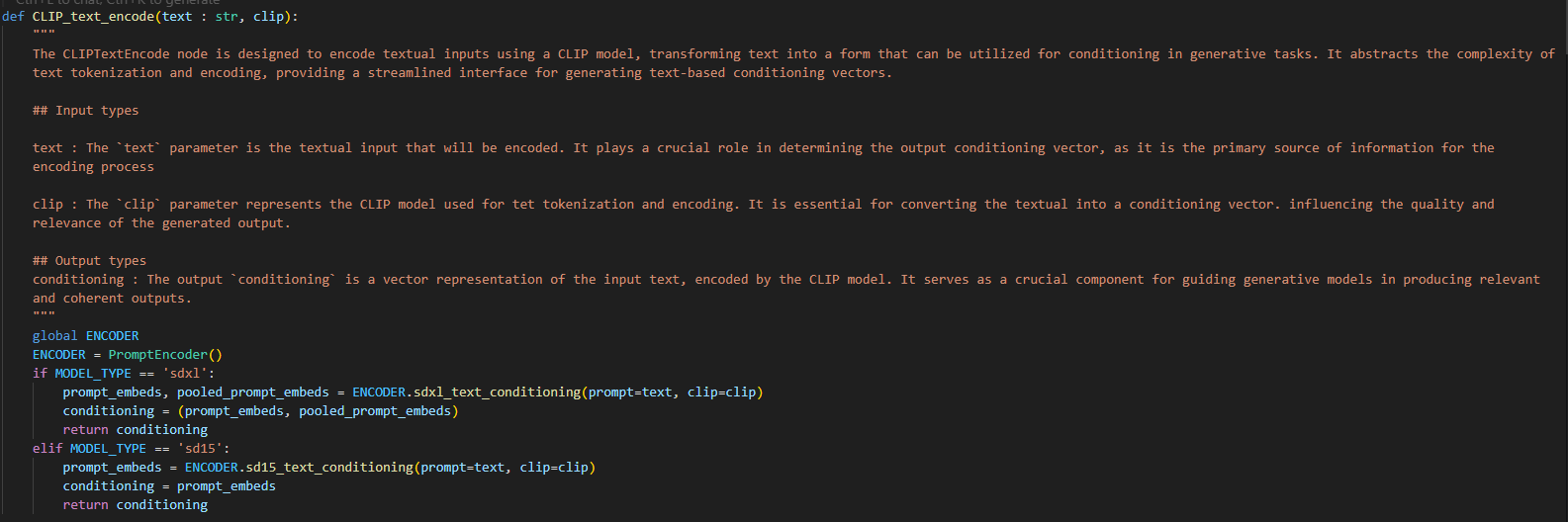
다시 처음에서 두번째 사진으로 돌아와서
def CLIP_text_encode(text : str, clip):
"""
The CLIPTextEncode node is designed to encode textual inputs using a CLIP model, transforming text into a form that can be utilized for conditioning in generative tasks. It abstracts the complexity of text tokenization and encoding, providing a streamlined interface for generating text-based conditioning vectors.
## Input types
text : The `text` parameter is the textual input that will be encoded. It plays a crucial role in determining the output conditioning vector, as it is the primary source of information for the encoding process
clip : The `clip` parameter represents the CLIP model used for tet tokenization and encoding. It is essential for converting the textual into a conditioning vector. influencing the quality and relevance of the generated output.
## Output types
conditioning : The output `conditioning` is a vector representation of the input text, encoded by the CLIP model. It serves as a crucial component for guiding generative models in producing relevant and coherent outputs.
"""
global ENCODER
ENCODER = PromptEncoder()
if MODEL_TYPE == 'sdxl':
prompt_embeds, pooled_prompt_embeds = ENCODER.sdxl_text_conditioning(prompt=text, clip=clip)
conditioning = (prompt_embeds, pooled_prompt_embeds)
return conditioning
elif MODEL_TYPE == 'sd15':
prompt_embeds = ENCODER.sd15_text_conditioning(prompt=text, clip=clip)
conditioning = prompt_embeds
return conditioningSDXL 모델이냐 SD15 모델이냐에 따라서 각기 다른 Output 값을 뱉어주면 ComfyUI Prompt의 Conditioning에 해당하는 부분이 완성됩니다.
