| 내용 | 링크 |
|---|---|
| 논문 | https://arxiv.org/pdf/2302.02948 |
Introduction
- 복잡한 도메인에서 많은 성과를 내고 있음(ex. google의 chip design)
- 이러한 성과들은 보통 simulator와의 많은 Interation을 통해 이뤄짐
- Chip design의 경우에도 환경을 simulation 할 수 있기 때문에 굉장히 많은 양의 데이터를 수집하는 것이 가능함
- 그러나 real world domain에서 데이터를 많이 모으는 것이 굉장히 expensive 함
- 예를 들어, robot 분야에서는 실제 robot을 이용해 학습을 시도하는 것은 엄청난 비용(돈, 시간 등)을 필요로 함
- 심지어 reward 가 sparse 하다면 더 많은 비용이 필요함
- 이런 비용적인 이슈를 해결하기 위해 'human expert'의 데이터를 학습에 활용할 수 있다면 얼마나 좋을까?
- 본 논문에서는 offline data를 학습 과정 중에 사용하여 sample efficiency를 높이거나 exploration을 촉진시킬 수 있다고 주장함
- 그리고 이런 방법론이 이론적으로 이미 증명되었고(Wagenmaker \& Pacchiano, 2022; Song et al., 2023), 실제 사례에서도 확인되었다고 함(Cabi et al., 2019; Nair et al., 2020; Lu et al., 2021)
- 일부 이전 연구들에서는 human expert 데이터를 pretrained model을 학습시키는데 주로 이용 했었음
- 그리고 online fine tuning 시 distribution shift가 발생할 수 있기 때문에 constraints를 이용했다고 함
- such as additional training time and hyperparamters, or limited improvement beyond the behavior policy
- 위 연구들을 사례로 생각해봤을 때 차라리 standard off-policy 알고리즘에서 offline data를 사용하면 online 환경의 exploration도 가능하기 때문에 이와 같은 distribution shift 문제를 해결할 수 있음
- 본 논문에서는 offline data를 학습 과정 중에 사용하여 sample efficiency를 높이거나 exploration을 촉진시킬 수 있다고 주장함
- 그래서 다음과 같은 질문을 생각해볼 수 있음 : can we simply apply existing off-policy methods to leverage offline data when learning online, without offline RL pre-training or explicit imitation terms that privilege the prior offline data?
- 그리고 단순하게 offline dataset을 online dataset에 합쳐서 적용하는 것은 상대적으로 성능 저하가 일어날 수 있음
- 아래 이미지를 보면 SAC + Offline data < fine tuning < 본 논문 제안 방법 (RLPD : Reinforcement Learning with Prior Data)로 성능 차이가 있는 것을 볼 수 있음

- 아래 이미지를 보면 SAC + Offline data < fine tuning < 본 논문 제안 방법 (RLPD : Reinforcement Learning with Prior Data)로 성능 차이가 있는 것을 볼 수 있음
- 본 논문에서는 단순 사용보다 몇 가지 설정이 필요하다고 함
- symmetric sampling
- Layer Normalization
- large ensemble
Related Work
Offline RL pre-training
- Ernst, D., Geurts, P., and Wehenkel, L. Tree-based batch mode reinforcement learning. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 6(18):503–556, 2005. URL http:// jmlr.org/papers/v6/ernst05a.html.
- Fujimoto, S., Meger, D., and Precup, D. Off-policy deep reinforcement learning without exploration. In Chaudhuri, K. and Salakhutdinov, R. (eds.), Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, volume 97 of Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, pp. 2052–2062. PMLR, 09–15 Jun 2019. URL https://proceedings.mlr.press/v97/ fujimoto19a.html.
- Levine, S., Kumar, A., Tucker, G., and Fu, J. Offline reinforcement learning: Tutorial, review, and perspectives on open problems, 2020. URL https://arxiv.org/ abs/2005.01643.
- Hester, T., Vecerik, M., Pietquin, O., Lanctot, M., Schaul, T., Piot, B., Horgan, D., Quan, J., Sendonaris, A., Osband, I., Dulac-Arnold, G., Agapiou, J., Leibo, J., and Gruslys, A. Deep q-learning from demonstrations. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 32(1), Apr. 2018. doi: 10.1609/ aaai.v32i1.11757. URL https://ojs.aaai.org/ index.php/AAAI/article/view/11757.
- Kalashnikov, D., Irpan, A., Pastor, P., Ibarz, J., Herzog, A., Jang, E., Quillen, D., Holly, E., Kalakrishnan, M., Vanhoucke, V., and Levine, S. Scalable deep reinforcement learning for vision-based robotic manipulation. In Billard, A., Dragan, A., Peters, J., and Morimoto, J. (eds.), Proceedings of The 2nd Conference on Robot Learning, volume 87 of Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, pp. 651–673. PMLR, 29–31 Oct 2018. URL https://proceedings.mlr.press/v87/ kalashnikov18a.html.
- Nair, A., Gupta, A., Dalal, M., and Levine, S. AWAC: Accelerating online reinforcement learning with offline datasets. arXiv, June 2020.
- Lee, S., Seo, Y., Lee, K., Abbeel, P., and Shin, J. Offlineto-online reinforcement learning via balanced replay and pessimistic q-ensemble. In 5th Annual Conference on Robot Learning, 2021. URL https://openreview. net/forum?id=AlJXhEI6J5W.
- Kostrikov, I., Nair, A., and Levine, S. Offline reinforcement learning with implicit q-learning. In International Conference on Learning Representations, 2022. URL https: //openreview.net/forum?id=68n2s9ZJWF8.
-> 본 논문의 방법론은 위 ref.에 비해 추가적인 pre-training 시간이나 hyperparameters tuning 없이도 간단하게 사용할 수 있다는 장점이 있음
Constraining to prior data
- Levine, S. and Koltun, V. Guided policy search. In Dasgupta, S. and McAllester, D. (eds.), Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Machine Learning, volume 28 of Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, pp. 1–9, Atlanta, Georgia, USA, 17–19 Jun 2013. PMLR. URL https://proceedings.mlr.press/v28/ levine13.html.
- Fox, R., Pakman, A., and Tishby, N. Taming the noise in reinforcement learning via soft updates. In 32nd Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence (UAI), 2016.
- Hester, T., Vecerik, M., Pietquin, O., Lanctot, M., Schaul, T., Piot, B., Horgan, D., Quan, J., Sendonaris, A., Osband, I., Dulac-Arnold, G., Agapiou, J., Leibo, J., and Gruslys, A. Deep q-learning from demonstrations. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 32(1), Apr. 2018. doi: 10.1609/ aaai.v32i1.11757. URL https://ojs.aaai.org/ index.php/AAAI/article/view/11757.
- Nair, A., McGrew, B., Andrychowicz, M., Zaremba, W., and Abbeel, P. Overcoming exploration in reinforcement learning with demonstrations. In 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 6292–6299. IEEE Press, 2018a. doi: 10.1109/ ICRA.2018.8463162. URL https://doi.org/10. 1109/ICRA.2018.8463162.
- Rajeswaran, A., Kumar, V., Gupta, A., Vezzani, G., Schulman, J., Todorov, E., and Levine, S. Learning Complex Dexterous Manipulation with Deep Reinforcement Learning and Demonstrations. In Proceedings of Robotics: Science and Systems (RSS), 2018.
- Rudner, T. G. J., Lu, C., Osborne, M., Gal, Y., and Teh, Y. W. On pathologies in KL-regularized reinforcement learning from expert demonstrations. In Beygelzimer, A., Dauphin, Y., Liang, P., and Vaughan, J. W. (eds.), Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2021. URL https: //openreview.net/forum?id=sS8rRmgAatA.
- Asada, H. and Hanafusa, H. Playback control of force teachable robots. Transactions of the Society of Instrument and Control Engineers, 15(3):410–411, 1979. doi: 10.9746/sicetr1965.15.410.
- Schaal, S. Learning from demonstration. In Mozer, M., Jordan, M., and Petsche, T. (eds.), Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, volume 9. MIT Press, 1996. URL https://proceedings. neurips.cc/paper/1996/file/ 68d13cf26c4b4f4f932e3eff990093ba-Paper. pdf.
-> Pre-training (behavior cloning 과 같은)은 데이터의 품질이 높아야 하는데, 본 논문은 offline dataset을 buffer 에 넣어서 학습함으로 데이터의 품질에 영향받지 않는다는 장점이 있음
Unconstrained methods with prior data
- Vecer ˇ ´ık, M., Hester, T., Scholz, J., Wang, F., Pietquin, O., Piot, B., Heess, N., Rothorl, T., Lampe, T., and Riedmiller, ¨ M. Leveraging demonstrations for deep reinforcement learning on robotics problems with sparse rewards. arXiv, July 2017.
- Hester, T., Vecerik, M., Pietquin, O., Lanctot, M., Schaul, T., Piot, B., Horgan, D., Quan, J., Sendonaris, A., Osband, I., Dulac-Arnold, G., Agapiou, J., Leibo, J., and Gruslys, A. Deep q-learning from demonstrations. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 32(1), Apr. 2018. doi: 10.1609/ aaai.v32i1.11757. URL https://ojs.aaai.org/ index.php/AAAI/article/view/11757.
- Nair, A., McGrew, B., Andrychowicz, M., Zaremba, W., and Abbeel, P. Overcoming exploration in reinforcement learning with demonstrations. In 2018 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA), pp. 6292– 6299. IEEE, 2018b
- Kalashnikov, D., Irpan, A., Pastor, P., Ibarz, J., Herzog, A., Jang, E., Quillen, D., Holly, E., Kalakrishnan, M., Vanhoucke, V., and Levine, S. Scalable deep reinforcement learning for vision-based robotic manipulation. In Billard, A., Dragan, A., Peters, J., and Morimoto, J. (eds.), Proceedings of The 2nd Conference on Robot Learning, volume 87 of Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, pp. 651–673. PMLR, 29–31 Oct 2018. URL https://proceedings.mlr.press/v87/ kalashnikov18a.html.
- Zhang, H., Xu, W., and Yu, H. Policy expansion for bridging offline-to-online reinforcement learning. In The Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations, 2023. URL https://openreview.net/forum? id=-Y34L45JR6z.
- Song, Y., Zhou, Y., Sekhari, A., Bagnell, D., Krishnamurthy, A., and Sun, W. Hybrid RL: Using both offline and online data can make RL efficient. In International Conference on Learning Representations, 2023. URL https:// openreview.net/forum?id=yyBis80iUuU. (-> 이 논문이 offline 데이터 사용의 이론, 실질의 중요성을 보인 논문)
-> 또 다른 연구들에서 Offline dataset을 학습에 직접적으로 사용하는 것이 도움이 됨을 보였음. offline data로 replay buffer를 초기화하거나, on-offline의 균형을 위해 sampling 전략을 사용는 등이 있음. 하지만 이와 같은 방법들을 직접적으로 사용하는 것이 벤치마크 성능을 높이기에 충분하지 않기 때문에 추가적인 방법들을 본 논문에서 제시하고 있음
Method
1. Design Choice 1: A Simple and Efficient Strategy to Incorporate Offline Data (symmetric sampling)
-
50 %는 replay buffer에서 sampling 하고 50%는 offline dataset에서 sampling 하는 방법
- 실험을 통해 찾은 적정 비율
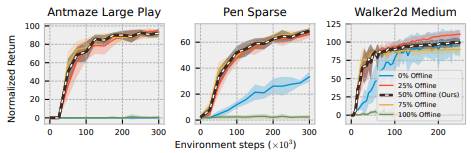
- 실험을 통해 찾은 적정 비율
-
그러나 symmectric sampling 만 가지고는 높은 성능을 얻을 수는 없고, 다른 desigh choice와 결합이 필요하다고 함
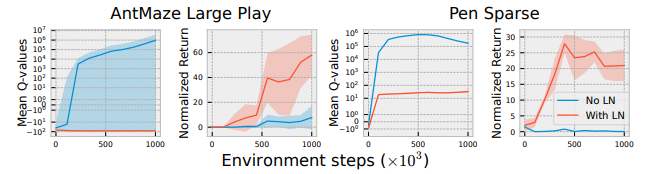
2. Design Choice 2: Layer Normalization Mitigates Catastrophic Overestimation (Layer Normalization)
- standard off-policy 알고리즘은 Out-of-Distribution (OOD) action에 대해 배운적이 없어서 정확하게 예측할 수 없고, function approximation을 이용하기 때문에 실제 값보다 overestimation (과대평가) 될 수 있음
- 이는 critic이 계속 증가하는 value를 따라잡고자 할 때 training 의 불안정이나 발산을 초래할 수 있음
- 보통 위와 같은 문제는 offline dataset만 이용해서 학습할 때 주로 발생함
- 본 논문에서는 online RL에 offline dataset을 함께 사용하면서 환경에서의 exloration을 통해 이와 같은 문제의 발생 가능성을 줄였지만 여전히 훈련이 불안정하거나 잘못된 예측을 통해 Q-value의 overestimation이 발생할 수 있음
- 이를 위해서 Layer Normalization 기법을 사용할 수 있다고 함
- Layer Normalization은 network가 OOD에서 예측할 때 값이 과도하게 커지지 않도록 제한하는 효과를 가짐
- 따라서 exploration을 직접적으로 제한하지 않으면서도, ciritic divergence 와 같은 문제를 줄일 수 있다고 함 (즉 exploration을 장려하면서 학습의 안정성을 유지)
3. Design Choice 3: Sample Efficient RL (random ensemble distillation)
- 이제 on-offline policy 각각의 장점을 유지하는 방법을 갖추게 됨
- 그러나 online RL 방법론들도 학습 중 overfitting에 의해 오히려 sample efficiency가 감소하는 문제가 있음
- 예를 들어, 3 match game에서 special block을 사용하는 쪽으로 overfitting 되면 그 이후부터 하는 exploration 에는 주로 special block을 사용하는 데이터들만 수집될 수 있기 때문에 sample efficiency가 떨어짐
- 따라서 이를 해결하기 위한 방법으로 random ensemble distillation을 활용한다고 함
- 이 외에도 L2 norm, dropout 등 다양한 정규화 방법들이 있음
- random ensemble distillation은 특히 sparse reward에서 잘 작동함
- 그리고 이미지 데이터에서 TD를 수행할 때 overfitting 문제가 발생할 수 있음에 주목하여 random shift augmentations을 활용함
4. Per-Environment Design Choices
- 그 외에도 실제 각 환경에 민감하게 작용될 수 있는 부분들을 control 하기 위해 hyperparameters tuning 이 필요함을 강조하고자 함
- 이전 구현체에서 코드를 가져올 때 hyperparameters는 나의 문제에 적합하지 않을 수 있음
- ex. Architecture, maximum entropy 등 도 동일하게 나에게 맞는 archi.를 적용해야 함
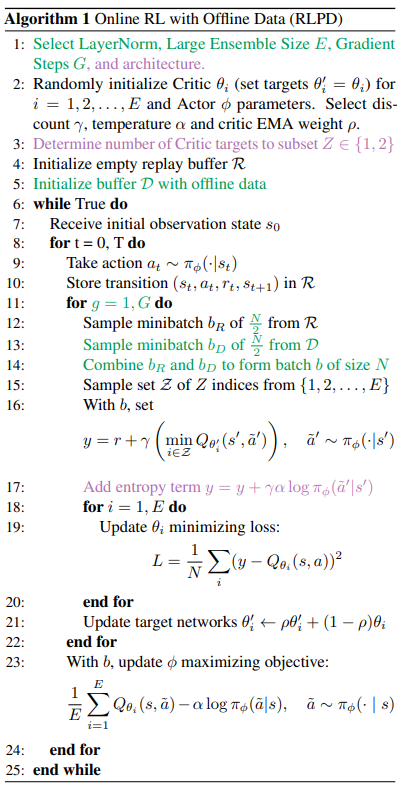
5. RLPD: Approach Overview
- 아래 peudo code에서 초록색 부분은 본 논문에서 중요한 접근 방법이고, 보라색 부분은 도메인마다 최적화 해야 할 부분을 의미함
Experiments
- 실험에서는 design choice에 대한 성능을 입증하면서, RLPD를 실무에 빠르게 적용시키기 위한 insight를 전달하고자 함. 따라서 아래 4가지 질문에 대한 답변을 진행함
1. Is RLPD competitive with prior work despite using no pre-training nor having explicit constraints?
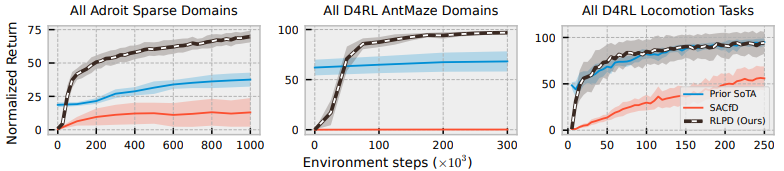
- SACfd : online replaly buffer 를 offline data로 initialize 한 실험 (이전 연구들)
- 해당 실험에서 RLPD가 Prior SoTA(pretraining을 이용한) 보다 다양한 도메인에서 좋은 성능을 내는 것 확인
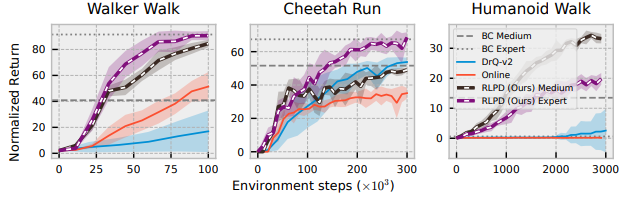
2. Does RLPD transfer to pixel-based environments?
- 문제 상황 : V-D4RL (Locomotion tasks) with only pixel dataset
- 위 문제는 최적화가 어려운 문제로 Behavior cloning 방법을 써도 높은 성능을 얻기 어려움
- 가장 어려운 humanoid walk tasks에서도 BC를 넘어서는 성능을 보임
- Medium, Expert : offline dataset의 품질
- DrQ-v2 : pixel을 이용하는 task에 대한 SOTA
3. Does LayerNorm mitigate value divergence?
- 실험 결과
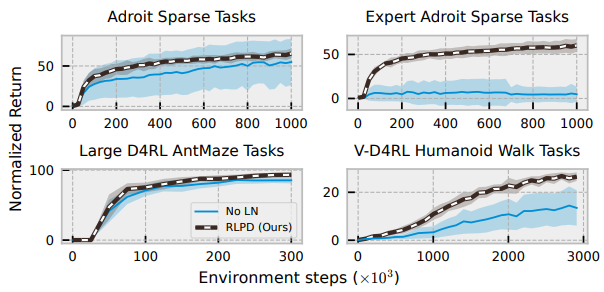
- 개인적 의견) 개인적으로 샘플링 비율이나 앙상블보다 본 논문에서 가장 성능에 큰 영향을 주는 기법인 것 같음
4. Does the proposed workflow around environment specific design choices lead to reliable performance?
- 가장 어려운 tasks 들을 기준으로 성능을 비교해 보았을 때도 가장 성능이 좋은 것을 확인함
- 의문) 비교 방법론들이 CDQ, Entropy backups, 2 layers인 이유?
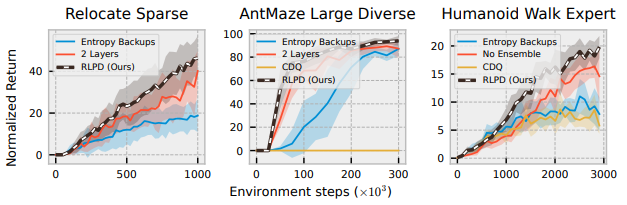
- 의문) 비교 방법론들이 CDQ, Entropy backups, 2 layers인 이유?
그 외
- Random ensemble 정규화 성능 비교
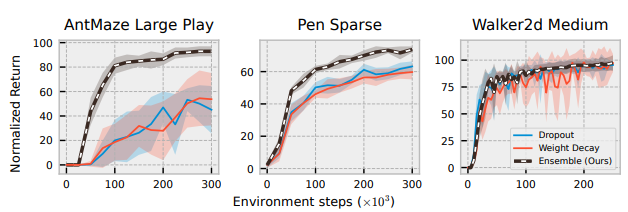
- Symmetric sampling 비교
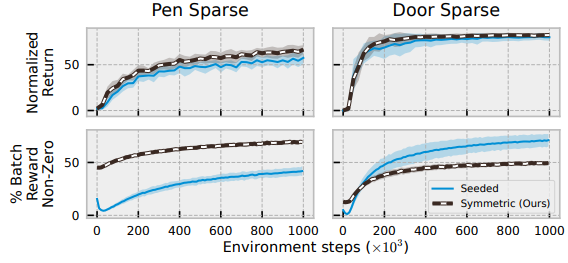
- Update To Data(UTD) 비교
- UTD : 강화 학습 알고리즘에서 환경 단계 당 수행하는 업데이트 횟수를 의미. 구체적으로, UTD 비율은 에이전트가 환경에서 한 단계 진행할 때(즉, 하나의 새로운 데이터 포인트를 수집할 때) 학습 네트워크를 업데이트하는 횟수를 나타냄.
- 예를 들어, UTD 비율이 4라면, 에이전트가 환경에서 한 단계 진행할 때마다 네트워크는 네 번 업데이트됨. 이 비율을 높이는 것은 오프라인 데이터를 더 빨리 "백업"할 수 있게 해주므로, 오프라인 데이터를 효과적으로 활용하고 학습 속도를 높이는 데 유용할 수 있음
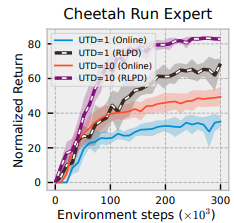
- 예를 들어, UTD 비율이 4라면, 에이전트가 환경에서 한 단계 진행할 때마다 네트워크는 네 번 업데이트됨. 이 비율을 높이는 것은 오프라인 데이터를 더 빨리 "백업"할 수 있게 해주므로, 오프라인 데이터를 효과적으로 활용하고 학습 속도를 높이는 데 유용할 수 있음
- UTD : 강화 학습 알고리즘에서 환경 단계 당 수행하는 업데이트 횟수를 의미. 구체적으로, UTD 비율은 에이전트가 환경에서 한 단계 진행할 때(즉, 하나의 새로운 데이터 포인트를 수집할 때) 학습 네트워크를 업데이트하는 횟수를 나타냄.
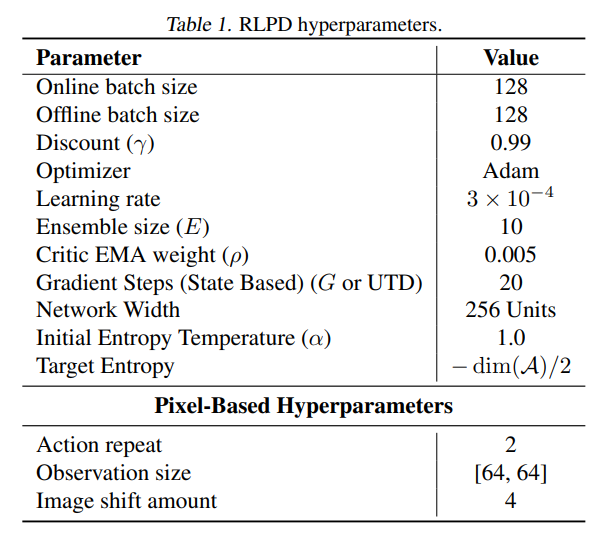
사용한 hyperparameters (참고용)
Conclusions
- 총 30개의 벤치마크 tasks로부터 좋은 성능을 얻을 수 있는 것 확인했고, 이전 연구 대비 최대 2.5배 성능이 증가하는 것을 확인함