paper : https://arxiv.org/pdf/2306.03346.pdf
demo : https://chongyi-zheng.github.io/stable_contrastive_rl/
Abstact
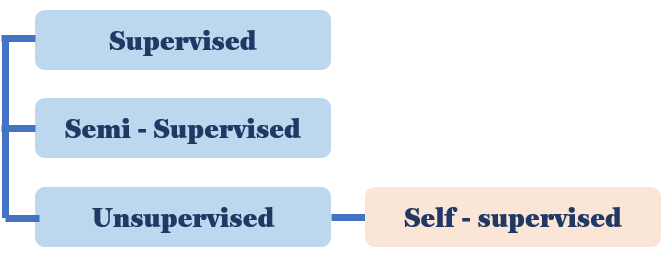
- self-supervised learning에 주로 의존하는 robot systems은 control strategies를 학습하는 데 필요한 human-annotations과 engineering effort를 줄일 수 있는 potential이 있음
- 컴퓨터 비전(CV)나 자연어처리(NLP)에서 self-supervised learning 을 활용해왔던 것과 같이, 사람이 설정한 reward와 labels 없이 마치 self-supervised learning처럼 로봇 시스템 문제를 강화학습으로 풀어보려 함
- 아직까지는 self-supervised learning 같은 RL 방법이 어떻게 실제 로봇 시스템에 적용될 수 있는지를 실제로 보여준 사례나 선행 연구는 거의 없음
- 따라서 본 논문에서는 먼저 (1) challenging simulated version을 먼저 연구함으로써, 좋은 성능을 가져오는 (성공률 2배) architecture와 hyper-params를 찾고 (2) Contrastive learning 기반의 self-supervised RL 알고리즘이 real-world robot manipulation tasks를 해결할 수 있음을 증명하고 있음
1. Introduction
Self-Supervised Learning (이하 SSL)
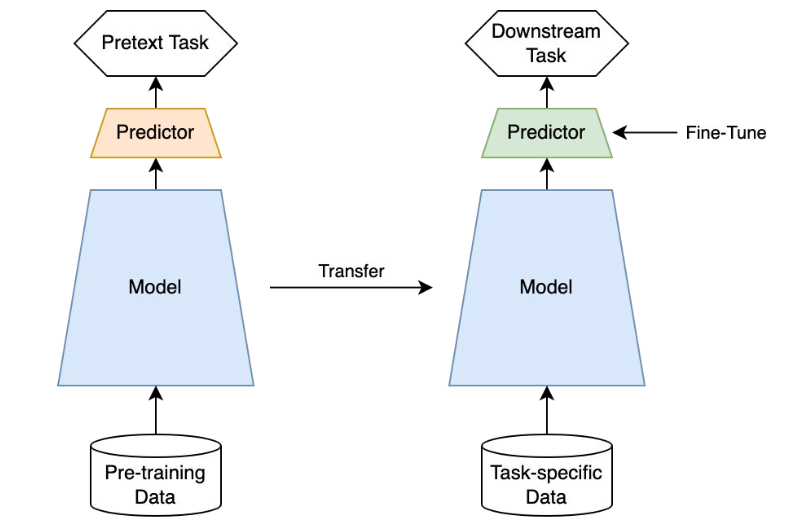
- SSL은 labels이 지정되지 않은 데이터(unlabeled data)를 활용해 downstream tasks에 대한 good representations을 얻는 방법이라고 함
- SSL은을 위해서는 pretext task (downstream task를 잘 풀기 위해 먼저 풀어보는 문제)를 학습하고 이를 통해 downstream task에 transfer 하는 방식으로 동작함
- 따라서 성능 평가도 downstream task를 통해 진행함
SSL with Robot
- SSL+RL 기반의 이전 연구들에서는 contrastive learning objective로 (1) compact representations (2) a goal-conditioned policy (3) corresponding value function을 동시에 학습했음 (Eysenbach et al., 2022)
- 로봇 관점에서 SSL은 reward 등 학습에 필요한 요소들을 수동으로 지정할 필요가 없기 때문에 굉장히 매력적이라고 함 (하지만 이건 로봇이 아니어도 매력적인 요소이지 않을까 싶음)
- 어쨌든, 이전 연구들은 real-world에 적용된 적이 없고 본 논문의 목적은 real-world 적용을 위한 SLL + RL 모델을 학습하는 것임
- 이를 위해 contrastive RL 방법에 중점을 두고 있음
- 본 논문은 learned representations 과 learned policies 모두에 초점을 맞춘 논문이라고 볼 수 있음
2. Related Work
Goal-conditioned RL
- goal-conditioned RL은 에이전트가 특정 목표를 달성하기 위해 학습하는 방법으로, 예를 들어 최적의 경로 찾기 등과 같은 문제가 goal-conditioned RL로 볼 수 있을 거 같음
- 보통 최적 경로같은 문제에서는 reward = | 현재 위치 - 목표 위치 |로 두어 별도의 reward tuning 없이도 쉽게 reward를 정의할 수 있음
- 따라서 goal-conditioned RL은 self-supervised 방법으로 (without human reward) 정의해 문제를 풀 수 있을 것 같음
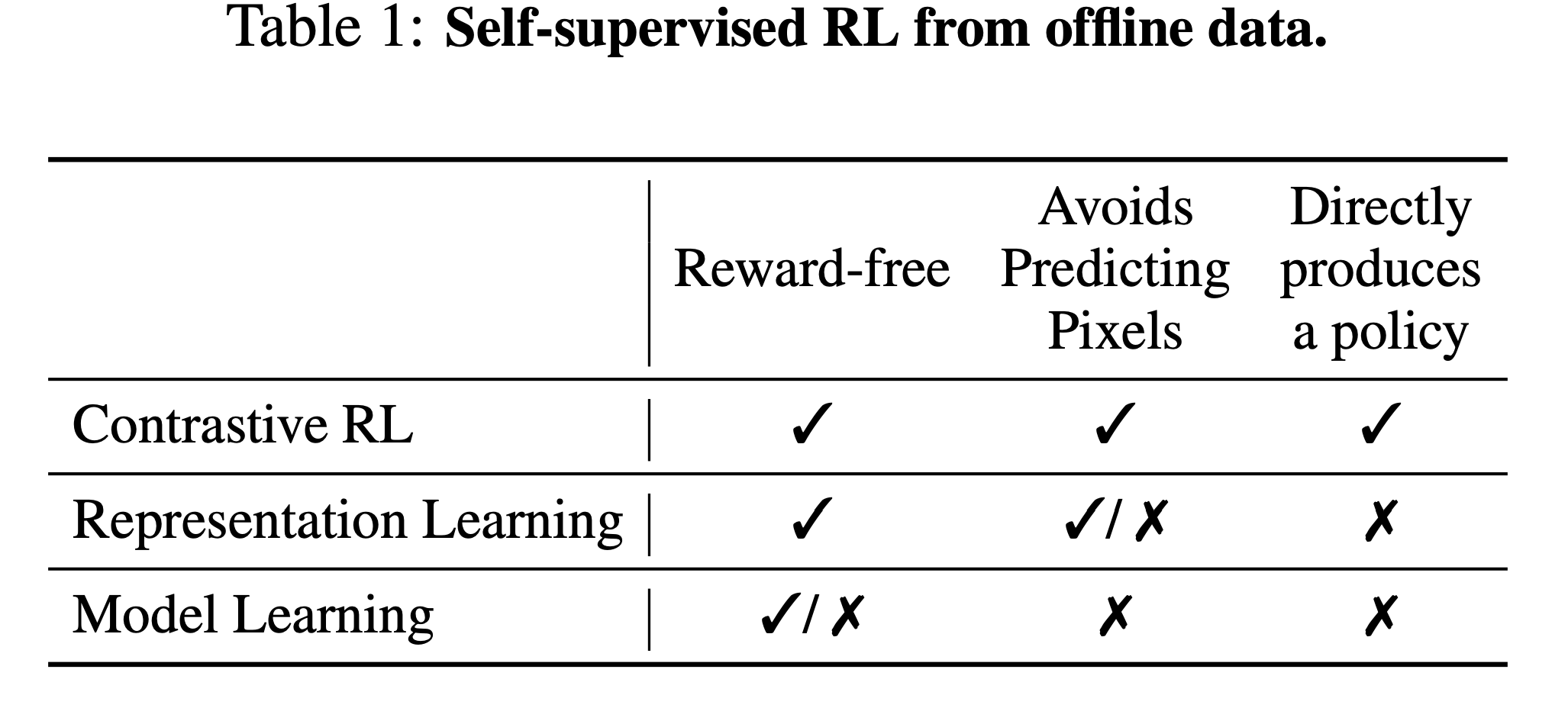
Representation Learning in RL
- RL 알고리즘에 offline dataset을 사용하는 방법 중 하나는 compact visual representations을 학습하는 것임
- 이전 연구들에서는 perception-specific loss나 data augmentation을 이용해 representation을 학습하기도 함
- 이런 방법들 모두 representation과 policy를 분리해서 학습하는데, 본 논문에서는 이런 분리 학습이 오히려 성능 저하를 야기할 수 있다고도 얘기하며 이를 실험으로 보여주고 있음
- 즉 적절한 SSL + RL 방법은 그 자체로도 good representation을 얻을 수 있다고 함
Model Learning in RL
- offline dataset을 사용하는 다른 한 방법은 explicit model을 학습하는 것임
- 이런 방법은 일단 one-step forward prediction과 auto-regressive imaginary rollouts을 가능하게 함
- 결과적으로 model을 만드는 것은 self-supervised problem이긴 하지만 실제로 이런 모델을 사용하기 위해서는 planning or RL을 위한 supervision이 필요하다고 함 (사실 이 부분에 대해서는 아직 이해가 가지 않음)
3. Contrastive RL and Design Decisions
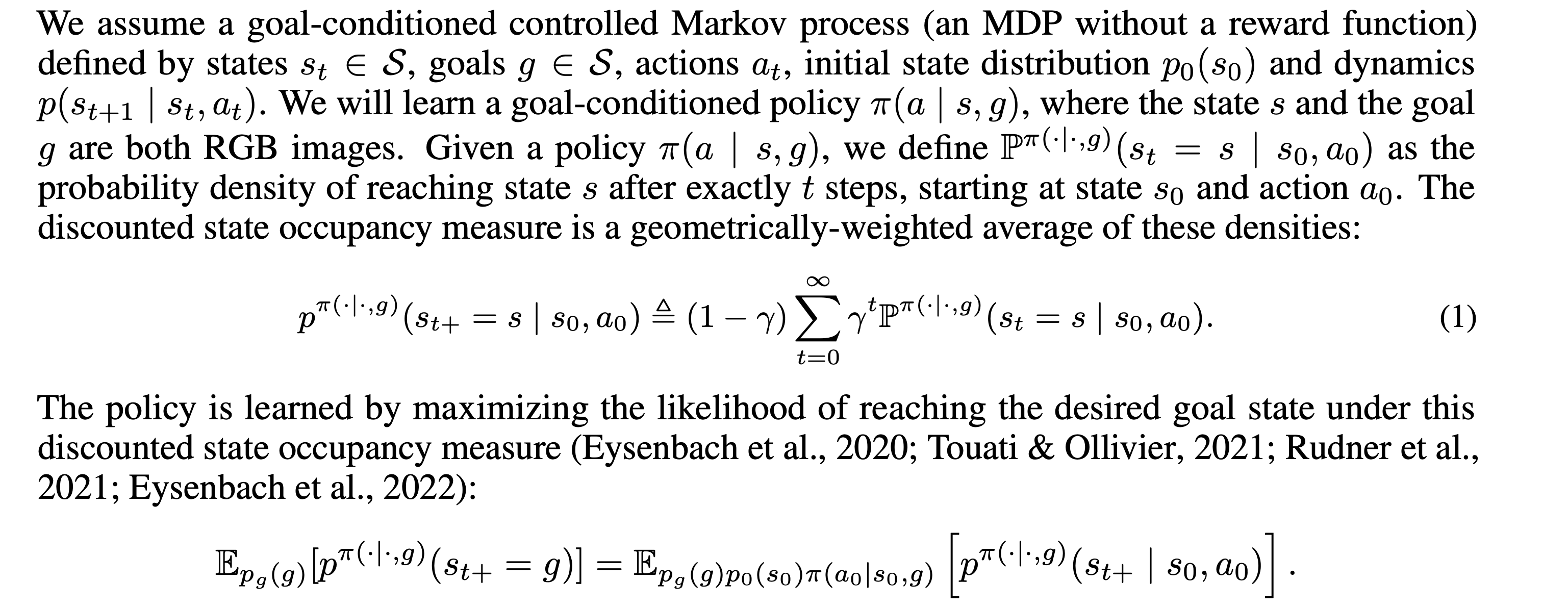
Preliminaries
-
notation
- : state
- : goals (아마 state와 동일한 set에서 가져오니까 goal states일 거 같음)
- : actions
- : inital state distribution,
- : dynamics
-
이전의 연구들처럼 contrastive representation learning을 위해 다음과 같은 정의를 함
- 라는 함수를 정의하고 있고, critic value를 이 reprentation과의 유사도로 정의함
- 그래서 다시 보면, contrastive RL은 average discounted state occupancy measure로 sampling 된 state의 future state를 구분하는 작업이라고 볼 수 있음
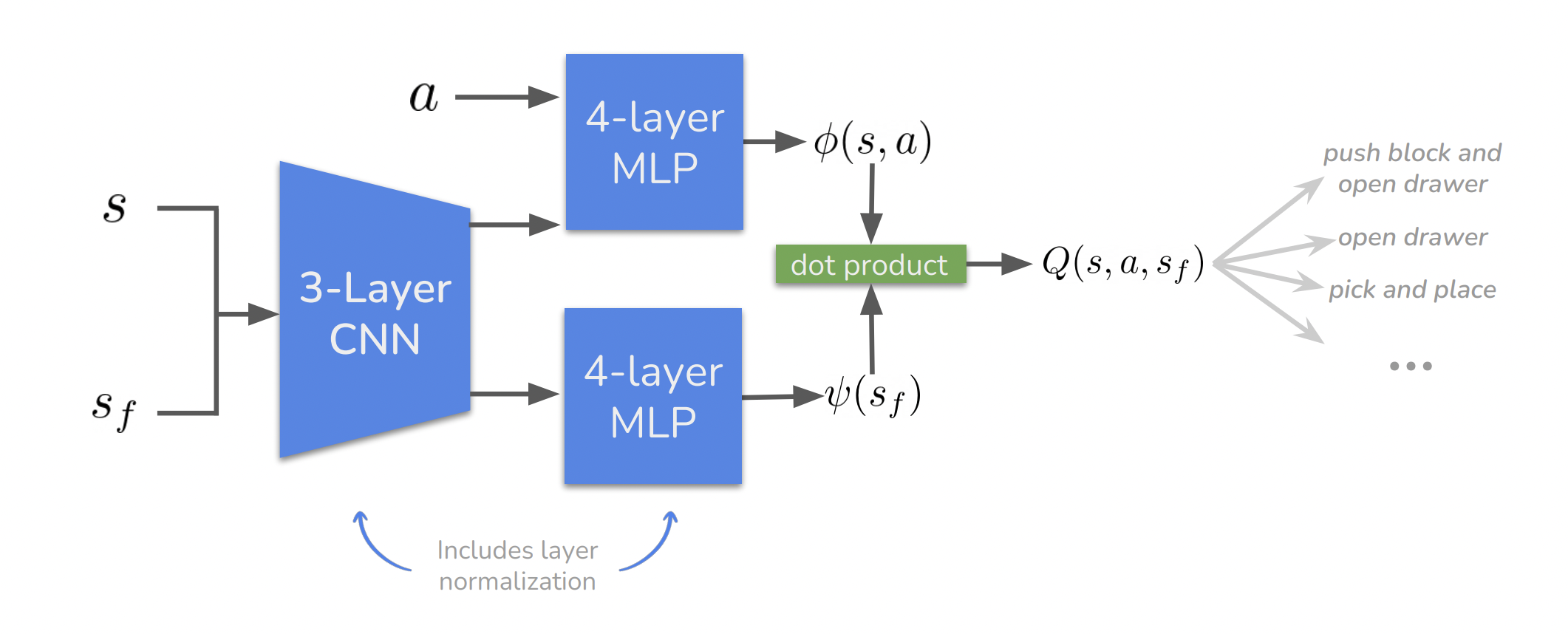
Design Decisions for stabilizing contrastive RL
아래 Design component를 기반으로 experiments를 진행하기 때문에 먼저 design
D1. Neural network architecture for image inputs
- CV나 NLP쪽에서는 architecture의 크기와 dataset의 크기를 키우면 더 높은 성능을 달성할 수 있음
- Resnets이나 transformers와 같은 대규모 networks는 RL 환경에도 적용되고 있지만, 작은 CNN이 일반적으로 많이 사용되고 있음
- 본 논문에서는 두 가지 측면에서을 연구함
(1) visual feature extracor : CNN vs Resnet
(2) contrastive representation : MLP의 width와 depth를 조절하는 실험
D2. Batch size
- CV쪽 연구들을 보면 contrastive learning에는 large batch sizes를 사용하면 성능이 잘 나오는 것을 볼 수 있음 (Chen et al., 2020; He et al., 2020; Grill et al., 2020; Chen et al., 2021b) 이를 통해 학습을 안정화하고 가속화할 수 있다고 함
- Contrastive RL도 비슷한 맥락으로 large batch size가 어떤 영향을 주는지 실험하고자 함
D3. Layer normalization
- various manipulation behaviors에 대한 diverse offline dataset을 이용해 학습을 진행할 때, 각기 다른 subsets에 따른 difference features and gradients를 갖게 된다고 추측하고 있음
- visual features에 대해 layer normalization을 진행하는 실험을 진행하고자 함 (Ba et al., 2016)
D4. Cold initialization
- Prior work를 보면, positive examples 간의 alignment가 contrastive representation learning에 중요하다고 함(Wang & Isola, 2020)
- 사실 엄청 와닿지는 않아서, positive examples 간의 alignment가 뭔지 잘 모르겠지만 유추해보면 representation 해야 하는 positive examples는 서로간의 유사성이 있어야 모델 입장에서도 덜 헷갈릴 거 같다는 생각이 들기는 함
- 어쨌든 이런 alignment를 위해서 초기 학습 단계에서 마지막 feedforward layer에 대한 weight initialization 진행하고자 함
- 더 디테일하게 보면 와 의 last layers를 UNIF로 초기화하고 서로 가깝게 유지될 수 있도록 함
D5. Data augmentation
- actor가 out-of-distribution actions을 할 때 페널티를 주기 위한 data augment 진행
4. Experiments
Pre-Questions
1. Which combination of those design factors is the most efficient one to drive contrastive RL in solving robotic tasks?
2. How does stable contrastive RL compare with prior offline goal-conditioned RL methods on simulated and real-world benchmarks?
3. Do representations learned by stable contrastive RL emerge properties that explain how it works?
4. Does the policy learned by our method benefit from the robustness and scalability of contrastive learning?
타 offline RL 방법론들과 downstream tasks 성능 비교
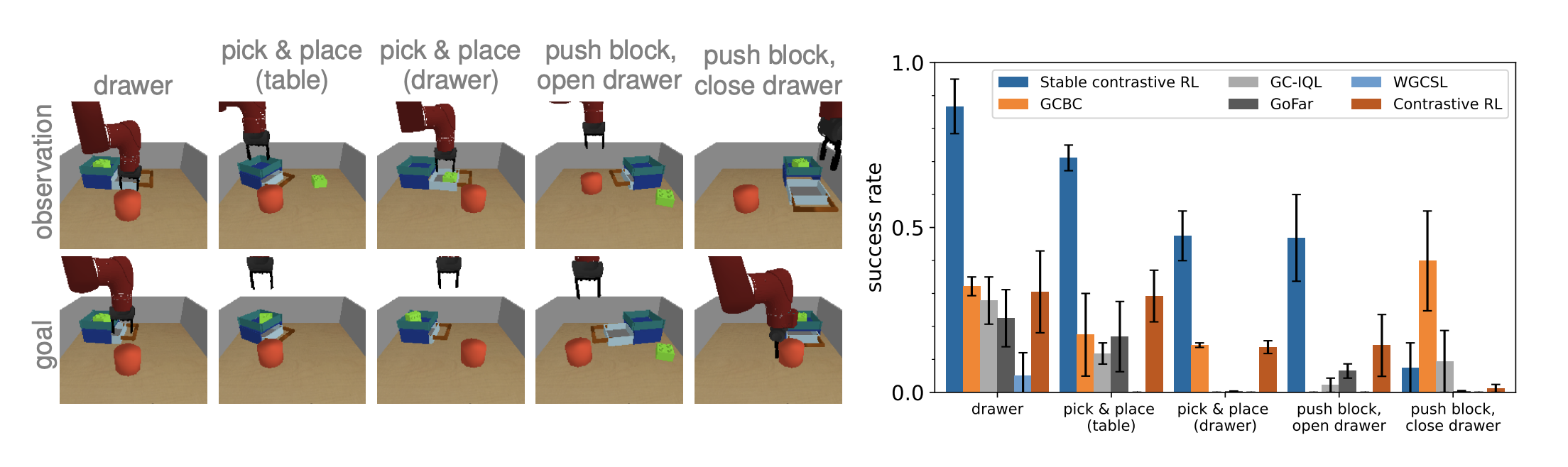
feature extractor 방법에 따른 성능 비교
-
이때 extractor는 offline dataset에 대해 학습시킨 모델을 의미(그냥 외부에서 pretrained 가져온 것이 아니라)
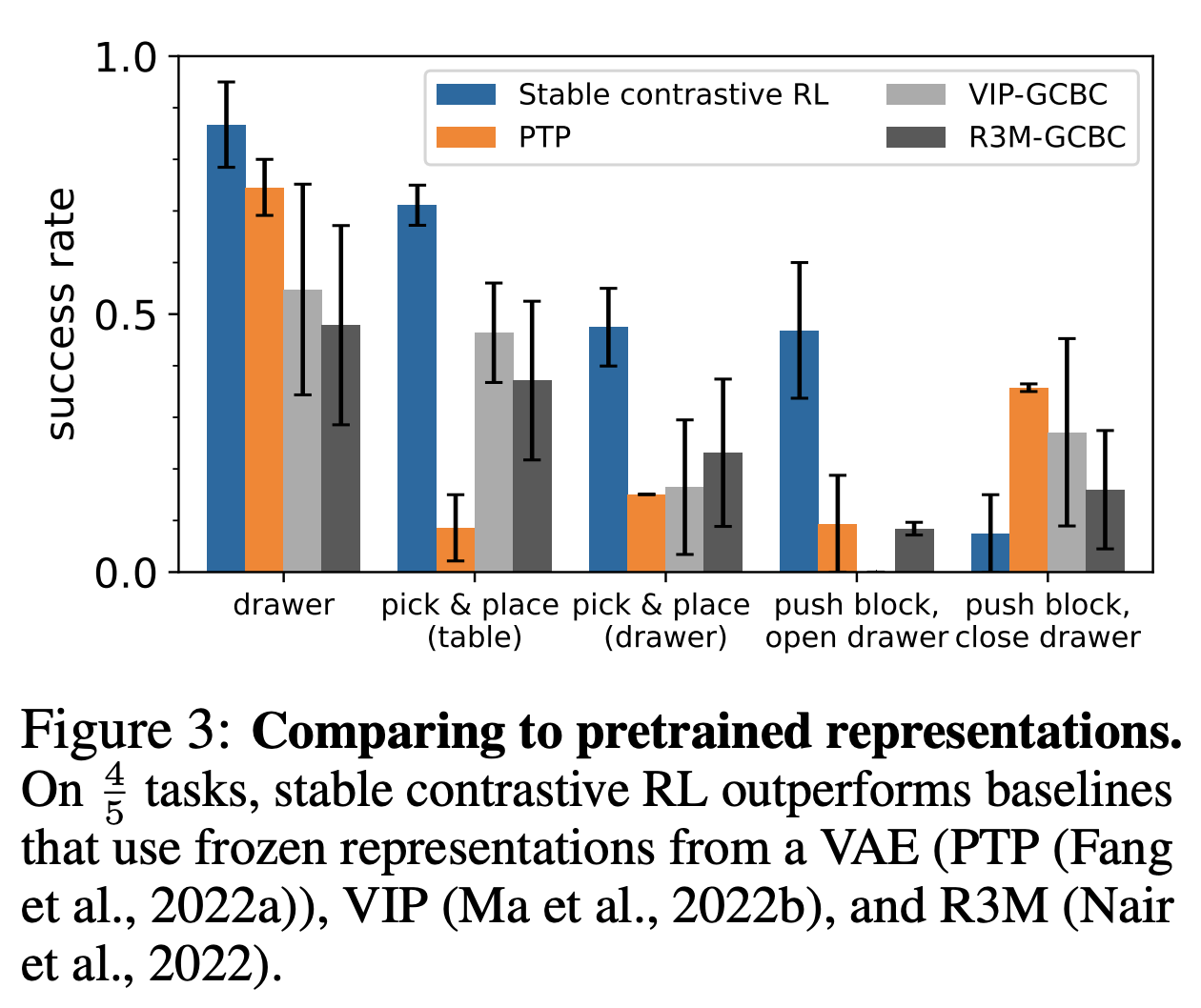
-
feature extractor에 따른 representation 이미지 비교
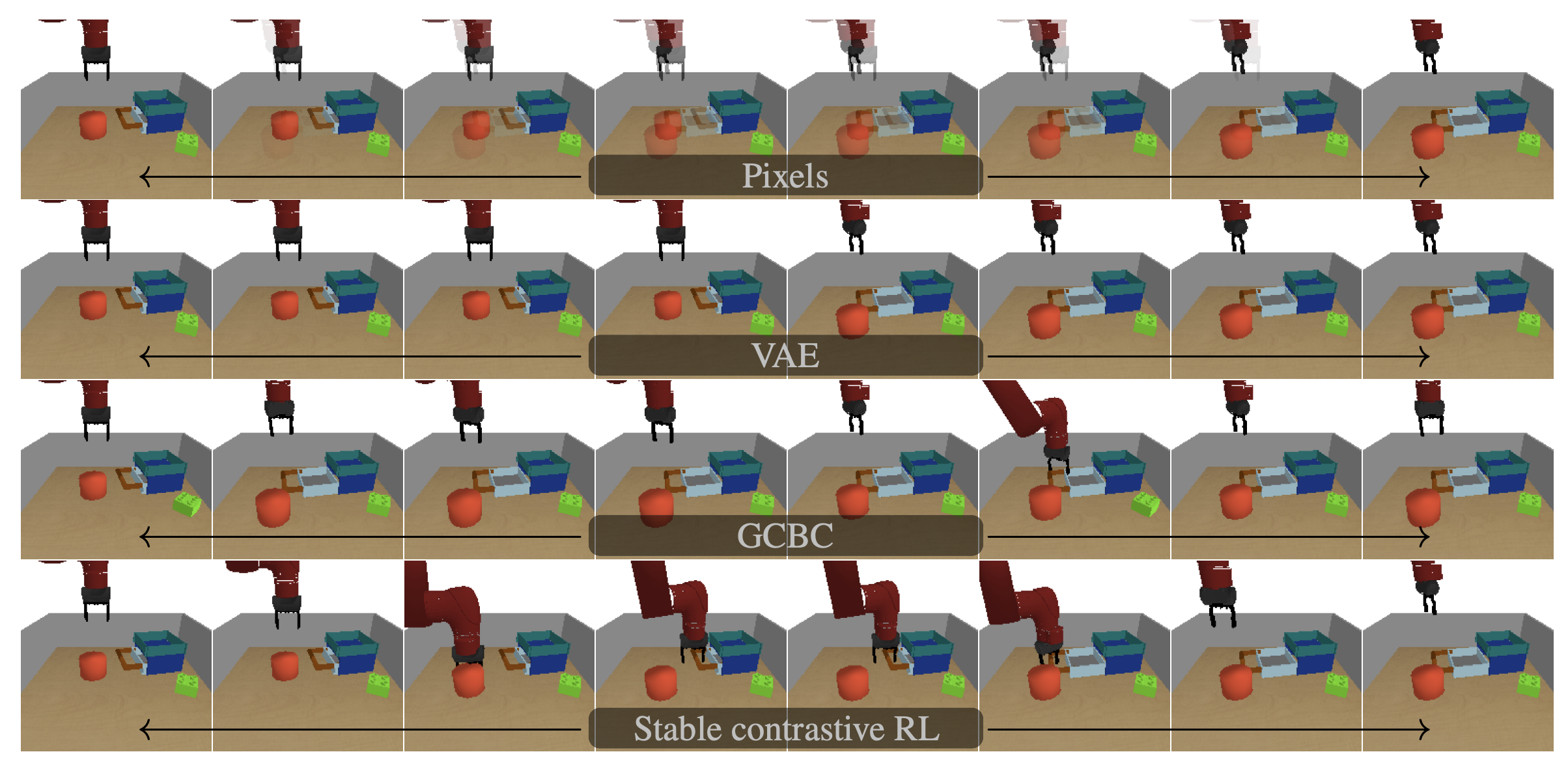
Conclusion
- 본 논문을 통해서 self-supervised RL에 맞는 design decisions을 연구함 (real-world robot manipulations tasks를 풀기 위한)
- 따라서 실험을 통해 architecture, batch size, normalization, initialization과 augmentation의 중요성을 입증함
Limitations
- CV나 NLP 타 연구들처럼 dataset과 model 크기에 따라 성능이 올라가는데, 본 연구에서는 매주 작은 사이즈의 dataset & model을 사용함