Introduction
The image of the world around us, which we carry in our head, is just a model. Nobody in his head imagines all the world, government or country. He has only selected concepts, and relationships between them, and uses those to represent the real system.
- Jay Write Forrester, 1971*
일상 생활을 할 때 어떠한 의사 결정을 하기 위해서는, 논리적인 흐름을 따를 때도 있지만 본능적이고 반사적으로 행동해야 할 때가 있음.
- 예를 들어, 야구를 할 때 타자는 배트를 어떻게 휘둘러야 할지를 굉장히 짧은 시간에 결정하고 행동해야만 함.
- 프로 선수들은 이런 일련의 과정들을 무의식적으로 진행하며, 행동의 계획을 세우기 위해 미래에 발생할 수 있는 시나리오들을 의식적으로 생각하거나 전개할 필요없이 예측에 따라 빠르게 행동할 수 있음.
본 논문의 저자는 위와 같은 관점에서 강화학습 문제를 바라보고 해결하고자 하였음.
- 이 논문이 나올 시점에 존재했던 대부분의 Model-based RL은 model로부터 에이전트를 학습하기는 하나, 여전히 실제 환경에서 에이전트를 학습했다고 함.
- 하지만 본 논문에서는 실제 환경을 생성된 환경으로 완전히 교체하고, world model에 의해 생성된 환경 내에서만 agent’s의 controller를 학습함.
Agent model
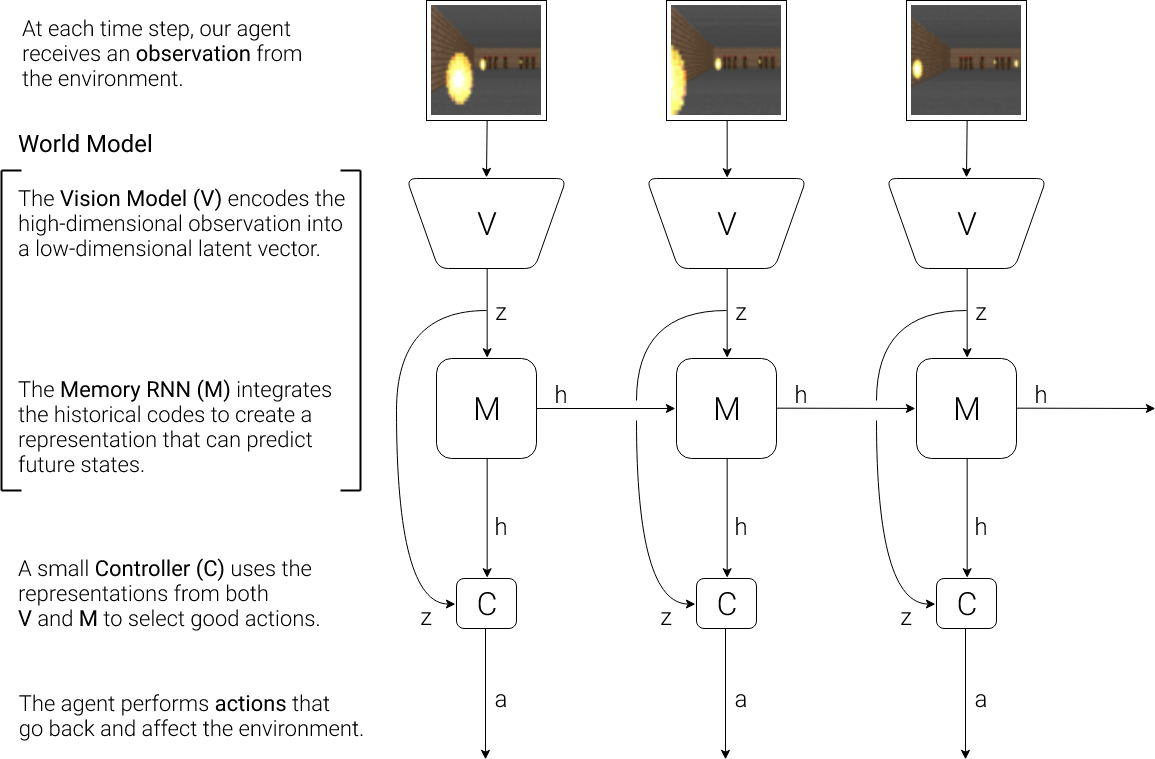
💡 Agent model은 세 개의 요소로 이루어져 있음.
(1) Vision model : Image Observation을 Memory RNN에 넣어주기 위해 image frame을 small latent vector z 로 변환해주는 component
(2) Memory RNN model : historical information 기반으로 미래를 예측하는 component
(3) Controller model : 이러한 예측에 따른 최적의 행동을 결정하는 component
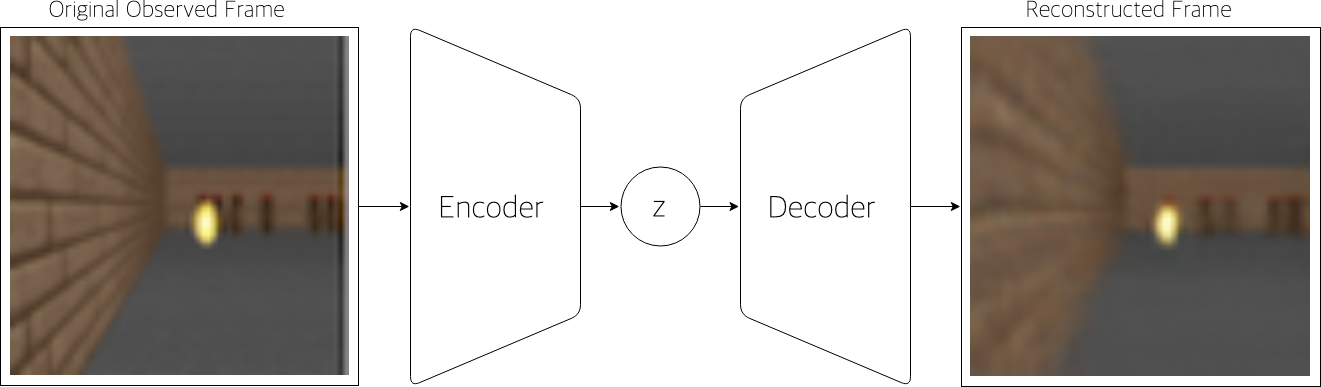
1. Vision model(V) : VAE model
본 논문에서 Vision model로 VAE(Variational Autoencoder)를 이용하여 state image로 부터 중요한 정보를 추출함.
- 즉 Observation을 small representation으로 변환하는 작업을 수행함.
- 이때 VAE를 통해 latent vector를 추출하는 이유는, 고차원 observation을 그대로 controller의 input으로 넣을 경우 policy network의 크기가 커져서 credit assignment problem을 유발할 수 있기 때문.
2. Memory RNN model(M) : MDN-RNN model
Observation을 small latent vector로 압축하는 것이 Vision model의 역할이라면, Memory RNN은 시간이 지남에 따라서 어떤 상황이 발생하는지를 예측하는 역할을 함.
- 많은 환경이 deterministic 하기 보다는 stochastic한 특성을 가지고 있기 때문에 이에 대한 대처 능력을 높이기 위해 Mixture Density Network(MDN)을 사용하고 있음.
- 본 논문에서는 MDN을 활용하여 RNN의 output으로 deterministic prediction인 z를 예측하기 보다, stochastic prediction인 probability density function 를 예측하고 있음.
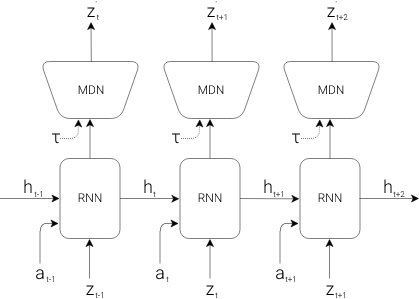
MDN 관련 좋은 설명 reference

- 는 높을 수록 불확실성이 높아진다고 함.
참고 : https://enfow.github.io/paper-review/reinforcement-learning/model-based-rl/2020/09/08/world_models/
[예시]
3. Controller model (C)
Contoller model은 최적의 행동을 결정하는 Policy임.
- V와 M과는 따로 학습을 진행하며, 최대한 심플하고 작게 만드는 것이 특징임.
- V와 M 모델과 다르게 파라미터의 갯수가 상대적으로 작기 때문에, C model을 업데이트 할 때 Covariance-Matrix Adaptation Evolution Strategy(CMA-ES)라고 불리우는 Evolution Strategy 알고리즘을 사용했다고 함.
일반적인 강화학습과 다르게, MDN-RNN의 이전 시점의 정보들을 포함하고 있는 hidden state h를 함께 사용하여서 action을 결정하게 됨.
- Evolution Strategy 알고리즘
-
Evolution strategy는 최적화 알고리즘 중 하나로 많은 후보 솔루션 중 “좋은 솔루션”을 선택하는 과정을 반복하면서 최적해를 찾는 알고리즘임.
env = gym.make('worlddomination-v0') # use our favourite ES solver = EvolutionStrategy() while True: # ask the ES to give set of params solutions = solver.ask() # create array to hold the results fitlist = np.zeros(solver.popsize) # evaluate for each given solution for i in range(solver.popsize): # init the agent with a solution agent = Agent(solutions[i]) # rollout env with this agent fitlist[i] = rollout(agent, env) # give scores results back to ES solver.tell(fitness_list) # get best param & fitness from ES bestsol, bestfit = solver.result() # see if our task is solved if bestfit > MY_REQUIREMENT: break
-
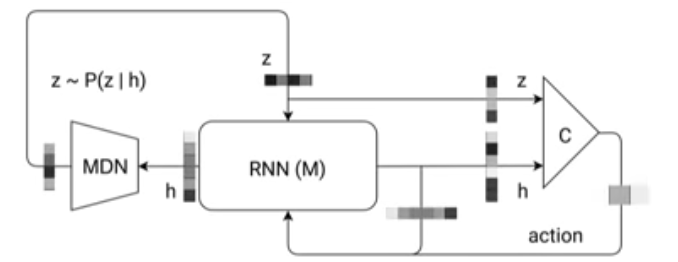
4. Putting Everything Together
- 위에 설명했던 각 components를 모아서 전체적인 학습 diagram을 보면 아래 그림과 같음.
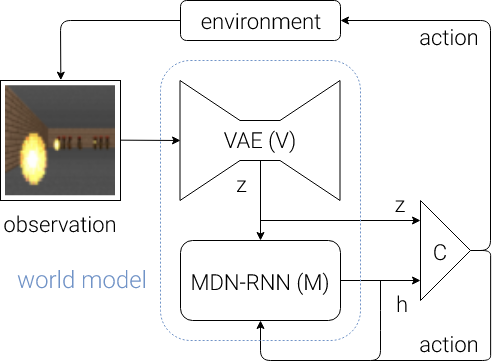
- Flow에 대한 자세한 step은 아래와 같고, 코드에서도 이해가 가능함.
(1) environment로 부터 observation을 받아서 V모델로 z를 출력하고
(2) z와 M model의 h를 concat하고 C model로 action a를 결정
(3) environment는 a 기반 next state를 구하고, M model은 hidden state를 update 함
def rollout(controller):
’’’ env, rnn, vae are ’’’
’’’ global variables ’’’
obs = env.reset()
h = rnn.initial_state()
done = False
cumulative_reward = 0
while not done:
z = vae.encode(obs)
a = controller.action([z, h])
obs, reward, done = env.step(a)
cumulative_reward += reward
h = rnn.forward([a, z, h])
return cumulative_rewardExperiment
Car Racing Experiment
Car Racing 예제는 3개의 continuous actions을 control하는 agent 를 학습시킴.
- 핸들 방향 : left / right , 가속, 브레이크
학습 순서는 아래와 같으며, 이때 reward information 을 Controller 학습 시에만 reward information을 사용한다고 함.
💡 Procedure:
(1) Collect 10,000 rollout from a random policy.
(2) Train VAE (V) to encode frames into .
(3) Train MDN-RNN (M) to model .
(4) Evolve linear controller (C) to maximize the expected cumulative reward of a rollout.
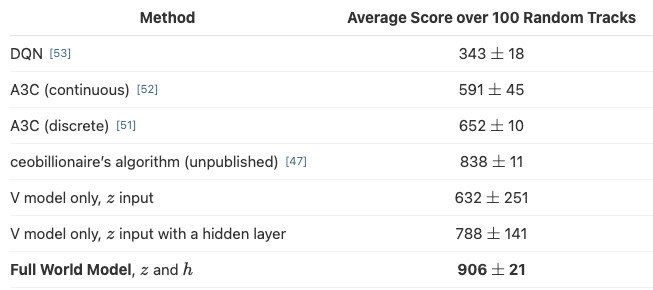
학습 결과를 보면, 기존 RL 방법론들 보다도 Full World Model을 사용했을 때 가장 average score가 높은 것을 확인할 수 있음.
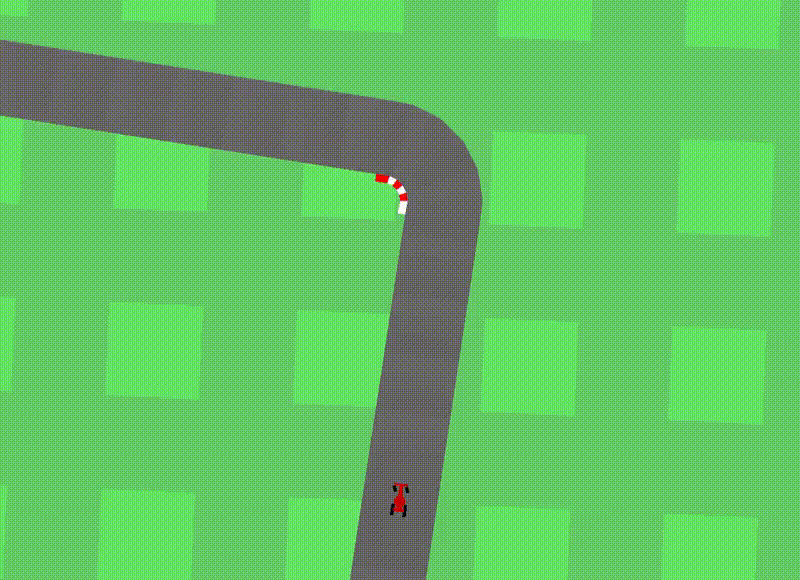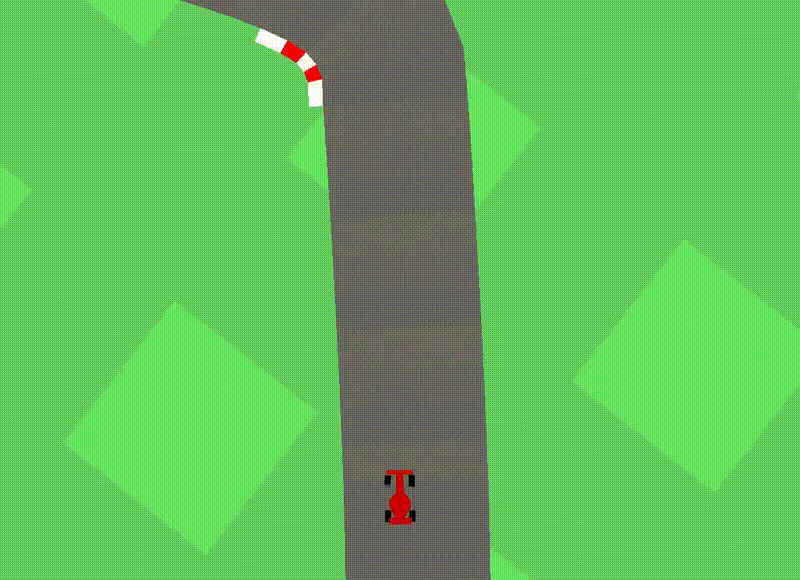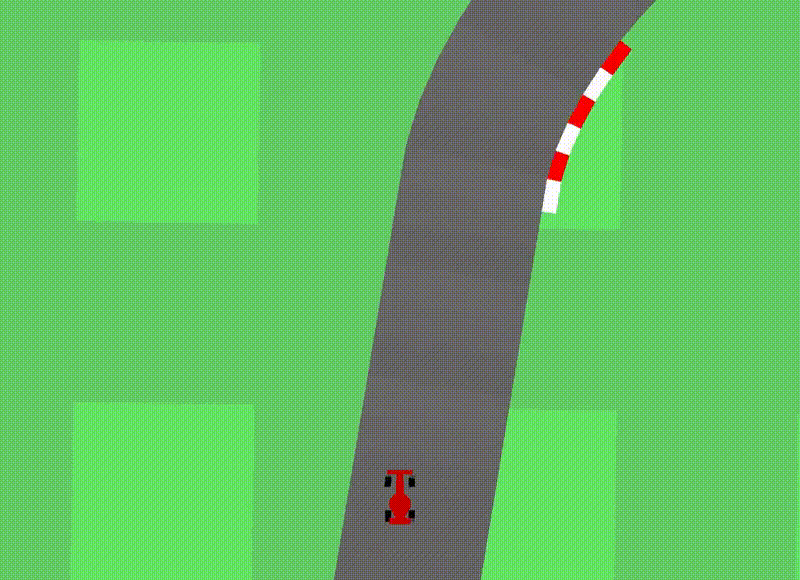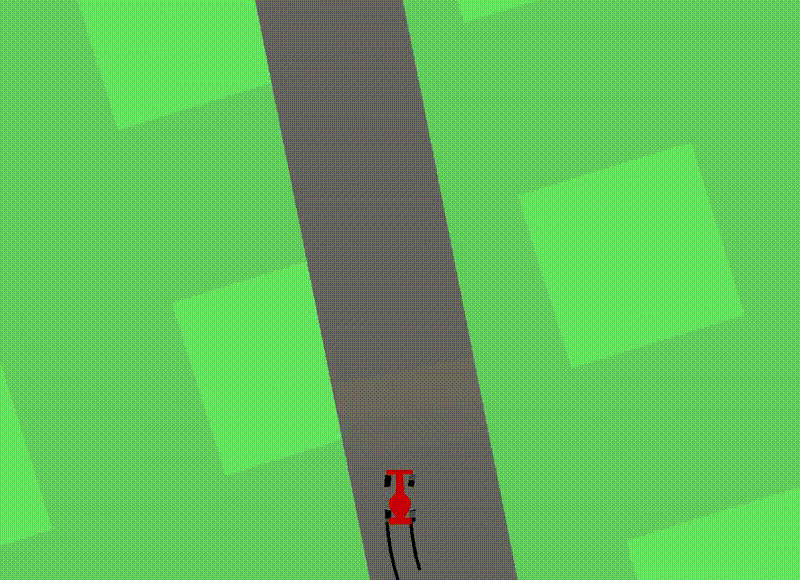
[Car Racing Dream]
- 위 Experiment 설명에서는 Controller도 rollout data를 기반으로 학습하는 것을 볼 수 있음.
- Dream에서는 아래 이미지처럼
- model에서 예측한 을 next state로 사용하여,
- 실제 environment 없이 진짜로 model을 활용하여 학습하는 실험을 확인할 수 있음.
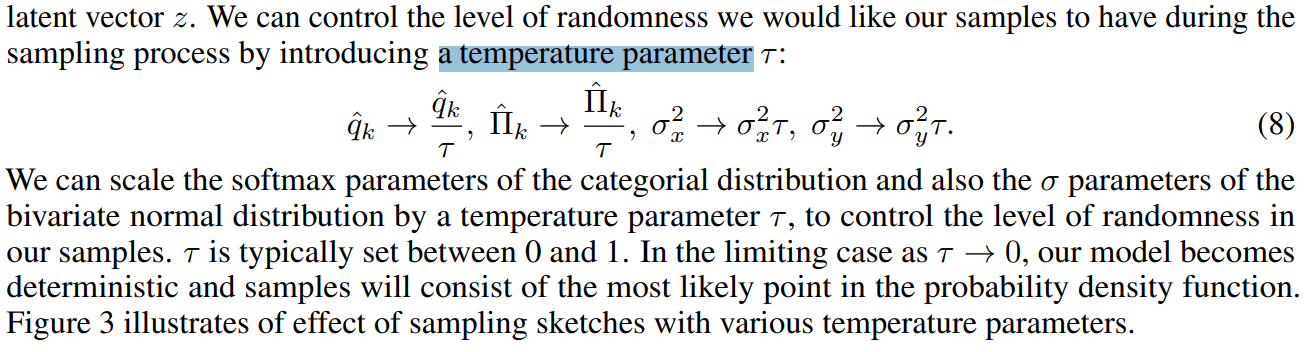
이때 앞서 설명했던 를 조절하면서 M을 통해 생성된 environment에 대한 uncertainty를 control 했다고 함.
VizDoom Experiment
- 지금까지는 실제 environment를 활용하여 policy를 학습시킨 후 dream environment 에서도 잘 작동되는지 확인했다면, VizDoom 예제에서는 dream environment에서 학습 시킨 policy를 실제 environment에서 작동시킬 수 있는지 확인하고자 함.
- VizDoom 예제는 agent가 fireballs를 최대한 오래 피하는 게임.
- 그렇기 때문에 explicit rewards가 없으며, 누적 보상으로는 생존 시간으로 정의된다고 함.
- 각 environment의 rollout은 최대 2100개의 time steps으로 이루어져 있고, 에이전트가 100회 이상 연속으로 생존한 평균 생존이 750 time steps보다 길면 solve된 것으로 인정됨.
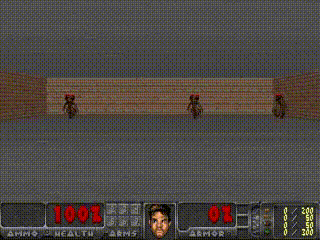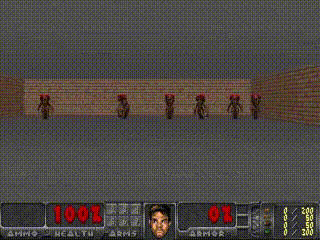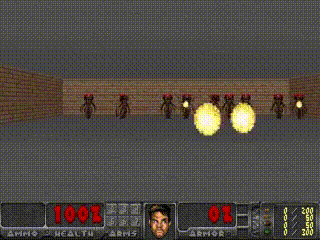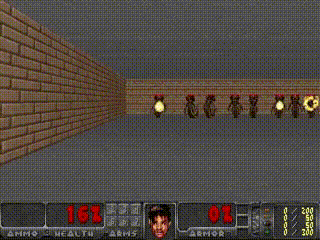
학습 순서는 아래와 같음.
앞서 봤던 car racing 예제와 다른 점으로는 M model이 next 외에도 agent가 죽었는지 아닌지에 대한 를 함께 예측한다는 것임.
💡 Procedure:
(1) Collect 10,000 rollout from a random policy.
(2) Train VAE (V) to encode frames into .
(3) Train MDN-RNN (M) to model .
(4) Evolve linear controller (C) to maximize the expected survival time inside the virtual environment.
(5) Deploy learned policy from (4) on actual environment.
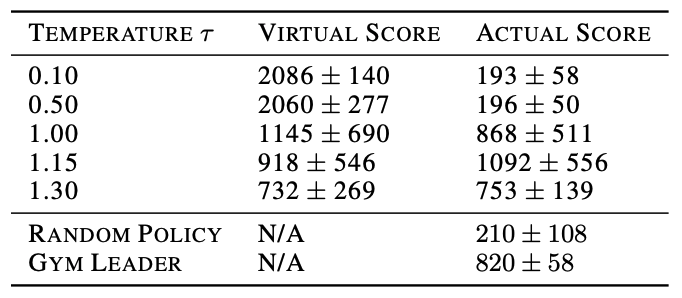
[Temperature 실험]
💡 Ha, D. and Eck, D. A neural representation of sketch drawings. ArXiv preprint, April 2017. URL https://magenta.tensorflow.org/ sketch-rnn-demo.
https://openreview.net/pdf?id=Hy6GHpkCW
Model에서 를 생성할 때 uncertainty를 조절하기 위한 방법으로 parameter 를 조절함.
- 가 클 수록 uncertainty를 많이 포함하고 있으며, Model이 생성한 environment가 random 성을 많이 가진다고 볼 수 있음.
- 따라서 가 작을 수록 에이전트 입장에서는 “배우기 쉬운” 환경이 되기 때문에 아래 표에서도 score 를 높게 가지는 것을 확인 가능함.
Iterative Training Procedure
지금까지의 experiments는 굉장히 단순한 tasks이라고 볼 수 있으나, 실제 문제들은 그렇게 단순하지 않음.
- 그렇기 때문에 V, M을 학습하고 C를 학습하는 구조보다 모델들을 지속적으로 업데이트하여 개선하는 프로세스가 필요함.
💡 Procedure:
(1) Initialize M, C with random model parameters.
(2) Rollout to actual environment N times. Save all actions and observations during
rollouts to storage.
(3) Train M to model model and train C to optimize expected reward inside of M.
(4) Go back to (2) if task has not been completed.
위 Procedure에서 볼 수 있듯, 앞선 experiments와는 다르게 M model은 (1)이 아닌 (2) 인 x, r, a, d를 예측하고 있음.
이와 관련하여서 복잡하고 정밀한 제어가 필요한 task를 배우는 경우, C model이 어떻게 행동할지 또한 M model이 예측하게 하여 C model이 보다 복잡한 환경에 잘 적응할 수 있도록 도울 수 있다고 함.
Reference
- 논문
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1803.10122.pdf
https://worldmodels.github.io/
- 영상 자료
[저자 발표] ha : https://youtu.be/HzA8LRqhujk
DSBA 연구실 : https://youtu.be/qm9kW9M4QyA
Siraj Raval : https://youtu.be/IZPKohYNri4
- 블로그
[world models] https://jay.tech.blog/2018/12/09/world-models/
[world models] https://enfow.github.io/paper-review/reinforcement-learning/model-based-rl/2020/09/08/world_models/
[evolutional] https://blog.otoro.net/2017/11/12/evolving-stable-strategies/
[evolutional] https://blog.otoro.net/2017/10/29/visual-evolution-strategies/
- 코드
[tf version] https://github.com/hardmaru/WorldModelsExperiments
[torch version] https://github.com/ctallec/world-models
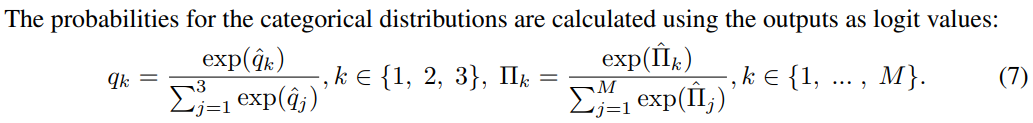
좋은 리뷰 해주셔서 감사합니다.