Mobile IP
- Extension of IP protocol
: That allows mobile computer to be connected to the Internet at any location
Stationary and Mobile Hosts
- Original IP addressing was based on the assumption that
: A host is stationary, attached to one specific network - The address is valid only when the host is attached to the network
: If the network changes, the address is no longer valid - Changing address
: Let the mobile host change its address as it goes to the new network - 2 major drawbacks
: Rebooting
: If the host roams from one network to another during a transmission, the exchange will be interrupted
This is because the ports and IP address of the client and the server must remain constant for the duration of the connection
2 Addresses
- Home address (HoA) and care-of address(CoA)
: Permanent address and a temporary address
: Permanent address associates the host with its home network (HN)
: When a host moves from one network to another, the CoA changes
= It is associated with the foreign network (FN), the network to which the host moves

Agents
- To make the change of address transparent to the rest of the Internet requires a home agent and a foreign agent
- Shown the home and the foreign agents as routers
: We need to emphasize that their specific function as an agent is perform in the application layer
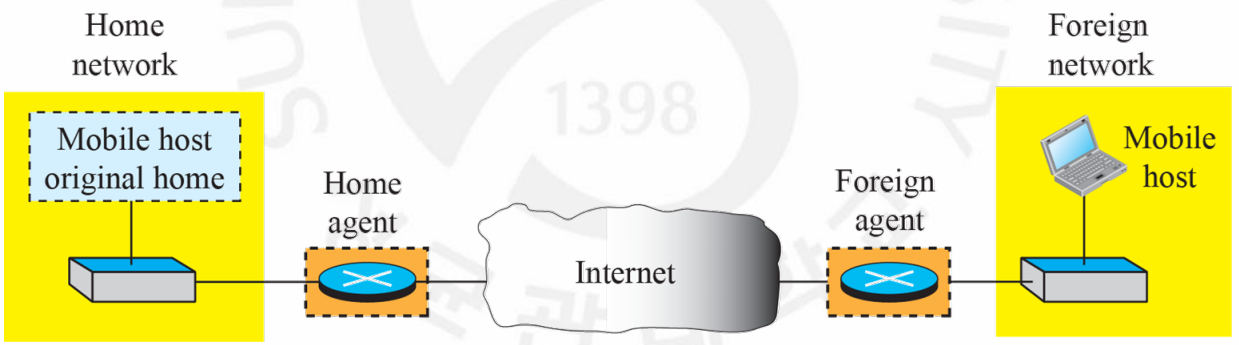
HA and FA
- Home agent(HA)
: A router attached to HN
: Acts on behalf of the mobile host when a remote host sends a packet to mobile host - Foreign agent(FA)
: A router attached to FN
: Foreign agent receives and delivers packets sent by the home agent to the mobile host
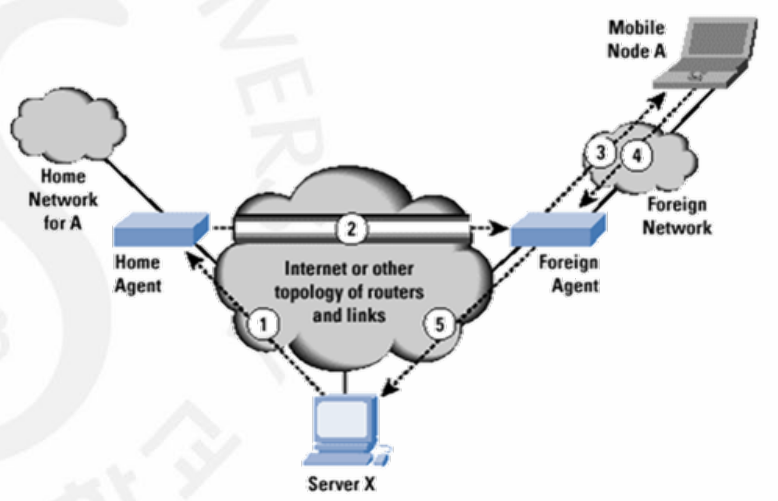
Data Transfer
-
From a remote host (RH) to HA
: RH sends a packet as though MH is at its home network
: Uses RH address as source and home address of mobile host as destination -
From HA to FA
: HA sends the packet to the foreign agent using the tunneling
: HA encapsulates the whole IP packet inside another IP packet using its address as the source and the foreign agent's addres as the destination -
From FA to MH
: When FA receives the packet, it removes the original packet
: Since DST address is home address of MH, FA consults a registry table to find the care-of Address of MH -
From MH to RH
: It sends as it does normally
: MH prepares a packet with its home address as SRC, and the address of RH as DST
Transparency
- RH is unaware of any movement by MH
: RH sends packet using home address of MH as DST
: It receives packets that have home address of MH as SRC
Double crossing
- Occurs when RH communicates with an MH that has moved to the same network as RH
- When MH sends a packet to RH, there is no inefficiency
- When RH sends a packet to MH, the packet crosses the Internet twice
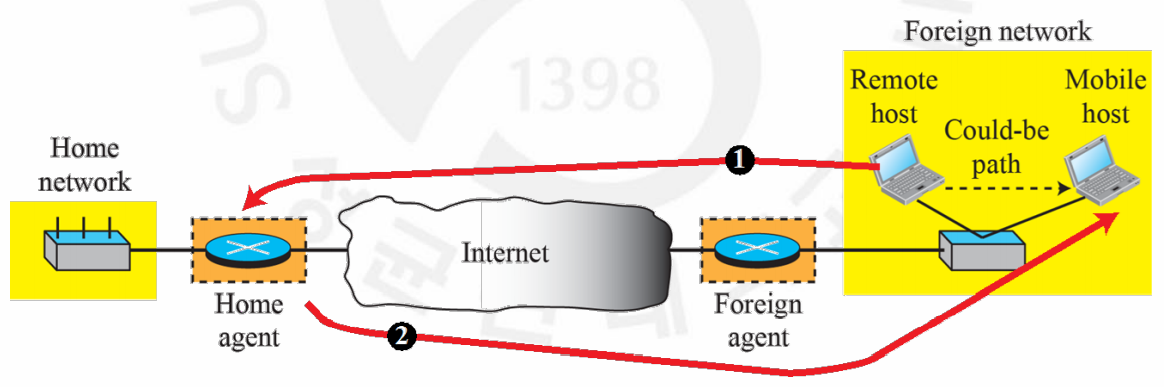
Triangle Routing
- Less severe
- Occurs when RH communicates with MH that is not attached to the same as MH
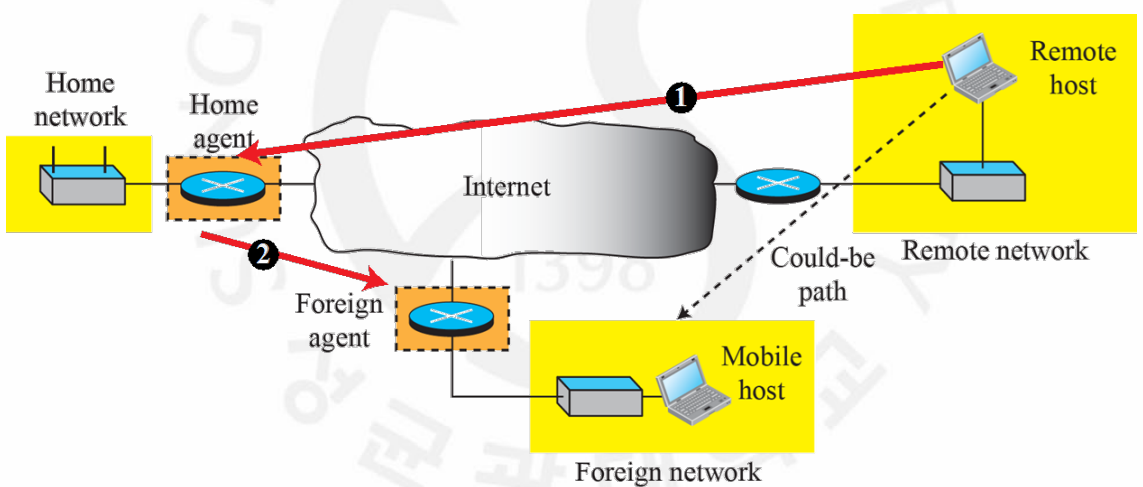
Intra-Domain Routing
Routing and Forwarding
- Main objective of network layer
: Transport packets from source to destination - Two mechanisms are used in network layer
1) Forwarding
: Algorithm use by each router to determine on which interface each packet should be sent to reach its destination or follow its virtual circuit
: Relies on the routing table maintained by each router
2) Routing
: Distributed algorithm that distributes to all routers the information that allows them to build their routing tables
Principles
- How to build routing table of each router?
: Include in the routing table of each router the path to allow it to reach each destination - Selection of the shortest paths
: How does "C" choose a next-hop one the path towards host "H"?
: Based on metrics
1) Minimum hop
2) Cost
3) Delay
4) 1/Throughput
Metrics
- An internet is a combination of networks connected by routers
- A metric is a cost assigned for passing through a network
- Total metric of a route is equal to the sum of metrics of networks that comprise route
- Router chooses the route with the shortes (smallest) metric
Intra and Inter Domain Routing
- Because Internet can be so large, one routing protocol cannot handle the task of updating routing tables of all routers
- Internet is divided into autonomous systems(AS)
: AS is a group of network and routers under authority of a single administration - Intra-domain routing
: Used for routing inside an AS - Inter-domain
: Used for routing between AS
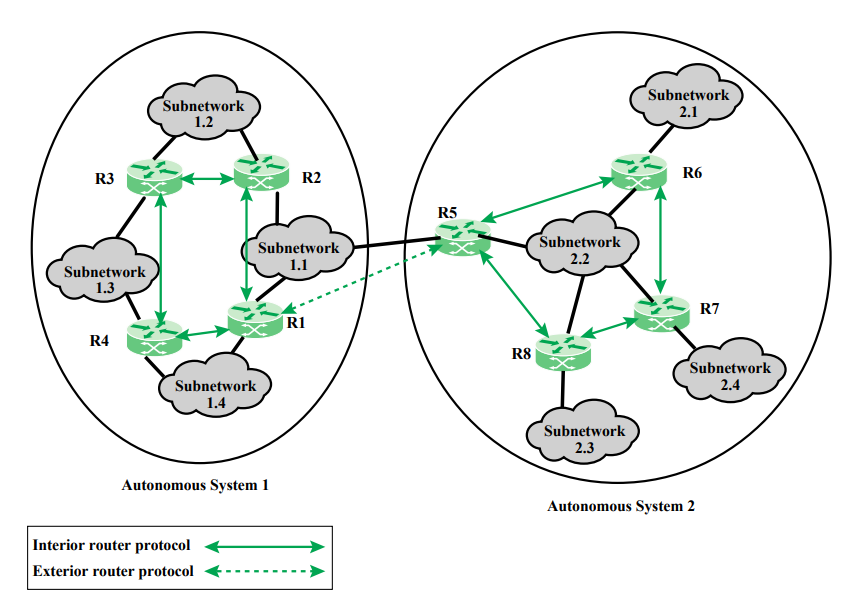
Popular Routing Protocols
- A routing protocol is a combination of rules and procedures that lets routers in the Internet inform each other of changes

Intra-Domain Routing
Static Routing
- Network manager computes all routing tables and downloads them on all routers
: Shortest path algorithms - Advantages of static routing
: Easy to use in small network
: Routing tables can be optimized easily - Drawbacks of static routing
: Does not adapt dynamically to network load
: How to deal with link and router failures?
Dynamic or Distributed Routing
- Routers exchange messages and use a distributed algorithm to build their routing tables
: Used in almost all networks - Advantages
: Can easily adapt routing tables to events - Drawbacks
: More complex to implement than static routing - Most common distributed routing methods
1) Distance vector routing
2) Link state routing
Shortest Path Algorithms
- Distance vector protocols
-- Neighbors exchange list of distances to destinations
-- Best next-hop determined for each destination
-- Distributed Bellman-Ford algorithm - Link State Protocol
-- Link state information flooded to all routers
-- Routers have complete topology information
-- Dijkstra's shortest first algorithm
2개의 댓글
Mobile IP is a communication protocol that allows mobile devices to maintain a constant IP address while moving between networks. Key components include the Home Address which represents the device's permanent IP address; the Care-of Address the temporary IP address while roaming; the Home Agent which manages communication between the mobile device and the internet; and the Foreign Agent which facilitates connectivity. Routing in Mobile IP involves intra-domain routing, ensuring efficient data transfer. This includes a 3D visualization of the estate that enhances understanding of network topology and dynamics. The 3D visualization of the estate is crucial for visualizing routing paths and network changes effectively.

Unlock your potential with the https://www.testsfile.com/Marketing-Cloud-Administrator-tests.html! This certification validates your expertise in managing and optimizing Marketing Cloud applications. Dive into key topics like data management, email marketing strategies, and automation tools. Equip yourself with the skills to drive successful marketing campaigns and enhance customer engagement. With a deep understanding of analytics and reporting, you’ll be able to measure success and make data-driven decisions. Prepare effectively with our comprehensive study guides and practice exams, ensuring you’re ready to ace the test. Propel your career forward and showcase your Marketing Cloud proficiency today!