[C#과 유니티, 실전 게임으로 제대로 시작하기]섹션4. 스터디
추상클래스
추상클래스와 추상메서드는 부모클래스에서 정의한 메서드를 자식클래스에서 반드시 재정의하도록 한다.
추상클래스 구조
abstract class 클래스_이름{
}
추상메서드 구조
접근_제한자 abstract 반환_타입 메서드_이름(매개변수);
자식클래스에서 재정의 구조
접근_제한자 override 반환_타입 메서드_이름(매개변수){
}
class Animal{
public void Move(){
Debug.Log("Move!");
}
}
class Bird : Animal {
public void Move(){ //Animal을 상속받기 때문에 Move함수가 없어도 상관 없다.
Debug.Log("Fly!");
}
}
class Fish : Animal {
public void Move(){
Debug.Log("Swim!");
}
}->반드시 상속받은 클래스에서 재정의가 필요할 때 추상클래스를 사용한다.
abstract class Animal{ // 추상클래스에서는 반드시 추상메서드만 구현할 수 있는건 아니다.
public abstract void Move(); //추상메서드는 반드시 추상클래스 안에서 구현되어야한다.
}
class Bird : Animal {
public override void Move(){
Debug.Log("Fly!");
}
}
class Fish : Animal {
public override void Move(){
Debug.Log("Swim!");
}
}인터페이스
인터페이스는 반드시 추상멤버만 구상할 수 있다. 인터페이스에서는 모두 추상멤버로 보기 때문에 abstract를 사용하지 않아도 된다. 인터페이스는 다중장착이 가능하다. 인터페이스는 클래스가 아니다.
인터페이스 구현
Interface 인터페이스_이름{
}
Interface ISword{ //인터페스를 구현할 때 이름의 앞에는 I를 붙여주는 것이 관례이다.
//float damage -> 인터페이스에서는 필드를 구현할 수 없다.
float Damage{get;set;}
void Attack();// abstract 생략
}
Interface IShield{
float DefensivePower {get;set;}
void Defend();
}
class Knight : ISword, IShield{ //여러개의 인터페이스를 장착하였다.
public float Damage {get;set;}
public float DefensivePower {get;set;}
public void Attack() {
}
public void Defend() {
}
}구조체
구조체는 어떤 대상을 추상화한 데이터의 구조이다.
주의해야할 점
- 구조체의 필드는 초기화할 수 없다.
- 구조체의 생성자는 반드시 모든 필드를 초기화해야 한다.
구조체의 구조
struct 구조체_이름{
}
void Start(){
point_struct point1=new Point_struct(1,1) //new연산자는 heap메모리에 공간을 할당시켜주는 역할을 한다.
Debug.Log(point1.GetPoint());
}
strcut Point_struct{
public int x;
public int y;
public Point_struct(int x, int y){
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
}
public string GetPoint(){
return $"({x},{y})";// $로 인하여 중괄호 안의 문자는 변수로 해석한다.
}
}
(1,1)이 콘솔창에 출력된다.
구조체와 클래스
구조체(값형)
void Start(){
Point_struct point1 = new Point_struct(3,3);
Point_struct point2 = point1;
point2.x=2;
point2.y=2;
Debug.Log(point1.GetPoint());
Debug.Log(point2.GetPoint());
}
strcut Point_struct{ //구조체로 Point_struct 선언한다.
public int x;
public int y;
public Point_struct(int x, int y){
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
}
public string GetPoint(){
return $"({x},{y})";
}
}(3,3)
(2,2) 값이 콘솔창에 출력된다.
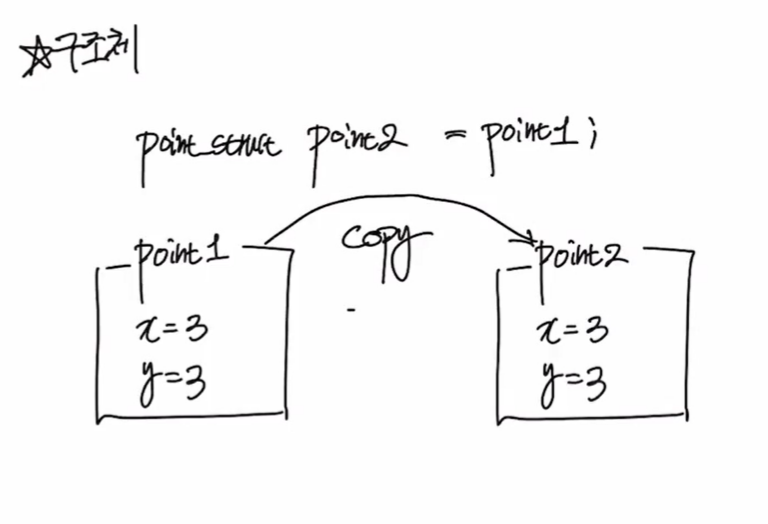
- 구조체의 변수 point1의 객체는 그대로 복사되어 point2가 된다.
따라서 point2의 값이 변해도 point1의 값은 변하지 않는다. - 즉, 변수에 객체를 대입한다고 했을 때 그 객체를 복사하는 개념이다.
- 구조체는 스택메모리에 객체가 생성된다. 변수를 대입하게 된다면 스택메모리가 하나 더 생기는 구조이다.
클래스(참조형)
void Start(){
Point point1 = new Point(3,3);
Point point2 = point1;
point2.x=2;
point2.y=2;
Debug.Log(point1.GetPoint());
Debug.Log(point2.GetPoint());
}
class Point{ //클래스로 Point 선언한다.
public int x;
public int y;
public Point(int x, int y){
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
}
public string GetPoint(){
return $"({x},{y})";
}
}
(2,2)
(2,2) 값이 콘솔창에 출력된다.
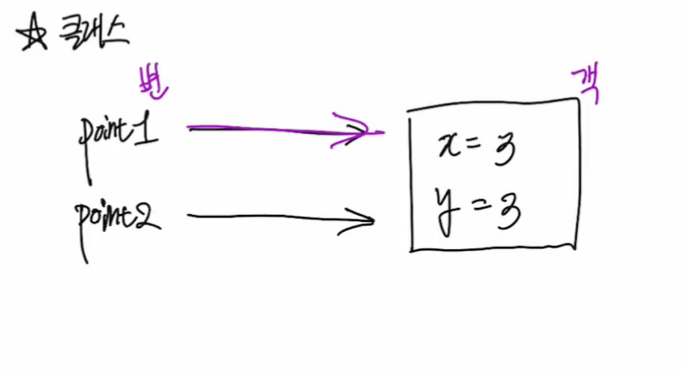
- 클래스의 변수는 객체를 가리키는 역할을 한다.
- Point point2 = point1;를 입력하였을 때 point1과 point2는 같은 객체를 가리키고 있기 때문에 두 변수의 값이 변한다.
- 구조체와 다르게 변수에 객체를 대입한다고 했을 때 그 객체를 복사하는 것이 아닌, 객체를 가리켜 참조하는 개념이다.
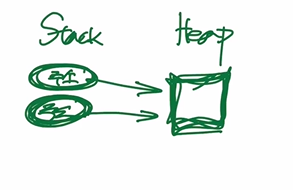
- 클래스는 힙메모리에 객체가 생성된다. 객체를 변수에 대입하게 된다면 스택메모리에 생성되어 힙메모리를 가리킨다. 스택메모리에는 힙메모리의 주소값이 저장된다.
void start(){
Point_struct point3; //스택메모리에 이미 객체가 저장되어있기 때문에 변수를 선언하는 것만으로도 x,y에 값을 대입할 수 있다.
point3.x=1;
point3.y=1;
Point point4;
//point4.x=1; -> new연산자로 heap메모리에 공간을 할당하지 않았기때문에 point4에는 객체가 존재하지 않는다. ->에러가 발생한다.
}네임스페이스
클래스들의 묶음을 네임스페이스라한다. 클래스들을 한 곳에 묶어 다른 클래스와 구분하기 위하여 네임스페이스를 이용한다.
네임스페이스 구조
namespace 네임스페이스_이름{
class 클래스_이름{}
.
.
.}
using UnityEngine //UnityEngine또한 네임스페이스로 구조되어있다.
public class NamespaceExample : MonoBehaviour //UnityEngine에 MonoBehaviour가 존재하기 때문에 using을 사용하여 MonoBehaviour클래스에 접근하였다.
{
void Start(){}
}네임스페이스 내에 있는 클래스에 접근하는 방법
1. using을 사용한다.
2. 네임스페이스이름.클래스이름 으로 네임스페이스를 부른다.
ex>
public class NamespaceExample : UnityEngine.MonoBehaviour // 2번째 방법으로 네임스페이스 내에 있는 클래스를 접근하였다.
{
void Start(){
exampleNS.A a = new exampleNS.A();
}
}
namespace exampleNS{
class A{}
class B{}
}인덱서
인덱서의 구조
접근_제한자 반환_타입 this[int index]{
get{}
set{}
}
void Start(){
Grade grades = new Grade();
grades.grades[0] = 20;
for (int i = 0; i<grades.grades.Length; i++){
Debug.Log(grades.grades[i]);
}
}
class Grade{
public int[] grades = {10, 50, 60, 40};
}
인덱서를 활용한 코드>
void Start(){
Grade gr = new Grade();
int[] grades = gr.grades;
grades[0] = 20;
for (int i = 0; i<grades.Length; i++){
Debug.Log(grades[i]);
}
}
class Grade{
public int[] grades = {10, 50, 60, 40};
public int this[int index]{
get{
return grade[index];
}
set{
grades[index] = value;
}
}
}
열거형
열거형의 구조
enum 열거형_이름{
요소1, 요소2, 요소3, ...
}
void Start(){
Debug.Log((int)Days.Mon); //(int)로 형변환 하였기 때문에 0의 값이 콘촐창에 출력된다.
Debug.Log((int)Days.Sat); //5의 값이 콘솔창에 출력된다.
}
enum Days{
Mon, Tue, Wed, Thu, Fri, Sat, Sun
}
//enum Days{
Mon, Tue, Wed, Thu=7, Fri, Sat, Sun //Thu는 7로 명시하였기에 Fri는 8, Sat은 9로 1씩 늘어난다.
}enum을 사용하면 실수할 가능성이 줄어든다. 또한 가독성이 높아진다.
string names = { "john", "chulsoo", "bbobbi", "noorungi"};
void Start(){
Debug.Log(names[(int)Names.bbobbi]); // Names.bbobbi의 값은 enum에서 2번째이다. (int)로 명시적형변환을 하였기 때문에 (int)Names.bbobbi는 2의 값을 가진다.
// 즉, names[(int)Names.bbobbi]는 names[2]와 같으며 names[2]는 string names에서 bbobbi임으로 bbobbi값이 콘솔창에 출력된다.
Debug.Log(names[(int)Names.noorungi]);
}
enum Names{
john, chulsoo, bbobbi, noorungi
}