Chapter 03. Coding attention mechanisms

https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch/tree/main/ch03
1. 긴 시퀀스를 모델링할 때 발생하는 문제
- 텍스트를 단어 단위로 번역하는 task는 source 언어와 target 언어 간의 문법 구조 차이로 인해 불가능하다.
- 트랜스포머 이전 기계 번역에는 encoder-decoder RNN이 사용되었다.
- 전체 input sequence를 요약한 표현을 만드는 hidden state를 사용한다.
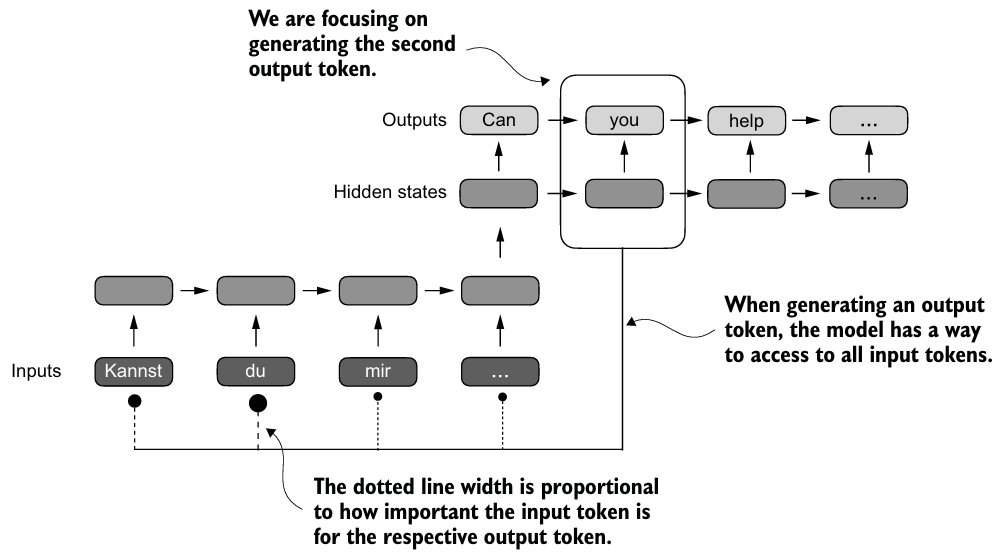
2. attention 메커니즘을 활용한 데이터 종속성 캡처
- Attention에서 텍스트 생성 디코더 부분은 선택적으로 input 토큰에 접근할 수 있다.
- 즉, 특정 입력 토큰이 특정 출력 토큰 생성 시 다른 토큰보다 더 중요한 의미를 지니고 있다.
self-attention은 input 표현을 향상시키기 위해 시퀀스 내의 각 position이 다른 모든 position과 상호작용하여 관련성을 결정할 수 있도록 하는 기술이다.
- GPT-2는 decoder-only 구조이기 때문에, self-attention을 사용하며 이는 query, key, value가 모두 같은 입력 시퀀스로부터 만들어진다.
- query, key, value는 모두 attention 연산에 필요한 matrix로 이후 설명된다.
- self-attention과 반대로 cross-attention은 Encoder-Decoder 등의 구조에서, decoder가 encoder의 출력(문맥)을 참고해야 할 때 사용된다.
- query, key, value는 서로 다른 입력 소스에서 나올 수 있다.
- GPT-like 모델은 질문과 답변을 한 줄로 연결된 하나의 시퀀스로 인식한다.
[질문 토큰들] + [SEP] + [답변 토큰들] - 이로 인해 GPT는 질문을 보면서도 self-attention만 사용해도 충분한 문맥 처리가 가능.
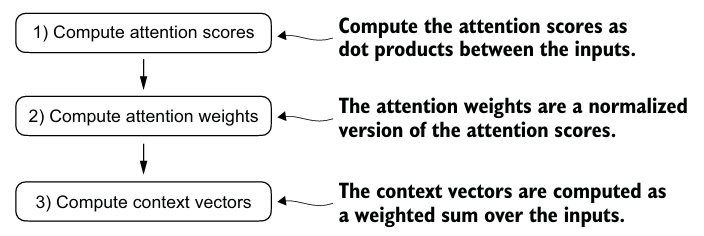
3. self-attention을 통한 입력의 다양한 부분에 주목하기
훈련되지 않는 가중치를 이용하여 간단한 self-attention mechanism을 구현해보자.
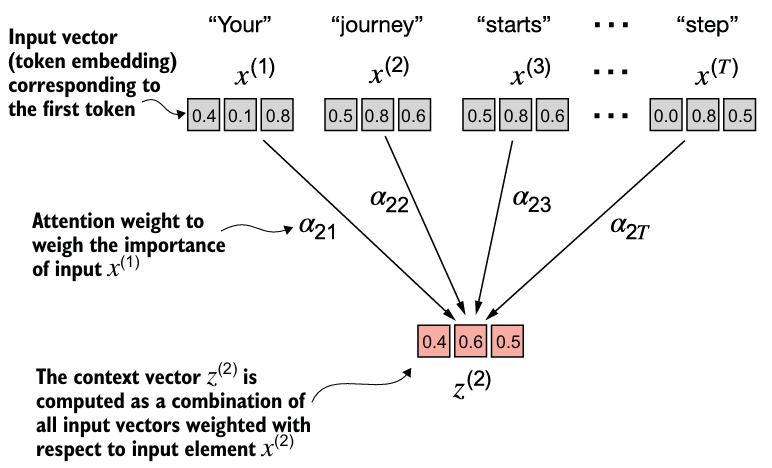
- input sequence의 element인 의 weight 합인 context vector 를 계산한다.
- e.g. 는 에 대한 ~의 가중치 합이다.
- Attention weight는 를 계산할 때 가 얼마나 기여했는지를 나타낸다.
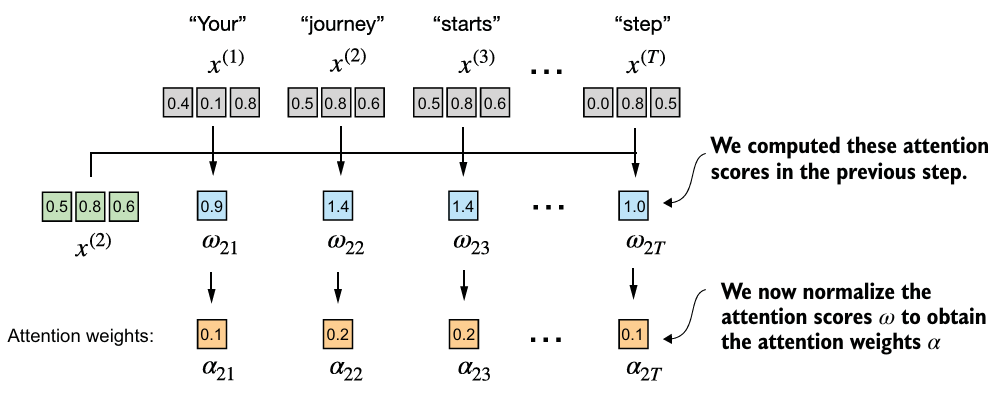
- 비정규화된 Attention weight를 attention scores라 부르고, 정규화되면 attention weights라 부른다.
- attention scores 계산
- e.g. 2번째 element를 query ()로 사용할 때 각 attention scores는 dot product를 적용하면 이다.
query = inputs[1] # 2nd input token is the query
attn_scores_2 = torch.empty(inputs.shape[0])
for i, x_i in enumerate(inputs):
# dot product (transpose not necessary here since they are 1-dim vectors)
attn_scores_2[i] = torch.dot(x_i, query)
print(attn_scores_2)- 정규화
- attention scores의 합으로 각 attention score를 나눌 수도 있지만, 대게 softmax function, 특히 underflow나 overflow를 방지하기 위해
torch.softmax()를 이용한다.
- attention scores의 합으로 각 attention score를 나눌 수도 있지만, 대게 softmax function, 특히 underflow나 overflow를 방지하기 위해
attn_weights_2 = torch.softmax(attn_scores_2, dim=0)
- 에 attention weights(를 곱하여 를 계산하고, 그 결과 벡터를 합한다.
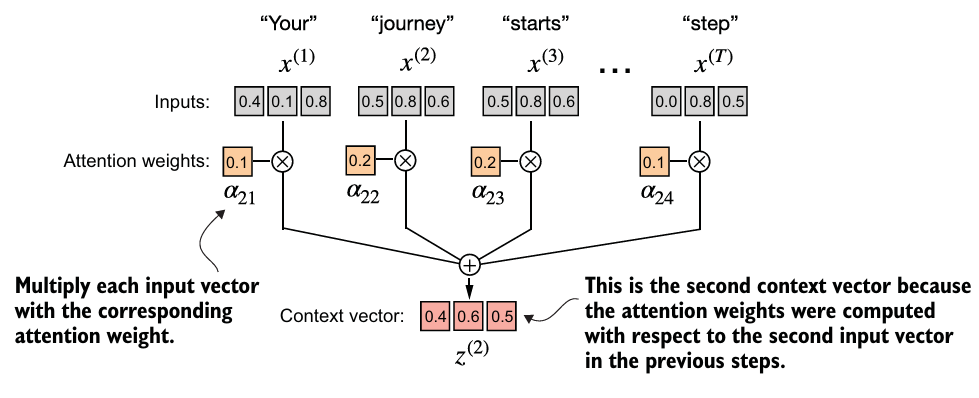
query = inputs[1] # 2nd input token is the query
context_vec_2 = torch.zeros(query.shape)
for i, x_i in enumerate(inputs):
context_vec_2 += attn_weights_2[i]*x_i모든 input 토큰에 대한 를 구해보자.
attn_scores = inputs @ inputs.T
attn_weights = torch.softmax(attn_scores, dim=-1)
all_context_vecs = attn_weights @ inputs4. 학습 가능한 가중치로 self-attention 구현하기
기존 트랜스포머 아키텍처에서 사용되는 self-attention mechanism인 scaled dot-product attention을 구현해보자.
- 이제는 더 나은 context vectors를 만들기 위해 trainable weight matrices가 존재한다.
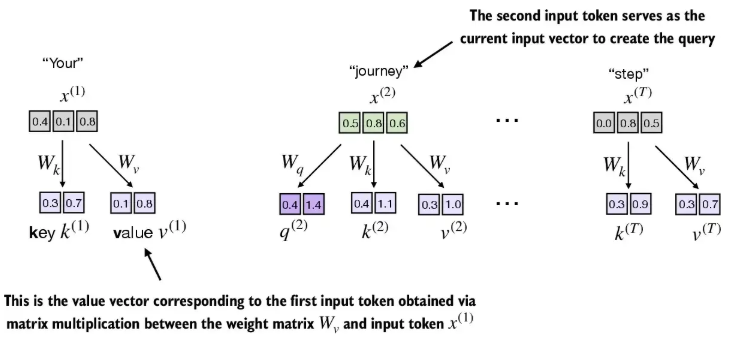
- matrices는 를 Query vector(), Key vector(), Value vector()에 투영하기 위해 사용된다.
- 와 의 차원은 같을 수도, 다를 수도 있다.
- matrices를 초기화 할 때는
requires_grad를 False로 두고, 훈련 동안은 True로 둔다.
W_query = torch.nn.Parameter(torch.rand(d_in, d_out), requires_grad=False)
W_key = torch.nn.Parameter(torch.rand(d_in, d_out), requires_grad=False)
W_value = torch.nn.Parameter(torch.rand(d_in, d_out), requires_grad=False)
keys = inputs @ W_key # 3D input 토큰을 2D 임베딩 공간에 투영
values = inputs @ W_value
attn_scores_2 = query_2 @ keys.T # All attention scores for given query- 앞선 구현과는 달리, 임베딩 차원의 제곱근으로 나누어서 스케일링한 후, context vector를 계산한다.
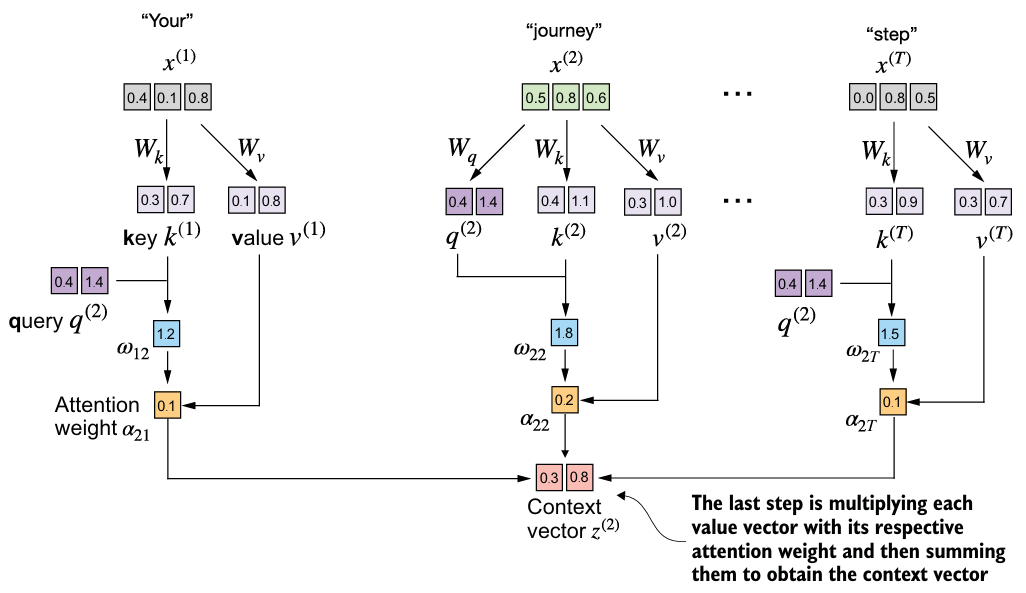
d_k = keys.shape[1] # 일단 x(2)에 대해서만 계산
attn_weights_2 = torch.softmax(attn_scores_2 / d_k**0.5, dim=-1)
context_vec_2 = attn_weights_2 @ valuesself-attention mechanism을 class로 구현하자.
nn.Linear에 bias를 사용하지 않으면 행렬 곱셈과 동일하며, weight 초기화 스키마로 인해nn.Parameter보다 안정적인 모델 훈련이 가능하다.
class SelfAttention_v2(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_in, d_out, qkv_bias=False):
super().__init__()
self.W_query = nn.Linear(d_in, d_out, bias=qkv_bias)
self.W_key = nn.Linear(d_in, d_out, bias=qkv_bias)
self.W_value = nn.Linear(d_in, d_out, bias=qkv_bias)
def forward(self, x):
keys = self.W_key(x)
queries = self.W_query(x)
values = self.W_value(x)
attn_scores = queries @ keys.T
attn_weights = torch.softmax(attn_scores / keys.shape[-1]**0.5, dim=-1)
context_vec = attn_weights @ values
return context_vec
torch.manual_seed(789)
sa_v2 = SelfAttention_v2(d_in, d_out)
print(sa_v2(inputs))5. causal attnetion으로 미래 단어 숨기기
causal attention은 대각선 위의 attention weights가 마스킹되어, 주어진 입력에 대해 LLM이 context vector를 계산하는 동안 future tokens을 활용할 수 없도록 보장한다.
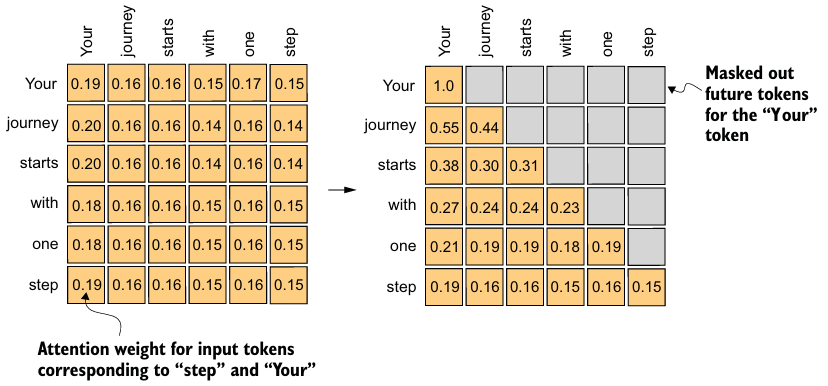
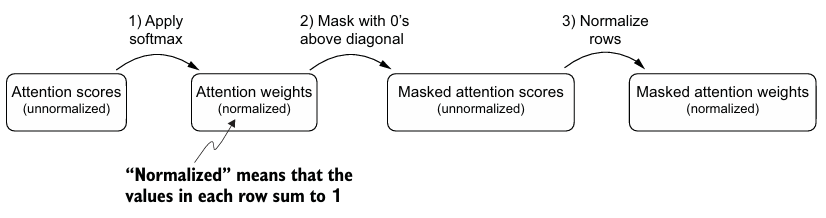
torch.tril함수를 통해 위 masked matrix를 만들 수 있다. 하지만 softmax 이후 mask가 적용되면 확률분포에 문제가 생길 수 있으므로, 행의 합이 1이 되도록 정규화를 해야한다.- 이러한 방식 대신, 대각선 위의 attention scores를 소프트맥스 함수에 들어가기 전에 음의 무한대로 masking하는 방법이 더 효율적이다.
mask = torch.triu(torch.ones(context_length, context_length), diagonal=1)
masked = attn_scores.masked_fill(mask.bool(), -torch.inf)
attn_weights = torch.softmax(masked / keys.shape[-1]**0.5, dim=-1)오버피팅을 줄이기 위해 훈련 동안 드롭아웃을 추가적으로 적용해보자.
- 드롭아웃은 attention weights와 value vectors를 곱한 후에도 적용될 수 있지만, attention weights를 계산한 후에 적용하는 것이 일반적이다.
- 드롭아웃 비율은 attention weights의 몇 퍼센트를 무작위로 마스킹하는지를 의미한다.
- e.g. %의 드롭아웃을 적용하면 non-dropped 값은 의 비율로 조정된다.
dropout = torch.nn.Dropout(0.5) # dropout rate of 50%
print(dropout(attn_weights))여러 개의 input과 causal, dropout masks가 적용된 self-attention을 구현해보자.
class CausalAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_in, d_out, context_length,
dropout, qkv_bias=False):
super().__init__()
self.d_out = d_out
self.W_query = nn.Linear(d_in, d_out, bias=qkv_bias)
self.W_key = nn.Linear(d_in, d_out, bias=qkv_bias)
self.W_value = nn.Linear(d_in, d_out, bias=qkv_bias)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout) # New
self.register_buffer('mask', torch.triu(torch.ones(context_length, context_length), diagonal=1)) # New
def forward(self, x):
b, num_tokens, d_in = x.shape # New batch dimension b
keys = self.W_key(x)
queries = self.W_query(x)
values = self.W_value(x)
attn_scores = queries @ keys.transpose(1, 2) # Changed transpose
attn_scores.masked_fill_( # New, _ ops are in-place
self.mask.bool()[:num_tokens, :num_tokens], -torch.inf) # `num_tokens` to account for cases where the number of tokens in the batch is smaller than the supported context_size
attn_weights = torch.softmax(
attn_scores / keys.shape[-1]**0.5, dim=-1
)
attn_weights = self.dropout(attn_weights) # New 드롭아웃
context_vec = attn_weights @ values
return context_vec
torch.manual_seed(123)
context_length = batch.shape[1]
ca = CausalAttention(d_in, d_out, context_length, 0.0)
context_vecs = ca(batch)torch.triu()를 사용하여 미래 시점의 정보가 사용되지 않도록 하고,register_buffer()를 사용하여 학습되지 않는 고정된 텐서로 등록한다.masked_fill_()을 사용하여 미래 시점의 attn_scores을 -∞로 설정한다.
6. single-head attention을 multi-head attention으로 확장하기

위 그림처럼 지금까지 구현한 single-head attention을 쌓아서 아래의 multi-head attention을 얻어보자.
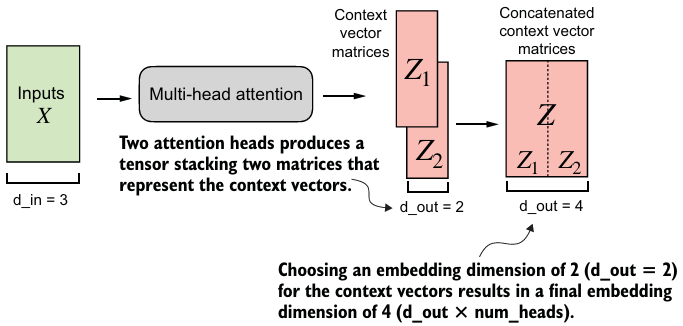
- multi-head attention은 학습된 서로 다른 linear 투영을 사용하여 attention mechanism을 여러 번 병렬로 실행하는 것이다.
- 이를 통해 모델은 different position에 있는 different representation subspaces 정보를 처리할 수 있다.
class MultiHeadAttentionWrapper(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_in, d_out, context_length, dropout, num_heads, qkv_bias=False):
super().__init__()
self.heads = nn.ModuleList(
[CausalAttention(d_in, d_out, context_length, dropout, qkv_bias)
for _ in range(num_heads)]
)
def forward(self, x):
return torch.cat([head(x) for head in self.heads], dim=-1)
torch.manual_seed(123)
context_length = batch.shape[1] # This is the number of tokens
d_in, d_out = 3, 2
mha = MultiHeadAttentionWrapper(
d_in, d_out, context_length, 0.0, num_heads=2
)
context_vecs = mha(batch)- key, query, value vectors 뿐만 아니라 context vector까지 포함하기 때문에 임베딩 차원은 4이고,
CausalAttention이 2개이므로 output 임베딩 차원은 4이다.
CausalAttention을 여러 개 감싸지 않고MultiHeadAttention이라는 독립형 클래스를 작성할 수 있고, 단일 attention heads를 합치지 않고 단일 , , 가중치 행렬을 생성하여 이를 각 attention head에 대한 개별 행렬로 나눌 수 있다.
class MultiHeadAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_in, d_out, context_length, dropout, num_heads, qkv_bias=False):
super().__init__()
assert (d_out % num_heads == 0), \
"d_out must be divisible by num_heads"
self.d_out = d_out
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.head_dim = d_out // num_heads # Reduce the projection dim to match desired output dim
self.W_query = nn.Linear(d_in, d_out, bias=qkv_bias)
self.W_key = nn.Linear(d_in, d_out, bias=qkv_bias)
self.W_value = nn.Linear(d_in, d_out, bias=qkv_bias)
self.out_proj = nn.Linear(d_out, d_out) # Linear layer to combine head outputs
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.register_buffer(
"mask",
torch.triu(torch.ones(context_length, context_length),
diagonal=1)
)
def forward(self, x):
b, num_tokens, d_in = x.shape
keys = self.W_key(x) # Shape: (b, num_tokens, d_out)
queries = self.W_query(x)
values = self.W_value(x)
# We implicitly split the matrix by adding a `num_heads` dimension
# Unroll last dim: (b, num_tokens, d_out) -> (b, num_tokens, num_heads, head_dim)
keys = keys.view(b, num_tokens, self.num_heads, self.head_dim)
values = values.view(b, num_tokens, self.num_heads, self.head_dim)
queries = queries.view(b, num_tokens, self.num_heads, self.head_dim)
# Transpose: (b, num_tokens, num_heads, head_dim) -> (b, num_heads, num_tokens, head_dim)
keys = keys.transpose(1, 2)
queries = queries.transpose(1, 2)
values = values.transpose(1, 2)
# Compute scaled dot-product attention (aka self-attention) with a causal mask
attn_scores = queries @ keys.transpose(2, 3) # Dot product for each head
# Original mask truncated to the number of tokens and converted to boolean
mask_bool = self.mask.bool()[:num_tokens, :num_tokens]
# Use the mask to fill attention scores
attn_scores.masked_fill_(mask_bool, -torch.inf)
attn_weights = torch.softmax(attn_scores / keys.shape[-1]**0.5, dim=-1)
attn_weights = self.dropout(attn_weights)
# Shape: (b, num_tokens, num_heads, head_dim)
context_vec = (attn_weights @ values).transpose(1, 2)
# Combine heads, where self.d_out = self.num_heads * self.head_dim
context_vec = context_vec.contiguous().view(b, num_tokens, self.d_out)
context_vec = self.out_proj(context_vec) # optional projection
return context_vec
torch.manual_seed(123)
batch_size, context_length, d_in = batch.shape
d_out = 2
mha = MultiHeadAttention(d_in, d_out, context_length, 0.0, num_heads=2)
context_vecs = mha(batch).view로 각 matrix를num_heads만큼 쪼개고, context vector를 구할 때 다시.contiguous()를 사용해 메모리 상의 연속성을 보장한 후 결합한다.- LLM의 일반적인 관례로 선형 투영 레이어(
self.out_proj)를 추가했지만, 모델링 성능에 영향을 미치지 않으며 없앨 수 있다는 연구가 등장했다.
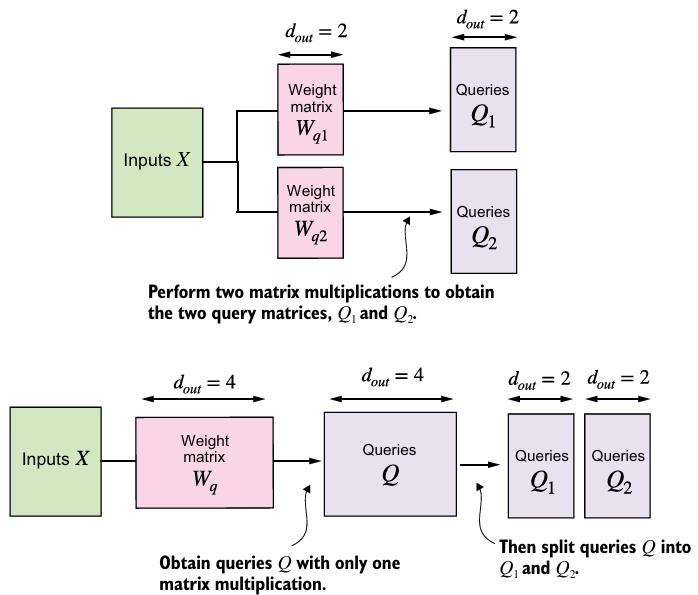
- 위 그림이
MultiHeadAttentionWrapper과MultiHeadAttention의 차이이다.- 위에서는 4차원 입력 텐서를 처리하여 행렬 곱셈이 마지막 두 차원(num_tokens, head_dim) 사이에서 수행된 후 개별 헤드에 대해 반복된다.
- 아래에서는 각 헤드에 대한 행렬 곱셈을 개별적으로 계산한다.
※ 결합된 가중치를 사용하는 alternative multi-head attention
- with combined weights
MultiHeadAttentionCombinedQKV클래스는 단일 가중치 행렬(self.qkv = nn.Linear(d_in, 3 * d_out, bias=qkv_bias))을 사용하며, 이를 통해 query, value, key를 계산한다.q, k, v = qkv.unbind(0)를 통해 각 값을 얻는다.
- with Einsum
torch.einsum을 사용하여 Einstein summation을 구현한다.- linear transformations을 구현하고, bias를 더해준 뒤, multi-head attention을 위해 Reshape 후 스케일링된 dot-product를 해준다.
- with PyTorch's scaled dot product attention and FlashAttention
- PyTorch의
scaled_dot_product_attention와 self-attention의 메모리 최적화된 버전인FlashAttention을 사용한다.- 기존 Attention은 GPU 연산 시, HBM(GPU 고대역폭 메모리)으로의 접근이 너무 많아 IO communication(Access time)이 bottle-neck되는 문제가 존재한다.
- titling과 recomputation 방법을 통해 S와 P를 HBM에 저장하지 않고 계산할 수 있게 된다.
- 이를 통해 Load / Write process를 줄이고 GPU의 SRAM에서 한번에 computation을 진행하는 방식으로 성능을 향상시켰다.
context_vec = nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention( queries, keys, values, attn_mask=None, dropout_p=use_dropout, is_causal=True)를 통해 context vector를 얻는다.
- PyTorch의
- with PyTorch's scaled dot product attention and without FlashAttention
- 명시적인 causal mask를 passing 함으로써, FlashAttention을 사용하지 않는다.
if self.context_length >= num_tokens: attn_mask = self.mask[:num_tokens, :num_tokens] else: attn_mask = self.mask[:self.context_length, :self.context_length]
- with PyTorch's torch.nn.MultiheadAttention
torch.nn.MultiheadAttention을 사용한다.self.multihead_attn = nn.MultiheadAttention(embed_dim=d_out, num_heads=num_heads, dropout=dropout, bias=qkv_bias, add_bias_kv=qkv_bias, batch_first=True,)
- with PyTorch's torch.nn.MultiheadAttention & scaled_dot_product_attention
MHAPyTorchClass인스턴스를 생성할 때 매개변수need_weights를 False로 두면,scaled_dot_product_attention를 사용한다.
- with PyTorch's FlexAttention
- 기존의 FlashAttention을 개선하여 메모리 효율성과 연산 속도를 극대화한 Attention mechanism이다.
- 다양한 Attention variants를 구현하는 유연한 API를 제공한다.
- 추가 메모리를 구현하지 않고 성능을 갖춘 FlashAttention Kernal을 만든다.
- PyTorch’s autograd를 이용하여 자동으로 역전파를 제공한다.
- attention mask의 sparsity를 활용하여 표준보다 더 나은 성능을 제공한다.
- 사용자 정의 함수
score_mod을 통한 attention score 수정이 가능하다.
context_vec = torch.nn.flex_attention(queries, keys, values, block_mask=attn_mask)
- 기존의 FlashAttention을 개선하여 메모리 효율성과 연산 속도를 극대화한 Attention mechanism이다.
※ PyTorch 버퍼의 이해
- PyTorch Buffer는 파라미터와 유사한 텐서 속성이지만 훈련 동안 업데이트되지 않는다.
- 매개변수와 함께 CPU, GPU 간 전송이 되어야 하기 때문에 GPU 계산 시 유용하다.
self.register_buffer를 통해 사용한다.- 사용하지 않으면,
masktensor가 GPU를 사용하더라도 PyTorch parameter가 아니므로 CPU에서 존재하기 때문에 오류가 발생한다.
self.mask = torch.triu(torch.ones(context_length, context_length), diagonal=1)
self.register_buffer("mask", torch.triu(torch.ones(context_length, context_length), diagonal=1))