Heap은 다음의 두 조건을 충족시키는 Binary Search Tree이다.
- 모양 : Complete Tree - 오른쪽은 비어도 괜찮은 트리
- 순서 : 모든 노드에 대하여 자식보다 우선순위가 높아야 한다.
- 따라서 Heap에서 가장 큰 값은 ROOT에 저장된 값이다.
- Heap은 array로 쉽게 구현될 수 있다.
CF ) array의 단점
1. 몇 개 들어갈 지 모른다.
2. 비어있는 값을 비워두긴 해야한다. 위치 계산을 위해. (근데 heap은 complete tree라서 상관없다)
Implementation
template<class ItemType>
struct HeapType
{
void ReHeapDown(int root, int bottom);
void ReheapUp(int root, int bottom);
ItemType* elements; // array to be allocated dynamically
int numElements; // 실제로 몇 개 쓰고 있는지
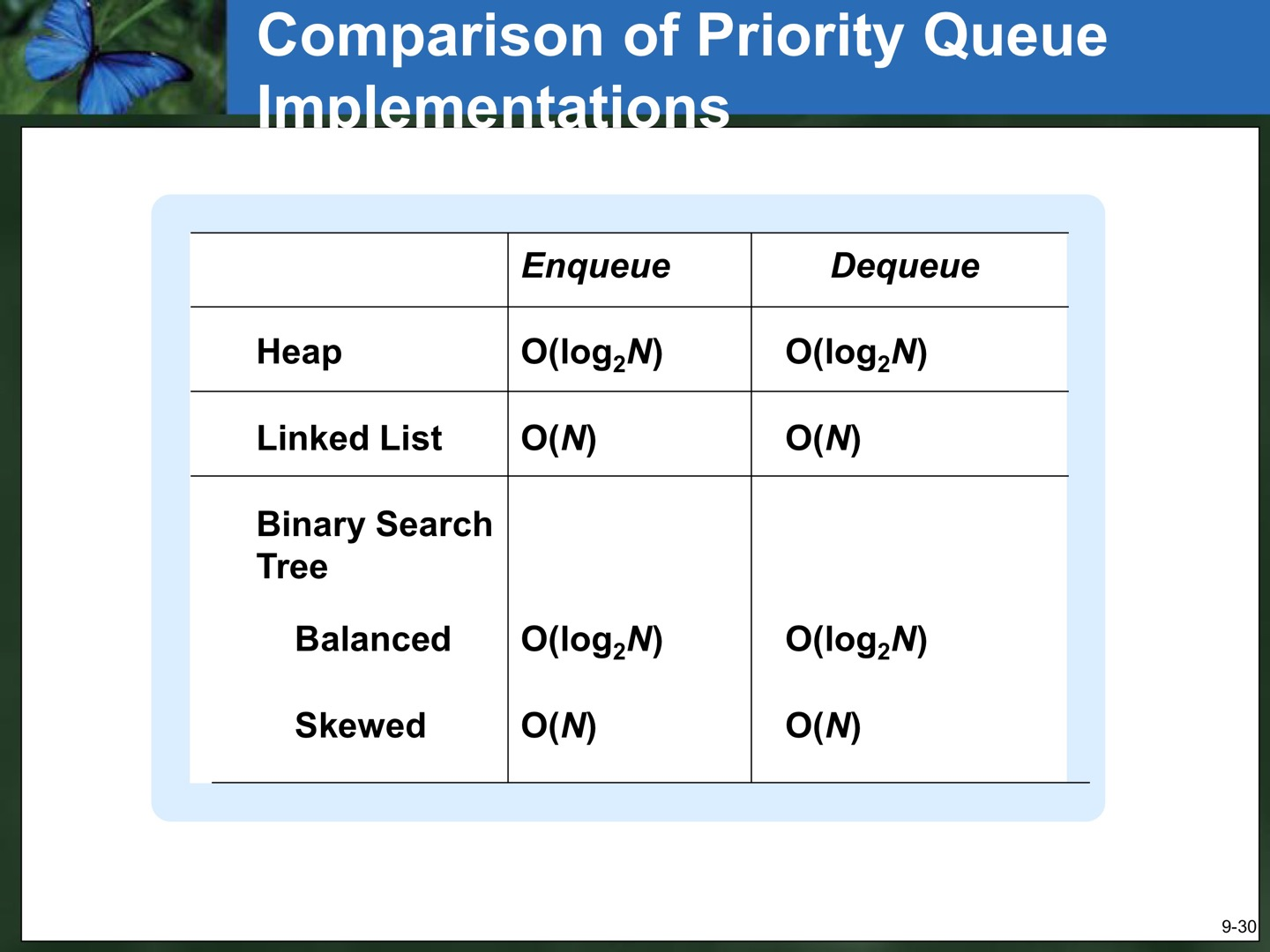
};- ReheapDown : root 때문에 heap이 아니라면, 위에 있는 애를 적당한 위치의 밑으로 내려보내자!
template<class ItemType>
void HeapType<ItemType>::ReheapDown(int root, int bottom)
// parameter
// root = 인덱스 번호
// bottom = 내려갈 번호 -> rightmost node in the last level
{
int maxChild;
int rightChild;
int leftChild;
leftChild = root*2 +1;
rightChild = root*2 +2;
// 1. leftChild가 있는가?
// 1-1. 있으면
if ( leftChild <= bottom )
{
// 2. child끼리 비교한다. 왼쪽과 오른쪽 중에서 어느게 더 큰지 찾는다.
// 2-1. 왼쪽만 있는 경우 = only one child. complete tree이므로 이 case만 고려
if ( leftChild == bottom ) /
maxChild = leftChild;
// 2-2. 2개의 child를 갖는 경우
else
{
// 3-1. 오른쪽이 더 큰 경우
if ( elements[leftChild] <= elements[rightChild] )
maxChild = rightChild;
// 3-2. 왼쪽이 더 큰 경우
else
maxChild = leftChild;
}
// 4. max를 찾았다. 이제 max보다 현재보다 작으면 바꾼다.
if ( elements[root] < elements[maxChild] )
{
Swap (elements[root], elements[maxChild]);
ReheapDown(maxChild, bottom); // maxChild를 root로 넣는다.
}
}
// 1-2. leftChild가 없으면 Do Nothing
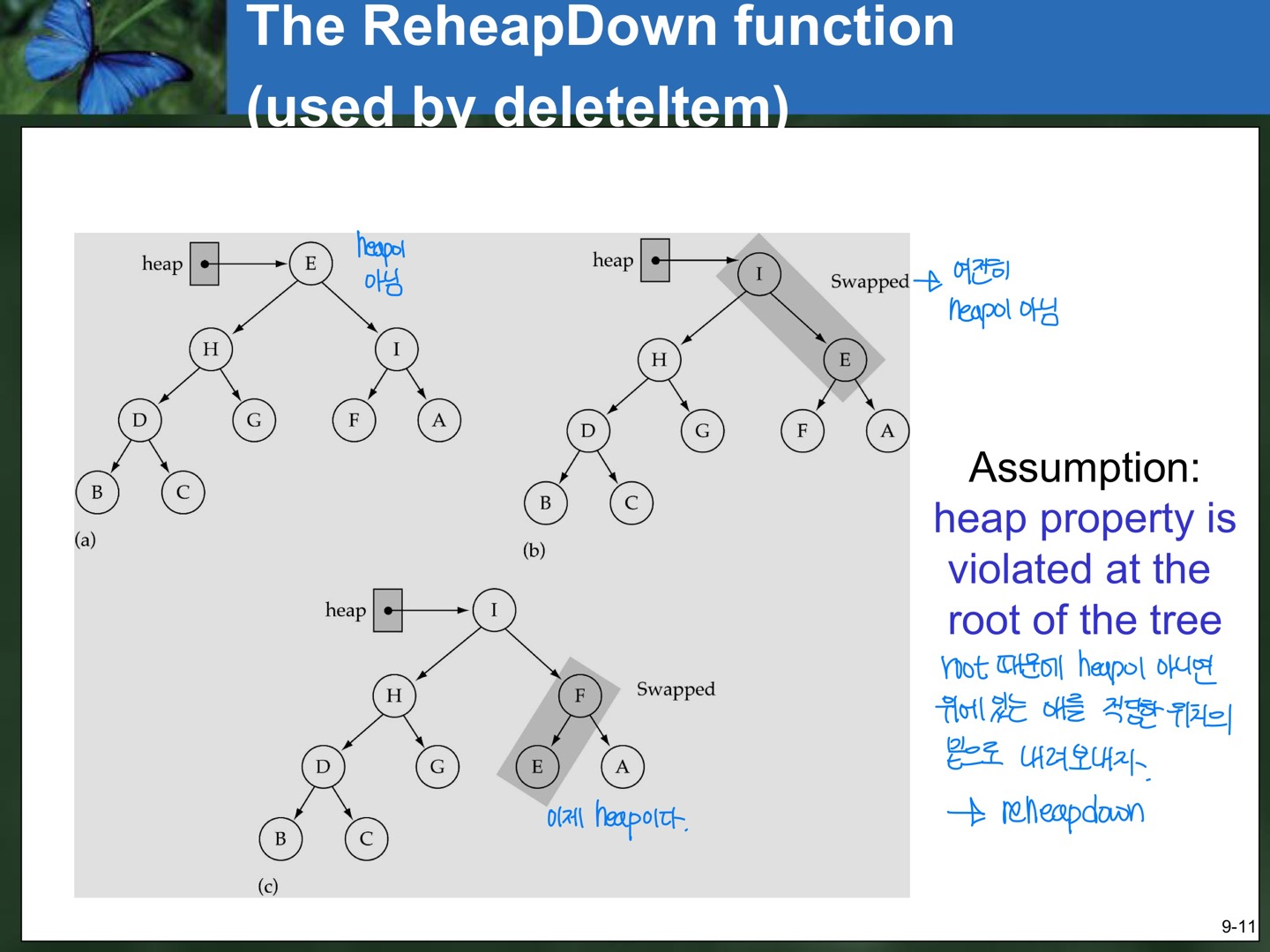
}- ReheapUp : 맨 아래 오른쪽 leaf 때문에 heap이 되지 않는 경우 적당히 위로 올려보낸다.
template<class ItemType>
void HeapType<ItemType>::ReheapUp(int root, int bottom)
// parameter : root는 고정, bottom 값은 바뀐다(올라감).
{
int parent;
// general case
if ( bottom > root ) // tree가 비어있지 않은 경우
{
parent = ( bottom - 1 ) / 2;
// 부모보다 현재 값이 크면 위로 올린다.
if ( elements[parent] < elements[bottom] )
{
Swap( elements[parent], elements[bottom] );
ReheapUp(root, parent); // bottom parameter에 parent 값을 넣는다.
}
}
// base case: bottom<=root인 경우. 계속 줄다가 root까지 올라간 경우.
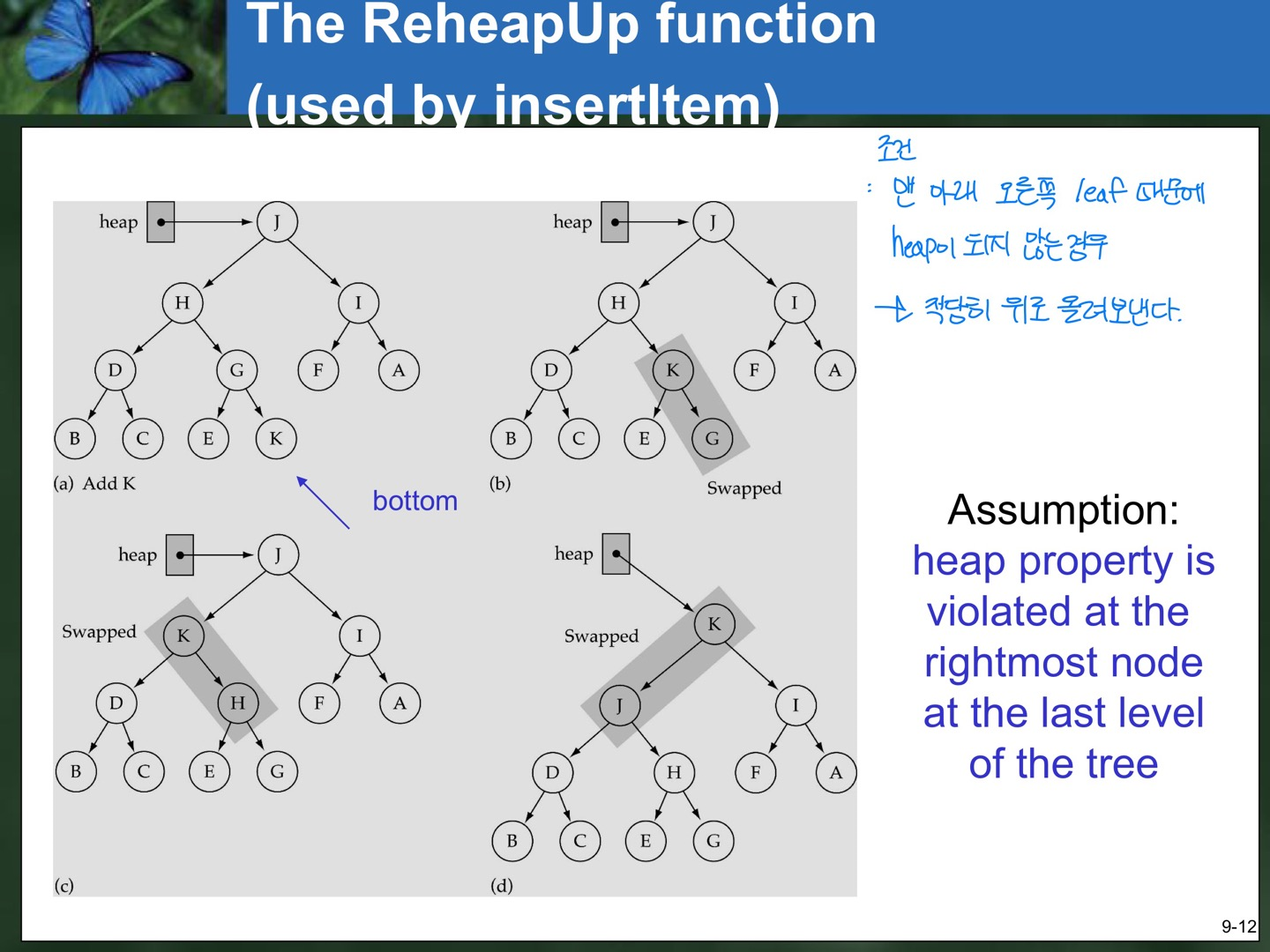
}Removing the largest element from the heap
< ROOT를 지우는 방법 >
- 1) 가장 오른쪽 밑에 있는 값을 root로 올려버린다.
- 2) 가장 오른쪽 밑에 있는 값을 지운다.
- 3) Root 때문에 Heap이 아니므로 ReheapDown으로 다시 Heap을 만든다.
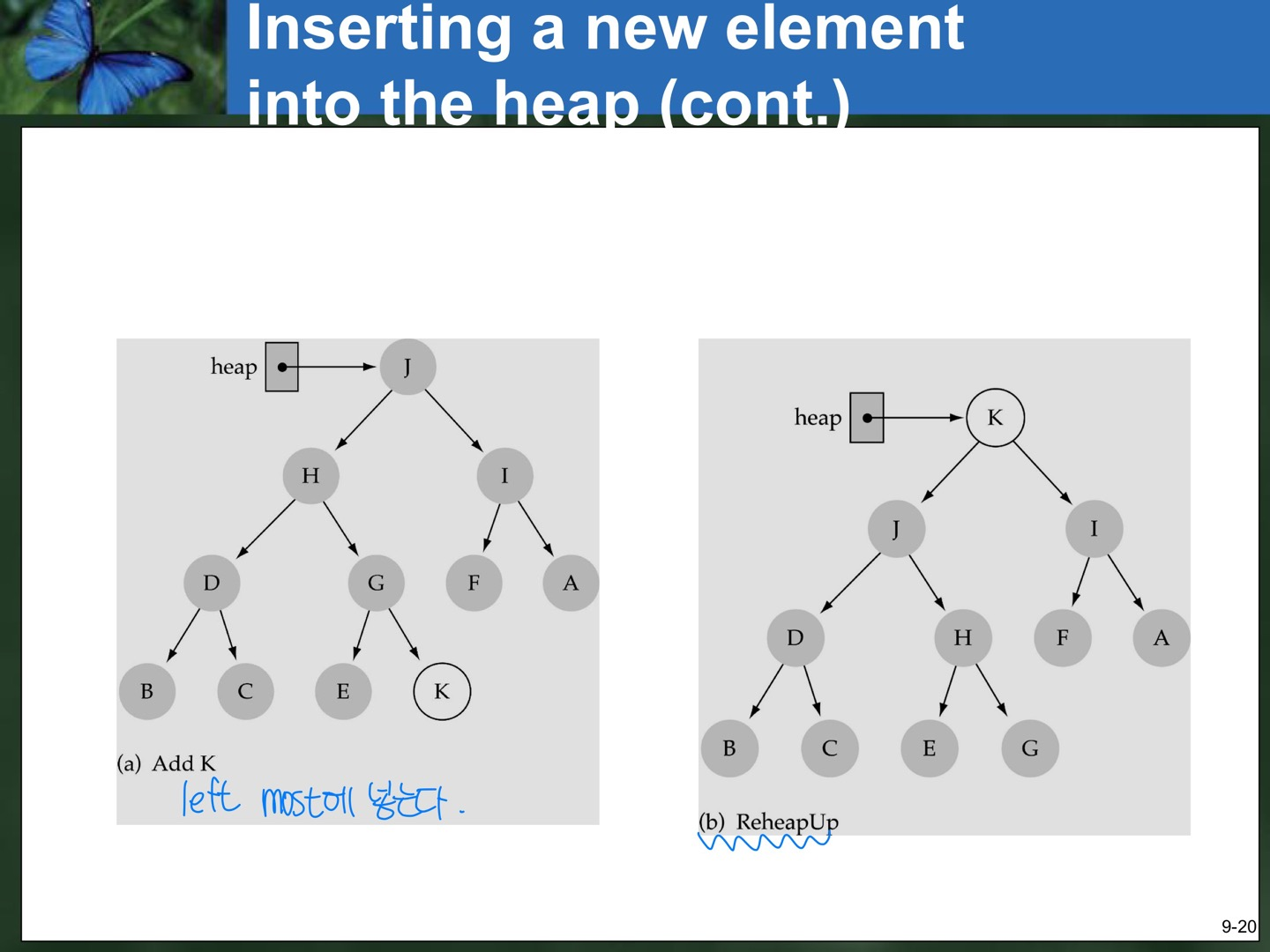
Inserting a new element into the heap
- 새 값을 가장 왼쪽 밑에 넣는다.
- 가장 끝 값 때문에 heap이 아니므로 ReHeapUp으로 다시 Heap을 만든다.
Priority Queue
📘 Implementation 방식 별 Time Complexity📘
- Unsorted List : Enqueue는 O(1), Dequeue는 O(N)
- Array-Based Sorted List : Enqueue가 O(N), Dequeue도 O(N)
- Linked Sorted List : Enqueue가 O(N), Dequeue도 O(N)
- Binary Search Tree : Enqueue와 Dequeue모두 평균적으로 O(logN)이지만 worst case(BST가 linked list 형태처럼 되는 경우)의 경우는 O(N)이 된다.
- Heap : worst case에도 O(logN) 보장
Declaration
class FullPQ() {};
class EmptyPQ() {};
template<class ItemType>
class PQType
{
public:
PQType(int);
~PQType();
void MakeEmpty();
bool IsEmpty() const;
bool IsFull() const;
void Enqueue(ItemType newItem);
void Dequeue(ItemType& item);
private:
int length;
HeapType<ItemType> items;
int maxItems;
};Constructor, Deconstructor, MakeEmpty
template<class ItemType>
PQType<ItemType>::PQType(int max)
{
maxItems=max;
items.elements=new ItemType[max];
length=0;
}
template<class ItemType>
void PQType<ItemType>::MakeEmpty()
{
length=0;
}
template<class ItemType>
PQType<ItemType>::~PQType()
{
delete [] items.elements;
}Dequeue
📘 Dequeue ConCept 📘
- Set item to root element from queue
- Move last leaf element into root position : leaf를 맨 위로 올린다.
- Decrement Length : 올린 애를 없애서 root를 지워버린다.
- itmes.ReheapDown(0,length-1); -ReheapDown으로 다시 heap을 만든다.
template<class ItemType>
void PQType<ItemType>::Dequeue(ItemType& item)
{
if(length==0)
throw EmptyPQ();
else
{
item=items.elements[0];
items.elements[0]=itmes.elements[length-1];
length--;
itmes.ReheapDown(0,length-1);
}
}Enqueue
📘 Enqueue ConCept 📘
- Increment length - 길이를 증가시키고
- Put newItem in next available position - 뒤에 새 값 넣고
- items.ReheapUp(0,length-1) - 맨 뒤때문에 heap이 아니니까 제 위치 찾아서 heap 되도록 한다.
template<class ItemType>
void PQType<ItemType>::Enqueue(ItemType newItem)
{
if (length==maxItems)
throw FullPQ();
else
{
length++;
itmes.elements[length-1]=newItem;
itmes.ReHeapUp(0,length-1);
}
}