1. 자료형
Boolean
- 값이 있으면 참이고 , 값이 없거나 0이면 다 거짓이다
- 문자열 / 리스트 / 숫자 등 무엇이든 있다면 참
- none / 0 / “” 등과 같이 아무것도 없는 데이터라면 false
연산자
산술연산자

- / , // , %의 차이를 인지해야할 필요
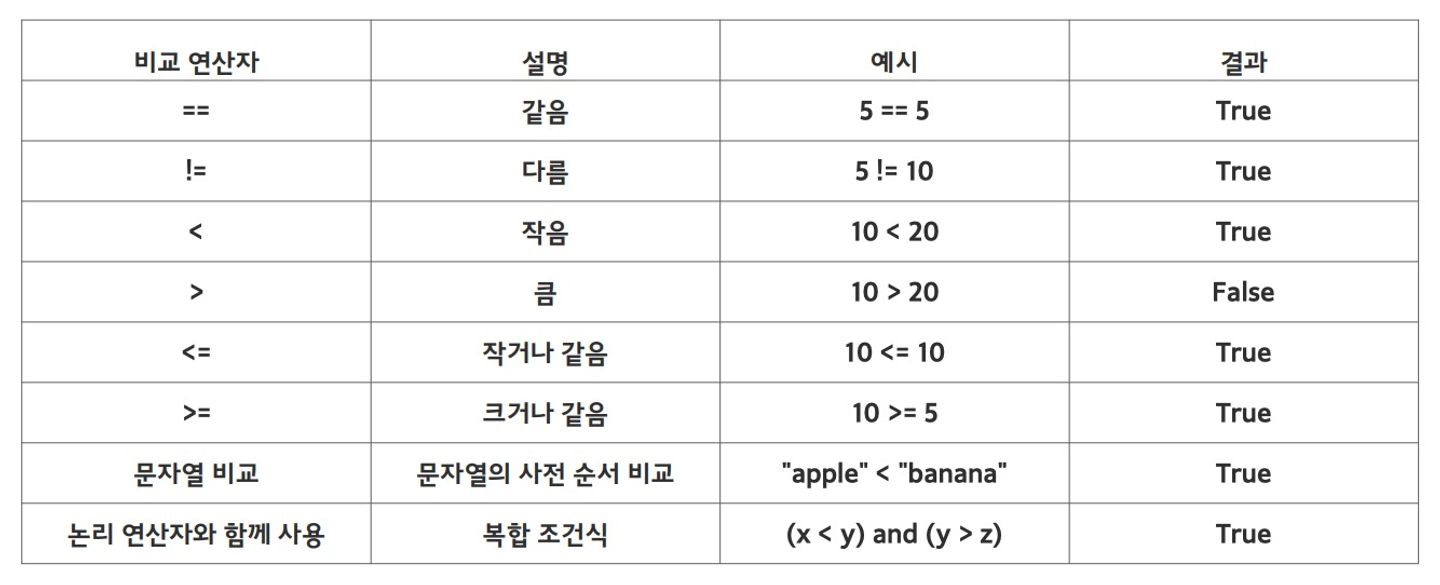
비교연산자
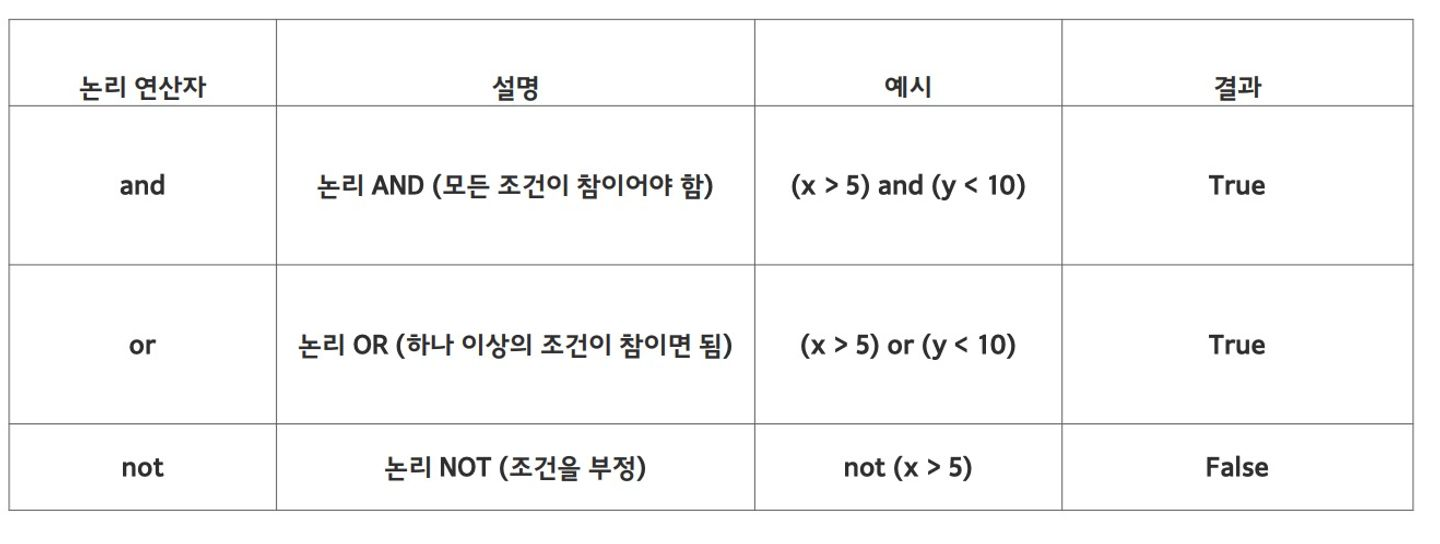
논리연산자
과제로 수행

payment = int(input(" 금액을 입력해주세요: "))
price = int(input(" 상품 가격은 얼마입니까? : "))
jan_don = payment - price
print(f'{payment}을 지불했습니다')
print(f'상품 가격은{price}이기 때문에')
print('거스름 돈은 500원', int(jan_don//500),'개')
print('100원', int((jan_don%500)//100),'개')
print('50원', int(((jan_don%500)//100)//50),'개')
print('10원', int((((jan_don%500)//100)//50)//10),'개')f 스트링?
- 입력 문자열을 간편하게 할 수 있는 기능
name = '김성회'
print(f'나의 이름은 {name}입니다')2. 조건문
조건문?
- 프로그래밍에서 사용되는 제어구조
- 프로그램 실행 흐름을 결정
- 조건문은 주어진 조건이 참 / 거짓인지에 따라 코드 블록을 실행
예시
- 비가 오는 날 우산을 가져간다
IF문
- 들여쓰기를 이용해 문장의 종속관계를 표현
- back - end에서 많이 활용됨
- 비교연산자와 함께 활용
money = 2000
if money >= 3000;
print("택시를 타고 가라")
else;
print("걸어가라") -> 걸어가라if / elif / else를 통해 활용
pocket = ['paper', 'cellphone', 'money']
if 'money' in pocket:
pass
else:
print('카드를꺼내라')리스트 안에서 if문을 돌릴 수 있음
pocket = ['paper','cellphone']
card = 1
if money in pocket:
print("택시 타고 가라")
elif card:
print("택시를 타고 가라")
else:
print("걸어가라")- 정수 값을 받아 True를 활용할 수 있음
실습 예제
height = int(input("키를 입력해주세요"))*0.01
weight = int(input("몸무게를 입력해주세요"))
bmi = weight / (height**2)
if bmi < 18.5:
print("저체중")
elif 22.9 > bmi >= 18.5:
print("정상")
elif 24.9 > bmi >= 22.9:
print("과체중")
elif 29.9 > bmi >= 25:
print("경도비만")
else:
print("고도비만")
#앞에 작성한 내용이 있다면 안작성해도 됨
# bmi <18.5 -> bmi < 22.9- 파이썬에선 선행된 문장에 포함이 안되면 다음도 그냥 기술하면 됨
반복문?
- Loop은 동일한 작업을 반복해서 수행해야 할 때 사용
- 일정 횟수만큼 코드를 반복실행 / 주어진 조건이 참인 동안 반복 실행
while 반복문
#나무를 열 번 찍고, 열번 찍으면 나무가 넘어간다
treeHit = 0
while treeHit < 10:
treeHit = treeHit + 1
print(f'나무를 {treeHit}번 찍었습니다')
if treeHit == 10:
print('나무 넘어갔습니다')- while과 if를 중첩해서 적용시킬 수 있음
- 많이 활용되는 문장이므로 주목
coffee = 10
money = 500
while money:
print('돈 받았습니다')
coffee = coffee - 1
print(f'남은 커피 양은 {coffee}개 입니다')
if not coffee:
break- while과 함께 사용되는 함수, break
- break: 반복문 자체를 종료
- continue: 현재 반복을 중지하고, 다음 반복
for 반복문
- n이 변수 / range는 범위 설정

- for문은 리스트 에서 사용할 수도 있음

- 튜플에서 언패킹을 통해 합을 구해볼 수도 있다
for i in range(0,10, 2): #단위도 가능함
print(i) -> 0,2,4,6,8- 범위 뿐만 아니라 단위 추가도 가능
score_list = [90, 25, 67, 56 , 80]
cutLine = 60
passCount = 0
for score in score_list:
if score > cutLine:
passCount += 1
# 직관성을 위해 i 변수 대신 score로 사용할 수도 있음
# i = i + 1 는 줄여서 i +=1
print(passCount)- 직관성을 위해 i 변수 대신 score로 사용할 수도 있음
- i = i + 1 는 줄여서 i +=1로 사용함.
# 60점 이상인 경우에 축하메세지를 보낸다
#for / continue 사용
scoreList = [90 , 25, 67, 45, 80]
cutLine = 60
for score in scoreList:
if score <= cutLine:
continue
print(f'{score}점 축하드립니다') -> 90 / 67 / 80- for문과 if문, 그리고 continue를 활용해도 가능하다
for문을 통한 list 제작
# 1-10리스트를 만들고 싶다
[num for num in range(1,11)]- 1부터 10 까지의 리스트를 만드는 방법
[num for num in range(1,11) if num%2 ==0]- 1~10 중 2로 나누어 떨어질 때만 num을 저장해줘
- for문을 각각 만드는 것보다 효율적이라는 것이 특징
result_list = []
for num in range(1,11):
if num % 2 == 0:
result_list.append(num)
result_list- 위 문장을 만들지 못하더라도 이 문장은 할 수 있어야 함
- append()함수를 통한 리스트 밸류 추가
#For 반복문을 중첩하여, 아래와 같이 * 기호를 피라미드로 출력하는 프로그램 제작
for i in range(5):
for j in range(5):
if i>=j:
print('*',end='')
print('')- for문을
- , end=’’ 을 통해 줄바꿈 프린트를 붙일 수 있음
- print(’’)는 뭐지?
for문과 If문을 이용하여, 정수를 입력 받아 정수의 약수를 구하는 프로그램 제작
num = int(input('값을 입력하세요'))
result = []
for i in range(1, num+1):
if num % i == 0:
result.append(i)
print(result)- 1과 num 자체가 약수가 된다라는 아이디어에서 시작
3. 파일 입출력
#파일 생성하기
f = open('text_file.txt', 'w') #mode = [r,w,a] read/write/add
f.close()- ‘r’: read. 파일 읽기만 할 때
- ‘w’:write 파일 새로운 내용 쓸 때
- ‘a’: add 새로운 내용 추가
#파일 생성 후 값 작성하기
f = open('text_file2.txt','w')
for i in range (1,11):
f.write(f'{i}번쨰 줄입니다.\n')
f.close()- open()함수를 통해 파일 열기
- , ‘n’을 통해 3가지 모드 선택
- close()으로 다시 종료
#파일 열어서 값 추가하기
f = open('text_file2.txt','a')
for i in range (11,20):
f.write(f'{i}번쨰 줄입니다.\n')
f.close()- open(’a’)를 통해 내용 추가
#한줄출력 + 반복문
f = open('text_file2.txt','r')
while True:
line = f.readline()
if not line:
break
print(line, end='')
f.close()- readline(): 한줄 출력
- 왜 True여야 하지?
- 왜 알아서 추가가 되는 거지?
with문으로 열기
with = open('text_file2.txt',)