KOSMOS-2.5: A Multimodal Literate Model
Tengchao Lv∗, Yupan Huang∗, Jingye Chen∗, Lei Cui∗ †, Shuming Ma, Yaoyao Chang, Shaohan Huang, Wenhui Wang, Li Dong, Weiyao Luo, Shaoxiang Wu, Guoxin Wang, Cha Zhang, Furu Wei†
Microsoft
23.09
implementation: git
Abstract
KOSMOS-2.5 제안:
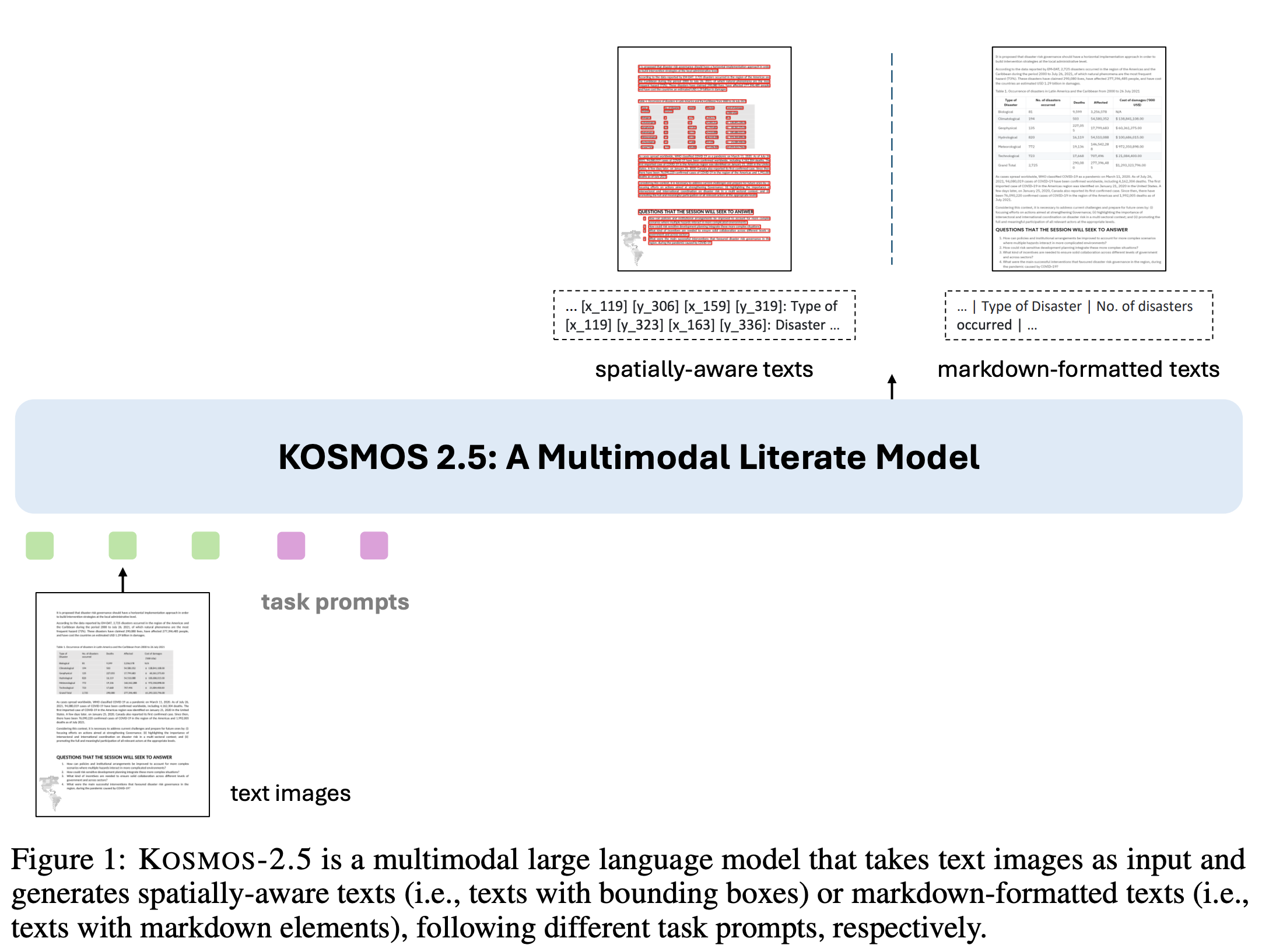
a multimodal literate model for machine reading of text-intensive images
- 2 distict cooperative transcription tasks 수행
- generating spatially aware text blocks:
이미지 내 text block의 spatial coordinate 위치 생성 - producing structured text output:
text style과 structures를 markdown 형태로 생성
- generating spatially aware text blocks:
- 다음 세 가지로 위 2 tasks가 가능하도록 함
- shared Transformer architecture
- task-specific prompts
- flexible text representations
- (1) end-to-end document level text recognition과 (2) image-to-markdown text generation으로 평가함.
- 더 나아가 supervised fine-tuning을 통해 text-intensive image understanding task로 확장 가능
Introduction
background
- LLM이 발전해왔으나 현재의 LLM은 textual information에 주로 집중하고 있으며, visual information은 이해하지 못함.
- Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) field에서는 이 한계를 극복하고자 해,
visual과 textual information을 single Transformer로 결합해 모델이 두 modality를 배울 수 있도록 함. - 존재하는 MLLM들은 lower resolution의 natural images에만 초점을 맞추고 있어, text images들로의 연구가 필요함.
- training 과정에서 text images들을 사용하고, model을 textual & visual information 기반으로 develop 시킴으로서, high-resolution text-intensive-images 관련 multimodal applications로의 가능성을 열음.
suggestion
- present
KOSMOS-2.5
a multimodal literate model
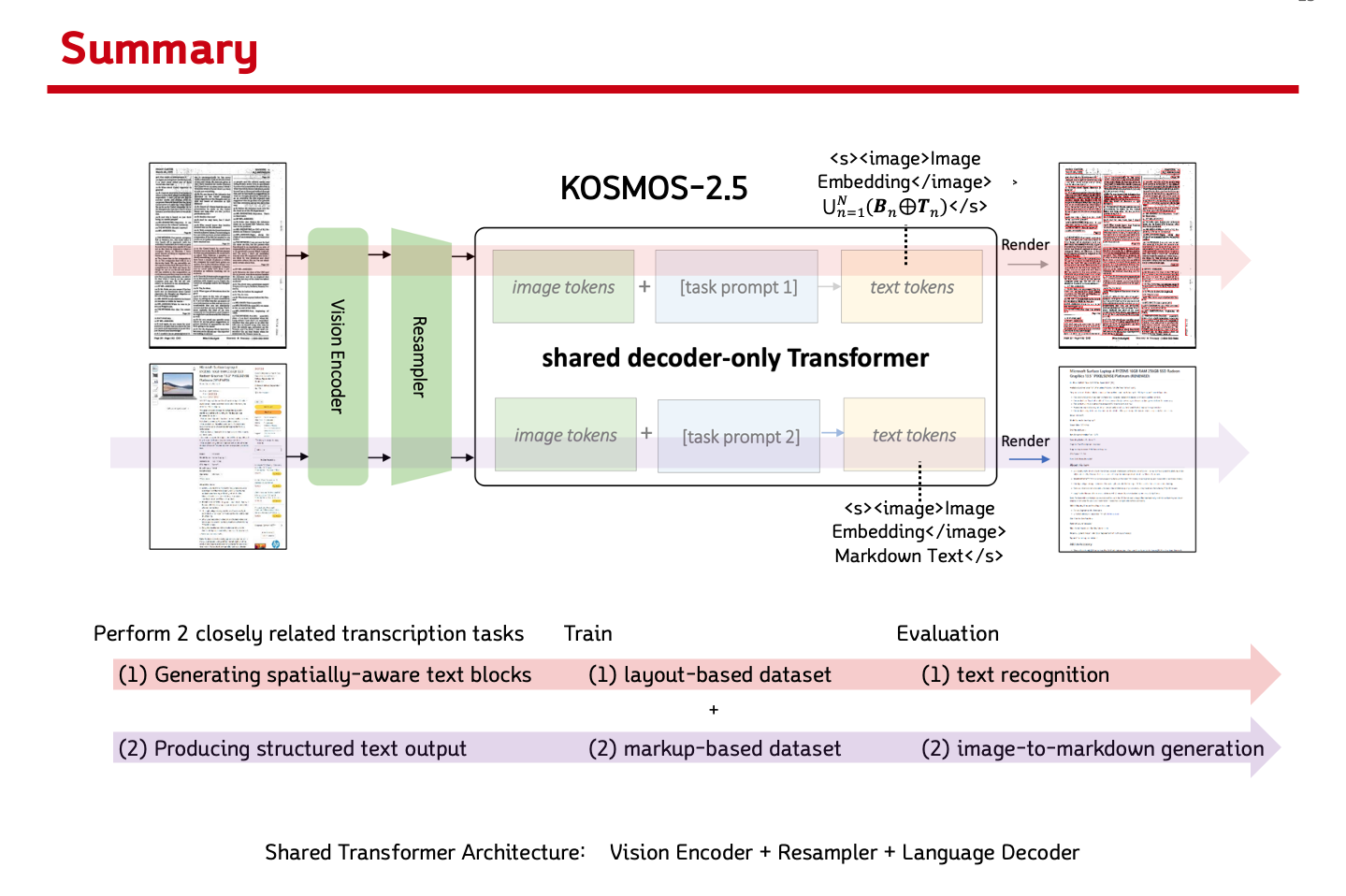
KOSMOS2의 장점에 text-intensive images의 이해를 도울 수 있도록 설계 2 closely related transcription tasks수행- spatially-aware text blocks 생성:
assigning text lines their corresponding spatial coordinates within the original text-rich image. - structured text output 생성:
capturing styles and structures in the markdown format.
- spatially-aware text blocks 생성:
a unified framework:
leveraging a shared Transformer architecture, task-specific prompts, and flexible text representations.architecture:
(1) ViT-based vision encoder +
(2) resampler module +
(3) Transformer-based language decoderpretraining:
text lines의 bounding boxes, plain markdown text들 포함한, large corpus of text-intensive imagesevaluation:
(1) end-to-end document-level text recognition
(2) markdown-formatted image-to-text generation- few-shot and zero-shot 시나리오에서도 성능이 좋아 text-rich images 포함한 real-world application 가능성 제시
Contributions
- KOSMOS-2.5는 text image understanding에 있어 encoder-only/encoder-decoder 모델에서 decoder-only 모델로 전환되는 중대한 paradigm shift를 제시한다. dual transcription tasks를 통합해 냐single unified model을 pretraining 한다.
- generative multimodel language modeling을 통합해, 다양한 downstream tasks들의 적용도 간소화함.
- multimodal literate 능력을 증명해 미래로의 가능성 제시.
Methods
architecture
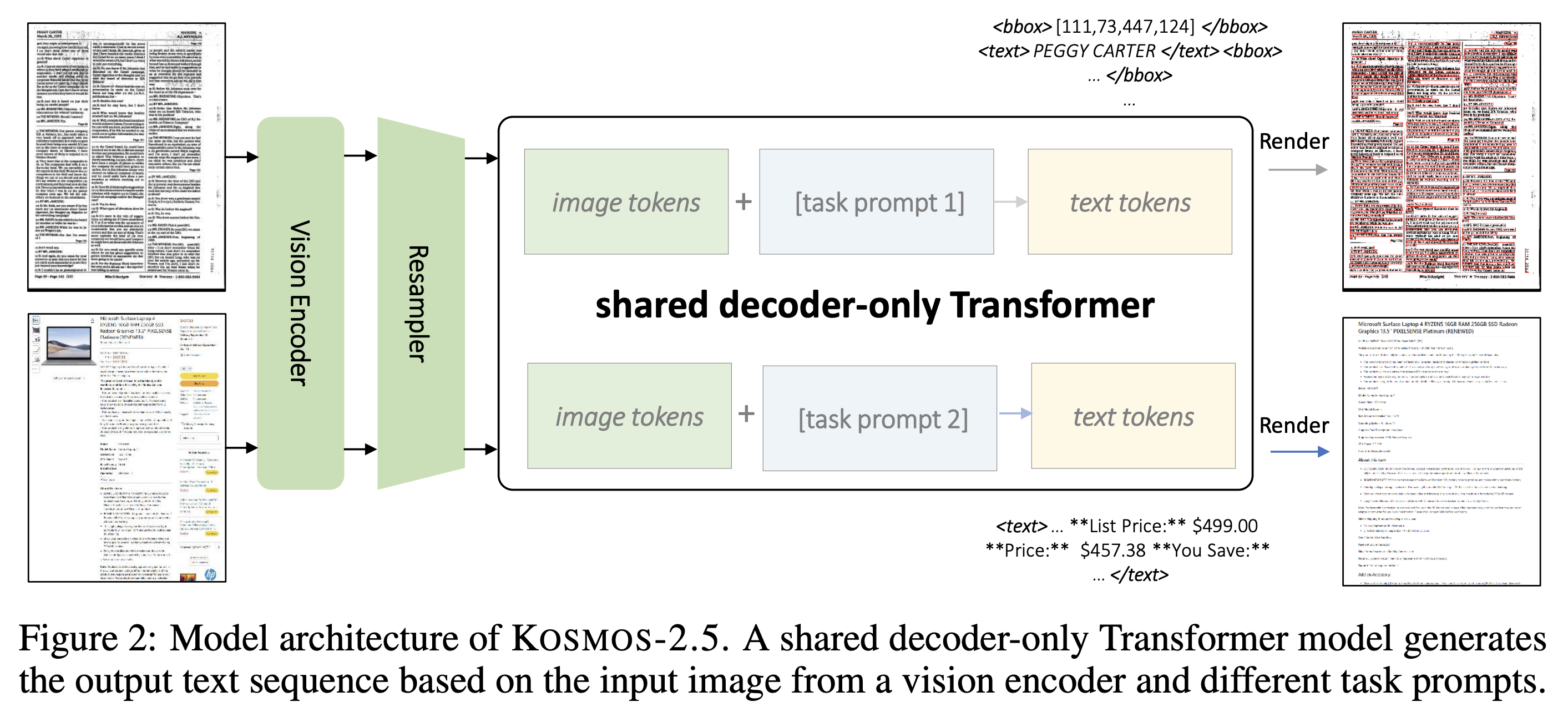
-
KOSMOS-2.5 = Vision Encoder + Resampler + Language Decoder -
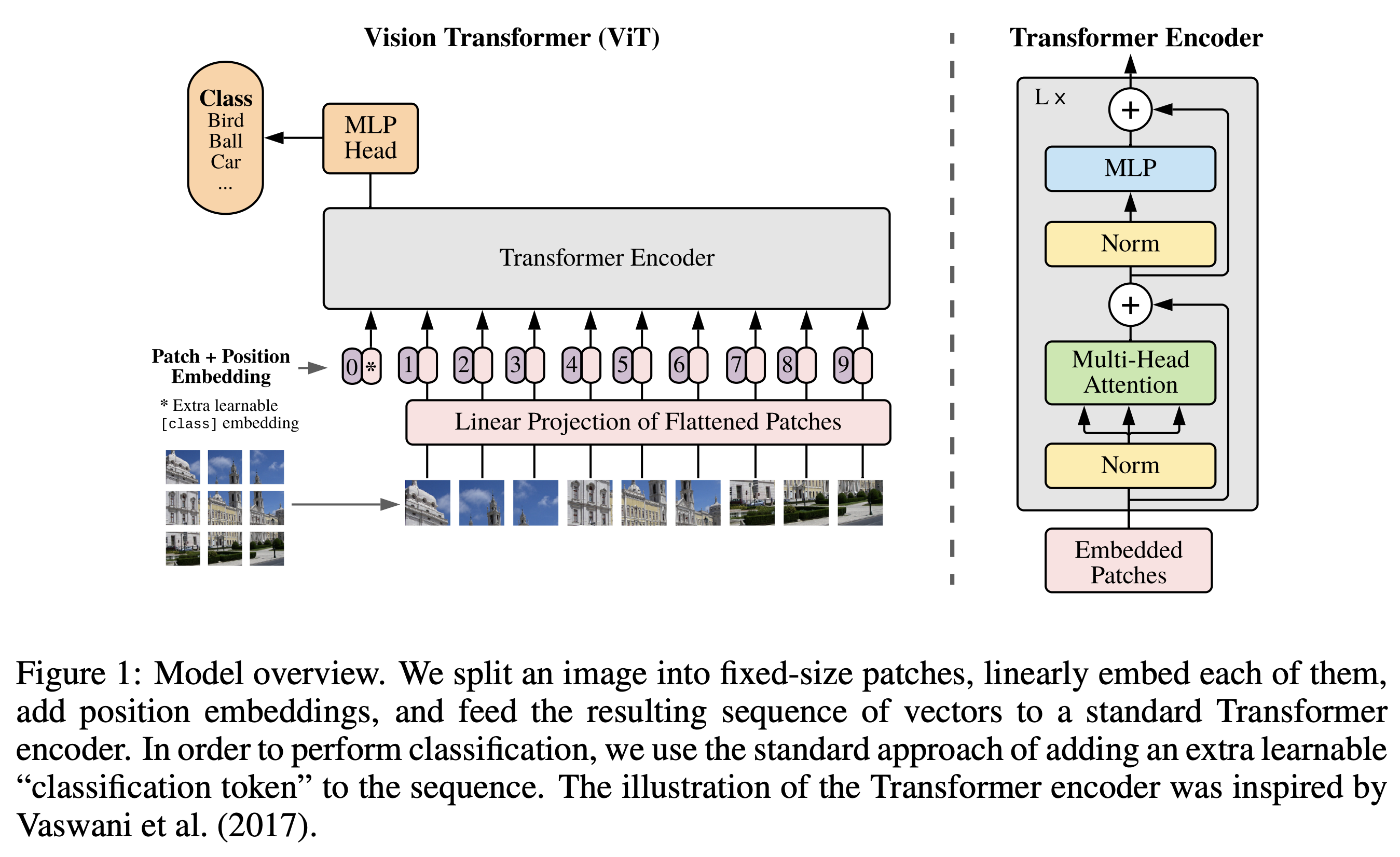
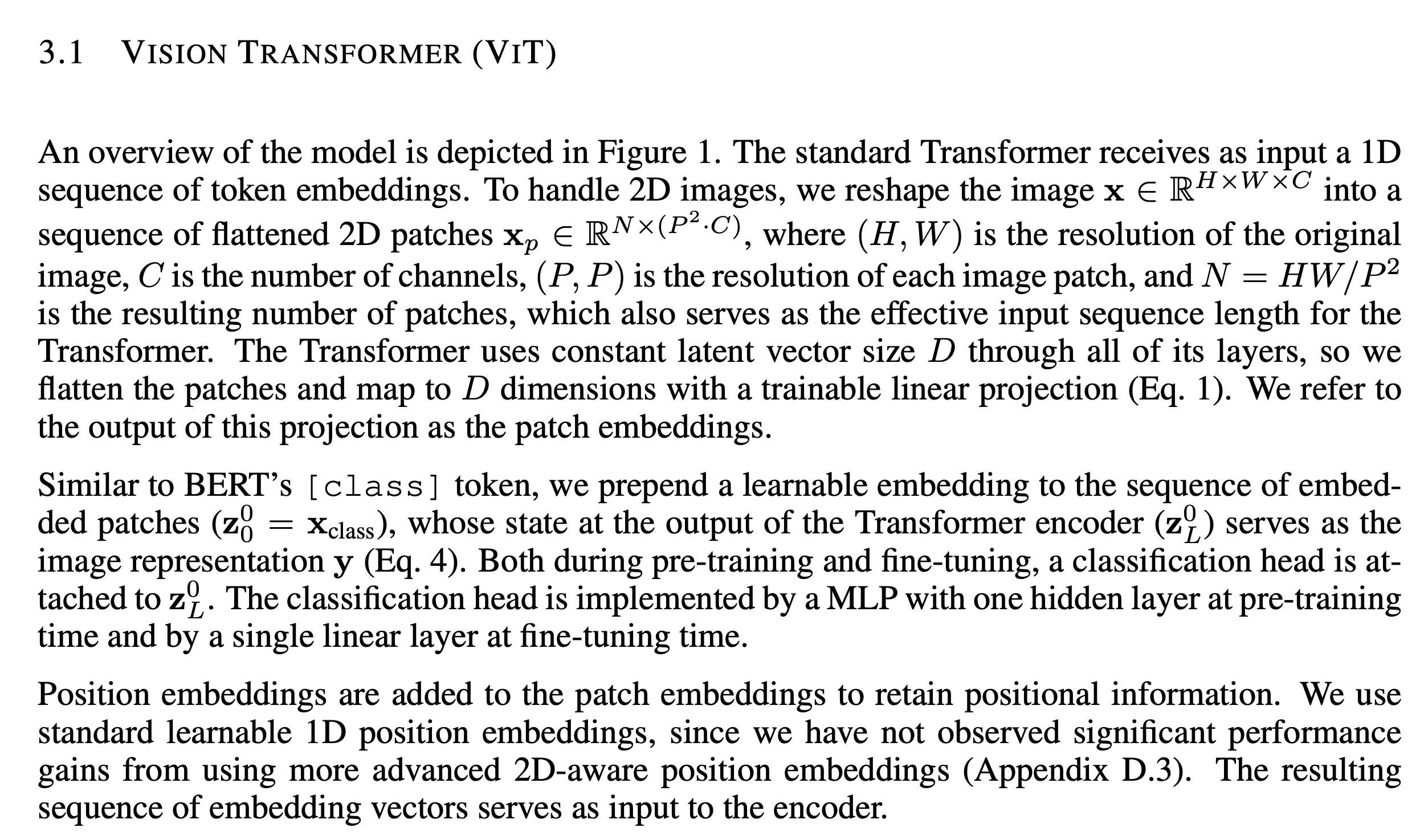
Vision Encoder: 아래 ViT의 vision encoderAn Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale
-
Perceiver Resampler다양한 개수의 Image나 Video Feature를 입력으로 받아 특정 크기의 visual output을 만들어냄.
-
Language Decoder: image와 text context를 기반으로 next token prediction하는 Transformer-based decoder
Image and Text Representations
-
Image Representation: Pix2Struct 처럼 고려해서 16x16 patch로 추출, 최대 sequence length L로 한정. 이후 Resampler가 attentive pooling mechanism으로써 image embedding크기를 줄여줌.Pix2Struct: Screenshot Parsing as Pretraining for Visual Language Understanding

aspect-ratio를 유지한채로 patch 추출 -
Text Representation: bounding box 포함한 text line 또는 plain markdown text들로 구성-
Text lines with bounding boxes-
bounding box 좌표를 discrete location token으로 바꿈
각 image dimension의 max length L이라고 할 때, 2L+2 specialized token이 필요함<x0>, <x1>, . . . , <xL−1>, <y0>, . . . , <yL−1>, <bbox>, </bbox> -
document T는 다음과 같이 구성됨
이 때 N개의 text line (n=1,2,...N) n번째 text line은 M_n개의 token으로 구성됨 따라서 각 text line은 T_n = {w_1^(n), w_2^(n), ..., w_{M_n}^(n)} 대응되는 bounding box는 B_n = <bbox><x_tl^(n)><y_tl^(n)><x_br^(n)><y_br^(n)></bbox> -
따라서 input은 다음과 같이 표기됨
<s><image>Image Embedding</image> Sum_{n=1}^{N} (Bn ⊕ Tn) </s> (⊕: concatenation)
-
-
Markdown text-
markdown 형태이므로 별도의 bounding box 없이 그대로 tokenized.
<s><image>Image Embedding</image>Markdown Text</s>.
-
-
Pretraining Data
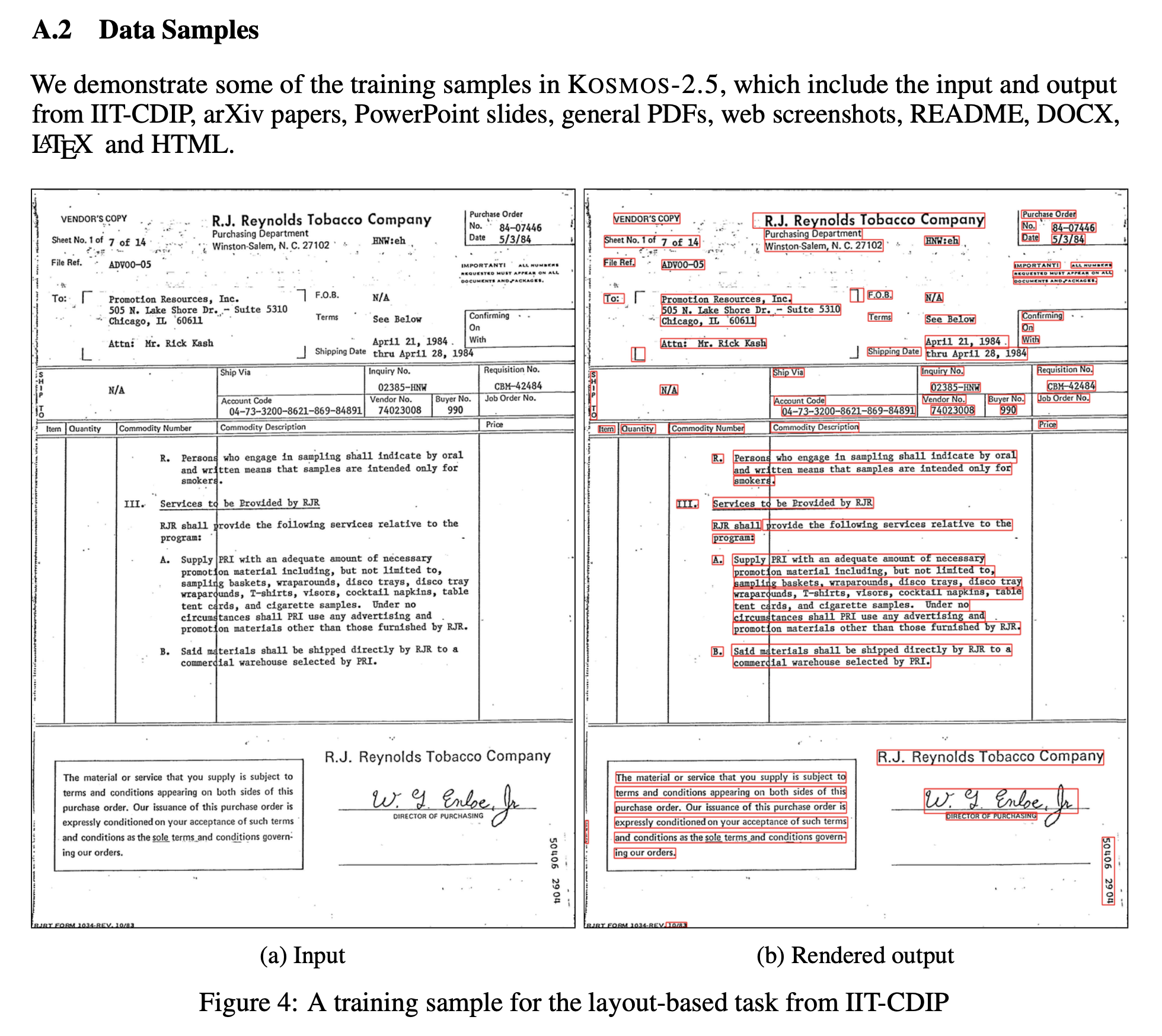
- For spatially-awared text blocks, use IIT-CDIP, arXiv papers, PowerPoint slides, General PDF, Web screenshots.
- For structured markdown text, use README, DOCS, LATEX, HTML
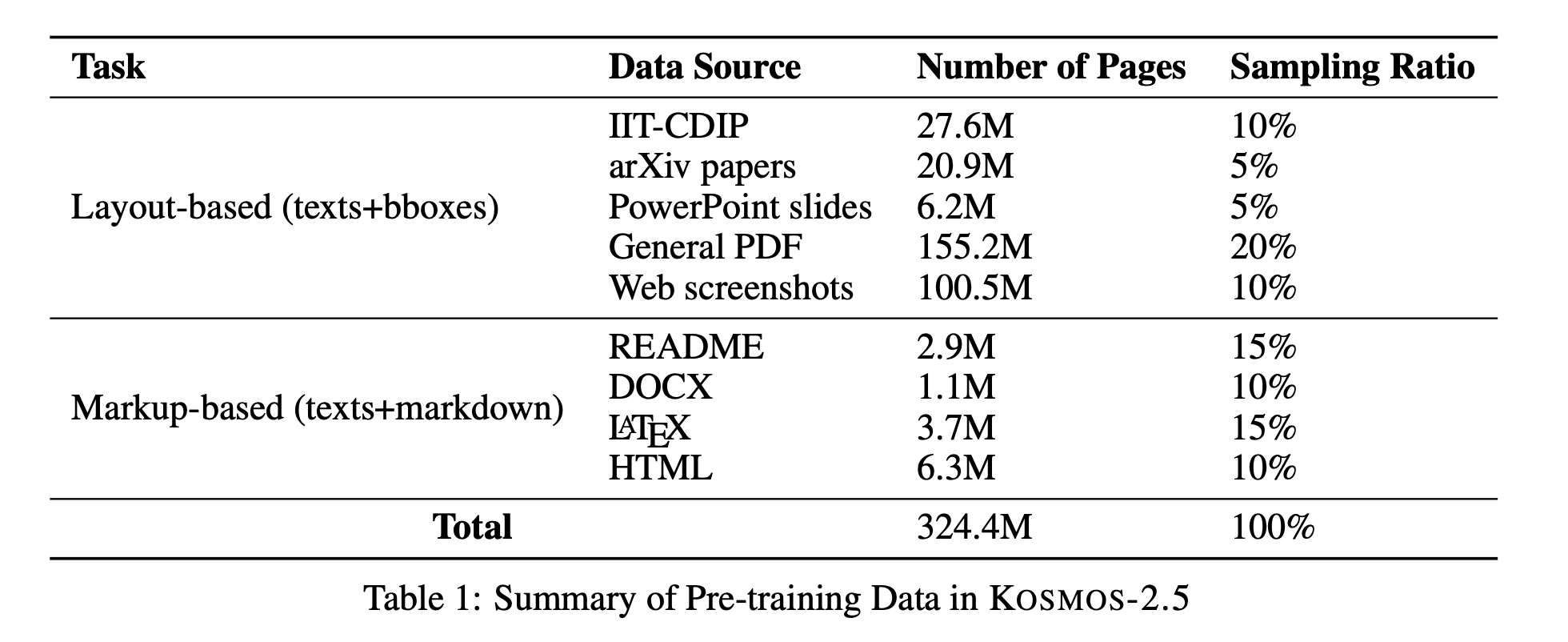 → 맹점: 단순 페이지 개수라서 얼마나 많은 token이 사용되었는지 체감이 어렵다.
→ 맹점: 단순 페이지 개수라서 얼마나 많은 token이 사용되었는지 체감이 어렵다.
Filtering & Quality Control
fastText 사용: non-English document 제거 (th=0.5)MinHash 사용: redundant pages 제거deduplication: paper와 같은 parameter 사용해 0.8 similarity 보이면 제거- image와 markdown 파일 사이의 token overlap을 평가해 IoU>=0.95이면 포함시킴
Experiments
Evaluations
Text Recognition 평가: word-level precision, recall, f1.
Google Document AI의 Document OCR결과 얻어진 text recognition 결과와 비교Image-to-markdown Generation:
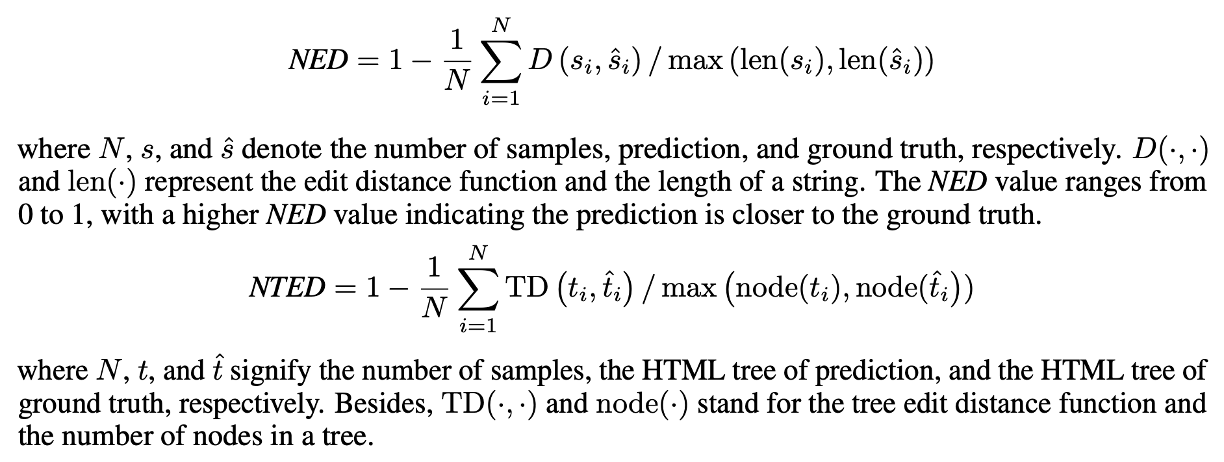
NED (normalized Edit Distance) & NTED (Normalized Tree Edit Distance) 이용
NTED는 markdown 같은 구조적 text에 단순 string 간 거리 비교하는 것은 한계가 있을 수 있어서 고안됨
1. markdown sequence를 HTML 형태로 바꾼 후
2. ZSS 알고리즘을 이용해 edit distance 계산하고
3. 동일 노드 안에 있는 edit distance를 normalized해 측정
Implementation Details
training hyperparameters- AdamW optimizer: beta=(0.9, 0.98)
- weight decay: 0.01
- dropout rate: 0.1
- learning rate: 2e-4 for 375 steps 후 남은 step 동안 linear decay to 0
- batch size: 가능한 computational resource에 맞춰서
model architecture- 총 parameter 수: 1.3B
- vision encoder: Pix2Struct-Large 모델 encoder로 initialize
- language decoder: 24 Transformer layers, 1,536 hidden layers, 6,144 FFN, 16 attention heads
training methods- layout-based data가 markup-based data보다 훨씬 많아서,
layout-based data로 100k steps 학습시킨 후에 위 언급한 두 가지 combined dataset으로 140k steps 학습 - Tokenization: SentencePiece → continuously sampled from 1 or multiple documents

- 모델이 robust할 수 있도록 TrOCR에서 사용한 data augmentation 방식 적용
TrOCR의 data augmentation:
- 6 kinds of image transformation + keeping original
중에 equal probability로 random sample 되도록 함
→ random rotation (-10~10 degrees), Gaussian blurring, image dilation, image erosion, downscaling, underlining
- layout-based data가 markup-based data보다 훨씬 많아서,
Performance
-
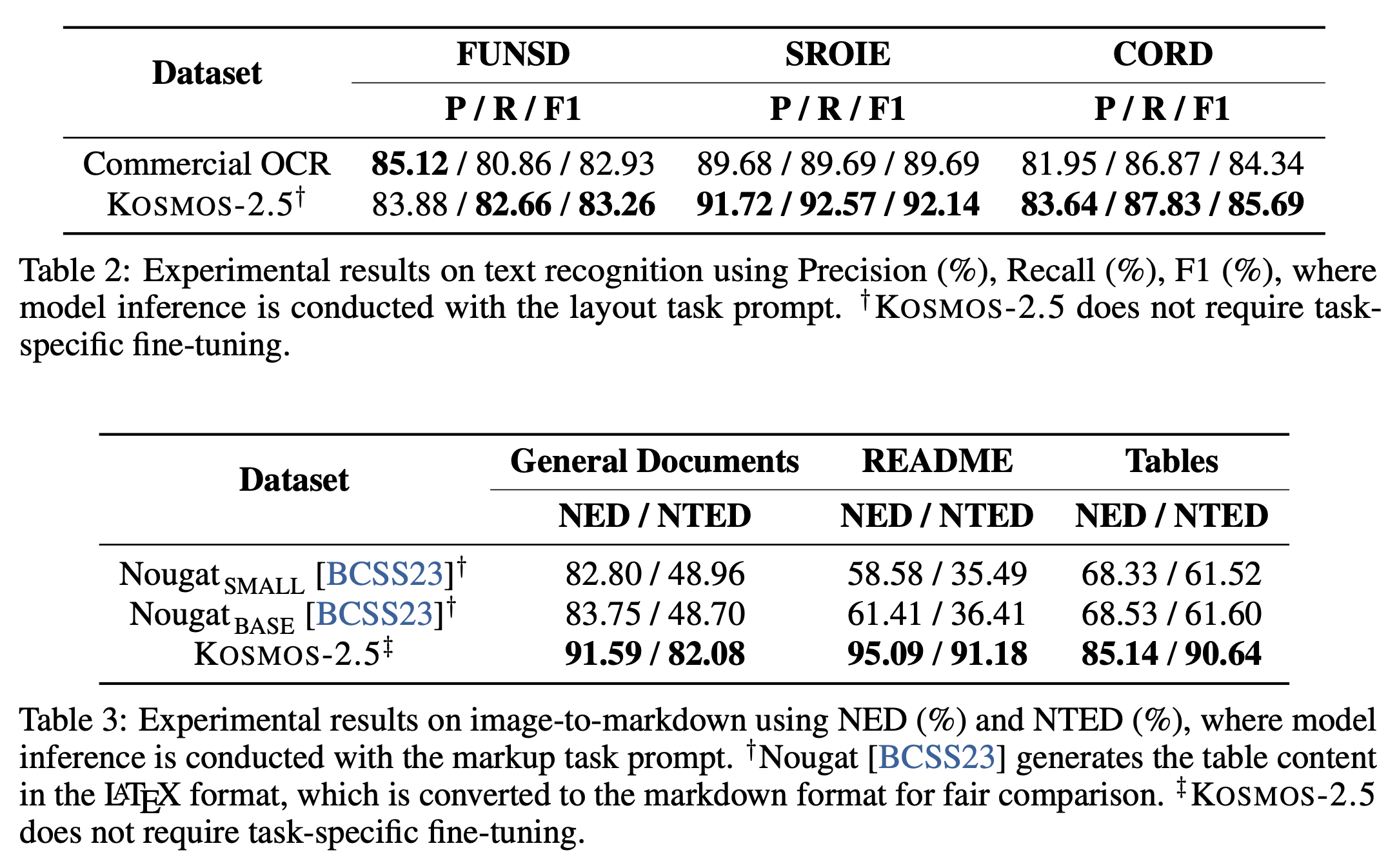
Quantitative Results:- text recognition의 경우, Google OCR보다 잘하고
image-to-markdown task의 경우, Nougat 알고리즘보다 잘함. - 따라서 다양한 task에서 KOSMOS-2.5의 뛰어난 성능을 보여줌.
- text recognition의 경우, Google OCR보다 잘하고
-
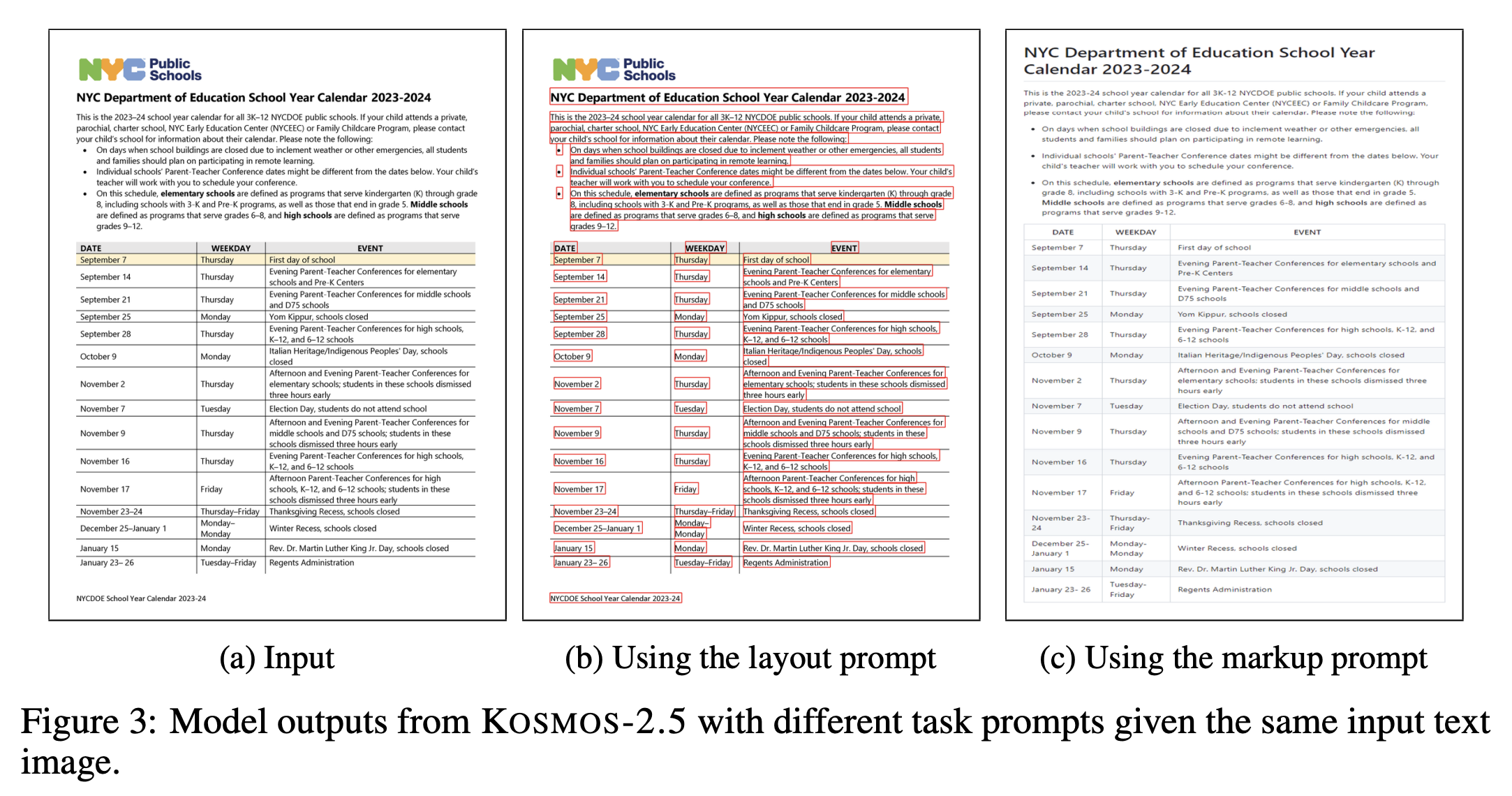
Qualitative Results:- task prompt에 따라서 bounding box를 포함한 text sequence를 잘 만들어내고, markup도 잘 생성해냄.

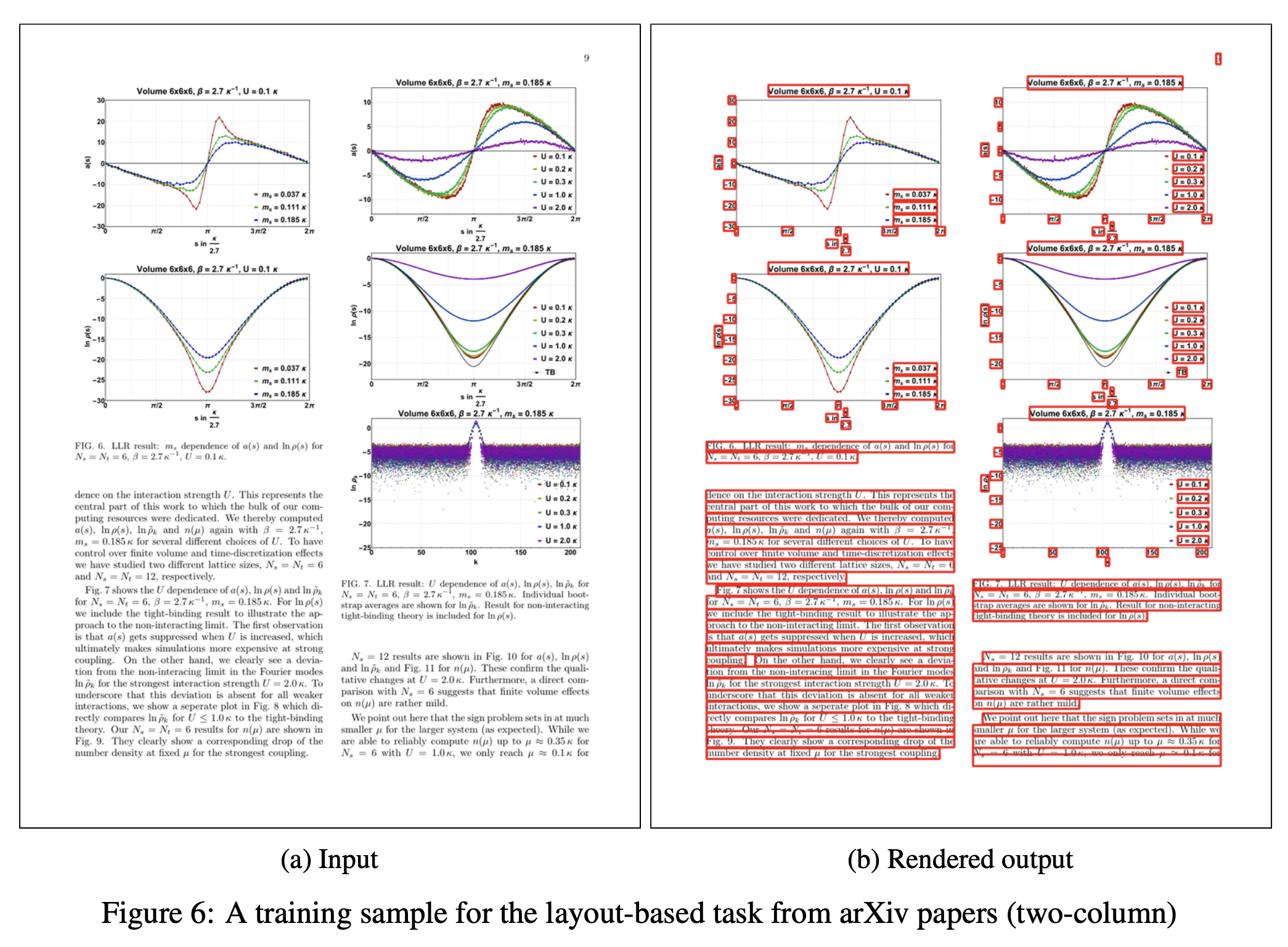
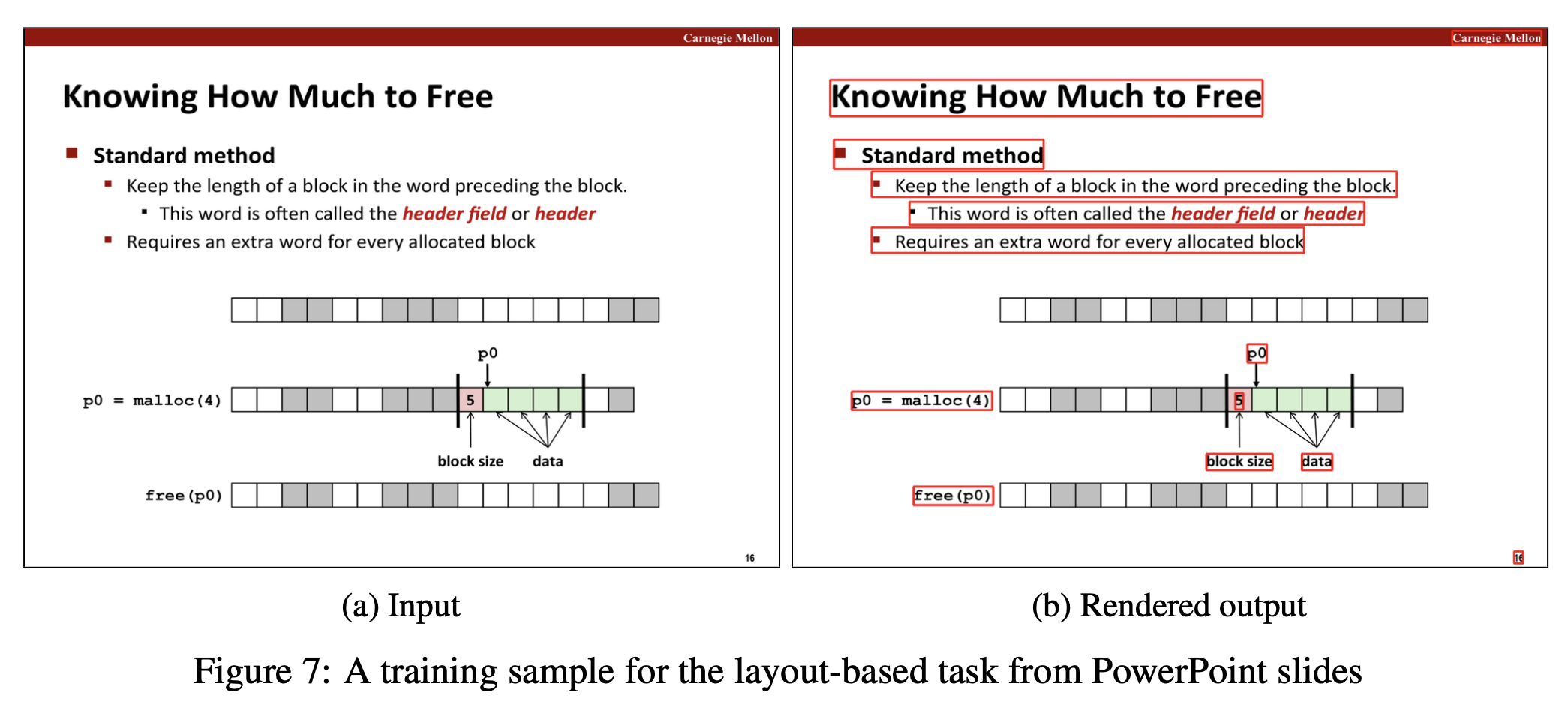

Conclusion
- multimodal literate model KOSMOS-2.5 제안.
Future work: KOSMOS-2.5의 한계점 극복 필요- natural language instruction을 사용한 document element들의 position에 대한 fine-grained control 할 수 없음. 극복 위해 instruction tuning도 가능할 듯
- 여러 page에 걸친 document에 대해서는 할 수 없음.
- task spectrum의 확장도 필요
Summary