NLP Task : 텍스트 분류(Text Classification)
- 실습 데이터 : 네이버 영화 리뷰 감성분석 데이터
- 네이버 영화의 댓글을 모아 구성된 한국어 텍스트 → 컬럼 : id, document(리뷰), label(부정, 긍정)
- 학습용 데이터 : 150,000개, 평가용 데이터 50,000개
- 코드 개요
- BERT 다국어 모델과 BERT 한국어 모델 비교 평가
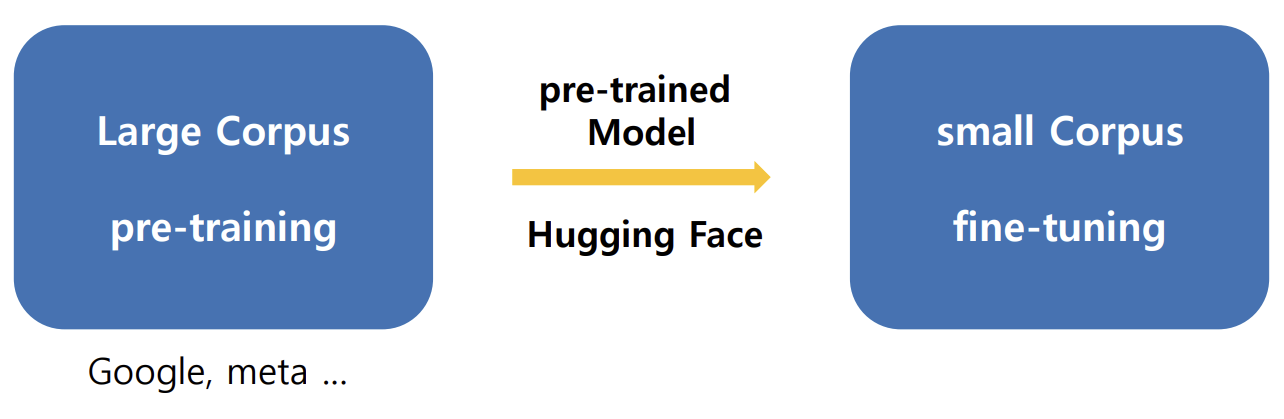
사전 학습(pre-training)과 미세 조정(fine-tuning)
- 사전 학습(pre-training)
- 많은 시간과 자원을 사용하여 방대한 양의 학습 데이터를 이용해서 모델의 파라미터(가중치)를 처음부터 학습시키는 과정
- 전이 학습(transfer learning)
- 사전 학습된 모델을 사용자가 원하는 새로운 과제에 적용하는 과정
- 미세 조정(fine-tuning)
- 사전 학습 모델이 가지고 있는 파라미터(가중치)를 사용자가 해결하고자 하는 과제에 대한 학습 데이터를 이용해서 추가적으로 학습하는 방법
- 사전 학습 모델이 가지고 있는 파라미터(가중치)를 초기값으로 사용해서 추가적인 학습을 통해 사용자가 가지고 있는 학습 데이터에 더 적합한 파라미터(가중치)를 얻는 것
- CV(이미지 처리)에서도 중요하게 활용됨
HuggingFace 라이브러리
- transformer를 기반으로 하는 다양한 딥러닝 모델들을 공유하는 개발자 커뮤니티
- 사전학습된 데이터를 공유
- url: https://huggingface.co/
- HuggingFace 라이브러리를 이용한 미세 조정 방식(파인튜닝)의 학습
텍스트 분류(Text Classification)
- 프로그래밍 과정
- BERT 다국어 모델 / 한국어 모델 Tokenizer 비교 테스트
- 학습용 데이터 생성
- 모델 생성
① BERT 다국어 모델
② BERT 한국어 모델
③ BERT 한국어 모델- 모델 컴파일
- 모델 학습
- 모델 저장
- 평가용 데이터 생성
- 모델 평가
BERT모델
- 입력층 > BERT > 출력층
- BERT : 입력층 + BERT layer
- Hugging Face : 출력
- AutoTokenizer : 모든 모델에 적용 가능한 Tokenizer
함수 및 메서드 정리
- 사전 학습된 토크나이저 객체 생성 / 사전 학습된 모델 객체 생성
- from_pretrained() 메소드 사용
- tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained(pretrained_model_name_or_path)
- model = TFBertForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(pretrained_model_name_or_path)
- pretrained_model_name_or_path : 다운로드 받을 모델 이름
- ~~ - cased : 대소문자 구분 (uncased : 대소문자 구분하지 않음)
- TFBertForSequenceClassification
- bert (TFBertMainLayer) : 사전 학습된 가중치
- dropout_379 (Dropout) : 딥러닝 모델의 과적합(overfitting)을 방지하기 위한 레이어
- 신경망의 일부 뉴런을 무작위로 비활성화(drop)하는 방법
- classifier (Dense) : 랜덤한 가중치를 파인튜닝 과정에서 학습시켜야할 가중치
- 파라미터 수 = (입력 차원 × 출력 차원) + 출력 차원
- bert는 기본적으로 768차원이고 num_labels = 2기 때문에 768*2 + 2 = 1358
- encode_plus() 메서드
- encode()의 기능 확장
- 텍스트 데이터를 BERT에 필요한 입력 형태로 변환 → 함수의 결과 값
① input_ids : 단어 사전을 참조하여 문장을 단어의 인덱스로 변환, BERT에 필요한 입력 형태 제공 (encode() 기본 기능)
② attention_mask : 패딩이 아닌 단어와 패딩인 부분을 구분(패딩이 아닌 단어:1, 패딩:0)
③ token_type_ids : 입력된 두 문장을 구분(첫번째 문장:0, 두번째 문장:1)- 문장을 최대 길이에 맞게 padding / truncation
- encode
- 문자 > 숫자화
- decode
- 숫자(encode된) > 문자화
- 예시)
- 결과값
encode_plus 파라미터
- text: 입력으로 사용할 단일 문장 또는 문장의 리스트
- padding: 시퀀스를 패딩하여 지정된 길이로 맞출지 여부
- truncation: 시퀀스가 길 경우 잘라낼지 여부
- max_length: 토큰화된 결과의 최대 길이 설정
- return_attention_mask: Attention Mask 반환 여부
- return_token_type_ids: 문장 간 구분을 위한 Segment ID 반환 여부
- text_pair: 두 번째 문장, 문장 쌍 입력 시 사용
- add_special_tokens: [CLS], [SEP] 등 특수 토큰 추가 여부
- return_tensors: 출력 데이터를 텐서 형식('pt', 'tf', 'np')으로 반환
- return_overflowing_tokens: 잘린 토큰을 반환할지 여부
- return_special_tokens_mask: 특수 토큰의 위치를 1로 표시하는 마스크 반환
- is_split_into_words: 입력이 이미 단어 단위로 분리되었는지 여부
- stride: 긴 텍스트를 겹쳐서 잘라낼지 설정
- pad_to_max_length: max_length로 패딩 여부(현재는 padding으로 대체됨)
- add_prefix_space: 모델에 따라 토큰화 시 공백 유지 여부
(이 시리즈의 모든 코드는 코랩환경에서 Python으로 작성하였습니다)
모델의 tokenizer Code 1 (tokenizer 임폴트)
#라이브러리 다운로드 / 임폴트
!pip install transformers
from transformers import BertTokenizer, AutoTokenizer
# 텍스트 문장 생성
text = '너와 함께한 시간 모두 눈부셨다. 날이 좋아서 날이 좋지 않아서 날이 적당해서 모든 날이 좋았다.'모델의 tokenizer Code 2 (BERT 다국어 모델 tokenizer)
# 사전 학습된 다국어 BERT Tokenizer 생성 > 다운로드
model_name = 'google-bert/bert-base-multilingual-cased'
token_mul = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)- google-bert/bert-base-multilingual-cased
- TensorFlow 기반
- pretrained 된 모델 : 가중치 최적화가 완료된 상태 (일반적으론 random)
# BERT 다국어 Tokenizer > 단어사전 확인
vocab_mul = token_mul.get_vocab()
print(vocab_mul)
print(f'{len(vocab_mul)}개')# 한국어 텍스트 데이터 > BERT 다국어 Tokenizer > 토큰화
# encode() > 토큰화 + 정수인코딩
encode_mul = token_mul.encode(text)
print(encode_mul)
# decode() > 정수로 표현된 토큰 > 한글로 변환
decode_mul = []
for idx in encode_mul:
token = token_mul.decode([idx])
decode_mul.append(token)
print(decode_mul)
print(len(decode_mul))모델의 tokenizer Code 3 (BERT 한국어 모델 tokenizer)
# 사전 학습된 한국어 BERT Tokenizer 생성 > 다운로드
model_name='klue/bert-base'
token_ko = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)- klue/bert-base
- PyTorch 기반
# BERT 한국어 Tokenizer > 단어사전 확인
vocab_ko = token_ko.get_vocab()
sorted_vocab1 = dict(sorted(vocab_ko.items(), key=lambda x:x[1]))
vocab_ko = sorted_vocab1
print(vocab_ko)
print(f'{len(vocab_ko)}개')# 한국어 텍스트 데이터 > BERT 한국어 Tokenizer > 토큰화
# encode() > 토큰화 + 정수인코딩
encode_ko = token_ko.encode(text)
print(encode_ko)
# decode() > 정수로 표현된 토큰 > 한글로 변환
decode_ko = []
for idx in encode_ko:
token = token_ko.decode([idx])
decode_ko.append(token)
print(decode_ko)
print(len(decode_ko))ELECTRA
- 2018년 모델인 BERT를 개선한 2020년 모델
- BERT는 입력text의 15%를 mask로 사용 > ELECTRA는 100% 사용
모델의 tokenizer Code 4 (ELECTRA 한국어 모델 tokenizer)
# 사전 학습된 한국어 ELECTRA Tokenizer 생성 > 다운로드
model_name='beomi/KcELECTRA-base-v2022'
token_ele = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)beomi/KcELECTRA-base-v2022
- PyTorch 기반
- electra는 dense layer가 두개
- classifier (TFElectraClass) = 592130
- 첫 번째 Dense 레이어:
- 입력 차원이 768이고, 중간에 임베딩 크기와 동일한 출력 차원을 갖는 레이어가 있기 때문에, 이 레이어의 파라미터는 (768 × 768) + 768 = 590,592
- 두 번째 Dense 레이어:
- 중간층의 출력 차원이 768이고, 최종 출력 차원이 2일 때, 이 레이어의 파라미터는 (768 × 2) + 2 = 1,538
- 두 Dense layer의 합 = 592130
# ELECTRA 한국어 Tokenizer > 단어사전 확인
vocab_ele = token_ele.get_vocab()
sorted_vocab1 = dict(sorted(vocab_ele.items(), key=lambda x:x[1]))
vocab_ele = sorted_vocab1
print(vocab_ele)
print(f'{len(vocab_ele)}개')# 한국어 텍스트 데이터 > ELECTRA 한국어 Tokenizer > 토큰화
# encode() > 토큰화 + 정수인코딩
encode_ele = token_ele.encode(text)
print(encode_ele)
# decode() > 정수로 표현된 토큰 > 한글로 변환
decode_ele = []
for idx in encode_ele:
token = token_ele.decode([idx])
decode_ele.append(token)
print(decode_ele)
print(len(decode_ele))모델의 데이터 생성 Code 1 (학습용 데이터 생성)
# 필요한 라이브러리 임폴트
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import tqdm- import tqdm
- 진행률을 시각적으로 표시하기 위해 사용하는 라이브러리
# 파일 경로 설정
file_path = '/content/drive/MyDrive/NLP/ratings_train.tsv'
# pd.read_csv() 호출
df_train = pd.read_csv(file_path, sep='\t')
print(df_train)# 누락 데이터의 수 확인
print(df_train.isnull().sum())
# 누락 데이터 제거
df_train = df_train.dropna()
print(df_train)모델의 데이터 생성 Code 2 (BERT 다국어 모델 데이터 생성)
# tokenizer.tokenize() 함수 > 전체 리뷰에 대한 토큰화 > 토큰의 길이 추출 1
# document 컬럼 추출 > 인덱싱
data = df_train.loc[:,'document']
#print(data)
# 전체 리뷰의 토큰 길이 측정
total_length_mul = []
for review in tqdm.tqdm(data):
tokens = token_mul.tokenize(review)
total_length_mul.append(len(tokens))# encode_plus() 함수 사용 > 입력 데이터 생성 함수 정의 1
def make_dataset_mul(sentence, max_length):
# encode_plus 함수 실행
encode_dict = token_mul.encode_plus(
text=sentence,
padding='max_length',
truncation=True,
max_length=max_length,
return_attention_mask=True,
return_token_type_ids=True
)
input_ids = encode_dict['input_ids'] # 결과 값(python dict) > 항목별 값 추출
attention_mask = encode_dict['attention_mask']
token_type_ids = encode_dict['token_type_ids']
return input_ids, attention_mask, token_type_ids# TFBertForSequenceClassification 다국어 모델 학습용 데이터 생성하기 1
# 생성된 학습용 데이터 저장
input_ids_mul = []
attention_masks_mul = []
token_type_ids_mul = []
# for문 + 함수 실행
for review in tqdm.tqdm(df_train.loc[:,'document']):
input_ids, attention_mask, token_type_id = make_dataset_mul(review, 50) # 사용자 정의 함수 호출
input_ids_mul.append(input_ids)
attention_masks_mul.append(attention_mask)
token_type_ids_mul.append(token_type_id)
# 결과 확인
print('\n', input_ids_mul[0])
print(attention_masks_mul[0])
print(token_type_ids_mul[0])
print(len(input_ids_mul))# 학습용 데이터 생성 결과 값 > 넘파이 배열로 변환 > np.array(list)
# np.array() 호출
input_ids_mul = np.array(input_ids_mul)
attention_masks_mul = np.array(attention_masks_mul)
token_type_ids_mul = np.array(token_type_ids_mul)# 생성된 학습용 데이터 병합 > x_train 생성
x_train_mul = input_ids_mul, attention_masks_mul, token_type_ids_mulencode_plus의 결과 값
- input_ids: 텍스트를 토큰화하고, 각 토큰을 정수로 변환한 리스트. 모델의 입력으로 사용됨
- attention_mask: 모델이 실제로 주목해야 할 토큰(1)과 무시해야 할 패딩 토큰(0)을 구분하는 마스크
- token_type_ids: 문장 쌍 입력 시 첫 번째 문장과 두 번째 문장을 구분하는 역할. 각각 0과 1로 구분됨
모델의 데이터 생성 Code 3 (BERT 한국어 모델 데이터 생성)
# tokenizer() 함수 > 전체 리뷰에 대한 토큰화 > 토큰의 길이 추출 2
# BERT 한국어 토크나이저 사용
total_length_ko = []
for review in tqdm.tqdm(data):
tokens = token_ko.tokenize(review)
total_length_ko.append(len(tokens))# encode_plus() 함수 사용 > 입력 데이터 생성 함수 정의 2
def make_dataset_ko(sentence, max_length):
# encode_plus 함수 실행
encode_dict = token_ko.encode_plus(
text=sentence,
padding='max_length',
truncation=True,
max_length=max_length,
return_attention_mask=True,
return_token_type_ids=True
)
input_ids = encode_dict['input_ids'] # 결과 값(python dict) > 항목별 값 추출
attention_mask = encode_dict['attention_mask']
token_type_ids = encode_dict['token_type_ids']
return input_ids, attention_mask, token_type_ids# TFBertForSequenceClassification 다국어 모델 학습용 데이터 생성하기 2
# 생성된 학습용 데이터 저장
input_ids_ko = []
attention_masks_ko = []
token_type_ids_ko = []
# for문 + 함수 실행
for review in tqdm.tqdm(df_train.loc[:,'document']):
input_ids, attention_mask, token_type_id = make_dataset_ko(review, 50) # 사용자 정의 함수 호출
input_ids_ko.append(input_ids)
attention_masks_ko.append(attention_mask)
token_type_ids_ko.append(token_type_id)
# 결과 확인
print('\n', input_ids_ko[0])
print(attention_masks_ko[0])
print(token_type_ids_ko[0])
print(len(input_ids_ko))# 학습용 데이터 생성 결과 값 > 넘파이 배열로 변환 > np.array(list)
# np.array() 호출
input_ids_ko = np.array(input_ids_ko)
attention_masks_ko = np.array(attention_masks_ko)
token_type_ids_ko = np.array(token_type_ids_ko)# 생성된 학습용 데이터 병합 > x_train 생성
x_train_ko = input_ids_ko, attention_masks_ko, token_type_ids_ko모델의 데이터 생성 Code 4 (ELECTRA 한국어 모델 데이터 생성)
# tokenizer() 함수 > 전체 리뷰에 대한 토큰화 > 토큰의 길이 추출 3
# ELECTRA 한국어 토그나이저 사용
total_length_ele = []
for review in tqdm.tqdm(data):
tokens = token_ele.tokenize(review)
total_length_ele.append(len(tokens))# encode_plus() 함수 사용 > 입력 데이터 생성 함수 정의 3
def make_dataset_ele(sentence, max_length):
# encode_plus 함수 실행
encode_dict = token_ele.encode_plus(
text=sentence,
padding='max_length',
truncation=True,
max_length=max_length,
return_attention_mask=True,
return_token_type_ids=True
)
input_ids = encode_dict['input_ids'] # 결과 값(python dict) > 항목별 값 추출
attention_mask = encode_dict['attention_mask']
token_type_ids = encode_dict['token_type_ids']
return input_ids, attention_mask, token_type_ids# TFBertForSequenceClassification 다국어 모델 학습용 데이터 생성하기 3
# 생성된 학습용 데이터 저장
input_ids_ele = []
attention_masks_ele = []
token_type_ids_ele = []
# for문 + 함수 실행
for review in tqdm.tqdm(df_train.loc[:,'document']):
input_ids, attention_mask, token_type_id = make_dataset_ele(review, 50) # 사용자 정의 함수 호출
input_ids_ele.append(input_ids)
attention_masks_ele.append(attention_mask)
token_type_ids_ele.append(token_type_id)
# 결과 확인
print('\n', input_ids_ele[0])
print(attention_masks_ele[0])
print(token_type_ids_ele[0])
print(len(input_ids_ele))# 학습용 데이터 생성 결과 값 > 넘파이 배열로 변환 > np.array(list)
# np.array() 호출
input_ids_ele = np.array(input_ids_ele)
attention_masks_ele = np.array(attention_masks_ele)
token_type_ids_ele = np.array(token_type_ids_ele)# 생성된 학습용 데이터 병합 > x_train 생성
x_train_ele = input_ids_ele, attention_masks_ele, token_type_ids_ele모델의 데이터 생성 Code 5 (통합 비교)
# 학습용 정답 레이블 생성 > y_train 생성
y_train = np.array(df_train.loc[:,'label'])# tokenizer.tokenize() 함수 > 리뷰1개에 대한 토큰화
# 대상 : 처번째 리뷰 데이터
sample1 = df_train.iloc[0,1]
print(sample1)
# BERT 다국어 tokenizer로 토큰화
result_mul = token_mul.tokenize(sample1)
print(result_mul)
# BERT 한국어 tokenizer로 토큰화
result_ko = token_ko.tokenize(sample1)
print(result_ko)
# ELECTRA 한국어 tokenizer로 토큰화
result_ele = token_ele.tokenize(sample1)
print(result_ele)# 띄어쓰기가 안된 문장에 대한 처리 결과 비교
#sample2 = df_train.iloc[2,1]
sample2 = df_train.iloc[28,1]
print(sample2)
# BERT 다국어 tokenizer로 토큰화
result_mul2 = token_mul.tokenize(sample2)
print(result_mul2)
# BERT 한국어 tokenizer로 토큰화
result_ko2 = token_ko.tokenize(sample2)
print(result_ko2)
# ELECTRA 한국어 tokenizer로 토큰화
result_ele2 = token_ele.tokenize(sample2)
print(result_ele2)# 전체 리뷰의 토큰 길이 비교
print(total_length_ko)
print(total_length_mul)
print(total_length_ele)# 영화 리뷰 별 토큰의 길이 > 통계 추출 > np.percentile(a, q) 비교
print(np.percentile(total_length_mul, [75, 90]))
print(np.percentile(total_length_ko, [75, 90]))
print(np.percentile(total_length_ele, [75, 90]))- np.percentile(a, q)
- a : 추출할 데이터
- q : q%에 해당하는 데이터의 값 (0~100)
# x_train 데이터 비교
print(x_train_mul)
print('-'*80)
print(x_train_ko)
print('-'*80)
print(x_train_ele)모델 생성 Code 1 (BERT 다국어 모델)
# 함수 임폴트
from transformers import TFBertForSequenceClassification
# pretrained 모델 다운로드
model_mul = 'google-bert/bert-base-multilingual-cased'
model_mul = TFBertForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(model_mul, num_labels=2)
# 모델의 구조 출력
model_mul.summary()- num_labels
- 출력층에서 출력할 유닛 수 (2개면 이진분류 n개(n>2)면 다중분류)
# 함수 임폴트
import tensorflow as tf
# compile 실행
opti = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate = 0.00005)
model_mul.compile(optimizer= opti, loss = model_mul.hf_compute_loss, metrics = ['accuracy'])- huggingface에서 제작한 전용 손실함수 : hf_compute_loss
- huggingface에서 가공한 bert와 electra 모델에서 사용 가능
# callbacks 설정
early_stop = tf.keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping(
monitor = 'val_loss',
patience = 1,
verbose = 1
)
# model 학습 진행
model_mul.fit(
x = x_train_mul,
y = y_train,
epochs = 3,
batch_size = 128,
validation_split = 0.2,
callbacks = [early_stop]
)# 저장 경로 설정
mul_save_path='/content/drive/MyDrive/NLP/tf_mul'
# 모델 저장 함수 실행
model_mul.save_pretrained(mul_save_path)모델 생성 Code 2 (BERT 한국어 모델)
# 함수 임폴트
from transformers import TFBertForSequenceClassification
# pretrained 모델 다운로드
model_ko='klue/bert-base'
model_ko = TFBertForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(model_ko, num_labels=2, from_pt=True)
# 모델의 구조 출력
model_ko.summary()# 함수 임폴트
import tensorflow as tf
# compile 실행
opti = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate = 0.00005)
model_ko.compile(optimizer= opti, loss = model_ko.hf_compute_loss, metrics = ['accuracy'])# callbacks 설정
early_stop = tf.keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping(
monitor = 'val_loss',
patience = 1,
verbose = 1
)
# model 학습 진행
model_ko.fit(
x = x_train_ko,
y = y_train,
epochs = 3,
batch_size = 128,
validation_split = 0.2,
callbacks = [early_stop]
)# 저장 경로 설정
ko_save_path='/content/drive/MyDrive/NLP/tf_ko'
# 모델 저장 함수 실행
model_ko.save_pretrained(ko_save_path)모델 생성 Code 3 (ELECTRA 한국어 모델)
from transformers import TFElectraForSequenceClassification
# pretrained 모델 다운로드
model_ele='beomi/KcELECTRA-base-v2022'
model_ele = TFElectraForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(model_ele, num_labels=2, from_pt=True)
# 모델의 구조 출력
model_ele.summary()# 함수 임폴트
import tensorflow as tf
# compile 실행
opti = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate = 0.00005)
model_ele.compile(optimizer= opti, loss = model_ele.hf_compute_loss, metrics = ['accuracy'])# callbacks 설정
early_stop = tf.keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping(
monitor = 'val_loss',
patience = 2,
verbose = 1
)
# model 학습 진행
model_ele.fit(
x = x_train_ele,
y = y_train,
epochs = 5,
batch_size = 128,
validation_split = 0.2,
callbacks = [early_stop]
)# 저장 경로 설정
ele_save_path='/content/drive/MyDrive/NLP/tf_ele'
# 모델 저장 함수 실행
model_ele.save_pretrained(ele_save_path)모델 평가 Code 1 (평가용 데이터 생성)
# 필요한 라이브러리 임폴트
import pandas as pd
import tqdm
# 파일 경로 설정
file_path='/content/drive/MyDrive/NLP/ratings_test.tsv'
# DataFrame 생성
df_test = pd.read_csv(file_path, sep='\t')
#print(f'평가용 데이터 확인 : \n{df_test}')
# 각 컬럼별 누락 데이터의 수 확인
num_nulls = df_test.isnull().sum()
#print(f'각 컬럼별 누락 데이터의 수 : \n{num_nulls}')
# 누락 데이터 제거 --> df.dropna()
df_test.dropna(inplace=True, ignore_index=True)
# 결과 확인하기
print(f'누락 제거 후 평가용 데이터 확인 : \n{df_test}')모델 평가 Code 2 (BERT 다국어 모델 평가)
# encode_plus() 함수 사용 --> 평가용 데이터 생성 함수 정의
def make_dataset_mul(sentence, max_len):
# encode_plus() 함수 실행 --> dict 생성
encoded_dict = token_mul.encode_plus(
text=sentence,
padding='max_length',
truncation=True,
max_length=max_len,
return_attention_mask=True,
return_token_type_ids=True
)
# 결과 값(python dict) --> 항목별 값 추출
input_ids = encoded_dict['input_ids']
attention_mask = encoded_dict['attention_mask']
token_type_ids = encoded_dict['token_type_ids']
return input_ids, attention_mask, token_type_ids# 평가용 데이터 생성 - BERT 한국어 분류 모델
# 생성된 평가용 데이터
input_ids_mul=[]
attention_mask_mul=[]
token_type_ids_mul=[]
# for문 + 사용자 정의 함수 실행
for review in tqdm.tqdm(df_test.loc[:, 'document']):
input_ids, attention_mask, token_type_ids = make_dataset_mul(sentence=review, max_len=42)
input_ids_mul.append(input_ids)
attention_mask_mul.append(attention_mask)
token_type_ids_mul.append(token_type_ids)# 평가용 데이터 생성 결과 --> 넘파이 배열로 변환 --> np.array(list)
# 필요한 라이브러리 임폴트
import numpy as np
# np.array() 호출
input_ids_mul = np.array(input_ids_mul)
attention_mask_mul = np.array(attention_mask_mul)
token_type_ids_mul = np.array(token_type_ids_mul)
# 생성된 평가용 데이터 병합 --> X_test
X_test_mul = [input_ids_mul, attention_mask_mul, token_type_ids_mul]
# 평가용 정답 레이블 생성
y_test = df_test.loc[:, 'label']# 학습된 모델 불러오기
# 필요한 함수 임폴트
from transformers import TFBertForSequenceClassification, TFElectraForSequenceClassification
# 폴더 경로 설정
mul_path='/content/drive/MyDrive/NLP/tf_mul'
# fine-tuning된 모델 불러오기
finetuned_mul = TFBertForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(mul_path)
# 모델 구조 확인
finetuned_mul.summary()# fine-tuning된 모델 컴파일
# 필요한 라이브러리 임폴트
import tensorflow as tf
# BERT 한국어 텍스트 분류 모델
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.00005)
finetuned_mul.compile(loss=finetuned_mul.hf_compute_loss, optimizer=optimizer, metrics=['accuracy'])# BERT 한국어 텍스트 분류 모델의 성능 평가
performance_mul = finetuned_mul.evaluate(
x = X_test_mul,
y = y_test,
batch_size=1024
)
print(f'BERT 한국어 텍스트 분류 모델의 성능 : {performance_mul}')모델 평가 Code 2 (BERT 한국어 모델 평가)
# encode_plus() 함수 사용 --> 평가용 데이터 생성 함수 정의
def make_dataset_ko(sentence, max_len):
# encode_plus() 함수 실행 --> dict 생성
encoded_dict = token_ko.encode_plus(
text=sentence,
padding='max_length',
truncation=True,
max_length=max_len,
return_attention_mask=True,
return_token_type_ids=True
)
# 결과 값(python dict) --> 항목별 값 추출
input_ids = encoded_dict['input_ids']
attention_mask = encoded_dict['attention_mask']
token_type_ids = encoded_dict['token_type_ids']
return input_ids, attention_mask, token_type_ids# 평가용 데이터 생성 - BERT 한국어 분류 모델
# 생성된 평가용 데이터
input_ids_ko=[]
attention_mask_ko=[]
token_type_ids_ko=[]
# for문 + 사용자 정의 함수 실행
for review in tqdm.tqdm(df_test.loc[:, 'document']):
input_ids, attention_mask, token_type_ids = make_dataset_ko(sentence=review, max_len=42)
input_ids_ko.append(input_ids)
attention_mask_ko.append(attention_mask)
token_type_ids_ko.append(token_type_ids)# 평가용 데이터 생성 결과 --> 넘파이 배열로 변환 --> np.array(list)
# 필요한 라이브러리 임폴트
import numpy as np
# np.array() 호출
input_ids_ko = np.array(input_ids_ko)
attention_mask_ko = np.array(attention_mask_ko)
token_type_ids_ko = np.array(token_type_ids_ko)
# 생성된 평가용 데이터 병합 --> X_test
X_test_ko = [input_ids_ko, attention_mask_ko, token_type_ids_ko]
# 평가용 정답 레이블 생성
y_test = df_test.loc[:, 'label']# 학습된 모델 불러오기
# 필요한 함수 임폴트
from transformers import TFBertForSequenceClassification, TFElectraForSequenceClassification
# 폴더 경로 설정
ko_path='/content/drive/MyDrive/NLP/tf_ko'
# fine-tuning된 모델 불러오기
finetuned_ko = TFBertForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(ko_path)
# 모델 구조 확인
finetuned_ko.summary()# fine-tuning된 모델 컴파일
# 필요한 라이브러리 임폴트
import tensorflow as tf
# BERT 한국어 텍스트 분류 모델
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.00005)
finetuned_ko.compile(loss=finetuned_ko.hf_compute_loss, optimizer=optimizer, metrics=['accuracy'])# BERT 한국어 텍스트 분류 모델의 성능 평가
performance_ko = finetuned_ko.evaluate(
x = X_test_ko,
y = y_test,
batch_size=1024
)
print(f'BERT 한국어 텍스트 분류 모델의 성능 : {performance_ko}')모델 평가 Code 3 (Electra 한국어 모델 평가)
# encode_plus() 함수 사용 --> 평가용 데이터 생성 함수 정의
def make_dataset_ele(sentence, max_len):
# encode_plus() 함수 실행 --> dict 생성
encoded_dict = token_ele.encode_plus(
text=sentence,
padding='max_length',
truncation=True,
max_length=max_len,
return_attention_mask=True,
return_token_type_ids=True
)
# 결과 값(python dict) --> 항목별 값 추출
input_ids = encoded_dict['input_ids']
attention_mask = encoded_dict['attention_mask']
token_type_ids = encoded_dict['token_type_ids']
return input_ids, attention_mask, token_type_ids# 평가용 데이터 생성 - BERT 한국어 분류 모델
# 생성된 평가용 데이터
input_ids_ele=[]
attention_mask_ele=[]
token_type_ids_ele=[]
# for문 + 사용자 정의 함수 실행
for review in tqdm.tqdm(df_test.loc[:, 'document']):
input_ids, attention_mask, token_type_ids = make_dataset_ele(sentence=review, max_len=42)
input_ids_ele.append(input_ids)
attention_mask_ele.append(attention_mask)
token_type_ids_ele.append(token_type_ids)# 평가용 데이터 생성 결과 --> 넘파이 배열로 변환 --> np.array(list)
# 필요한 라이브러리 임폴트
import numpy as np
# np.array() 호출
input_ids_ele = np.array(input_ids_ele)
attention_mask_ele = np.array(attention_mask_ele)
token_type_ids_ele = np.array(token_type_ids_ele)
# 생성된 평가용 데이터 병합 --> X_test
X_test_ele = [input_ids_ele, attention_mask_ele, token_type_ids_ele]
# 평가용 정답 레이블 생성
y_test = df_test.loc[:, 'label']# 학습된 모델 불러오기
# 필요한 함수 임폴트
from transformers import TFBertForSequenceClassification, TFElectraForSequenceClassification
# 폴더 경로 설정
ele_path='/content/drive/MyDrive/NLP/tf_ele'
# fine-tuning된 모델 불러오기
finetuned_ele = TFBertForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(ele_path)
# 모델 구조 확인
finetuned_ele.summary()# fine-tuning된 모델 컴파일
# 필요한 라이브러리 임폴트
import tensorflow as tf
# BERT 한국어 텍스트 분류 모델
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.00005)
finetuned_ele.compile(loss=finetuned_ele.hf_compute_loss, optimizer=optimizer, metrics=['accuracy'])# BERT 한국어 텍스트 분류 모델의 성능 평가
performance_ele = finetuned_ele.evaluate(
x = X_test_ele,
y = y_test,
batch_size=1024
)
print(f'BERT 한국어 텍스트 분류 모델의 성능 : {performance_ele}')참고자료
google-bert/bert-base-multilingual-cased huggingface(104개 언어를 한번에 처리할 수 있는 모델)