list를 stack과 queue로 사용해보자
자료구조에서 대표적으로 언급되는 데이터 참조 방식이다.
- Stack
- 물건을 쌓아올린 것처럼 데이터를 쌓아올린 구조
- 가장 나중에 삽입된 데이터가 가장 먼저 삭제된다 (LIFO, last-in-last-out)
- 데이터 삽입을
push, 데이터 삭제를pop이라고 한다 - 데이터 가장 윗 부분을
top이라고 하며, 공식 명칭은stack pointer다
- Queue
- Stack과 마찬가지로 삽입 & 삭제가 제한적인 자료 구조로, 양끝에서 자료 추출 가능
- 가장 먼저 삽입된 데이터가 가장 먼저 삭제된다 (FIFO, first-in-first-out)
- 구조의 머리 부분을
front, 꼬리 부분을rear라고 한다
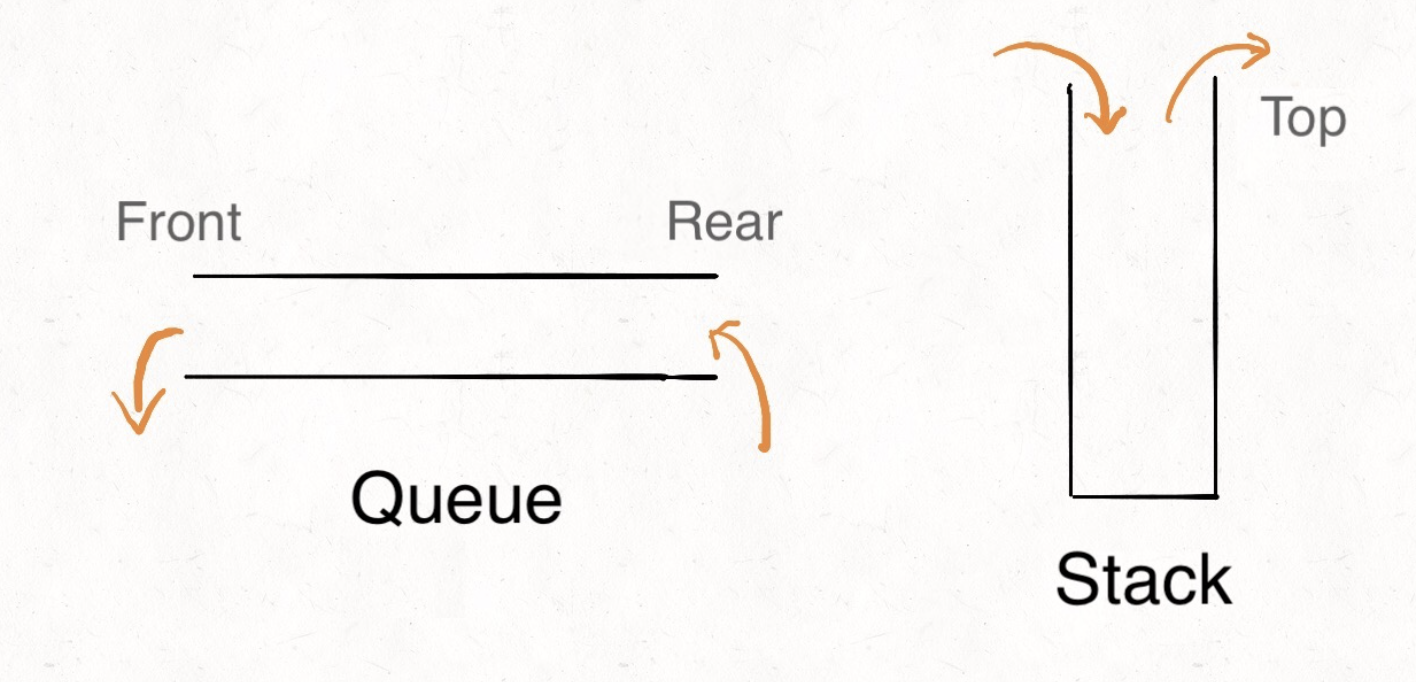
이미지 출처: https://labuladong.gitbook.io/algo-en/ii.-data-structure/implementqueueusingstacksimplementstackusingqueues
list & stack
몇 가지 메소드를 사용하면 list를 stack으로 사용할 수 있다.
stack = [1,2,3]
stack.append(4)
stack.append(5)
print(stack)
>>> [1,2,3,4,5]
stack.pop() #top에 있는 요소 제거 (5)
stack.pop() #top에 있는 요소 제거 (4)
print(stack)
>>> [1,2,3]list & queue
list를 통해 queue를 구현하려면, collections 를 사용하면 효율적이다.
collections.deque를 통해 appendleft(), popleft()를 사용할 수 있다.
from collections import deque
#데이터 추가
queue = deque(['apple','banana','pineapple'])
queue.appendleft('grape') #rear 추가
print(queue)
>>> deque(['grape', 'apple', 'banana', 'pineapple']) #type: collections.deque
#데이터 삭제
queue = deque(['apple','banana','pineapple'])
queue.popleft() #front 제거 (apple)
print(queue)
>>> deque(['banana', 'pineapple'])Additional: stack 구현하기
문제)
주어진 문자열에서, 중복된 문자를 없애고 만들 수 있는 가장 빠른(사전 기준) 단어 조합 만들기
풀이)
from collections import Counter
lst = 'cbacdcbc'
myDict = Counter(lst) #{'c':4, 'b':2, 'a':1, 'd':1}
stack = []
for char in lst:
myDict[char] -= 1
if not stack:
stack.append(char)
elif char in stack:
pass
else:
while stack and stack[-1] > char and myDict[stack[-1]] != 0:
stack.pop()
stack.append(char)
result = ''.join(stack)
print(stack)
>>> 'acdb'Counter를 활용,lst를 dict 형태로 바꾼다.- 빈 list
stack을 선언한다. - 문자열
lst에서 하나씩char을 꺼내stack에 삽입 혹은 삭제한다.- 만약
stack이 빈 열일 경우,char을 삽입한다. - 만약
stack이 빈 열이 아닐 경우:stack[-1]이char보다 뒤에 있을 경우,stack[-1]은 삭제- 그리고 해당
char을 삽입 - 이 때
stack[-1]이 더 이상myDict에 없다면, 그대로 두고char을 그 뒤에 삽입
- 만약
char이stack에 이미 있다면, pass 한다.
- 만약
(220625 update) Stack과 Queue는 언제 쓰는가?
stack, queue 등의 자료구조는 보통 ADT라고 부르며, 자료구조의 한 형태다. (ADT: Abstract Data Type, 추상 자료형)
그렇기 때문에, 이를 위한 정확한 코드가 있는 것이 아니라 '구조 양식' 정도라고 봐야하겠다.
위키백과에서 '추상 자료형'을 검색하면 '추상 자료형'과 '추상적 자료구조'가 약간 개념이 다른데, 연산에 대한 시간 복잡도 명기 유무의 차이가 있다.
어쨌든, 아래와 같이 stack/queue는 다양한 상황에 적용된다.
- 웹브라우저에서 '뒤로가기' 클릭 (stack)
- 문서 작성하다가
ctrl+z를 눌러서 되돌리기 (stack) - 소비자 주문 처리 (queue)
- 콜센터 백엔드 - 전화 온 순서대로 상담 (queue)

이미지 출처: https://youtu.be/Nk_dGScimz8
참고 자료
python 공식 문서
https://labuladong.gitbook.io/algo-en/ii.-data-structure/implementqueueusingstacksimplementstackusingqueues
https://youtu.be/Nk_dGScimz8
