1. Introduction
함수는 주로 텍스트 처리를 위해 쓰이며 $(fn, arguments) 혹은 ${fn, arguments} 와 같은 형식으로 호출한다:
bar := ${subst not, totally, "I am not superman"}
all:
@echo $(bar)만일 공백이나 따옴표를 치환하고 싶을 땐 변수를 사용하라:
comma := ,
empty:=
space := $(empty) $(empty)
foo := a b c
bar := ${subst $(space),$(comma),$(foo))
all:
@echo $(bar)인자들의 시작에 공백을 추가하지 마라. 이는 문자열의 한 부분으로 취급된다:
comma := ,
empty:=
space := $(empty) $(empty)
foo := a b c
bar := $(subst $(space), $(comma) , $(foo))
all:
@echo $(bar)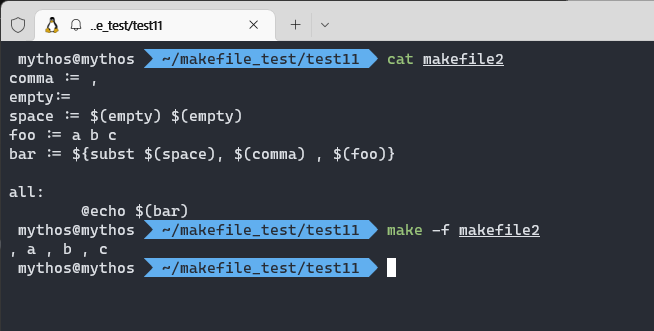
2. String Substitution
${patsubst pattern,replace,text) 는 다음과 같이 동작한다:
Finds whitespace-separated words in text that match pattern and replaces them with replacement. Here pattern may contain a ‘%’ which acts as a wildcard, matching any number of any characters within a word. If replacement also contains a ‘%’, the ‘%’ is replaced by the text that matched the ‘%’ in pattern. Only the first ‘%’ in the pattern and replacement is treated this way; any subsequent ‘%’ is unchanged.
text내에서 공백으로 나뉘어진 단어들 중pattern과 일치하는 것들을 찾고, 이들을replacement로 치환한다.- 위
pattern이%를 포함하고 있다면 이는 단어 내에서 어떤 문자든 그 길이에 관계 없이 일치된 것들로 취급되는wildcard로써 동작한다. - 만일
replacement또한%를 포함한다면%는pattern에서%로 일치되어진 문자들로 치환된다. pattern과replace내에서 오직 첫 번째%만이 이러한 방식으로 취급되어진다. 그 이후의%는 변하지 않는다.
치환 참조 ${text:pattern=replacement} 는 위의 축약형이다.
그 다음으로 접미사(suffix) 에 대한 치환만을 수행하는 ${text:suffix=replacement} 가 존재한다. 단, 여기에서 % 는 사용되지 않는다.
foo := a.o b.o l.a c.o
one := $(patsubst %.o,%.c,$(foo))
# This is a shorthand for the above
two := $(foo:%.o=%.c)
# This is the suffix-only shorthand, and is also equivalent to the above.
three := $(foo:.o=.c)
all:
echo $(one)
echo $(two)
echo $(three)3. foreach 함수
foreach 함수는 다음과 같다: ${foreach var,list,text}. 이는 list 내의 단어들 (공백으로 나뉘어진) 을 text 로 변환한다. var 는 list 내의 각 단어들로 설정되고, text 는 각 단어들에 대해 확장된다.
이하의 예시는 각 단어에 느낌표를 덧붙인다:
foo := who are you
# For each "word" in foo, output that same word with an exclamation after
bar := $(foreach wrd,$(foo),$(wrd)!)
all:
# Output is "who! are! you!"
@echo $(bar)4. if 함수
if 함수는 첫 번째 인자가 비었는지 확인한다. 만일 그렇다면 두 번째 인자를 실행하그, 그렇지 않은 경우 세 번째를 실행한다:
foo := $(if this-is-not-empty,then!,else!)
empty :=
bar := $(if $(empty),then!,else!)
all:
@echo $(foo)
@echo $(bar)5. call 함수
make 는 간단한 함수들의 생성을 지원한다. 변수를 생성함으로써 함수를 "정의" 할 수 있으나, 매개변수로 $(0), $(1), etc. 를 써야 한다. 그 뒤에 특수한 call 함수를 사용하여 함수를 호출할 수 있다. 문법은 ${call variable,param,param} 이다. $(0) 는 변수인 반면, $(1), $(2), etc. 는 매개변수이다.
sweet_new_fn = Variable Name: $(0) First: $(1) Second: $(2) Empty Variable: $(3)
all:
# Outputs "Variable Name: sweet_new_fn First: go Second: tigers Empty Variable:"
@echo $(call sweet_new_fn, go, tigers)6. shell 함수
shell 함수는 shell 을 부르지만 개행을 공백으로 치환한다.
all:
@echo $(shell ls -la) # Very ugly because the newlines are gone!출처
[사이트] https://makefiletutorial.com/#flavors-and-modification
[사이트] https://www.gnu.org/software/make/manual/html_node/Text-Functions.html#Text-Functions
