
Decision Transformer: Reinforcement Learning via Sequence Modeling
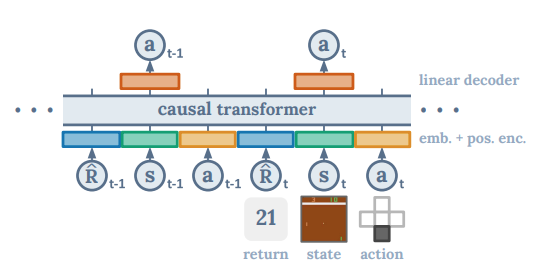
Decision Transformer는 시퀀스 모델링 문제를 해결하기 위해 강화학습을 사용한 프레임워크. 트랜스포머 구조에서 단순하고, 확장성 있게 적용할 수 있다. 그리고 GPT계열의 모델과 BERT 모델들 관련해서 발전된 것을 적용할 수 있다. Decision Transformer는 강화학습의 문제를 conditional sequence modeling으로 바꾼다. 이전의 강화학습 접근법에서 value function에 접근하거나 policy gradient를 계산 햇던것과는 달리 Decision Transformer의 경우 causally masked Transformer를 활용해서 단순하게 optimal action들을 얻는다.
autoregressive model이 원하는 결과(reward), 과거의 상태, 액션들에 대해 조절함으로써 Decision Transformer 모델은 원하는 결과를 얻기 위한 미래의 행동들을 생성할 수 있다.
Decision Transformer의 모습은 단순하지만, Atari, OpenAI Gym, Key-to-Door에서 SOTA를 달성했다.
Code
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import transformers
from decision_transformer.models.model import TrajectoryModel
from decision_transformer.models.trajectory_gpt2 import GPT2Model
class DecisionTransformer(TrajectoryModel):
"""
This model uses GPT to model (Return_1, state_1, action_1, Return_2, state_2, ...)
"""
def __init__(
self,
state_dim,
act_dim,
hidden_size,
max_length=None,
max_ep_len=4096,
action_tanh=True,
**kwargs
):
super().__init__(state_dim, act_dim, max_length=max_length)
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
config = transformers.GPT2Config(
vocab_size=1, # doesn't matter -- we don't use the vocab
n_embd=hidden_size,
**kwargs
)
# note: the only difference between this GPT2Model and the default Huggingface version
# is that the positional embeddings are removed (since we'll add those ourselves)
self.transformer = GPT2Model(config)
self.embed_timestep = nn.Embedding(max_ep_len, hidden_size)
self.embed_return = torch.nn.Linear(1, hidden_size)
self.embed_state = torch.nn.Linear(self.state_dim, hidden_size)
self.embed_action = torch.nn.Linear(self.act_dim, hidden_size)
self.embed_ln = nn.LayerNorm(hidden_size)
# note: we don't predict states or returns for the paper
self.predict_state = torch.nn.Linear(hidden_size, self.state_dim)
self.predict_action = nn.Sequential(
*([nn.Linear(hidden_size, self.act_dim)] + ([nn.Tanh()] if action_tanh else []))
)
self.predict_return = torch.nn.Linear(hidden_size, 1)
def forward(self, states, actions, rewards, returns_to_go, timesteps, attention_mask=None):
batch_size, seq_length = states.shape[0], states.shape[1]
if attention_mask is None:
# attention mask for GPT: 1 if can be attended to, 0 if not
attention_mask = torch.ones((batch_size, seq_length), dtype=torch.long)
# embed each modality with a different head
state_embeddings = self.embed_state(states)
action_embeddings = self.embed_action(actions)
returns_embeddings = self.embed_return(returns_to_go)
time_embeddings = self.embed_timestep(timesteps)
# time embeddings are treated similar to positional embeddings
state_embeddings = state_embeddings + time_embeddings
action_embeddings = action_embeddings + time_embeddings
returns_embeddings = returns_embeddings + time_embeddings
# this makes the sequence look like (R_1, s_1, a_1, R_2, s_2, a_2, ...)
# which works nice in an autoregressive sense since states predict actions
stacked_inputs = torch.stack(
(returns_embeddings, state_embeddings, action_embeddings), dim=1
).permute(0, 2, 1, 3).reshape(batch_size, 3*seq_length, self.hidden_size)
stacked_inputs = self.embed_ln(stacked_inputs)
# to make the attention mask fit the stacked inputs, have to stack it as well
stacked_attention_mask = torch.stack(
(attention_mask, attention_mask, attention_mask), dim=1
).permute(0, 2, 1).reshape(batch_size, 3*seq_length)
# we feed in the input embeddings (not word indices as in NLP) to the model
transformer_outputs = self.transformer(
inputs_embeds=stacked_inputs,
attention_mask=stacked_attention_mask,
)
x = transformer_outputs['last_hidden_state']
# reshape x so that the second dimension corresponds to the original
# returns (0), states (1), or actions (2); i.e. x[:,1,t] is the token for s_t
x = x.reshape(batch_size, seq_length, 3, self.hidden_size).permute(0, 2, 1, 3)
# get predictions
return_preds = self.predict_return(x[:,2]) # predict next return given state and action
state_preds = self.predict_state(x[:,2]) # predict next state given state and action
action_preds = self.predict_action(x[:,1]) # predict next action given state
return state_preds, action_preds, return_preds
def get_action(self, states, actions, rewards, returns_to_go, timesteps, **kwargs):
# we don't care about the past rewards in this model
states = states.reshape(1, -1, self.state_dim)
actions = actions.reshape(1, -1, self.act_dim)
returns_to_go = returns_to_go.reshape(1, -1, 1)
timesteps = timesteps.reshape(1, -1)
if self.max_length is not None:
states = states[:,-self.max_length:]
actions = actions[:,-self.max_length:]
returns_to_go = returns_to_go[:,-self.max_length:]
timesteps = timesteps[:,-self.max_length:]
# pad all tokens to sequence length
attention_mask = torch.cat([torch.zeros(self.max_length-states.shape[1]), torch.ones(states.shape[1])])
attention_mask = attention_mask.to(dtype=torch.long, device=states.device).reshape(1, -1)
states = torch.cat(
[torch.zeros((states.shape[0], self.max_length-states.shape[1], self.state_dim), device=states.device), states],
dim=1).to(dtype=torch.float32)
actions = torch.cat(
[torch.zeros((actions.shape[0], self.max_length - actions.shape[1], self.act_dim),
device=actions.device), actions],
dim=1).to(dtype=torch.float32)
returns_to_go = torch.cat(
[torch.zeros((returns_to_go.shape[0], self.max_length-returns_to_go.shape[1], 1), device=returns_to_go.device), returns_to_go],
dim=1).to(dtype=torch.float32)
timesteps = torch.cat(
[torch.zeros((timesteps.shape[0], self.max_length-timesteps.shape[1]), device=timesteps.device), timesteps],
dim=1
).to(dtype=torch.long)
else:
attention_mask = None
_, action_preds, return_preds = self.forward(
states, actions, None, returns_to_go, timesteps, attention_mask=attention_mask, **kwargs)
return action_preds[0,-1]