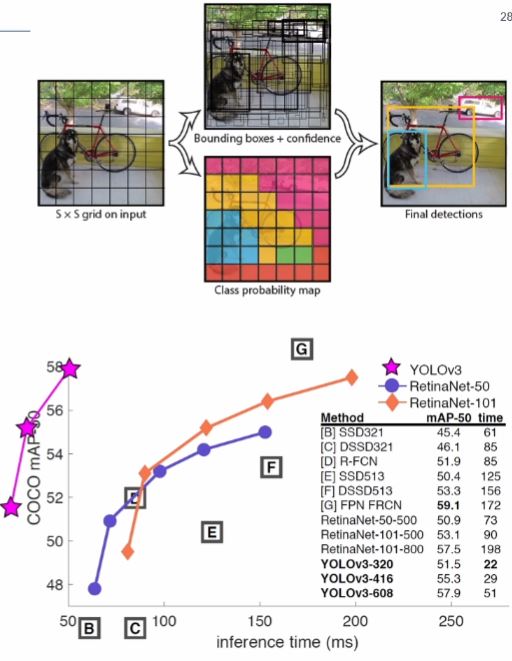
YOLO 개요
YOLOv3 객체 검출
-
YOLO란?
- You Only Look Once
- 실시간 객체 검출 딥러닝 알고리즘
- https://pjreddie.com/darknet/yolo/
-
YOLOv3
- 2018년 4월 발표된 Tech Report
- 기존 객체 검출 방법과 성능은 비슷하고 속도는 훨씬 빠름
- COCO 데이터셋 사용
- https://cocodataset.org/
- 80개 클래스 객체 검출
-
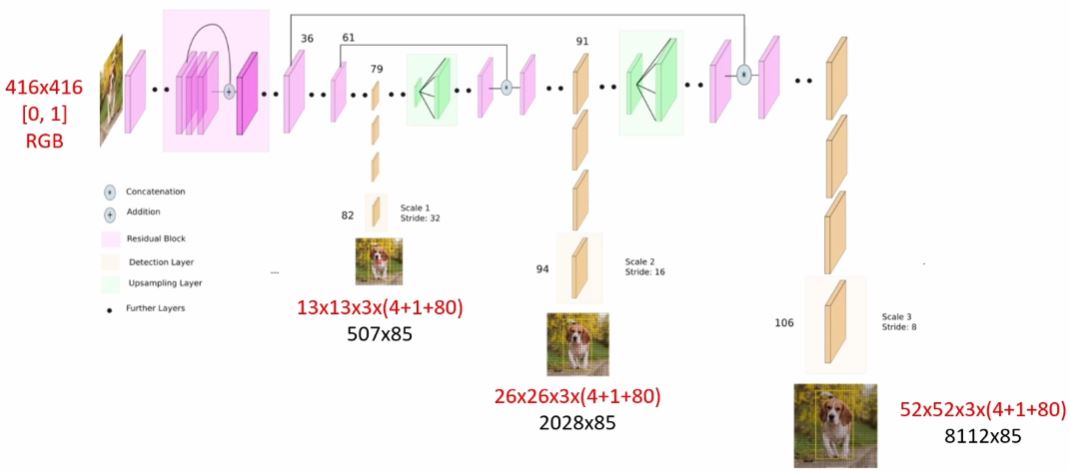
YOLOv3 네트워크 구조
- 입력은 하나지만 출력은 3군데로 나누어져있음
-
YOLOv3 입력
- Size: (320,320),(416,416),(608,608)
- Scale: 0.00392(1/255.)
- Mean: [0,0,0]
- RGB: true
-
YOLOv3 출력
- 3개의 출력 레이어
- "yolo_82" 레이어 출력: 507x85, CV_32FC1
- "yolo_94" 레이어 출력: 2028x85, CV_32FC1
- "yolo_106" 레이어 출력: 8112x85, CV_32FC1
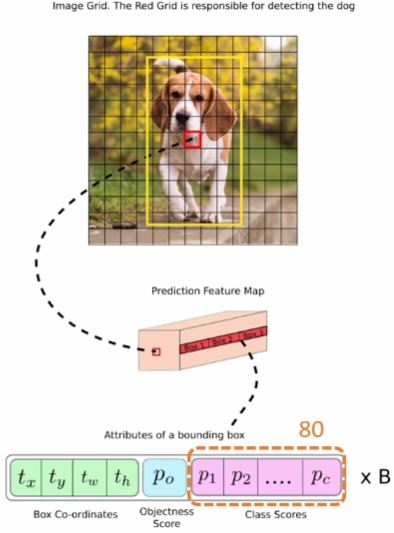
- 85개중 앞4개()
- 는 바운딩 박스에서 가운데 센터 포인트의 좌표
- 는 바운딩 박스의 가로크기, 세로 크기
- 라는 5번째 column값은 특정 클래스일 확률
- 나머지 80개의 column은 1번클래스부터 80번클래스에 대한 확률값 혹은 confidence값
- 80개의 column중에서 가장 확률이 높은 index에 해당하는 클래스에 바운딩 박스가 속한다.
- 85개중 앞4개()
-
YOLOv3 모델 & 설정 파일 다운로드
OpenCV YOLO v3 예제 프로그램
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include "opencv2/opencv.hpp"
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
using namespace cv::dnn;
int main()
{
// These files can be downloaded here: https://pjreddie.com/darknet/yolo/
const String config = "yolov3.cfg";
const String model = "yolov3.weights";
const float confThreshold = 0.5f;
const float nmsThreshold = 0.4f;
Net net = readNet(config, model); // readnet함수 이용하여 객체 생성
if (net.empty()) {
cerr << "Network load failed!" << endl;
return -1;
}
#if 0 // cpu로
net.setPreferableTarget(DNN_TARGET_CPU);
net.setPreferableBackend(DNN_BACKEND_OPENCV);
#else // gpu로
net.setPreferableTarget(DNN_TARGET_CUDA);
net.setPreferableBackend(DNN_BACKEND_CUDA);
#endif
// Class name file can be downloaded here: https://github.com/pjreddie/darknet/tree/master/data/
vector<string> classNamesVec;
ifstream classNamesFile("coco.names"); //coco names 불러와서
if (classNamesFile.is_open()) {
string className = "";
while (std::getline(classNamesFile, className))
classNamesVec.push_back(className); // vector에 한줄한줄 추가
}
// Video file open
VideoCapture cap("Pexels Videos 1721294.mp4");
if (!cap.isOpened()) {
cerr << "Video open failed!" << endl;
return -1;
}
// Get the names of the output layers
vector<String> outputLayers = net.getUnconnectedOutLayersNames(); // 3개의 아웃풋 레이어 이름반환함수
Mat frame;
while (true) {
cap >> frame;
if (frame.empty())
break;
// Convert Mat to batch of images
Mat blob = blobFromImage(frame, 1 / 255.f, Size(416, 416), Scalar(), true); // 1/255.f = 0~1사이 정규화, 영상의 blob크기 416,416, swap rb = true
// Set the network input
net.setInput(blob); // blob을 네트워크의 입력으로 주고
// compute output
vector<Mat> outs;
net.forward(outs, outputLayers);
vector<double> layersTimings;
double time_ms = net.getPerfProfile(layersTimings) * 1000 / getTickFrequency();
putText(frame, format("FPS: %.2f ; time: %.2f ms", 1000.f / time_ms, time_ms),
Point(20, 30), 0, 0.75, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 1, LINE_AA);
vector<int> classIds;
vector<float> confidences;
vector<Rect> boxes;
for (auto& out : outs) {
// Scan through all the bounding boxes output from the network and keep only the
// ones with high confidence scores. Assign the box's class label as the class
// with the highest score for the box.
float* data = (float*)out.data;
for (int j = 0; j < out.rows; ++j, data += out.cols) {
Mat scores = out.row(j).colRange(5, out.cols);
double confidence;
Point classIdPoint;
// Get the value and location of the maximum score
minMaxLoc(scores, 0, &confidence, 0, &classIdPoint);
if (confidence > confThreshold) {
int cx = (int)(data[0] * frame.cols);
int cy = (int)(data[1] * frame.rows);
int bw = (int)(data[2] * frame.cols);
int bh = (int)(data[3] * frame.rows);
int sx = cx - bw / 2;
int sy = cy - bh / 2;
classIds.push_back(classIdPoint.x);
confidences.push_back((float)confidence);
boxes.push_back(Rect(sx, sy, bw, bh));
}
}
}
// Perform non maximum suppression to eliminate redundant overlapping boxes with
// lower confidences
vector<int> indices;
NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, confThreshold, nmsThreshold, indices); // 중복되는 박스중 좋은 바운딩박스 하나만 남겨주는 함수
// nmsThreshold: 겹쳐진 기준, 0.4로 줌. 겹쳐진 비율이 40% 이상이면
// confidences가 confThreshold보다 가장 높은것 하나만 남겨둔다.
// boxes를 삭제하는 것이 아닌 가장 좋은 index를 indices라는 vec<int>에 저장
for (size_t i = 0; i < indices.size(); ++i) {
int idx = indices[i];
int sx = boxes[idx].x;
int sy = boxes[idx].y;
rectangle(frame, boxes[idx], Scalar(0, 255, 0));
string label = format("%.2f", confidences[idx]);
label = classNamesVec[classIds[idx]] + ":" + label;
int baseLine = 0;
Size labelSize = getTextSize(label, FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1, &baseLine);
rectangle(frame, Rect(sx, sy, labelSize.width, labelSize.height + baseLine),
Scalar(0, 255, 0), FILLED);
putText(frame, label, Point(sx, sy + labelSize.height), FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, Scalar(), 1, LINE_AA);
}
imshow("frame", frame);
if (waitKey(1) == 27)
break;
}
}