Linear Regression
= +
: 실제값
: 예측값
: 평균값
: 가중치(기울기)
: 편향(y절편)
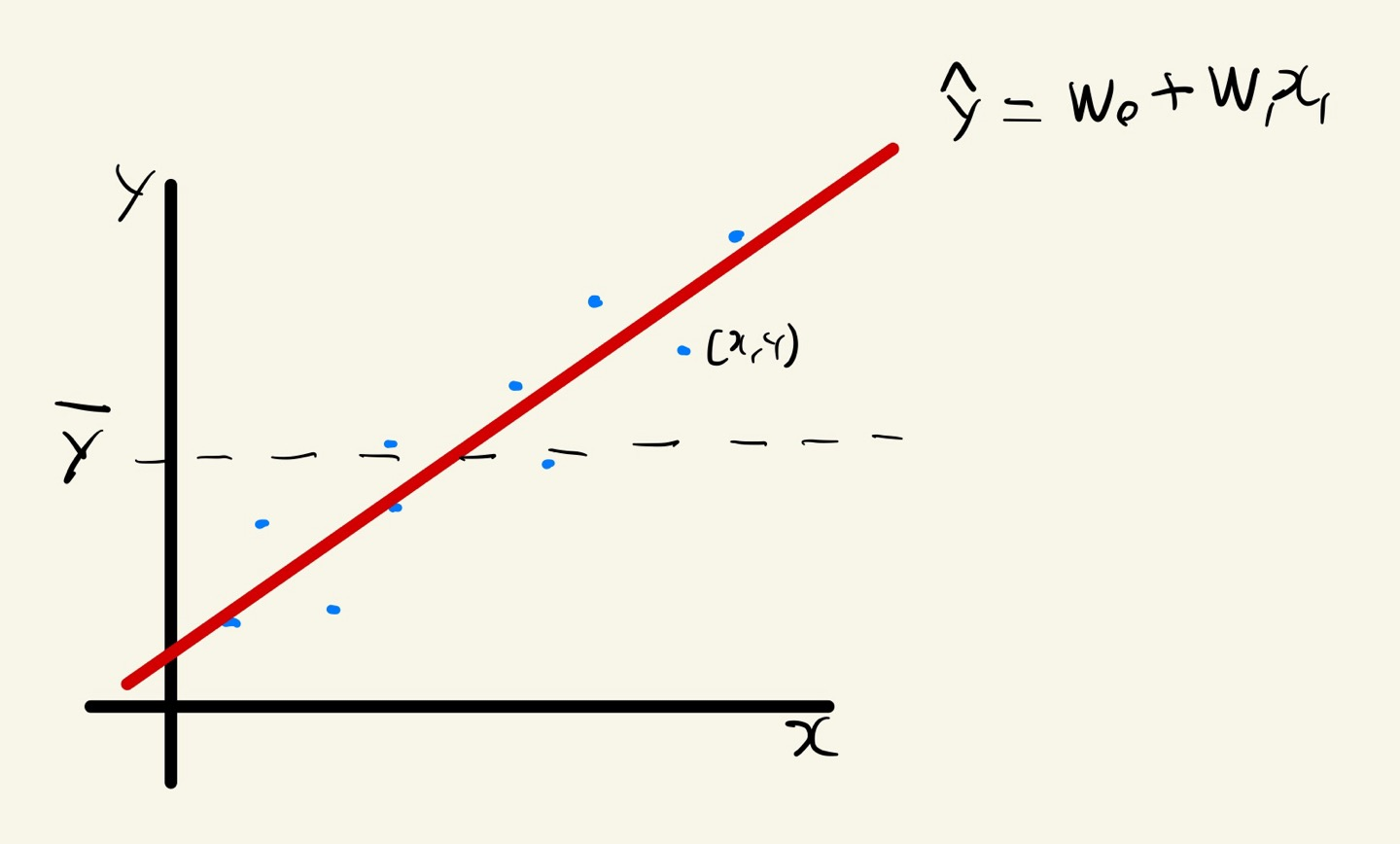
- 최적의 회귀모델은 전체 데이터의 오차 합의 최소가 되는 모델을 의미한다
- 독립변수 개수로 단순 회구와 다중 회귀로 분류
(1) 단순회귀
- 독립변수 하나가 종소변수에 영향을 미치는 선형 회귀
- 모델 학습 후 회귀계수 확인
coef_: 회귀계수(가중치)intercept_: 편향
y = -1 + 5.21x 로 표현
(2) 다중회귀
- 여러 독립변수가 종속변수에 영향을 미치는 선형 회귀
- 여러 개의 x값이 필요
y = +9 + 2.65 - 15.60 + 1.16$x_3 으로 표현
(3) 모델구현
Linear Regression은 회귀모델에서만 사용 가능함
# 회귀모델 불러오기
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
# 회귀모델 평가지표 불러오기
from sklearn.metrics import mean_absolute_error, r2_scoreK-Nearest Neighbor
-
k 최근접 이웃
-
학습용 데이터에서 k개의 최근접 이웃을 찾아 그 값들로 새로운 값을 예측함
-
k 값에 따라 예측 값이 달라져서 적절한 k 값 찾아야함
- (n_neighbors=5)이 기본 값
-
k를 1로 설정안함
-
k를 홀수로 설정
-
회귀와 분류에 모두에 사용된다.
(1) 스케일링
- 스케일링 여부에 따라 KNN 모델 성능이 달라짐
- 평가용 데이터에도 학습용데이터를 기준으로 스케일링을 수행함
정규화 (Normalization)
- 각 변수의 값이 0과 1사이 값이 됨
# 정규화 전
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 2))
plt.boxplot(x_train, vert=False, labels=list(x))
plt.show()
# 정규화 방법 1
# 최댓값, 최솟값 구하기
x_max = x_train.max()
x_min = x_train.min()
# 정규화
x_train = (x_train - x_min) / (x_max - x_min)
x_test = (x_test - x_min) / (x_max - x_min)
# 정규화 방법 2
# 모듈 불러오기
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
# 정규화
scaler = MinMaxScaler()
# scaler.fit(x_train)
x_train = scaler.fit_transform(x_train)
x_test = scaler.transform(x_test)
# 정규화 후
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 2))
plt.boxplot(x_train, vert=False, labels=list(x))
plt.show()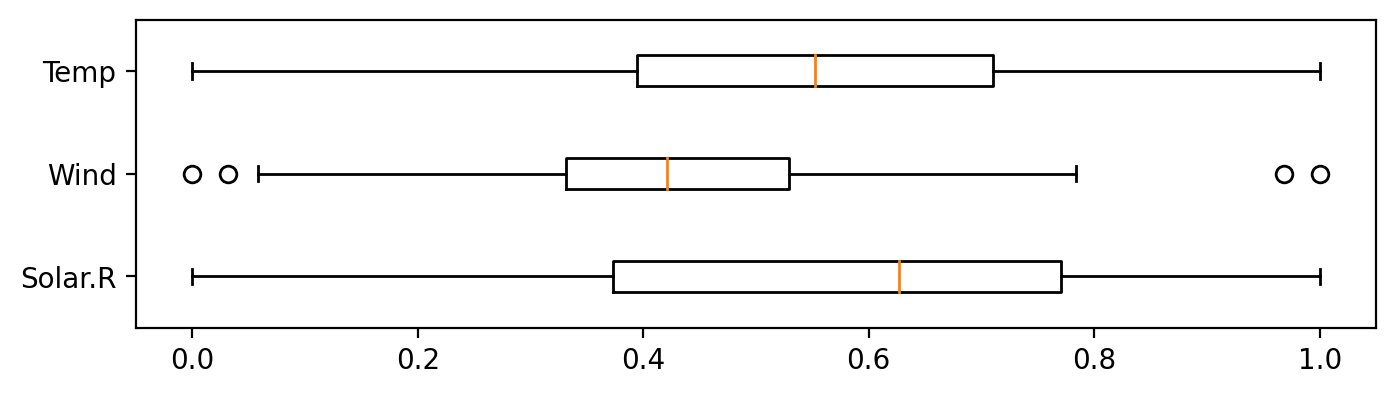
표준화 (Standardization)
- 각 변수의 평균이 0, 표준편차가 1이 됨
(2) 회귀 모델
- k개 값의 평균을 계산하여 값을 예측함
# 1단계: 불러오기
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsRegressor
from sklearn.metrics import mean_absolute_error, r2_score
# 2단계: 선언하기
model = KNeighborsRegressor(n_neighbors=5)
# 3단계: 학습하기
model.fit(x_train, y_train)
# 4단계 예측하기
y_pred = model.predict(x_test)
# 5단계: 평가하기
print('Mae: ', mean_absolute_error(y_test, y_pred))
print('R2: ', r2_score(y_test, y_pred))
# 예측값, 실젯값 시각화
plt.plot(y_test.values, label='Actual')
plt.plot(y_pred, label='Predicted')
plt.legend()
plt.ylabel('Ozone')
plt.show()
- 시각화 하여 모델성능을 비교할 수 있음
(3) 분류 모델
- 가장 많이 포함된 유형으로 분류
# 1단계: 불러오기
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, classification_report
# 2단계: 선언하기
model = KNeighborsClassifier()
# 3단계: 학습하기
model.fit(x_train, y_train)
# 4단계: 예측하기
y_pred = model.predict(x_test)
# 5단계: 평가하기
print(confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred))
print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred))분류의 경우 시각화가 어려움
가변수화 (주의)
데이터프레임에서 x와 y 데이터를 분리하고 난 뒤
가변수화를 진행한다.
# 가변수화 대상: Gender, JobSatisfaction, MaritalStatus, OverTime
dum = ['Gender', 'JobSatisfaction', 'MaritalStatus', 'OverTime']
# 가변수화
x = pd.get_dummies(x, columns=dum, drop_first=True, dtype=int)
# 확인
x.head()- 위 처럼 가변수화하는 데이터를 data가 아닌 x에 저장해줘야 한다.
- 이유는 이미 data라는 데이터프레임을 이미 x, y 분리하여 x에 저장했기 때문
Decision Tree
- 나무가지가 뻗는 형태로 분류해 나감
- 분류와 회귀 모두에 사용되는 지도학습 알고리즘
- 스케일링이나 전처리의 영향이 적음
- 과정을 눈으로 확인 가능(화이트박스모델)
- 과적합으로 모델 성능이 떨어지기 쉬움
- 트리깊이를 제한하는 가지치기 필요(max_depth)
- 분류 모델
- 마지막 노드에 있는 샘플들의 최빈값을 예측값으로 반환
- 회귀 모델
- MSE
- 마지막 노드에 있는 샘플들의 평균을 예측값으로 반환
(1) 불순도
- 순도가 높을 수록 분류가 잘된 모델임
- 불순도 수치화 지표
- 지니 불순도
- 분류 후 얼마나 잘 분류했는지 평가하느 지표
- 지니 불순도가 낮을수록 순도가 높음
- 0 ~ 0.5 사이의 값
- 완벽 분류의 경우 0
- 완벽하게 섞이면 0.5
- 엔트로피
- 0 ~ 1 사이의 값
- 완벽 분류의 경우 0
- 완벽하게 섞이면 1
- 지니 불순도
(2) 정보이득
- 정보이득이 크다 = 어떤 속성으로 분할할대 불순도가 줄어든다
- 정보이득이 가장 큰 속성부터 분할함
(3) 가지치기
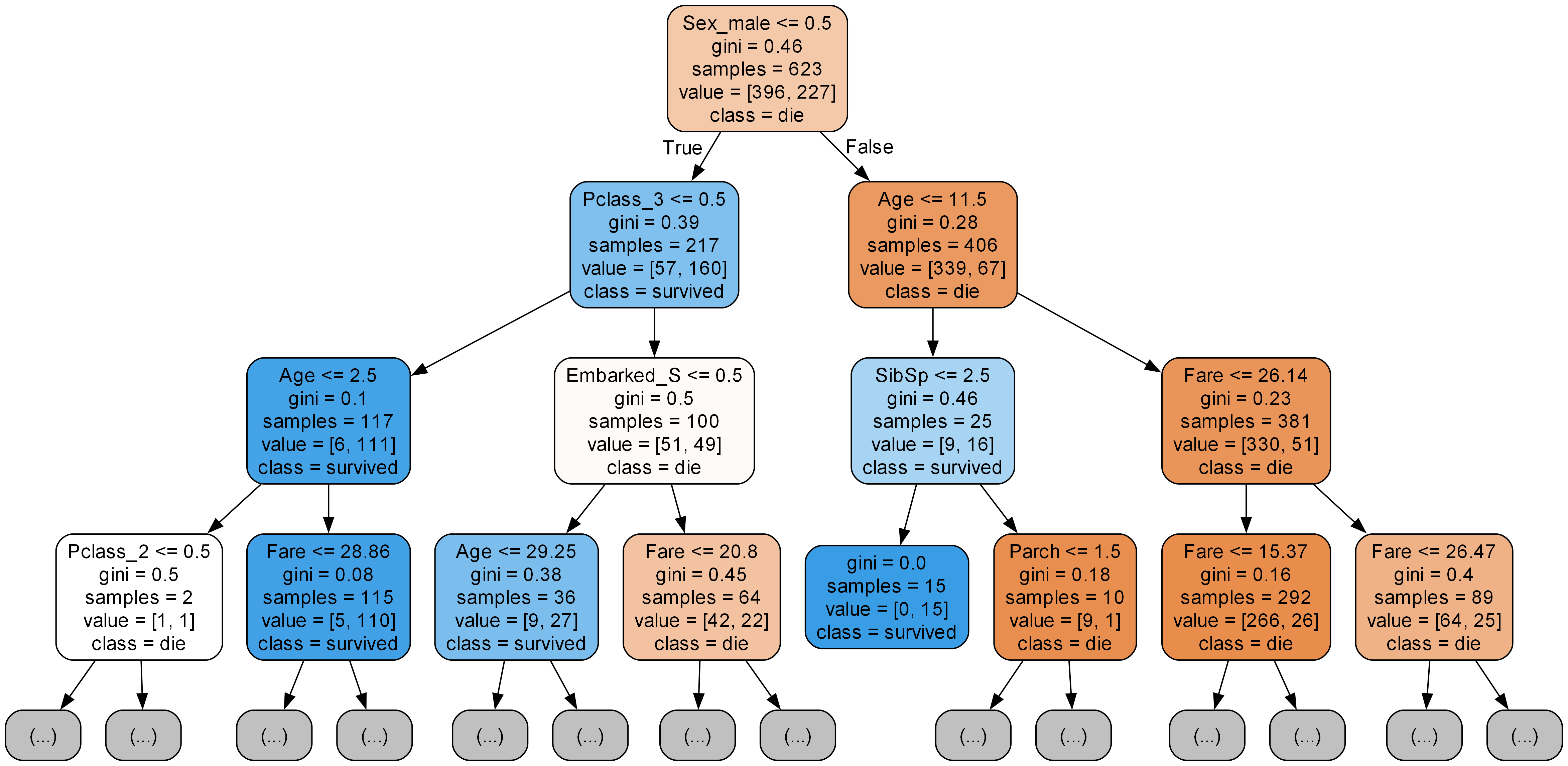
- 색이 진할수록 분류가 잘된 것임
max_depth,min_samples_leaf,min_samples_split- 학습데이터 성능은 낮아지나, 평가데이터 성능 향상
- max_depth
- 트리의 최대 깊이 (디폴트값 None)
- min_samples_split
- 노드를 분할하기 위한 최소한의 샘플 개수 (디폴트값 2)
- 과적합 방지 목적
- min_samples_leaf
- 리프노드가 되기위한 최소한의 샘플 수 (디폴트값 1)
(4) 시각화 expot_graphviz
export_graphviz
# 시각화 모듈 불러오기
from sklearn.tree import export_graphviz
from IPython.display import Image
# 이미지 파일 만들기
export_graphviz(model, # 모델 이름
out_file='tree.dot', # 파일 이름
feature_names=list(x), # Feature 이름
class_names=['die', 'survived'], # Target Class 이름
rounded=True, # 둥근 테두리
precision=2, # 불순도 소숫점 자리수
max_depth=3, # 표시할 트리 깊이
filled=True) # 박스 내부 채우기
# 파일 변환
!dot tree.dot -Tpng -otree.png -Gdpi=300
# 이미지 파일 표시
Image(filename='tree.png')변수중요도 feature_importances_
- featureimportances 속성값으로 변수 중요도 확인
- 값이 클 수록 feature 의 중요도가 높음
# 변수 중요도
plt.figure(figsize=(5, 5))
plt.barh(list(x), model.feature_importances_)
# plt.barh(list(x), model.best_estimator_.feature_importances_)
plt.show()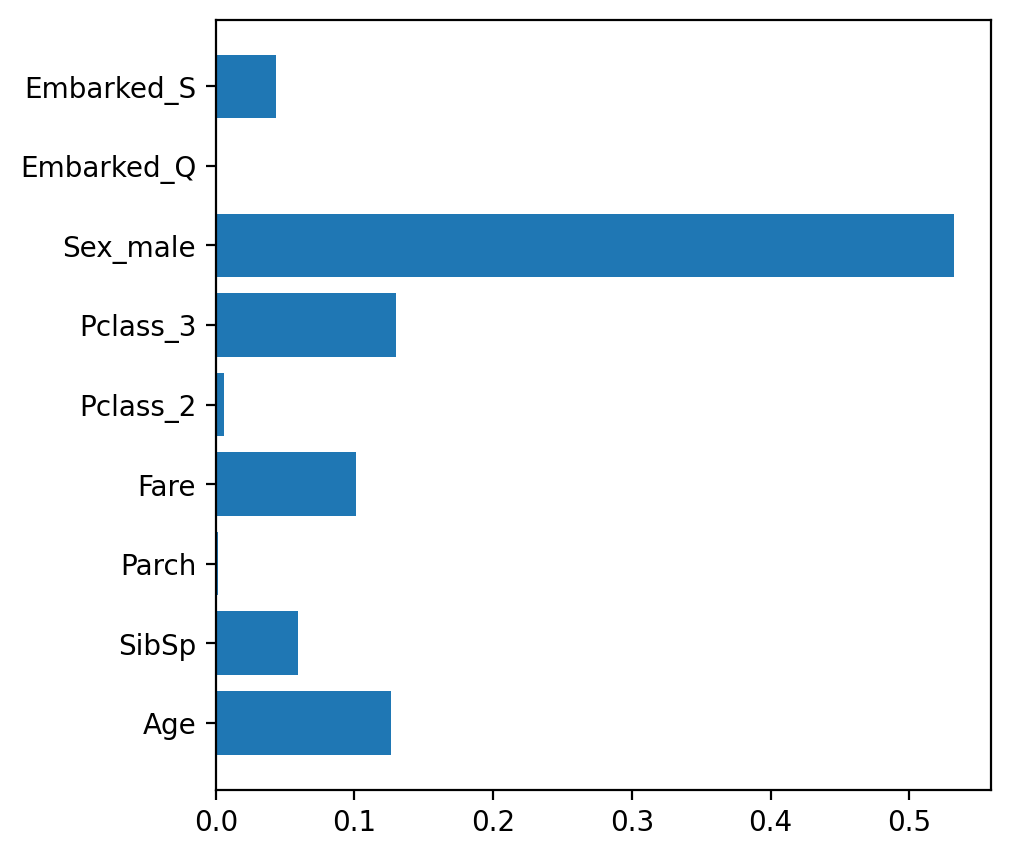
- 중요도를 기준으로 정렬
# 데이터프레임 만들기
df = pd.DataFrame()
df['feature'] = list(x)
df['importance'] = model.feature_importances_
df.sort_values(by='importance', ascending=True, inplace=True)
# 시각화
plt.figure(figsize=(5, 5))
plt.barh(df['feature'], df['importance'])
plt.show()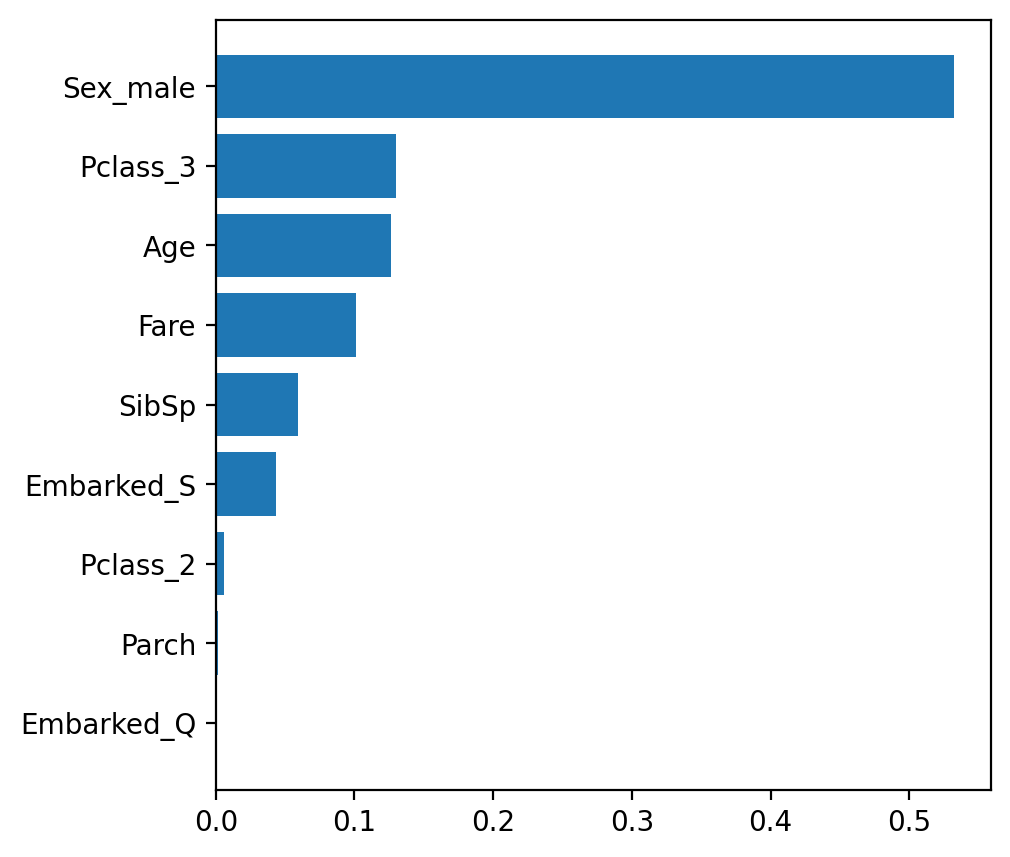
(5) 분류 모델 구현
# 1단계: 불러오기
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, classification_report
# 2단계: 선언하기
model = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=5, random_state=1)
# 3단계: 학습하기
model.fit(x_train, y_train)
# 4단계: 예측하기
y_pred = model.predict(x_test)
# 5단계 평가하기
print(confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred))
print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred))(6) 회귀 모델 구현
# 1단계: 불러오기
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor
from sklearn.metrics import mean_absolute_error, r2_score
# 2단계: 선언하기
model = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=5)
# 3단계: 학습하기
model.fit(x_train, y_train)
# 4단계: 예측하기
y_pred = model.predict(x_test)
# 5단계 평가하기
print(mean_absolute_error(y_test, y_pred))
print(r2_score(y_test, y_pred))
