앙상블
- 여러개의 모델을 결합하여 강력한 모델을 생성한다.
- 여러 모델을 결합하기 위한 방법
- 보팅(voting)
- 배깅(bagging)
- 부스팅(Boosting)
- 스태킹(Stacking)
1. 보팅(voting)
- 여러 모델들(다른 알고리즘)의 예측 결과를 투표를 통해 최종 결과를 결정하는 방법
- 하드보팅: 다수 모델이 예측한 값이 최종 결과값
- 소프트보팅: 모든 모델이 예측한 값의 확률 평균을 구한뒤 가장 높은 확률값을 가진 것을 선택
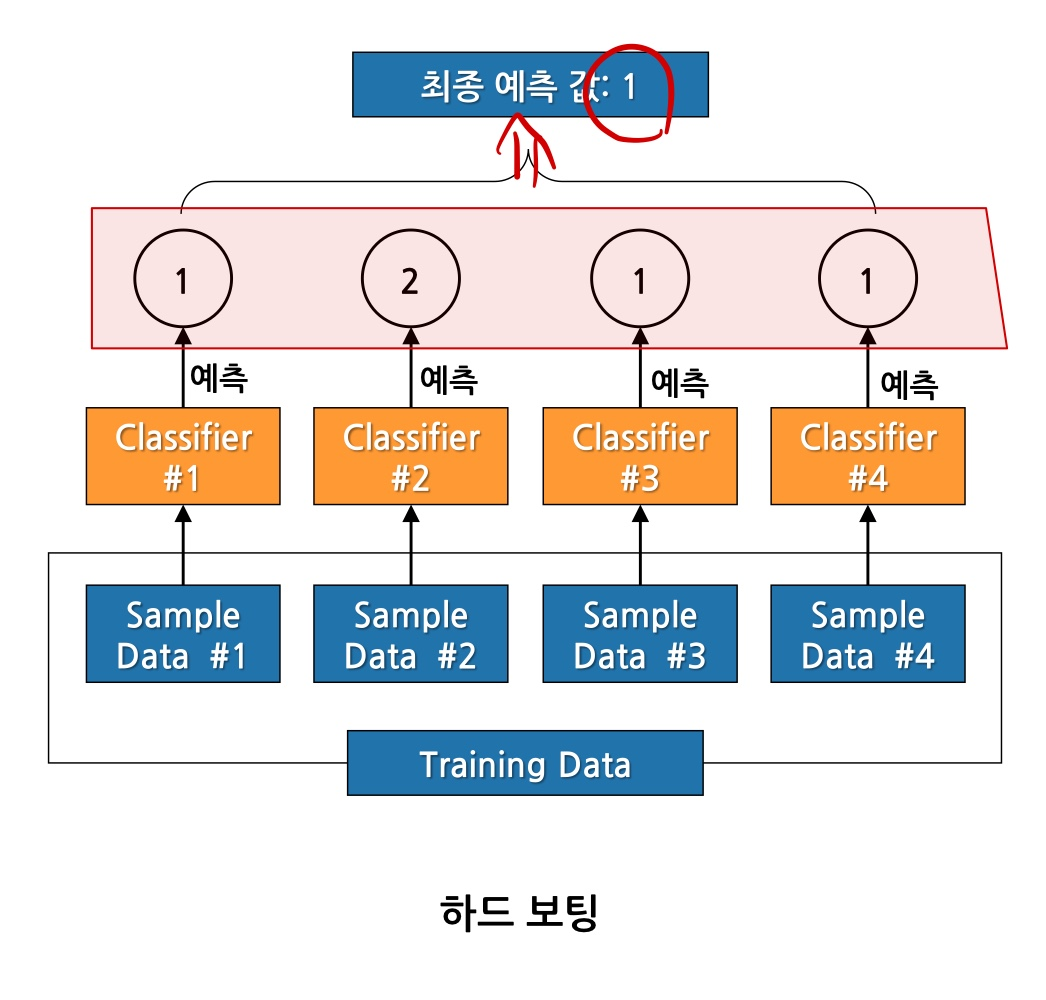
하드보팅
- 각각의 샘플에서 분류되어 예측한 값들을 보고 가장 많은 것을 최종 결과값으로 선택함
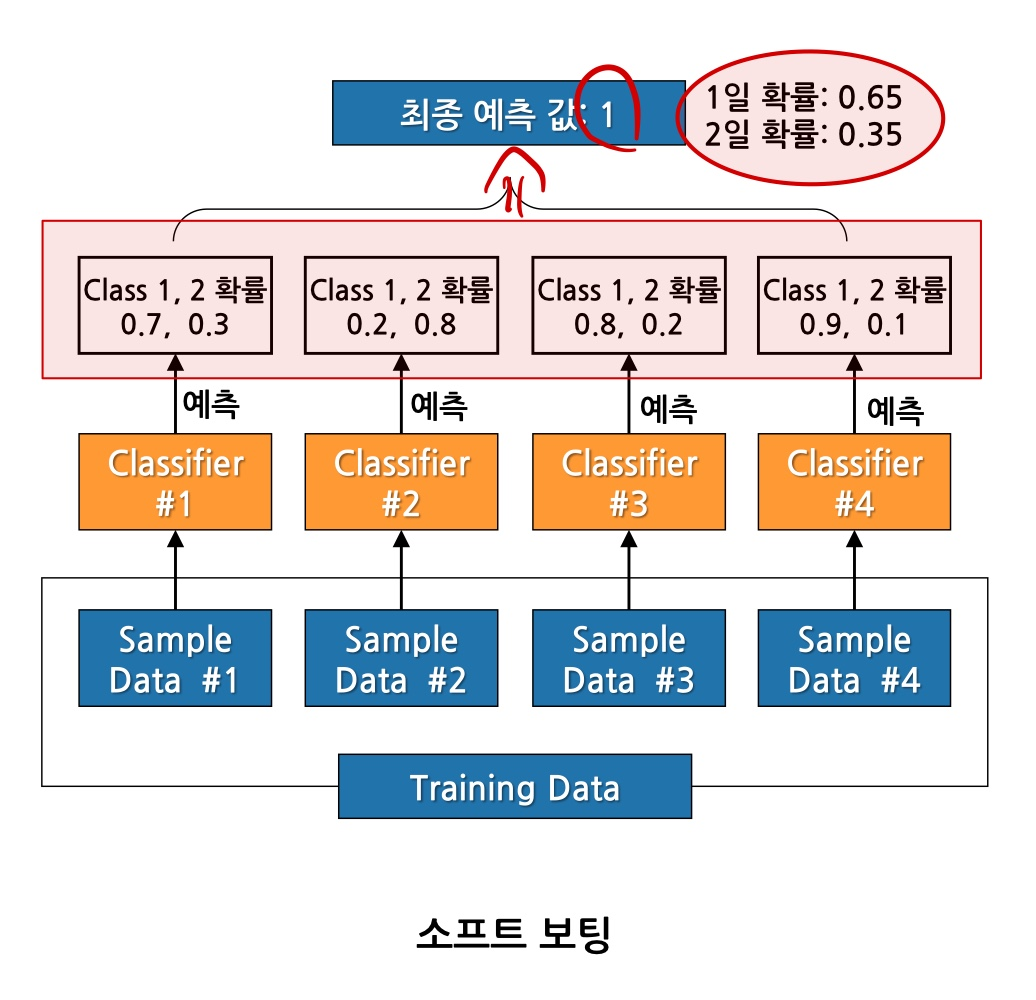
소프트보팅
- 각각의 샘플에서 분류되어 확률을 모두 비교한 뒤 평균을 내서 그 확률이 높은 것을 선택함
2. 배깅(bagging)
- Bootstrap Aggregating의 약자로 복원 추출의 의미를 가진다.
- 복원추출한 데이터로 모델들을 학습시킨 후, 예측 결과를 집계하여 최종 결과를 얻는 방법
- 중복 허용
- 범주형 데이터 => 투표 방식(voting)으로 집계
- 연속형 데이터 => 평균으로 결과 집계
Random Forest 가 대표적인 배깅 알고리즘
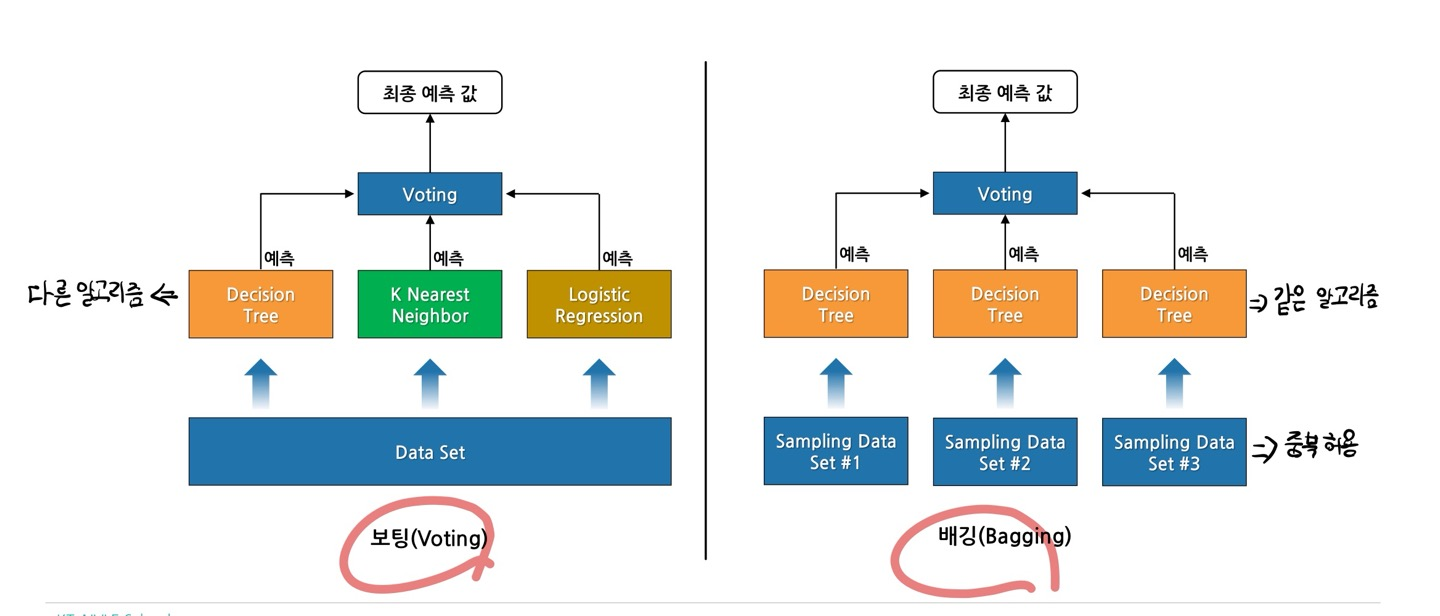
- 보팅은 각각 다른 알고리즘에서 예측되고, 데이터가 중복되지 않는다.
- 배깅은 같은 알고리즘에서 예측되고, 데이터 중복이 허용된다/.
Random Forest
- 배깅의 대표적 알고리즘
- Decision Tree 모델을 사용하여 데이터 샘플링함
- 1) 학습데이터에서 복원추출한 샘플을 여러개 뽑아옴
- 2) 각 샘플에서 Decision Tree를 활용하여 각각 다른 트리가 나옴
- 3) 나온 트리마다 예측이 다름
- 4) 범주형이면 보팅으로 집계
- 4) 연속형이면 평균으로 집계
주요 하이퍼파라미터
n_estimators
- 만들어질 Decision Tree개수 지정 (디폴트:100)
max_depth
Random Forest-회귀모델
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
from sklearn.metrics import mean_absolute_error, r2_score
model = RandomForestRegressor(max_depth=5,
n_estimators=100,
random_state=1)
Random Forest-분류모델
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, classification_report
model = RandomForestRegressor(max_depth=5,
n_estimators=100,
random_state=1)
3. 부스팅(Boosting)
- 이전 모델이 제대로 예측하지 못한 데이터에 가중치를 부여하여 다음 모델이 학습과 예측을 진행하는 방법
- 성능은 좋지만, 속도가 느리고 과적합 발생 가능성이 있음
- 대표적인 알고리즘:
XGBoost, LightGBM
Gradient Boost
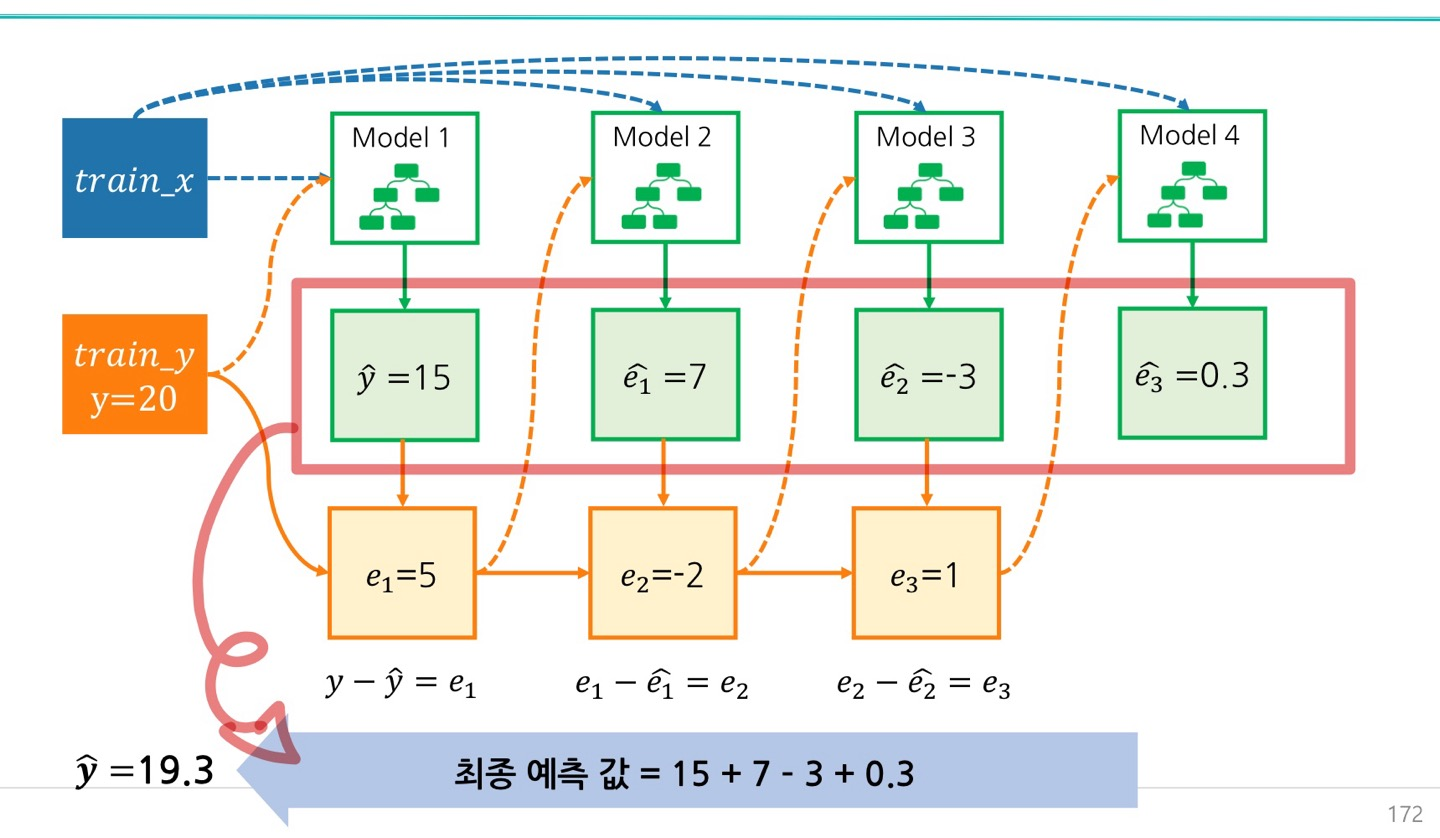
- 실제값 y는 20임
- 예측값 y는 15, 오차 5
- 오차 예측값은 7, 오차 -2
- 오차 예측값은 -3, 오차 1
이런식으로 예측 값의 합이 최종 y의 예측 값이 된다.
XGBoost
- eXtreme Gradient Boosting
- 부스팅을 구현한 대표적 알고리즘 중 하나 GBM
- GBM 알고리즘을 병렬 학습이 가능하도록 구현한 것 => XGBoost
- 결측치를 자체적으로 처리할 수 있음
주요 하이퍼파라미터
n_estimators
- 개수가 많을수록 일정 수준까지 성능이 좋아질 수 있음 (디폴트:100)
- 너무 많으면 학습시간 소요
max_depth
- 트리의 최대 깊이 (디폴트:6)
- 0을 지정하면 깊이 제한이 없어짐
XGBoost-회귀모델
from xgboost import XGBRegressor
from sklearn.metrics import mean_absolute_errorm r2_score
model = XGBRegressor(max_depth=5,
n_estimators=100,
random_state=1)
plt.figure(figsize=(5, 5))
plt.barh(list(x), model.feature_importances_)
plt.show()
XGBoost-분류모델
from xgboost import XGBClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, classification_report
model = XGBClassifier(max_depth=5,
n_estimators=100,
random_state=1)
plt.figure(figsize=(5, 5))
plt.barh(list(x), model.feature_importances_)
plt.show()
LightGBM-분류모델
from lightgbm import LGBMClassifier
model = LGBMClassifier(max_depth=5, random_state=1, verbose=-100)
4. 스태킹(Stacking)
- 여러 모델의 예측 값을 최종 모델의 학습데이터로 사용하여 예측하는 방법
[시각화]Graphviz 사용방법
from sklearn.tree import export_graphviz
from IPython.display import Image
from sklearn.tree import export_graphviz
from IPython.display import Image
export_graphviz(model,
out_file='tree.dot',
feature_names=list(x),
class_names=['die', 'survived'],
rounded=True,
precision=2,
max_depth=3,
filled=True)
!dot tree.dot -Tpng -otree.png -Gdpi=300
Image(filename='tree.png')





