미니프로젝트 1, 2일차
차량 공유 업체의 차량 사용 전 후에 촬영하는 차량의 정상/ 파손 이미지 무작위 수집을하여 분류하는 모델을 만들었다.
- 데이터 전처리
- CNN 모델링
- Transfer learning
세가지 과제를 중점으로 수행하였다.
1. 데이터 전처리
먼저 데이터를 zip 파일 형식으로 불러와 압축해제하여 구글드라이브와 연결하여 불러오는 형식으로 진행하였다.
# 데이터 압축해제 함수
def dataset_extract(file_name) :
with zipfile.ZipFile(file_name, 'r') as zip_ref :
file_list = zip_ref.namelist()
if os.path.exists(f'/content/{file_name[-14:-4]}/') :
print(f'데이터셋 폴더가 이미 존재합니다.')
return
else :
for f in tqdm(file_list, desc='Extracting', unit='files') :
zip_ref.extract(member=f, path=f'/content/{file_name[-14:-4]}/')
# 구글 드라이브와 코랩 연결
from google.colab import drive
drive.mount('/content/drive')
# 데이터 압축해제 (경로 설정 중요)
dataset_extract('/content/drive/MyDrive/KT_deep_visualize/mini4/Car_Images.zip')압축해제를 하면 Car_images가 구글 로컬환경에 생성되어 내부에 normal과 abnormal 폴더가 있다.
# 폴더별 이미지 데이터 갯수 확인
import glob
path = '/content/Car_Images/'
print(f'정상 차량 이미지 수: {len(glob.glob(path+"normal/*"))}' )
print(f'정상 차량 이미지 수: {len(glob.glob(path+"abnormal/*"))}' )여기서 이미지 데이터는 glob.glob('경로')로 불러온다.
import random
# 정상 차량 랜덤 이미지 확인 및 형태 확인
rand_n = np.random.randint( 0, len(glob.glob(path+"normal/*"))-1 )
plt.figure(figsize=(5,5))
img = plt.imread(glob.glob(path+"normal/*")[rand_n])
plt.imshow(img)
plt.show()
print(f'이미지의 형태는 다음과 같다 : {img.shape}')
# 파손 차량 랜덤 이미지 확인 및 형태 확인
rand_n = np.random.randint( 0, len(glob.glob(path+"normal/*"))-1 )
plt.figure(figsize=(5,5))
img = plt.imread(glob.glob(path+"abnormal/*")[rand_n])
plt.imshow(img)
plt.show()
print(f'이미지의 형태는 다음과 같다 : {img.shape}')이후 데이터 전처리를 위해 y변수에 정상차량은 0, 파손차량은 1로 하여 그 개수만큼 y_normal과 y_abnormal 변수에 0과 1을 넣어준다.
# 정상 차량은 0, 파손 차량은 1
y_normal = np.zeros((302,))
y_abnormal = np.ones((303,))np.hstack() 을 사용하여 배열을 가로로 쌓아서 하나의 배열로 만들어준다.
# 정상 차량 어레이와 파손 차량 어레이 합치기
y_total = np.hstack((y_normal, y_abnormal))
y_total.shapex 데이터 리스트를 통합한다.
x_total_list = glob.glob(path+"normal/*") + glob.glob(path+"abnormal/*")
x_total_list[:5]데이터셋 분리
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# (1) train set, test set을 90:10의 비율로 분리
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test =\
train_test_split(x_total_list, y_total, test_size=0.1, random_state=2024)
x_train, x_val, y_train, y_val =\
train_test_split(x_train, y_train, test_size=0.1, random_state=2024)데이터를 모델링 하기 위해서는 np.array 형태로 데이터셋을 만들어야 한다.(reshape)
np.array로 만드는 함수를 생성해봄
import keras
# 데이터 reshape
def x_preprocessing(img_list) :
bin_list = []
for img in tqdm(img_list) :
img = keras.utils.load_img( img, target_size=(128, 128) )
img = keras.utils.img_to_array(img)
bin_list.append(img)
return np.array(bin_list)
x_tr_arr = x_preprocessing(x_train)
x_val_arr = x_preprocessing(x_val)
x_te_arr = x_preprocessing(x_test)2. CNN 모델링
# 기본 CNN
# 1. 세션 클리어
clear_session()
# 2. 모델 선언
model1 = Sequential()
model1.add( Input(shape=(128, 128, 3)) )
model1.add( Conv2D(16, (3,3), (1,1), 'same', activation='relu') )
model1.add( BatchNormalization() )
model1.add( Dropout(0.4) )
model1.add( Conv2D(32, (3,3), (1,1), 'same', activation='relu') )
model1.add( MaxPool2D((2,2), (2,2)) )
model1.add( BatchNormalization() )
model1.add( Dropout(0.4) )
model1.add( Conv2D(64, (3,3), (1,1), 'same', activation='relu') )
model1.add( MaxPool2D((2,2), (2,2)) )
model1.add( BatchNormalization() )
model1.add( Dropout(0.4) )
model1.add( Flatten() )
model1.add( Dense(128, activation='relu') )
model1.add( Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
model1.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='binary_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy']
)
model1.summary()이 방법으로 레이어층 마지막에 Dense를 더 겹겹이 쌓을수록 정확도가 높게 나왔다.
# Early Stopping
es = EarlyStopping(monitor='val_loss',
min_delta=0.3,
patience=10,
verbose=1,
restore_best_weights=True
)
model1.fit(x_tr_arr, y_train, validation_data=(x_val_arr, y_val),
epochs=10000,
callbacks=[es]
)
# 평가
model1.evaluate(x_te_arr, y_test)
# 예측
y_pred_1 = model1.predict(x_te_arr)
pred_1 = np.where(y_pred_1 >=0.5, 1, 0)
print(confusion_matrix(y_test, pred_1))
print(classification_report(y_test, pred_1))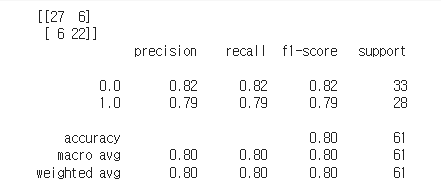
이런 결과가 나온다.
image_dataset_from_directory
from keras.utils import image_dataset_from_directory
idfd_train, idfd_valid = image_dataset_from_directory('/content/Car_Images/',
label_mode='binary',
image_size=(128,128),
shuffle=True,
seed=2024,
validation_split=0.2,
subset='both'
)이걸 사용하여 Transfer learning을 진행할 것이다.
3. Transfer Learning
Inception V3
from keras.applications.inception_v3 import InceptionV3
base_model = InceptionV3(include_top=False,
weights='imagenet',
input_shape=(128,128,3)
)
base_model.trainable = False
base_model.layers[2].trainable = False
# 모델 구조 설계
## Functional API
clear_session()
i_l = Input(shape=(128,128,3))
aug = keras.layers.Rescaling(1./255)(i_l)
aug = keras.layers.RandomFlip()(aug)
aug = keras.layers.RandomRotation(0.2)(aug)
base = base_model(aug)
h_l = keras.layers.GlobalAvgPool2D()(base)
o_l = Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')(h_l)
model2 = Model(i_l, o_l)
model2.summary()
# 컴파일
model2.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='binary_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
# 학습
hist2 = model2.fit(idfd_train, validation_data=idfd_valid,
epochs=1000, verbose=1,
callbacks=[es, rlrp]
)
y_pred2 = model2.predict(x_te_arr)
y_pred2 = np.where(y_pred2>=0.5, 1, 0)
# 성능 평가
print( classification_report(y_test, y_pred2) )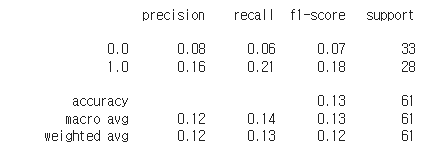
이미지 데이터수가 많이 작은 관계로 좋은 성능을 기대하기 어렵다.

