Let's go to understand GAIL algorithms.
IRL
IRL is extremely expensive to run, requiring reinforcement learning in an inner loop.
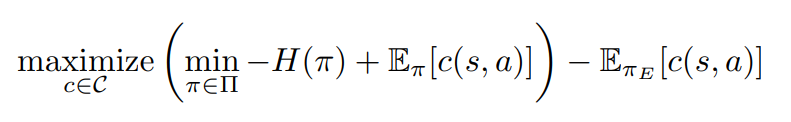
H is π's entropy, c is cost function.
Expert policy's cost function(not reward function) would be low with actual optimal action, and high without one.
So maximizing above object seems reasonable.
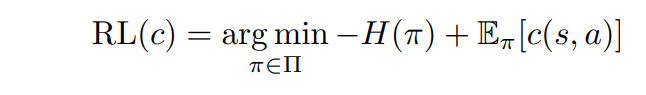
And get agent by reinforcement learning.
GAIL
GAIL can be described as 'Doing IRL and RL simultaneously'.
reward function
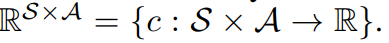
GAIL define reward fucntion like that.
I think ideal reward function would be SxAxS -> R, because it is matter to know what next state is.
But since all calculations are performed statistically, it doesn't seem to cause any problems to simply return the average reward.
IRL
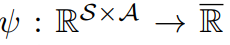
Since we use neural network, we should care about overfitting.
So convex cost function regularizer is incorporated.
I don't know what it is in detail now.
I just guess it is regularizer, it is convex.
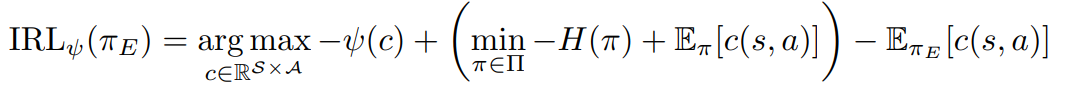
And combining with RL(c)
occupancy measure
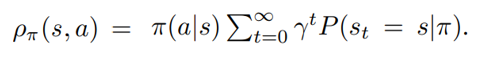
The occupancy measure can be interpreted as the distribution of state-action pairs that an agent encounters when navigating the environment with policy π.
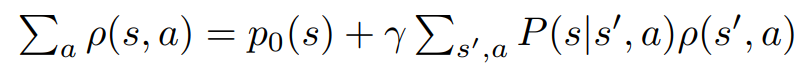
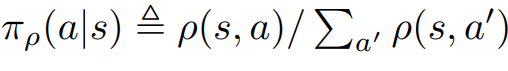
Above two equation is true.
One is about distribution of states, another one is about probability of actions.
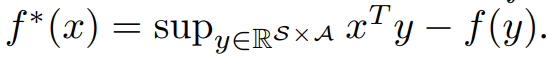
for a function f, its convex conjugate f∗ is difined like that.
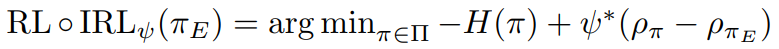
The proof is in the paper.
~~~ pass
GAIL Algorithm
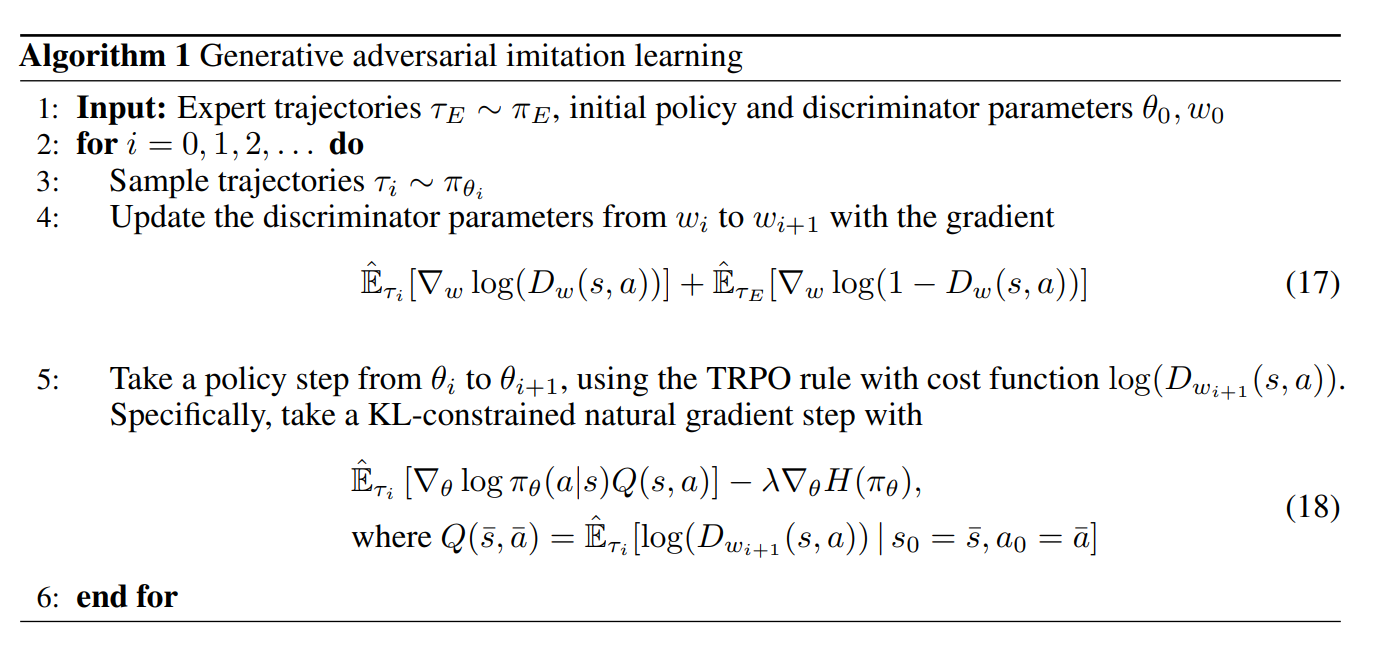
I gave up halfway through because it's too difficult.
But when I look at the final pseudocode, the GAIL algorithm seems much simpler.
It feels like the author just applied GAN to imitation learning, achieved good performance, and then analyzed it mathematically.
