Data inefficiency is a critical issue in RL.
And sometimes it could be dangerous to interact with real world.
Offline RL has an advantage in this regard.
We should know the history of deep reinforcement learning.
There was a field of reinforcement learning without neural network.
It works under the assumption of performing calculations infinitely.
And it couldn't be applied with infinite state or action settings.
In ideal setting, reinforcement learning can find optimal policy.
By applying neural network to reinforcement learning, it become impossible to find optimal policy, but it is possible be applied with infinite state or action settings.(Deep Reinforcement Learning)
Reinforcement learning works with the on-policy learning.
On-policy learning is a method of interacting with the environment in an online setting.
There is off-policy way in deep reinforcement learning, replay memory.
It is used to reduce data correlation, and it remove past memory and add new data to avoid deviating significantly from on-policy.
Offline RL don't interact with environment.
It use data which collected previously.
Offline RL
Off-Policy Evaluation via Importance Sampling
I organized the contents about importance sampling.
https://velog.io/@nrye4286/%EB%B9%84%ED%99%9C%EC%84%B1%EC%A0%95%EC%B1%85%EB%B0%A9%EB%B2%95
It is not usually used because importance sampling suffer from high variance, and this variance increases dramatically in the sequential setting.
Offline Model-Based Reinforcement Learning
This way is to training environment model, and exploiting the model.
Model Exploitation and Distribution Shift
Policy find the way which maximize rewards.
Because environment model is not perfect, it could be possible to return high reward in out-of-distribution area. This would be critical.
MOPO(Model-based Offline Policy Optimization)
To explain simply
First, training model and environment with the offline data.
Second, making k step trajectory from offline data as initial state.
Third, training policy.
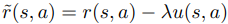
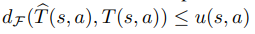
To aviod overfitting on out-of-distribution area which have potential to return high reward than exact reward, they introduce uncertainty-penalized reward.
u(error estimator) becomes higher when the transition dynamics differ from the real ones.
With u, the estimated reward is mathematically lower than the exact reward.
The proof is in the paper.
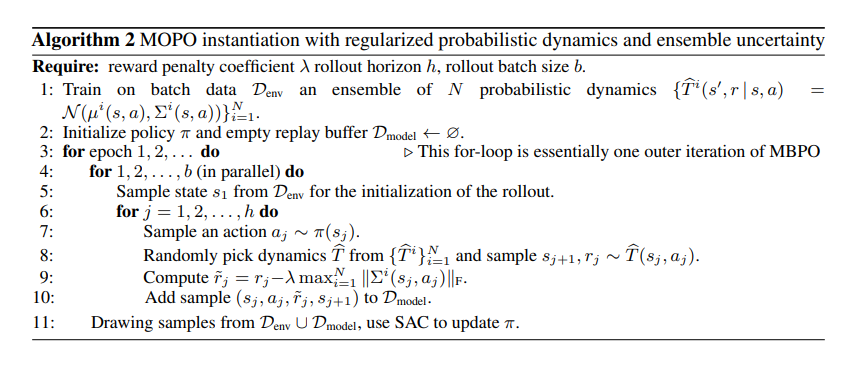
Simple explain:
T(s',r|s,a) predict two types of outputs, one is for mean(μ), another is for standard deviation(Σ).
After supervised learning, uncertainty-penalized reward which calculated with standard deciation is stored in replay buffer.
And do RL with replay buffer.
