오늘은 Driver에 대하여 알아보겠습니다.
Driver란 무엇인가?
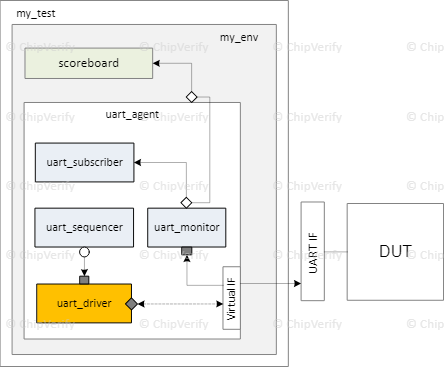
Driver는 Sequence를 Sequencer로부터 받아 DUT에 전달하는 역할을 수행하는 컴포넌트입니다.
Sequence와 어떤 메카니즘으로 data packet들을 주고받는지는 Sequence 관련 글에서 확인하실 수 있습니다!

작성법
작성법은 어렵지 않습니다. 처음 작성하시는 분들을 위해서 하나하나 설명드리겠습니다.
1~4번까지는 대부분의 driver에서 같은 형태를 가질 것입니다.
1. Driver는 uvm_driver라는 class를 extend해서 사용됩니다.
class example_driver extends uvm_driver;2. Macro를 사용해 factory에 등록합니다.
class example_driver extends uvm_driver;
`uvm_component_utils (example_driver)Factory에 등록하는 macro에 관련한 내용은 Sequence를 참고해주세요.
3. 생성자 함수를 만듭니다.
class example_driver extends uvm_driver;
`uvm_component_utils (example_driver)
function new (string name = "example_driver", uvm_component parent = null);
super.new (name, parent);
endfunction4. Build_phase에서 Virtual Interface를 Get합니다.
virtual example_if vif; //Interface에 대한 handle 선언
virtual function void build_phase (uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase (phase);
if (! uvm_config_db #(virtual if_name) :: get (this, "", "vif", vif)) begin
`uvm_fatal (get_type_name (), "Didn't get handle to virtual interface if_name")
end //vif를 get하지 못하면 fatal을 발생시켜라
endfunctionDriver는 미리 선언된 Interface를 사용하기 때문에, Build_phase에서 그러한 virtual interface(vif로 줄여 부르고는 합니다)를 get해야합니다. 더 상위 하이라키에서 set해줘야 하위 하이라키에서 get할 수 있기 때문에 어디선가 set해줬을 겁니다. 보통 인터넷의 예제에선 TEST component에서 set해줍니다.
uvm_config_db::get: UVM Configuration Database를 통해 vif라는 이름의 가상 인터페이스를 가져옵니다.
this: 이 코드가 작성된 객체.
"": 경로를 지정하는 데 사용. 빈 문자열은 현재 범위를 의미.
"vif": 가상 인터페이스의 이름.
vif: 가져온 값을 저장할 변수.
uvm_fatal은 vif를 get하지 못했을 경우 발생하도록 작성되어있으며, fatal이 발생하면 시뮬레이션을 중단합니다.
여기까지는 거의 고정적으로 작성하게 됩니다.
5. Run_phase에서 시나리오를 작성합니다.
run_phase에 원하는 시나리오를 작성하면 됩니다.
만약 item과 interface가 아래와 같다면,
////item////
class Item extends uvm_sequence_item;
`uvm_object_utils(Item)
rand bit in;
bit out;
function new(string name = "Item");
super.new(name);
endfunction
endclass
////interface////
interface example_if (input bit clk);
logic rstn;
logic in;
logic out;
clocking cb @(posedge clk);
default input #1step output #3ns;
input out;
output in;
endclocking
endinterface아래처럼 driver를 작성할 수 있습니다.
virtual task run_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.run_phase(phase);
forever begin
Item m_item; //handle 생성
seq_item_port.get_next_item(m_item); //sequence와 handshake
drive_item(m_item); //아래에 정의된 task
seq_item_port.item_done();
end
endtask
virtual task drive_item(Item m_item);
@(vif.cb);
vif.cb.in <= m_item.in;
endtask- 데이터 전달 방식은 쉽게 말해서 interface에 data를 넣는 방식으로 작동합니다.
- 그럼 data를 받은 interface가 DUT에 data를 전달해주죠.
- 위의 예시는
posedge clk마다in값을 새롭게 넣어주네요.in값은 매 클락 randomize될 것입니다(randomize 부분은 sequence에 작성되었을 것입니다).
이게 전부입니다. 요약하자면,
- Sequence에서 온 data packet을 dut로 전달해주기 위해 interface에 값을 넣어주는 역할을 수행하며,
- sequence와는 handshake방식으로 소통한다.
- Build_phase에서 vif를 get해줘야하며,
- run_phase에서 시나리오를 작성한다.
이상입니다~~
읽어주셔서 감사합니다.
Reference
https://www.chipverify.com/uvm/uvm-verification-testbench-example
https://www.chipverify.com/uvm/uvm-driver

