참고 : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q3HU2vEhD5Y
Generative Model
= assigning density functions to images + sampling
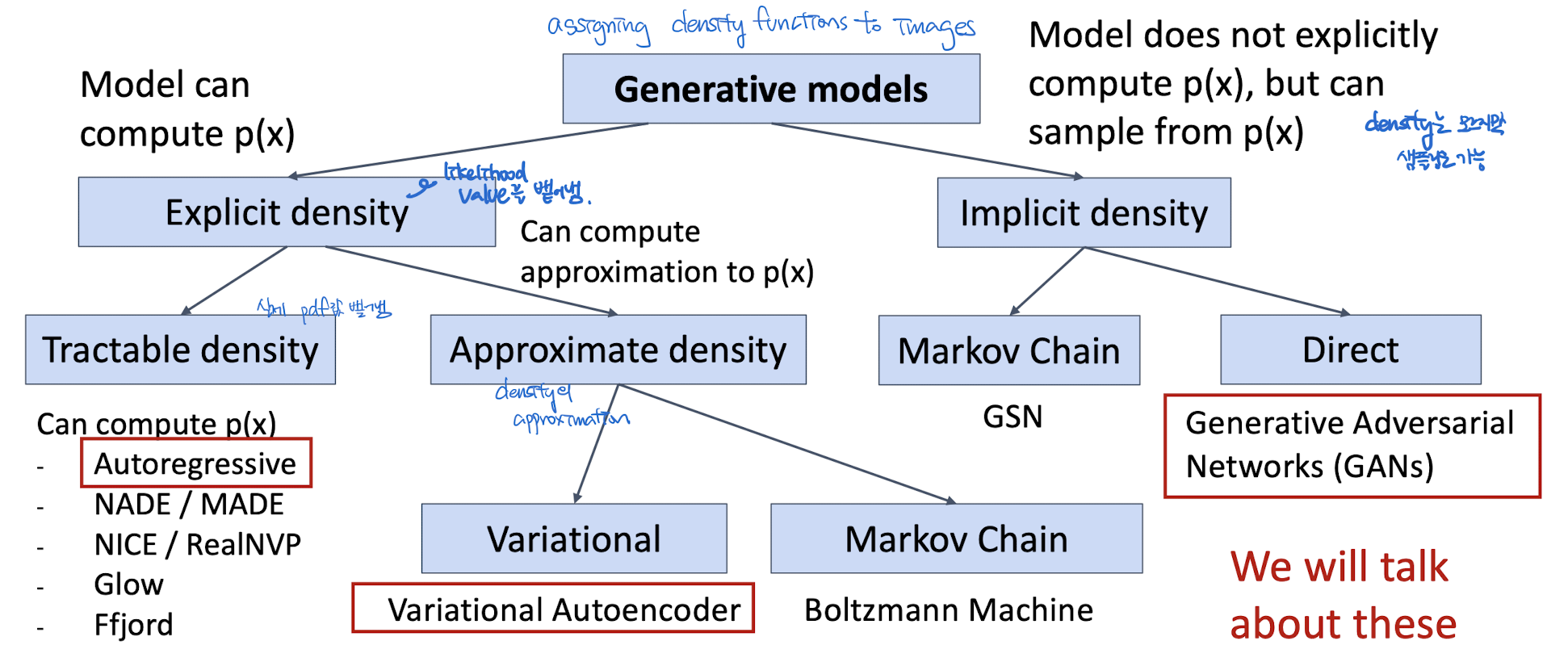
Figure adapted from Ian Goodfellow, Tutorial on Generative Adversarial Networks, 2017.
Explicit Density Estimation
x (image 혹은 pixel)의 확률 분포를 구할 수 있음. Explicit하게!
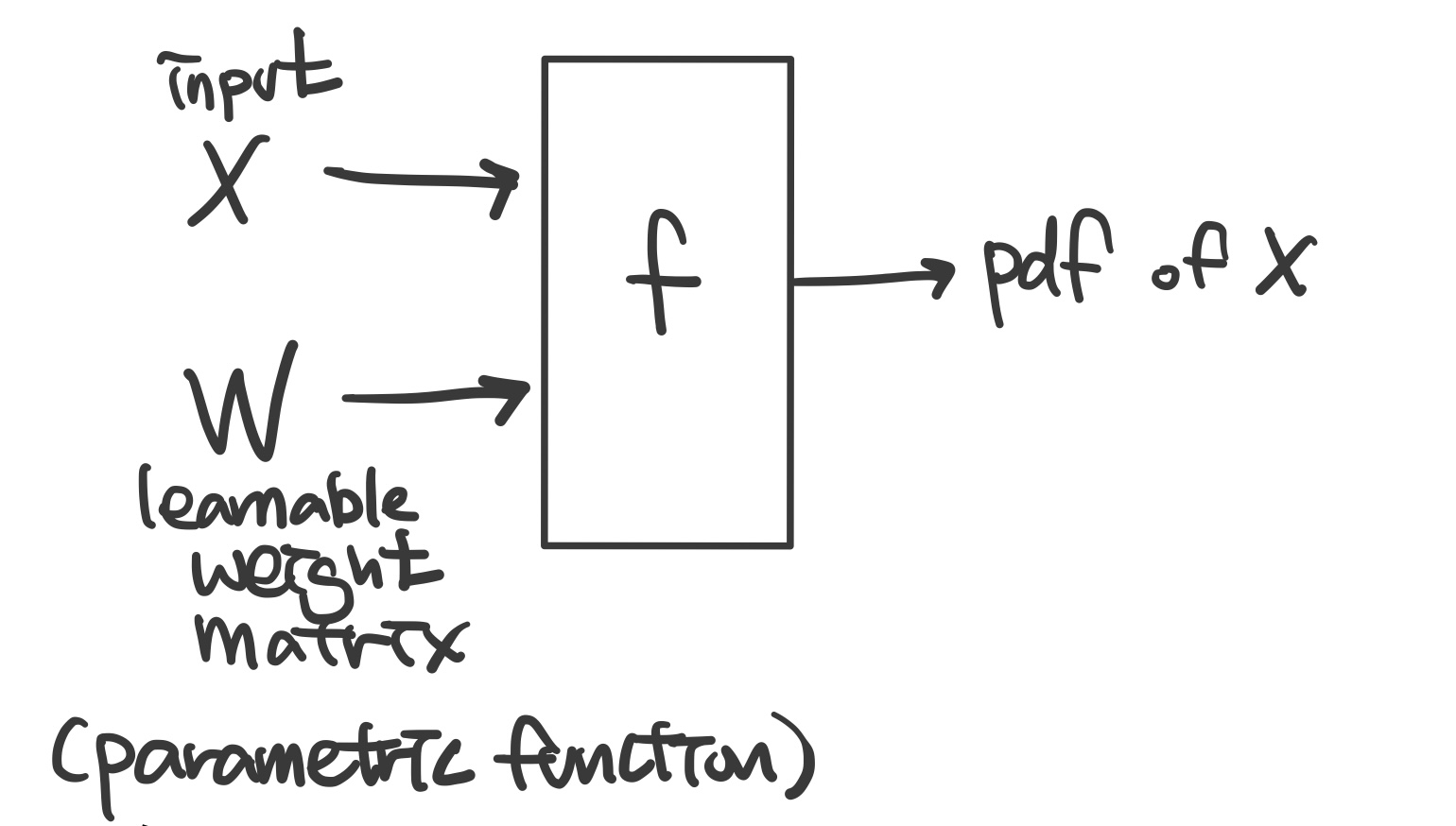
Goal: Write down an explicit function for p(x) = f(x,W)
Training : Maximum Likelihood Estimator
Tractable
- x의 joint pdf를 구하는데, 실제 값을 정확하게 구할 수 있음.
- 즉, 명시적으로 Loss function의 값을 구할 수 있고, 최적화 함수의 값을 정확히 계산 가능.
- x의 joint pdf를 구하는데, 조건부 확률로 분해해서 → RNN 적용한다
AutoRegressive Model : 1. Pixel RNN / 2. Pixel CNN
- !! Explicit density 중에서도 Tractable density model 임
- x의 joint pdf를 구하는데, 조건부 확률로 분해해서 → RNN 적용한다
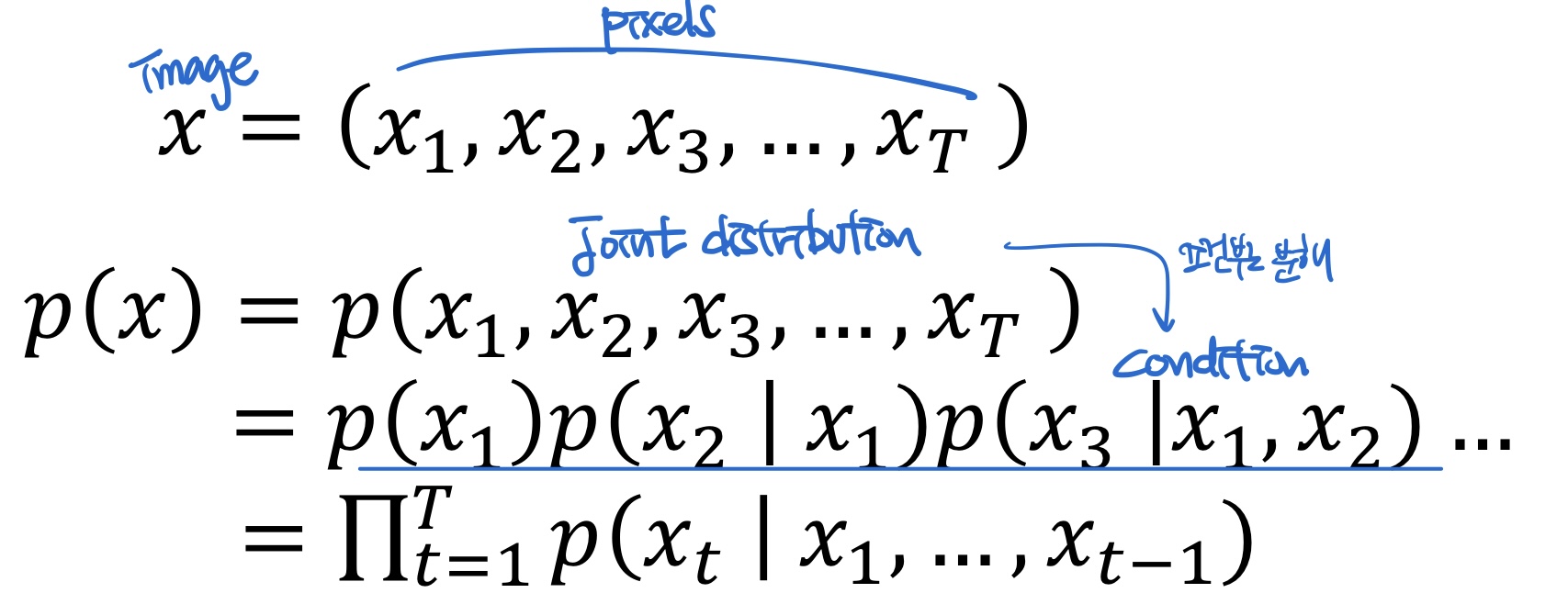
1. Pixel RNN / 2. Pixel CNN
-
👍
- Can explicitly compute likelihood p(x) = 모델 성능 평가 쉬움
- Explicit likelihood of training data gives good evaluation metric
- Good samples
-
👎
- Sequential generation => slow
1. Pixel RNN
모델의 output인 x의 확률분포가 Explicit + Trackable
즉, 모델이 구한 확률 분포에서 sampling을 하면 생성하고자 하는 이미지의 픽셀값이 정해진다고 보면 됨
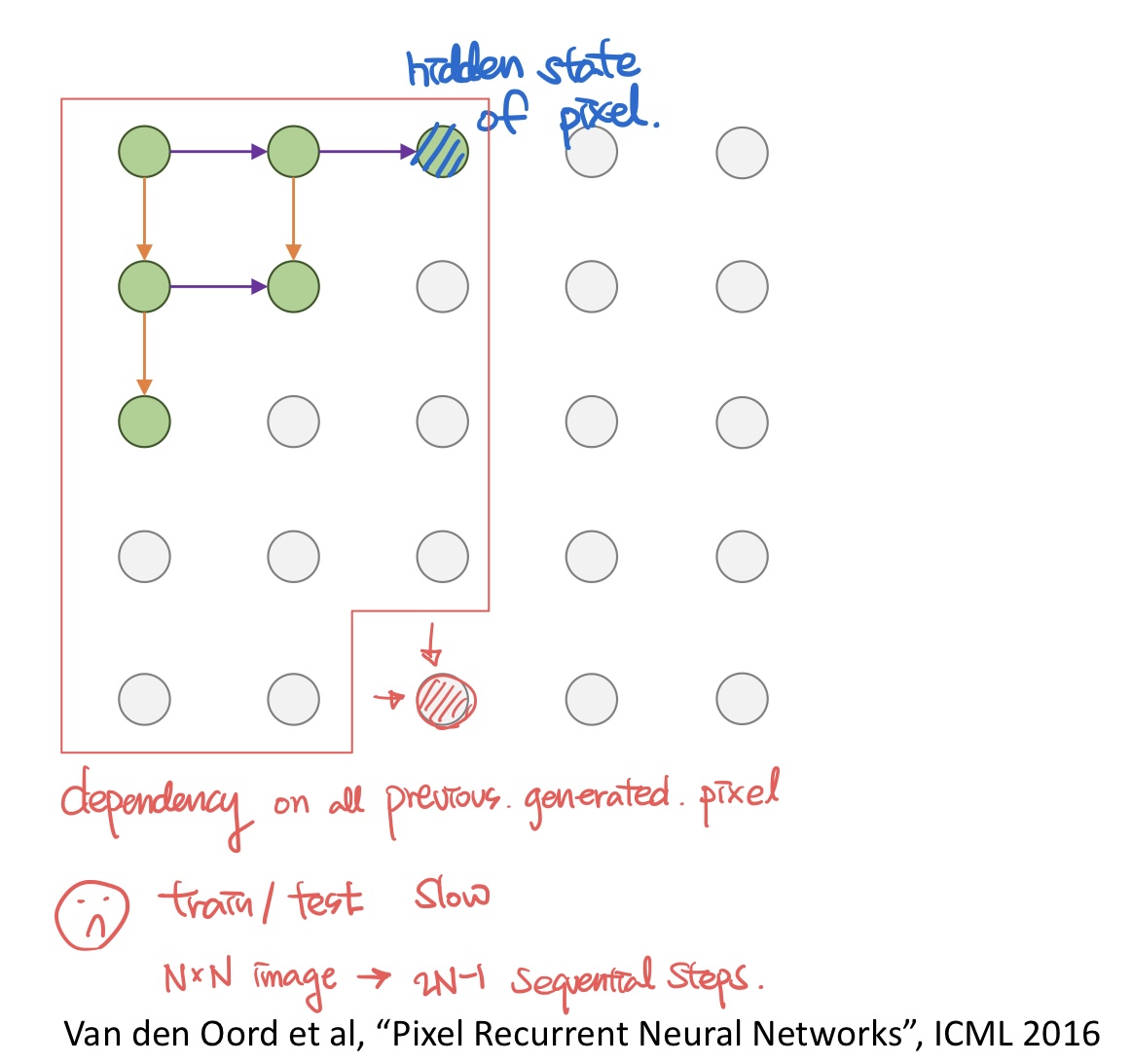
- Generate image pixels one at a time, starting at the upper left corner
- 👎
- Each pixel depends implicity on all pixels above and to the left
- train/test time 둘다 slow
2. Pixel CNN
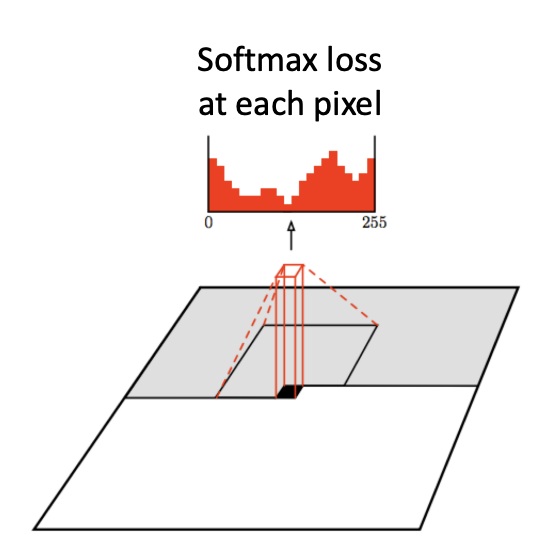 - Training: maximize likelihood of training images
- Training: maximize likelihood of training images
- 👍
- Dependency on previous pixels now modeled using a CNN over context region
- Training is faster than PixelRNN ( parallelize convolutions since context region values known from training images)
- 👎
- Still generate image pixels starting from corner
- Generation must still proceed sequentially => still slow
