
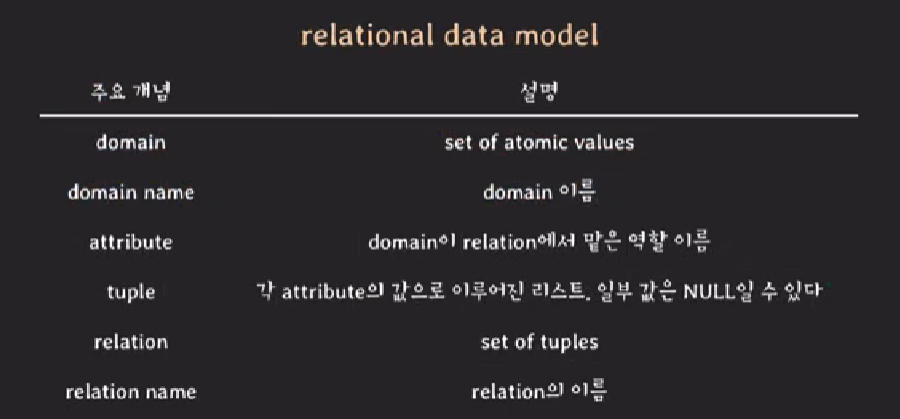
relational data model
relational data model을 배우기 위해서 선행해야할 지식을 먼저 알아보자
선행지식
1. set
- 서로 다른 elements를 가지는 collection
- 하나의 set에서 elements의 순서는 중요하지 않다.
- e.g.) {1, 3, 11, 4, 7}
2. relation in mathematics
-
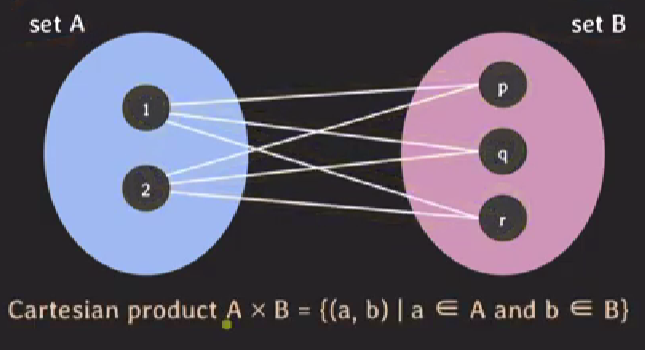
-
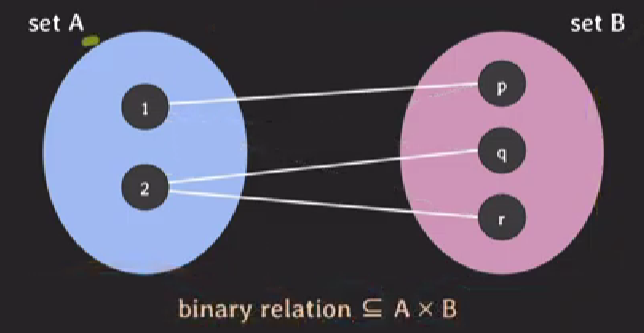
-
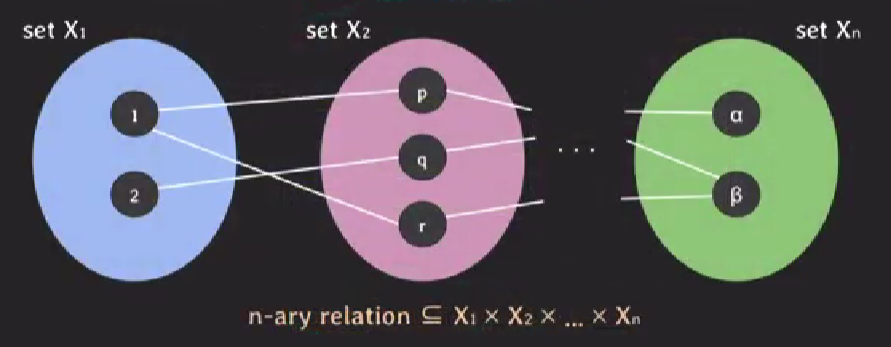
-
subset of Cartesian product(Cartesian product의 부분집합이다.)
-
set of tuples(Tuples들의 집합이다.)
3. relation in mathmatics & relational data model
relational data model
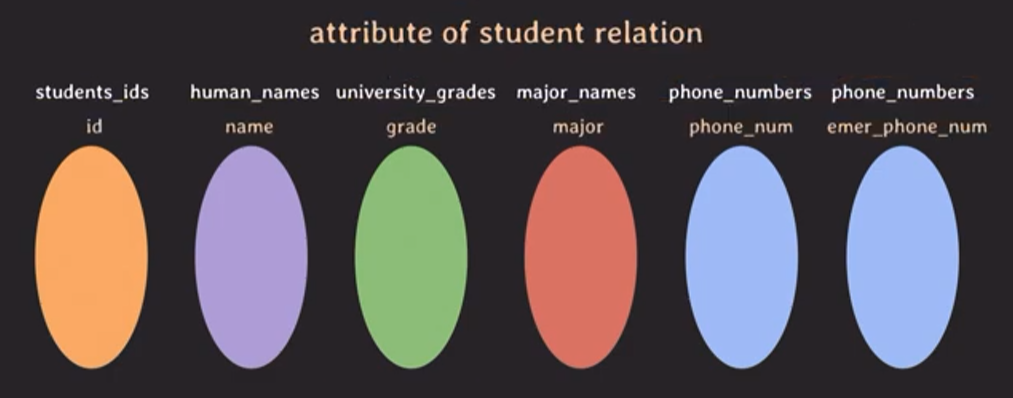
student relation을 예로 들어 relational data model을 이해해 보겠습니다.
domain 정의하기
- students_ids : 학번 집합, 7자리 integer 정수
- human_names : 사람 이름 집합, 문자열
- university_grades : 대학교 학년 집합, {1, 2, 3, 4}
- major_names : 대학교에서 배우는 전공 이름 집합
- phone_numbers : 핸드폰 번호 집합
attribute of student relation
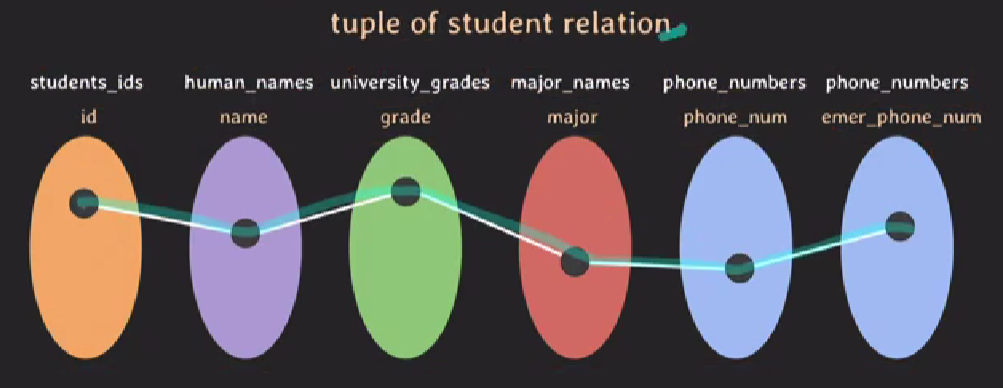
tuple of student relation
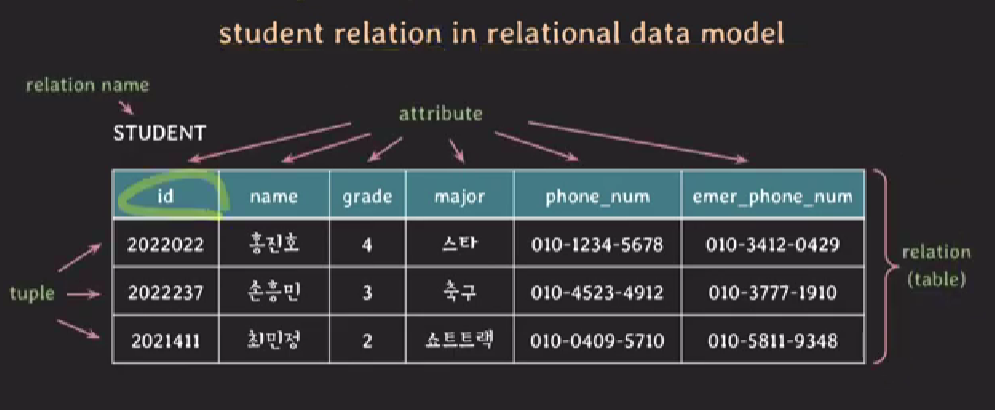
student relation in relational data model
relational data model
relation schema
- relation의 구조를 나타낸다.
- relation 이름과 attributes 리스트로 표기된다.
- e.g. STUDENT(id, name, grade, major, phone_num, emer_phone_num)
- attributes와 관련된 constraints도 포함한다.
degree of a relation
- relation schema에서 attributes의 수
- e.g. STUDENT(id, name, grade, major, phone_num, emer_phone_num) -> degree 6
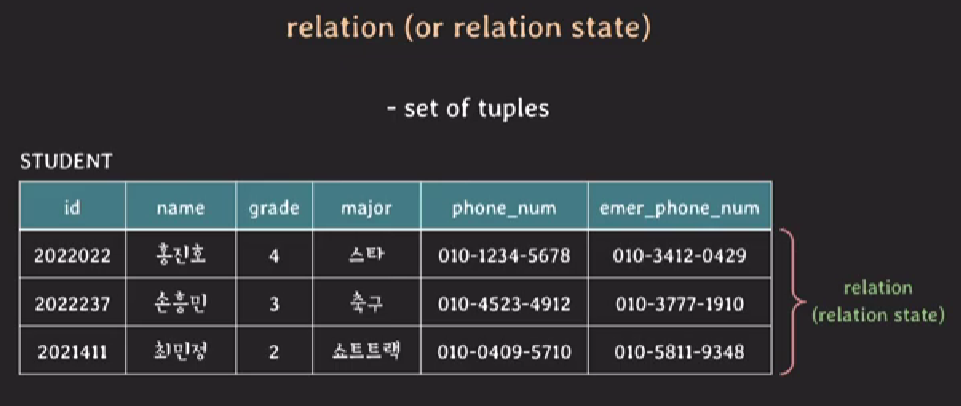
relation (or relation state)
- set of tuples
relational database
- relational data model에 기반하여 구조화된 database
- relational database는 여러 개의 relations로 구성된다.
relational database schema
- relation schemas set + integrity constraints set
relation의 특징들
relation의 특징들
-
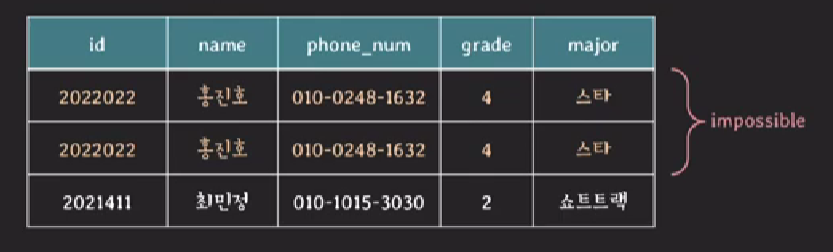
-
relation은 중복된 tuple을 가질 수 없다. (relation is set of tuples)
-
relation의 tuple을 식별하기 위해 attribute의 부분 집합을 key로 설정한다.
-
relation에서 tuple의 순서는 중요하지 않다.
-
하나의 relation에서 attribute의 이름은 중복되면 안된다.
-
하나의 tuple에서 attribute의 순서는 중요하지 않다.
-
attribute는 atomic 해야 한다. (composite or multivalued attribute 허용 안됨)
-

NULL의 의미
NULL의 의미
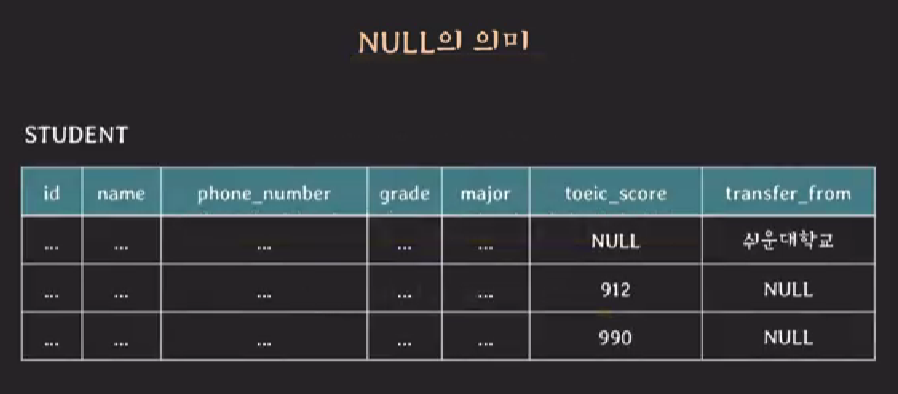
- 값이 존재하지 않는다.
- 값이 존재하나 아직 그 값이 무엇인지 알지 못한다.
- 해당 사항과 관련이 없다.
keys
superkey
- relation에서 tuples를 unique하게 식별할 수 있는 attributes set
- e.g. PLAYER(id, name, team_id, back_number, birth_date)의 superkey는 {id, name, team_id, back_number, birth_date}, {id, name}, {name, team_id, back_number}, ... etc
candidate key
- 어느 한 attribute라도 제거하면 unique하게 tuples를 식별할 수 없는 super key
- key or minimal superkey
- e.g. PLAYER(id, name, team_id, back_number, birth_date)의 candidate key는 {id}, {team_id, back_number}
primary key
- relation에서 tuples를 unique하게 식별하기 위해 선택된 candidate key
- e.g. PLAYER(id, name, team_id, back_number, birth_date)의 primary key는 {id} or {team_id, back_number}
unique key
- primary key가 아닌 candidate keys
- alternate key
- e.g. PLAYER(id, name, team_id, back_number, birth_date)의 unique key는 {team_id, back_number}
foreign key
- 다른 relation의 PK를 참조하는 attributes set
- e.g. PLAYER(id, name, team_id, back_number, birth_date)와 TEAM(id, name, manager)가 있을 때 foreign key는 PLAYER의 {team_id}
constraints
constraints 뜻
- relational database의 relations들이 언제나 항상 지켜줘야 하는 제약 사항
implicit constraints
- relational data model 자체가 가지는 constraints
- relation은 중복되는 tuple을 가질 수 없다.
- relation 내에서는 같은 이름의 attribute를 가질 수 없다.
schema-based constraints
- 주로 DDL을 통해 schema에 직접 명시할 수 있는 constraints
- explicit constraints
schema-based constraints의 종류
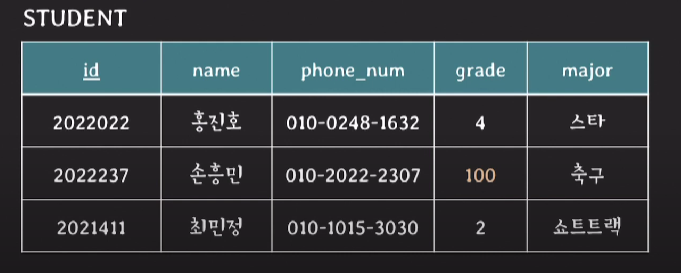
1. domain constraint
- attribute의 value는 해당 attribute의 domain에 속한 value여야 한다.
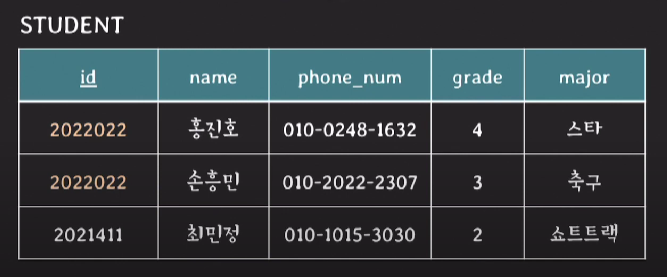
2. key constraint
- 서로 다른 tuples는 같은 value의 key를 가질 수 없다.
3. NULL value constraint
- attribute가 NOT NULL로 명시됐다면 NULL을 값으로 가질 수 없다.
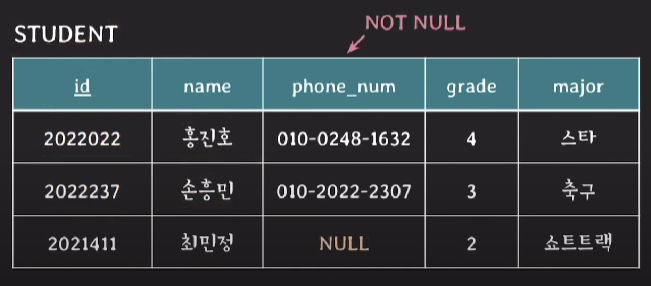
4. entity integrity constraint
- primary key는 value에 NULL을 가질 수 없다.
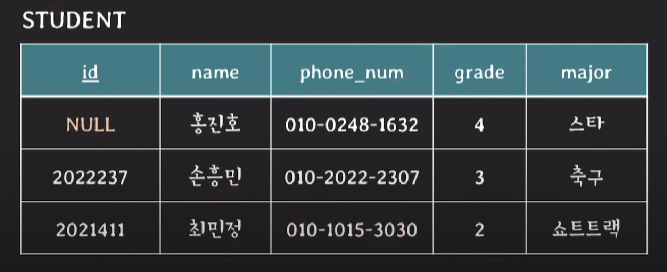
5. referential integrity constraint
- FK와 PK는 도메인이 같아야 하고 PK에 없는 values를 FK가 값으로 가질 수 없다.
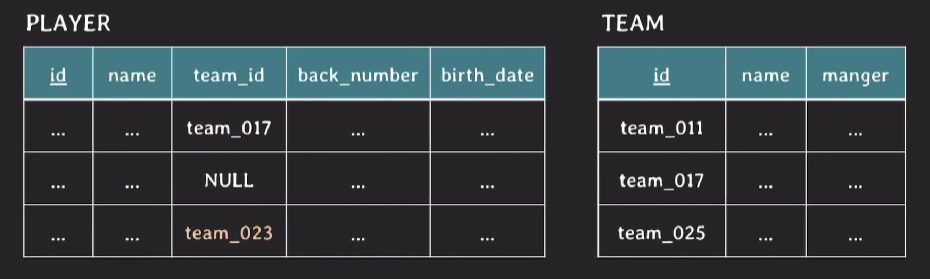

우와 정말 깔끔하네요!!! 굿자